M&D.A 5: Temperature Measurement Technology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
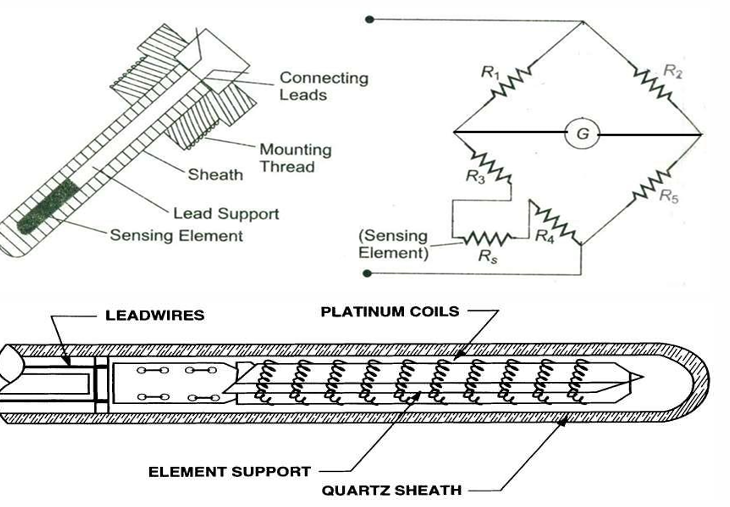
What is a resistance thermometer and how is it typically constructed?
A resistance thermometer consists of a sensing element (often platinum), connecting leads, a sheath, and is used in a bridge circuit to measure temperature-dependent resistance changes.
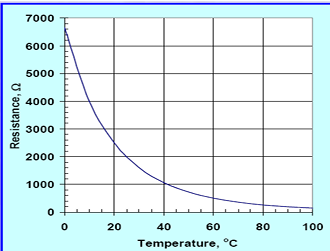
What is a thermistor and how does its resistance change with temperature?
A thermistor is a thermally sensitive resistor whose resistance decreases non-linearly as temperature increases. It is a passive transducer.
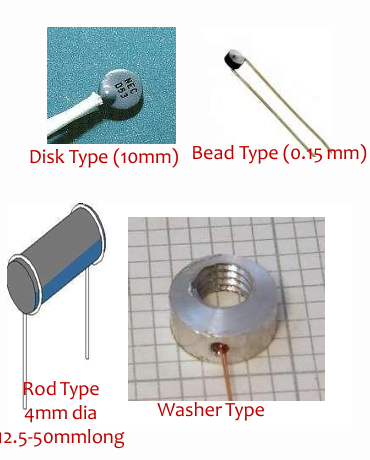
Name four common physical forms of thermistors.
Disk type, bead type, rod type, and washer type.
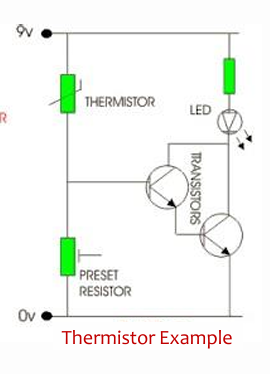
Describe a basic thermistor circuit application.
thermistor can be used in a circuit with an LED and transistors to detect temperature changes. Heating the thermistor alters its resistance and changes the output.
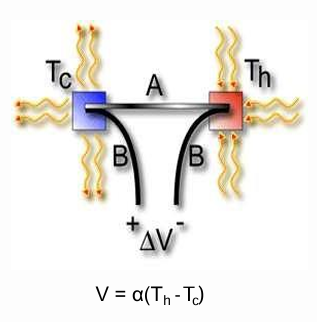
What is the basic principle of a thermocouple?
A thermocouple generates a voltage proportional to the temperature difference between two junctions of dissimilar metals, based on the Seebeck effect.
State the equation relating thermocouple voltage to temperature difference.
V = α(Th - Tc), where V is the voltage, α is the Seebeck coefficient, Th is the hot junction temperature, and Tc is the cold junction temperature.
What are the main physical principles used in temperature measurement instruments?
