Immune responses and transplants
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
the body’s ability to resist disease
immunity
what are the 3 functions the immune response serves
defense
homeostasis
survaeillance
______- a substance that elicits and immune response
unique to the person and enables body to recognize itself
Self: HLA proteins label cells of the individual; immune system ignores self-cells
Non-self: immune system recognizes specific non-self antigens as foreign; development of a specific response to that particular antigen; memory cells produced to respond quickly to antigen
antigen
what are the 3 common problems occuring when the immune response is altered
-Inflammation
-Infection
-Tissue integrity
explain the primary and secondary immune responses
Primary response
-First exposure to antigen
-1 to 2 weeks before antibody titer reaches efficacy
Secondary Response
-Repeat exposure to the same antigen
-More rapid response, with efficacy in 1 to 3 days
explain innate immunity

explain acquired immunity

explain the central (primary) lymphoid structures and cells

explain the peripheral lymphoid structures and cells

explain macrophages:

explain lymphocytes:

explain B lymphocytes

explain T lymphocytes:

explain NK cells:

explain dendritic cells:

explain cytokines:

what are antibodies?

explain the different types of antibodies

what is the complement system?

list the chemical mediators

explain humoral immunity

explain cell mediated immunity

what are the effects of aging on the immune system (immunosenescence)

what are some lab/ diagnostic tests for immun responses and transplants
Titer - Measures levels of serum immunoglobulins
Indirect Coombs’ test - Detects Rh blood incompatibility
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) – Detects antibodies such as IgE, HIV & other diseases
Increased with Type I hypersensitivity
Used when taking a drug that interferes with testing such as steroids or antihistamines) and cannot stop taking, cannot tolerate skin scratches, or has a skin disorder
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) typing - Tissue matching before transplantation procedures
Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) determination
-Used for differential diagnosis of autoimmune disease
-Positive result is not confirmatory
CBC with WBC differential
-Decrease lymphocyte count with immunodeficiency
-Increase eosinophil count with Type 1 hypersensitivity
explain skin testing:

explain the post procedure of skin testing:

for skin testing, what is a negative response
wheal is less than 0.5 cm in diameter after 15-30 mins of application

what are the different ways there can be an altered immune response
__________ occurs when the body does not recognize self-proteins and reacts against self-antigens.
Autoimmune disease
explain a type 1- allergic reaction hypersensitivity reaction:

what is anaphylaxis/ anaphylactic shock manifested by

causes of allergic rxns and anaphylaxis
Drugs
§Aspirin
§Chemotherapy drugs
§Insulin
§Local anesthetics
§NSAIDs
§Antibiotics – cephalosporins, penicillins, sulfonamides, tetracyclines
Foods – eggs, milk, nuts, peanuts, shellfish, fish, chocolate, strawberries
Insect Venoms
§Wasps, hornets, yellow jackets, bumblebees, ants
Treatment Measures
§Allergenic extracts used in immunotherapy
§Blood products
§Iodine-contrast media for CT scan
Animal Sera
§Diphtheria antitoxin
§Rabies antitoxin
§Snake venom antitoxin
§Tetanus antitoxin
explain prevention of hypersensitivity reaction

allergic rxn manifestations

interventions for allergic rxns without anaphylaxis:

anaphylaxis clinical manifestations

anaphylaxis treatment:

explain a type II cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction:
-IgG or IgM binds to antigen on cell surface-activates complement resulting in cytolysis or enhanced phagocytosis
-Hemolytic Transfusion Reactions – recipient receives ABO-incompatible blood from a donor

explain goodpasture syndrome:
§ rare autoimmune disorder most common in young adults who smoke
§Autoantibodies are made against the glomerular and alveolar basement membrane
§Usually not diagnosed until significant involvement occurs
§Clinical manifestations: shortness of breath, hemoptysis, decrease urine output, edema, weight gain, hypertension, tachycardia, hematuria, weakness, anemia
§Treatment: suppress the autoimmune response with medications such as corticosteroids and plasmaphoresis
explain a type III hypersensitivity reaction

explain a type IV hypersensitivity reaction:

explain a latex allergy

latex cross reactive foods

latex allergy prevention and interventions:

