Introduction to Organizational Behavior and Job Satisfaction
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
210 Terms
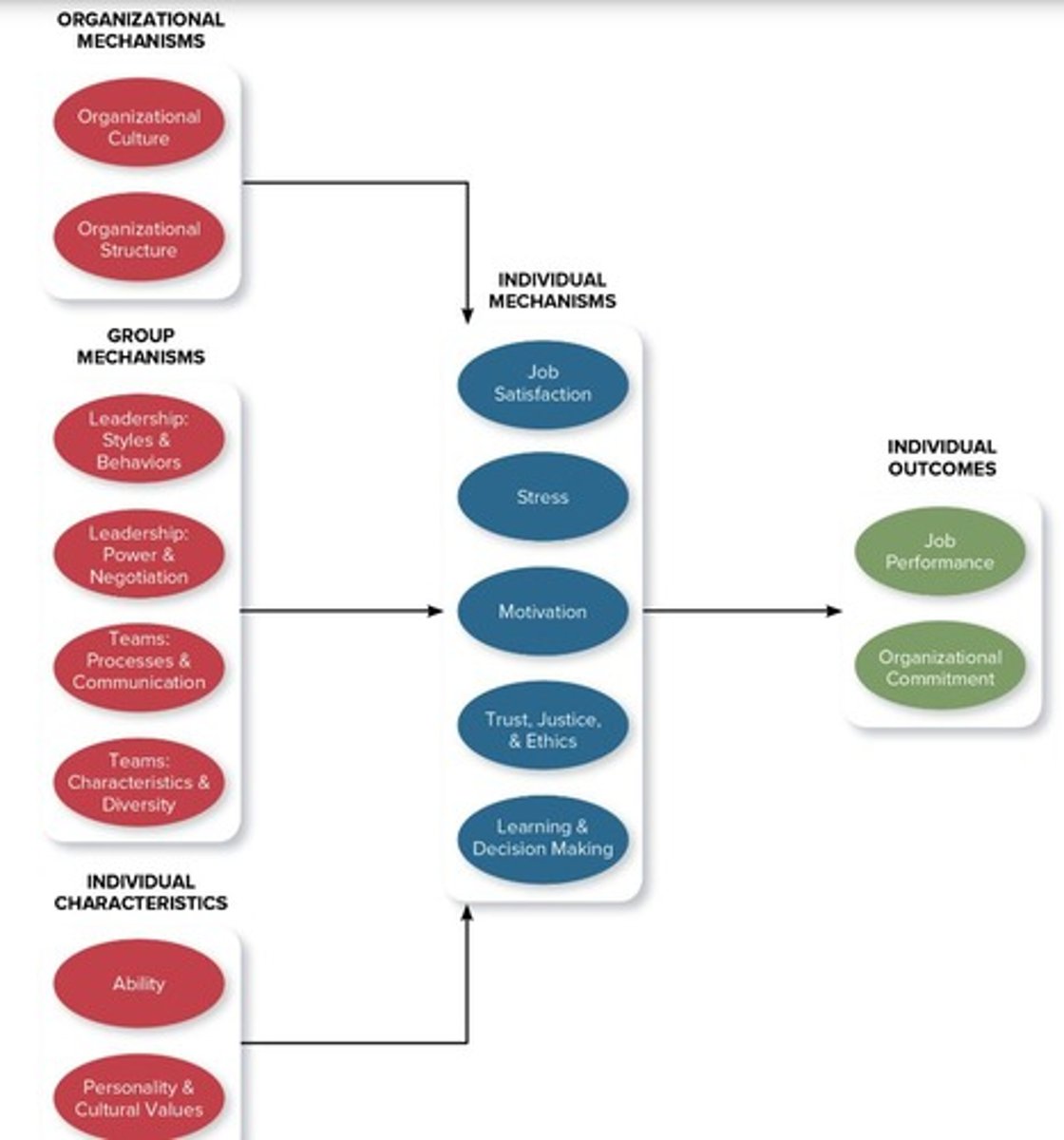
Organizational Behavior (OB)
Study of attitudes and behaviors in organizations.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
Application of OB theories to manage workforce.
Strategic Management
Corporate tactics influencing organizational profitability.
Firm Diversification
Variety of products/services affecting profitability.
Industrial Psychology
Research on job performance and individual traits.
Social Psychology
Study of emotions and team processes.
Sociology
Research on team characteristics and structure.
Anthropology
Study of organizational culture.
Economics
Focus on motivation and decision-making processes.
Job Satisfaction
Employee feelings about their job roles.
Stress
Psychological response to job demands.
Motivation
Forces driving work effort and engagement.
Trust, Justice, and Ethics
Perception of fairness and integrity in business.