Thermoelectric Effect
Resistance Change
Semiconductor Sensitivity
Radiative Heat Emission
Thermography
Thermal Expansion
Resonant Frequency Change
Fibre Optic Sensitivity
Acoustic Thermometry
Colour Change
Change of State
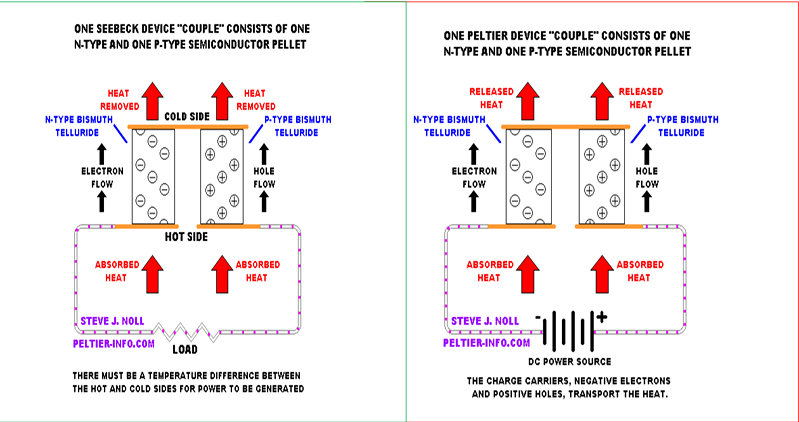
What are the Seebeck and Peltier Effects?
Seebeck Effect:
The generation of voltage when there is a temperature difference between two dissimilar conductors.Peltier Effect:
The generation of heat or cooling at a junction when current passes through two different conductors.
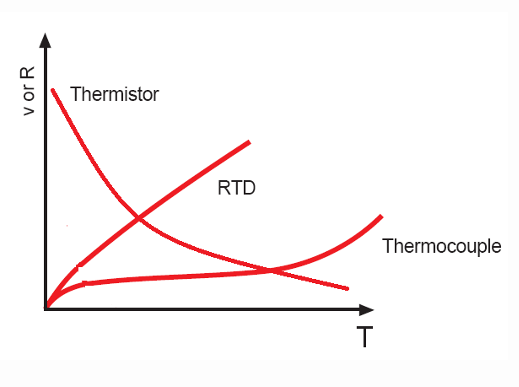
Comparison of Temperature Sensors: thermistors, RTDs and thermocouples
Thermistors:
Show a rapid non-linear decrease in resistance as temperature increases.RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors):
Have an approximately linear increase in resistance with temperature.Thermocouples:
Produce a gradual increase in voltage as the temperature difference between two junctions increases.
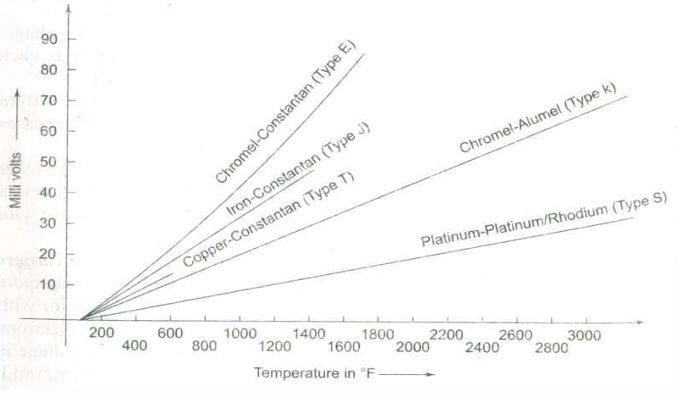
How does the output voltage of different thermocouple types vary with temperature?
Each thermocouple type has a characteristic output voltage vs. temperature curve, with Type E having the steepest increase, and Type S the slowest. Output voltage increases with temperature for all types.
Describe a basic thermocouple circuit setup.
A basic setup includes two dissimilar metals joined at a hot junction (heated) and a cold junction (reference, often in an ice bath). A voltmeter measures the generated voltage due to the temperature difference.
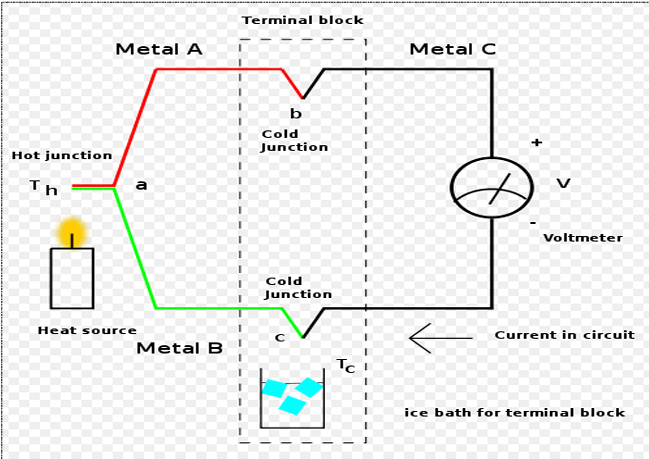
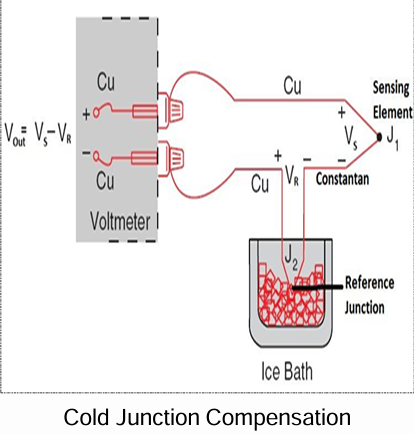
Why are compensation circuits necessary for thermocouple measurements, and how is cold junction compensation typically achieved?
