Quiz 1 EDCI
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
All citizens in society
broad civil rights law prohibiting discrimination against people with disabilities in all public life areas
ensures facility accessibility
mandates reasonable accommodations
protects wider range than IDEA
Civil Rights Act of 1964
Title VI prohibited discrimination based on race, color, or national origin in federally funded programs
ensures equal access to education
covers all school programs and services
foundation for EEL protections
Title IX (1972)
Prohibit sex-based discrimination in federally funded education programs
protects LGBTQI+ students
ensures equal access to advanced programs
addresses harassment and bullying
Texas Education Code (TEC) & Texas Administrative Code (TAC)
State laws governing education that align with federal requirements while providing Texas-specific procedures for serving diverse learners
Admission, Review, and Dismissal (ARD) Committee
Texas equivalent of IEP team, determines eligibility, develop IEPs, and makes placement decisions for students with disabilities.
Child Find Mandate
Texas district must actively locate, identify, and evaluate all children with disabilities (birth- 21) needing special education services
Emergent Billingual students support
state-approved processes for identifying, assessing, and providing bilingual education and ESL programs for non-English speaking students
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
is the landmark federal law ensuring all eligible children with disabilities receive a Free Appropriate Education (FAPE) tailored to their unique needs.
Free Appropriate Education (FAPE)
guarantee specialized instruction and related services at no cost to families
Least Restrictive Environment (LRE)
Students educated with non-disabled peers to maximum extent appropriate
Individualized Education Program (IEP)
Detailed written plan outlining goals, services, and accommodations
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act (1973)
civil rights law protecting individuals with disabilities from discrimination in programs receiving federal funding.
key difference from IDEA: dose not require formal IEP but mandates acommondations through a “504 Plan” to ensure cirriculum access
SPECIAL EDUCATION INITIAL REFERRAL TIME
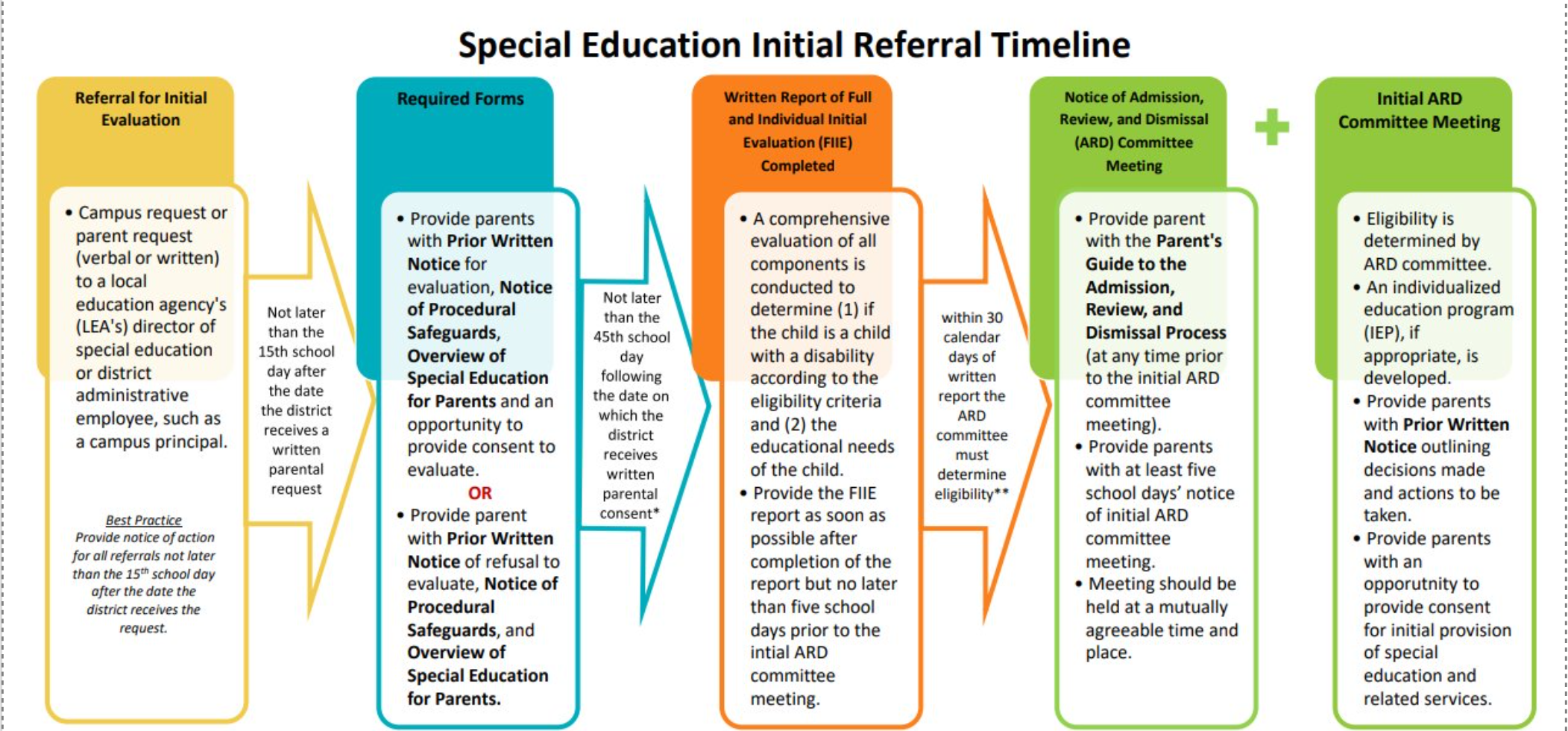
Lau v. Nichols (1974)
Supreme Court ruled that identical services to ELL students violate civil rights. School must take “affirmative steps” to overcome language barriers
Castaneda v. Pickard (1981)
Established three-part test for bilingual program compliance: sound theory, effective implementation, and proven effectiveness
Equal Educational Opportunity Act (1974)
Prohibits discrimination and requires schools to take action to overcome language barriers that impede equal participation
Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)
requires states to report on EEL performance and holds schools accountable for closing achievement gaps
Identification of EELs
home language survey
what language is used in the child home most of time?
what language dose the child use most of the time?
who are the students who are exceptional?
Do not have Individualized Education Program
still struggling in school
struggling students
prior knowledge of issues and family situation
find out issues without requiring disclosure
high expectations for all students performance
difference as key to helping learn
signs of struggling students
the impact of trauma
Thinking differently: A therapy dog as emotional support for a school
Jerome Mack Middle School
Dog senses stress, stays as necessary