Learning and Decision Making
Acquiring knowledge for accurate job judgments.
Personality
Individual traits influencing workplace behavior.
Cultural Values
Shared beliefs affecting employee actions.
Ability
Cognitive, emotional, and physical skills of employees.
Organizational Structure
Framework dictating unit communication and connection.
Organizational Culture
Shared values shaping organizational behavior.
Resource-Based View
Framework assessing resource value for firms.
Rule of 1/8th
Only 12% of firms invest in employee development.
Socially Complex Resources
Cultural and relational assets difficult to replicate.
Method of experience
Based on consistent observations and personal experience.
Method of intuition
Relies on self-evident truths or obvious conclusions.
Method of authority
Information from respected sources or agencies.
Method of science
Relies on replicated scientific studies and samples.
Theory
Collection of assertions about variable relationships.
Hypothesis
Prediction specifying relationships between variables.
Correlation
Statistical relationship between two variables.
Perfect negative correlation
Correlation value of -1 indicates strong inverse relationship.
Perfect positive correlation
Correlation value of 1 indicates strong direct relationship.
Causal inferences
Determining if one variable causes another.
Meta-analysis
Calculates weighted average of multiple correlations.
Evidence-based management
Management decisions based on scientific findings.
Analytics
Data-driven approach to guide decision making.
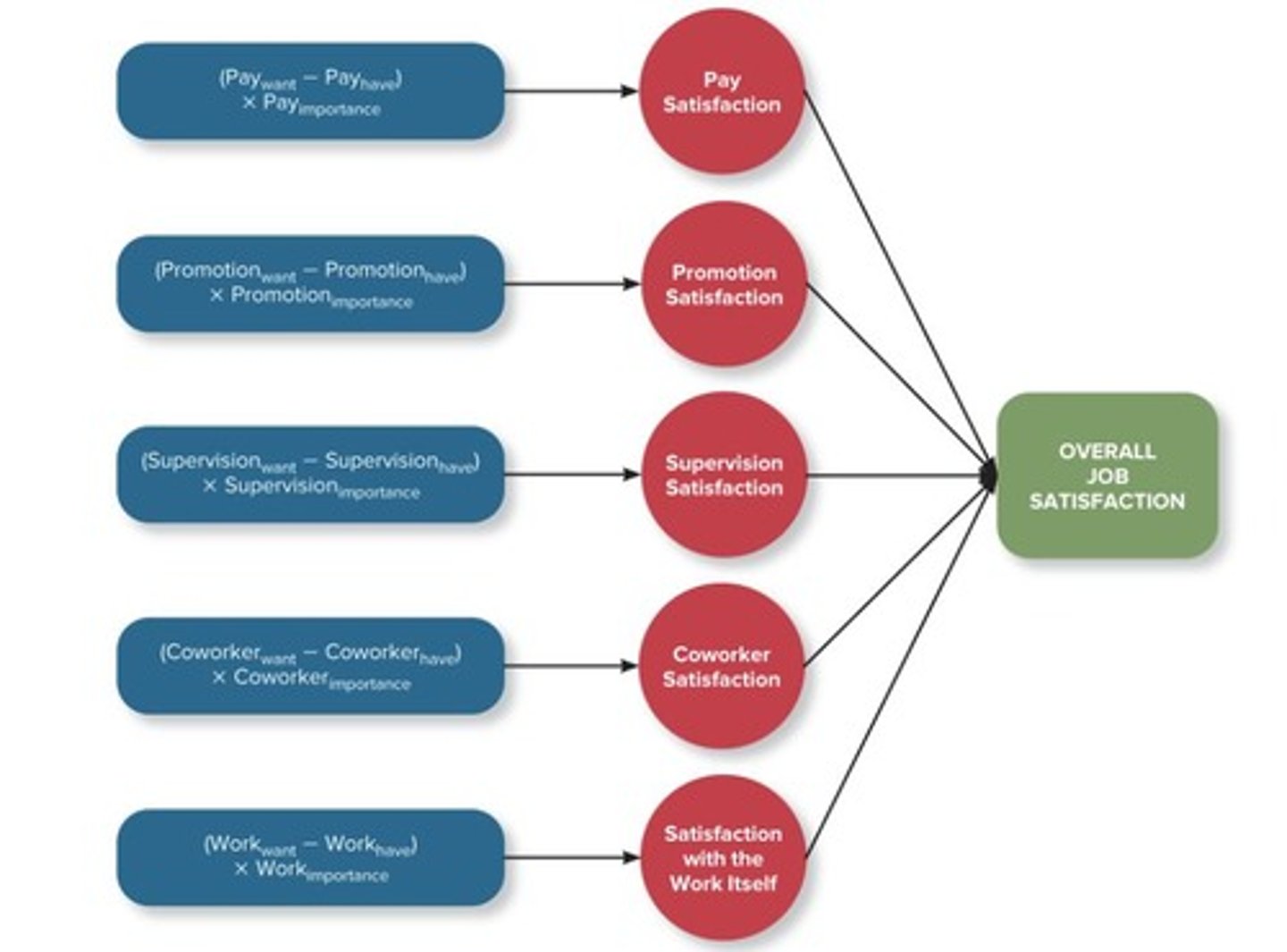
Job satisfaction
Emotional state from appraisal of job experiences.