Compensation circuits ensure accurate hot junction measurements by accounting for the cold junction temperature. Cold junction compensation is achieved by using an ice bath or thermistor with an isothermal block.
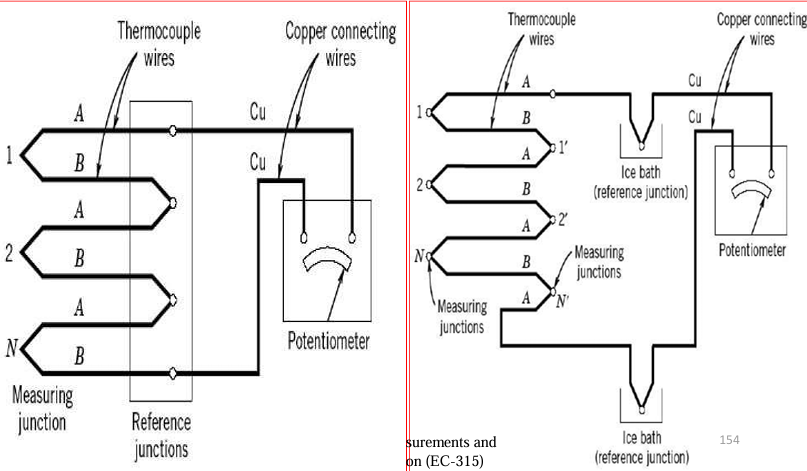
What is a thermopile, and how do thermocouples measure average temperature?
A thermopile is a series of thermocouples connected in series to amplify the voltage output for better sensitivity.
Average temperature can be calculated by connecting thermocouples in parallel and averaging the individual outputs.
What are the main physical constructions of thermocouples?
Metal tube type, hypodermic type, and washer type.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of thermocouples?
Advantages: Wide temperature range, rugged construction.
Disadvantages: Require compensation circuits, non-linear emf vs. temperature.
What is a Wheatstone Bridge, and how does it work?
A Wheatstone Bridge is an electrical circuit that measures unknown resistance by balancing two legs, providing highly accurate resistance measurements.
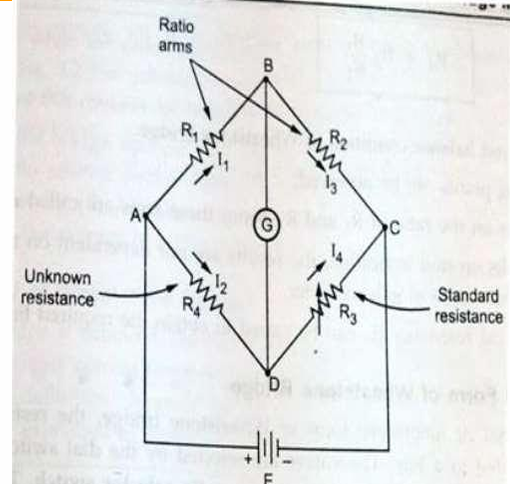
What is the balance condition equation for a Wheatstone Bridge?
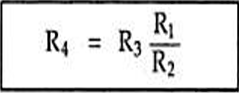
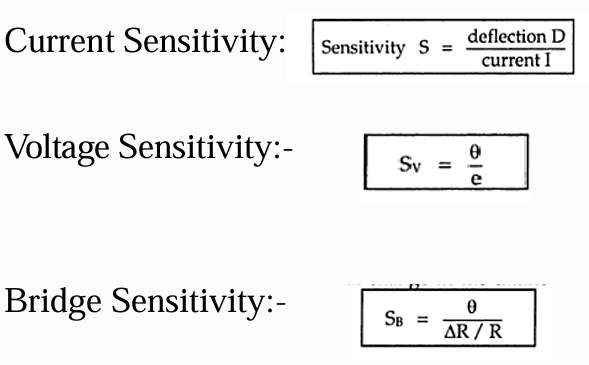
Define current sensitivity, voltage sensitivity, and bridge sensitivity in a Wheatstone Bridge.