students with disabilities
largely determined by IDEA of 1990
Medical vs. social conceptualizations
neurodiversity: different way of thinking
disabilities in 14.5% of school population
IEP for identified disabilities
if severe, support by teaching/health assistant
Identify students with disabilities
students who are gifted and talented
association with high intellectual functioning
creative, artistic, specific fields
overrepresentation of white and asian americans
goal of challenging the undereducated
advanced placement, honor classes, enrichment programs
accleration as effective approach
challenge of multiple grade levels
programs not serving all eligible students
inclusion
integration into general education classroom
goal to ensure access, support, enrichment
adapt curriculum, modify instruction
pull-out or push-in programs
Two in three enrolled in general education 2020
not pulled during language arts or mathematics
receive supplemental/alternative reading instruction
often integrated in music, art, physical education
individualized education programs (IEP)
impact to learning abilitu, functional activities
realistic, mesaurable annual goals
descripition of accommodations/modifications
participation in non-academic activities
particpation in state and district-wide assessments.
mesuresment of progress, parents informed
triennial: reevaluation every three years
family involvement
value, respect; partners in education
includes meetings, conferences, activities
variation between personal responsibilities, school expectations
identify, build on strengths
universal design for learning
accessible for range of abilities, characteristics
focus on classroom and instruction
opening access, improved education
how can teachers meet the needs of all students
co-teaching, popular model
issues of becoming glorified support teachers
better results when planning/working together
response to Intervention (RTI)
Help before getting too far behind
help prevent misidentification
school intervention team
increasing levels of intensity (tiers)
differentiated instruction
provides multiple options for learning
models student-centered learning
learn about readiness, formative assessment
engagement through students interest
accommodations and modifications
individualization of instruction
accommodation: help students access
modifications: change what is taught
contentious issues: providing services when schools are closed
monitioring disproportionate placement
biases can interfere with judgement
disproportionately boys, ELs, low income
socially constructed nature of disability categories
monitor data of referrals for testing
how can educators dismantle ableism in the classroom
Ableism: prejudice, discrimination based on differences
creation of IDEA, ADA through activism
most students learning in same classrooms
provide positive, accessible classrooms
assimilation
process by which groups adopt or change the dominant culture
socialization
process of learning the social norms of the culture
student and family diversity in us schools
religious diversity,
socioeconomic diversity
ability diversity
diversity of gender and sexual preference
racial and ethnic diversity
the role of cultures in students lives and the classroom
defines who we are
provides acceptable patterns of behavior
determines how we think, feel, and behave in society
imposes order and meaning on our experiences
predicts how others will behave in certain situations
characteristics of culture
learned, shared, and dynamic
cultural identity
race, ethnicity, gender, socioeconomic status, language, religion, sexual orientation, mental/physical abilities, age