guidelines for preventing allergic latex reactions

what are the hypersensitivity medications
Antipruritic Drugs
-Topical – protect skin and relieve itching
-Ex: calamine lotion, coal tar solutions, camphor
Mast Cell-Stabilizing Drugs
-Inhalant or intranasal
-Used in allergic rhinitis
-Ex: Cromolyn
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
-Blocks leukotriene-allergic inflammatory process
-Oral treatment of allergic rhinitis and asthma
-Ex: Montelukast (Singulair)
Antihistamines
-Block histamine receptors, alleviating the effects of histamine
-Take at onset of symptoms
-Ex: diphenhydramine
Decongestants
-Ex: phenylephrine, pseudoephedrine
Sympathomimetics
-Ex: epinephrine IM or IV
-Treatment of choice for anaphylaxis-related vasodilation & bronchodilation
Corticosteroids
-Anti-inflammatory effects – intranasal or oral
explain immunotherapy or allergy shots

nursing management for immunotherapy:

explain hypersensitivity therapies:

explain immunodeficiency:

explain primary deficiencies and secondary or acquired immunodeficiencies:

explain transplantation:

types of transplantation:

explain hematopoietic stem cell transplantation

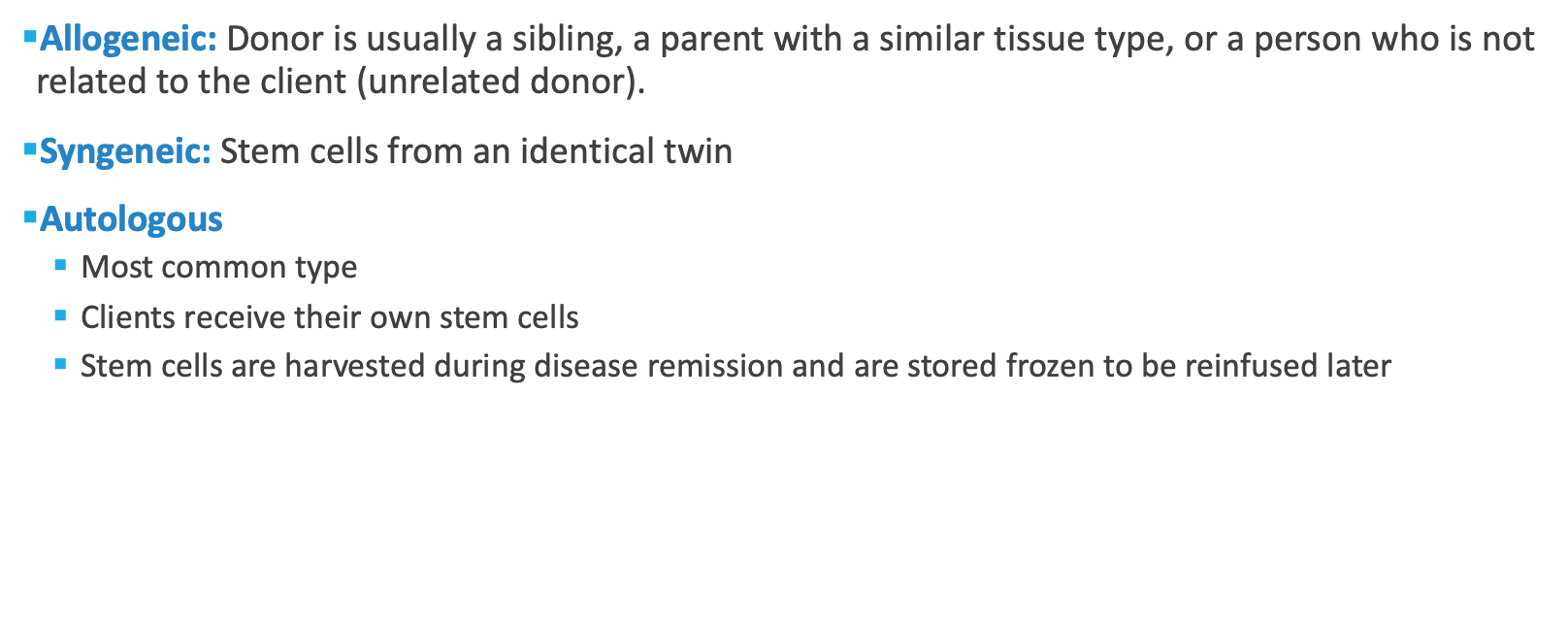
what are the types of donor stem cells
explain the harvest procedure for transplantation

what are the conditioning regimens for transplantation

what are the general pre-transplantation care guidelines

explain transplantation

explain engraftment

explain post- transplantation care:

explain tissue and organ transplant rejection
Chronic, late rejection: Occurs after months or years:
Due to antibody-mediated immune responses
Causes fibrosis and scarring
Difficult to manage
Treatment is supportive & outcomes not as good as the acute rejection
Interventions: Life-long immunosuppressive medications
Increase current dose of medications
Add corticosteroids if already discontinued
Add polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies if not already taking

explain graft vs host disease

treatment and prevention of graft vs host disease