What happens to the Wheatstone Bridge under small unbalance conditions?
A small change in resistance (ΔR) in one arm creates an unbalance, resulting in a measurable voltage (Vth) across the galvanometer terminals. This voltage can be calculated using Thevenin's method
What is the significance of Wheatstone Bridge in strain gauge measurement?
The Wheatstone Bridge is sensitive to small resistance changes, making it ideal for detecting tiny variations in resistance from strain gauges due to applied strain.
What is a strain gauge, and what does it measure?
A strain gauge is a passive transducer that converts mechanical displacement (strain) into a change in electrical resistance.
How is a strain gauge typically measured using a Wheatstone Bridge?
A strain gauge is connected into a Wheatstone Bridge circuit, where the change in resistance due to applied strain alters the balance, producing a measurable output.
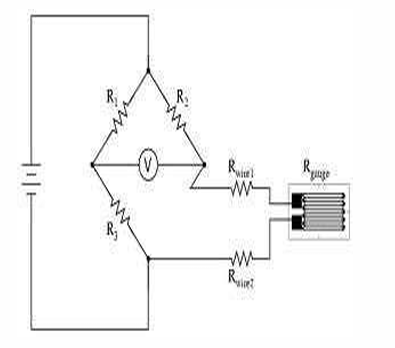
What is the formula relating Wheatstone Bridge output voltage to strain in a strain gauge?
where:
e = output voltage
K = gauge factor
ε = strain
E = input voltage
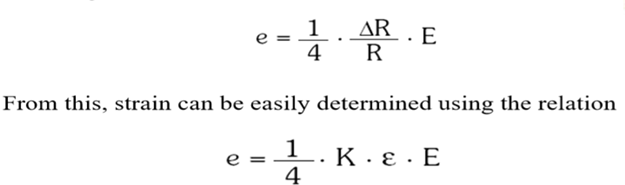
What is a full bridge configuration in strain gauge measurement?
A full bridge configuration replaces all four resistors in the Wheatstone Bridge with strain gauges, improving sensitivity.
The output voltage formula is:

Provide the general formula for Wheatstone Bridge output voltage.
The Wheatstone Bridge measures the unbalance in a circuit caused by a change in resistance. The general output voltage formula is:
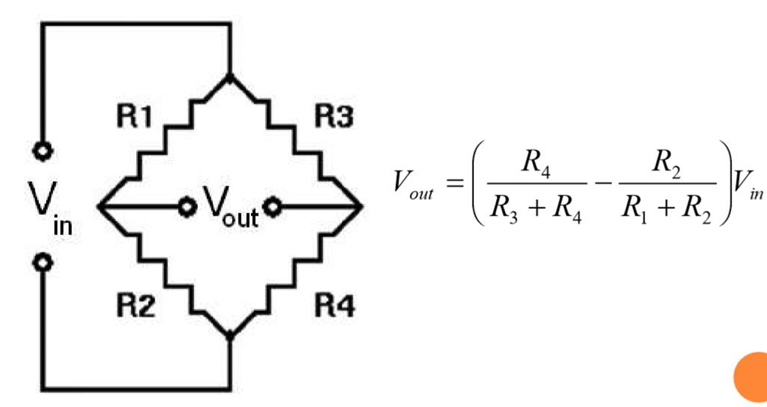
Describe the general block diagram of a strain gauge measurement system.
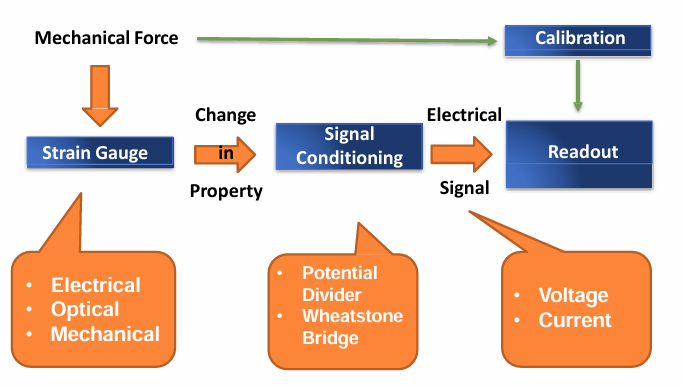
What are the main components in a strain gauge measurement system with amplification and digitization?