Values
Conscious and subconscious desires individuals seek.
Value-percept theory
Job satisfaction based on perceived value fulfillment.
Dissatisfaction formula
Dissatisfaction = (Vwant - Vhave) x Vimportance.
Vwant
Value an employee desires from their job.
Vhave
Value supplied by the job to the employee.
Vimportance
Significance of the value to the employee.
Pay satisfaction
Employee feelings about fairness and adequacy of pay.
Promotion satisfaction
Feelings about fairness and frequency of promotions.
Supervision satisfaction
Feelings about boss's competence and communication.
Coworker Satisfaction
Contentment with colleagues' intelligence and helpfulness.
Satisfaction with Work Itself
Feelings about job tasks' challenge and interest.
Scientific Management
Focuses on efficiency through task simplification.
Critical Psychological States
Key factors influencing job satisfaction.
Meaningfulness of Work
Perception of work's significance to personal beliefs.
Responsibility for Outcomes
Feeling of being a key driver of results.
Knowledge of Results
Awareness of performance quality in job tasks.
Job Characteristics Theory
Framework identifying traits of satisfying jobs.
Variety
Diversity of skills and tasks in a job.
Identity
Completing a recognizable piece of work.
Significance
Impact of job on others and society.
Autonomy
Freedom and independence in job performance.
Feedback
Direct performance information from job activities.
Employee Philosophies
Personal beliefs aligning with workplace values.
Job Task Satisfaction
Contentment with the nature of job tasks.
Workplace Relationships
Interactions with coworkers affecting job satisfaction.
Organizational Profitability
Financial success linked to employee productivity.
Task Challenge
Degree of difficulty in job responsibilities.
Job Simplification
Reducing task complexity to enhance efficiency.
Psychological Impact
Emotional effects of job characteristics on employees.
Work-Life Balance
Time spent with coworkers versus family.
Knowledge and skill
Employee aptitude and competence for job success.
Growth need strength
Desire for personal development among employees.
Job characteristics theory
Framework to enhance employee satisfaction through job design.
Job enrichment
Expanding job duties for increased variety and autonomy.
Job crafting
Proactively reshaping jobs to enhance satisfaction.
Moods
Mild, prolonged emotional states not caused by specific events.
Affective events theory
Workplace events trigger emotional reactions influencing attitudes.
Emotions
Intense, short-lived feelings directed at specific causes.
Employee satisfaction
Fluctuating levels of contentment in the workplace.
Learning
Permanent changes in knowledge or skills from experience.
Decision making
Process of generating and choosing alternatives to solve problems.
Affective reactions
Emotional responses that influence work attitudes and behaviors.
Variety in jobs
Diverse tasks that can enhance employee satisfaction.
Autonomy in jobs
Employee control over their work and decision-making.
Job identity
Employee's sense of purpose and ownership in their work.
Employee competence
Ability to perform job tasks effectively.
Expertise
Knowledge and skills distinguishing experts from novices.
Experience
Key factor in differentiating learning levels.
Learning Behaviors
Observable actions indicating knowledge acquisition.
Permanent Behavior
Indicates successful learning by an employee.
Explicit Knowledge
Easily communicated information.
Tacit Knowledge
Knowledge gained through personal experience.
Reinforcement
Methods to encourage desirable employee behaviors.
Operant Conditioning
Learning through behavior-consequence associations.
Positive Reinforcement
Reward following desired behavior to encourage repetition.
Negative Reinforcement
Removal of unpleasant outcome to encourage desired behavior.
Punishment
Unpleasant consequence following an undesired behavior.
Extinction
Removal of consequence to reduce unwanted behavior.
Antecedent
Signals indicating expected behaviors or actions.
Contingencies of Reinforcement
Four consequences modifying employee behavior.
Continuous Cycle of Reinforcement
Repetition strengthens behavior through ongoing reinforcement.
Timing of Reinforcement
Critical factor influencing effectiveness of reinforcement.
Desired Outcomes
Results that reinforce specific employee behaviors.
Undesired Behaviors
Actions that organizations aim to reduce.