Acute and chronic wound management
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Acute wound definition
An acute wound is defined as a wound that has yet to progress through the stages of healing. Acute wounds are able to heal by:
1) Primary intention- wound is cleaned and edges approximated by glue, sutures or staples.
2) Secondary intention- Wounds are left open to heal on their own, due to infection or high risk of infection.
3) Surgical wounds are left open deliberately for a few days in cases like edema.
Acute wounds clinical presentation
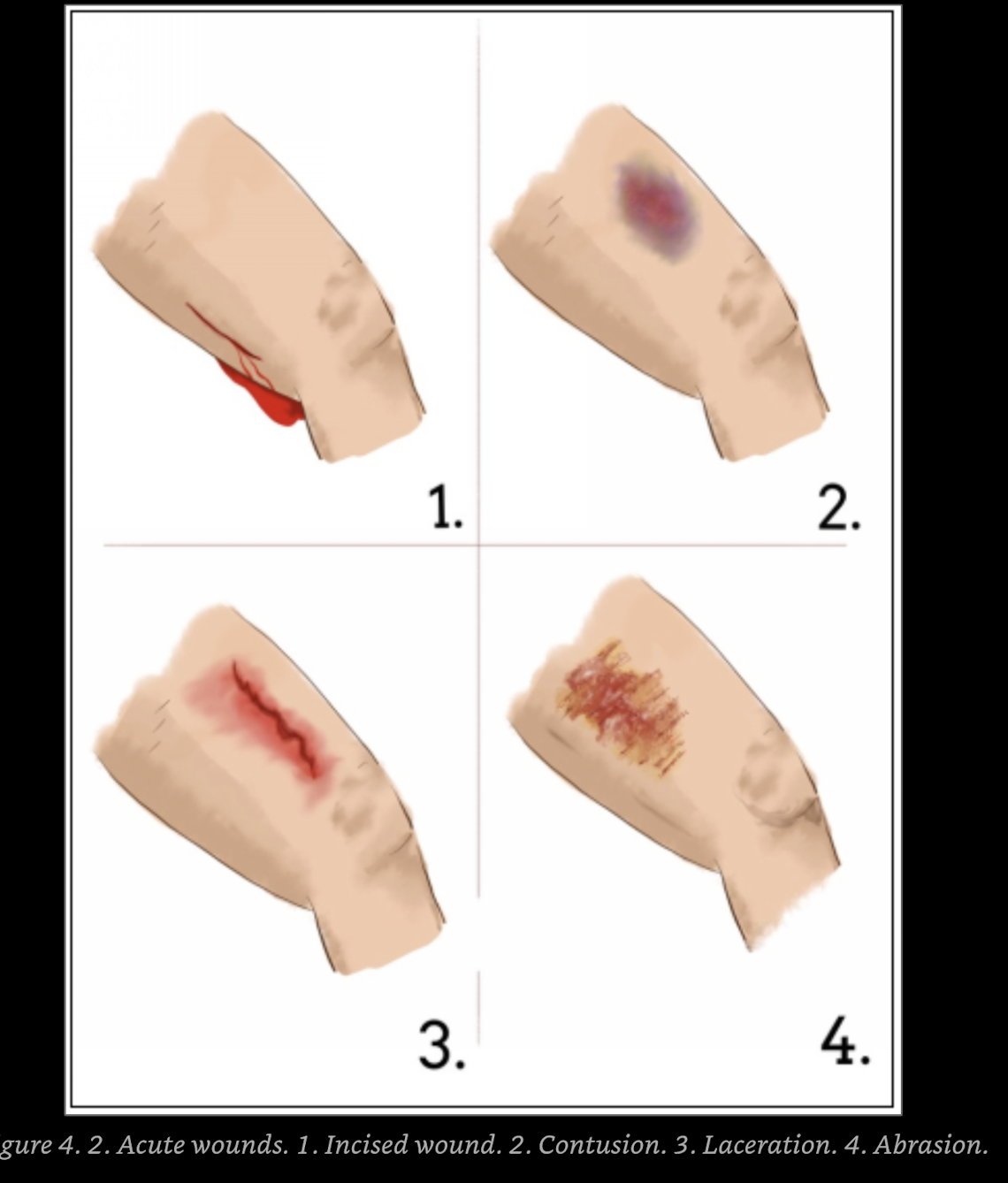
Abrasions or grazes, caused by tangenrtial application of blunt force.
Lacerations- Blunt force tears, shear or crush skin
Incuided wounds- Produced by sharp edges, such as knives and glass shards.
Contusions- blunt force disrupting superficial capillaries
Puncture wounds- Sharp points or edges produce puncture wounds.
Chronic wounds
Defined as wounds that have failed yo proceed through the orderly process that produces satisfactory anatomical and functional integrity.
Skin ulcers- Usually occur in traumatised or vascular compromised soft tissue, which are considered chronic in nature.
Ischemic arterial ulcers-Happens because of a lack of blood supply and are painful presentation. they are usually located on the most distal portions of the extremities and are associated with other symptoms of peripheral vascular diseases.
Diabetic ulcers- affects 10-15% of diabetic patients. Ischemia secondary to vascular disease, impedes healing by reducing supply of oxygen and other nutrients.
Wound management
Wound cleaning and coverage is very important. Can be covered by synthetic or natural dressing. Grafts or cured epidermal cells, which is for temporary coverage. Grafts of only dermal components, prevents wound contraction and greater mechanical stability.
Vacuum-assited wound closure- NPWT is a method to draw out fluid and infection from a wound and help it heal