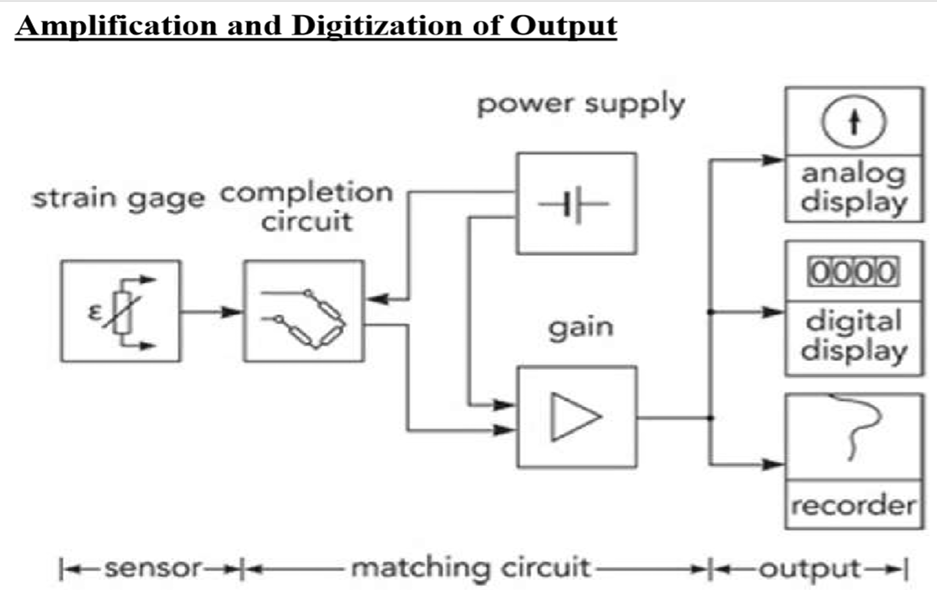
List the three main ways strain gauges are classified by working principle, mounting, and construction.
By working principle: Mechanical, Electrical, Piezoelectric.
By mounting: Bonded, Unbonded.
By construction: Foil, Semiconductor, Photoelectric
How does an electrical strain gauge work (including bonded strain gauges)?
An electrical strain gauge measures the change in resistance of a wire, foil, or bonded material (e.g., metallic wire, etched foil, or semiconductor bar) as it is stretched or compressed, inferring strain from the resistance change.
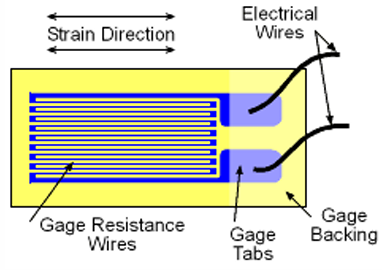
How does an electrical strain gauge work (including bonded strain gauges)?
An electrical strain gauge measures the change in resistance of a wire, foil, or bonded material (e.g., metallic wire, etched foil, or semiconductor bar) as it is stretched or compressed, inferring strain from the resistance change.
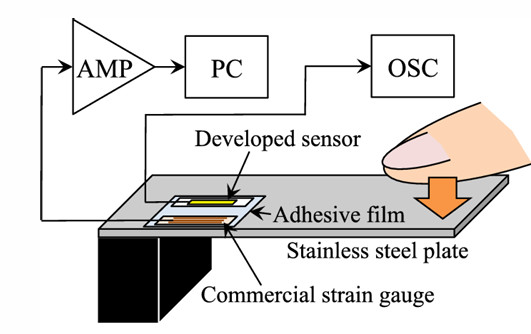
What is a foil strain gauge and how is it used?
A foil strain gauge has a metal foil grid pattern photo-etched on an insulator. It is used to determine strain value and direction by measuring resistance changes relative to nominal resistance and sensitivity factor.
What is a semiconductor strain gauge and its typical application?
A semiconductor strain gauge (piezoresistor) relies on the piezoresistive effect of silicon or germanium, measuring resistance change with stress. It is preferred for small strain measurements.
List at least four applications of strain gauges.
Residual stress measurement
vibration measurement
torque measurement
bending and deflection measurement
compression and tension measurement
general strain measurement.
Name three possible sources of error in strain gauge load cell signals.
Improper loading/orientation
friction between bearing plate and load cell bonding faults
What is cross-sensitivity in strain gauge measurements?
Cross-sensitivity refers to the strain gauge responding to strains in directions other than the intended measurement direction, causing errors