B1.1 Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are the 3 functions of carbohydrates?
Energy source – released from glucose during respiration
Energy store – e.g. starch & glycogen
Structural – cellulose
What are monosaccharides and what are their properties?
‘Monomers’ of carbohydrates
All monosaccharides have similar properties:
Soluble in water - why is this useful in living organisms?
Sweet tasting
Form crystals
Chemically stable
Yields high levels of energy when broken down - what important reaction uses glucose as a reactant?
Draw Alpha and Beta glucose.
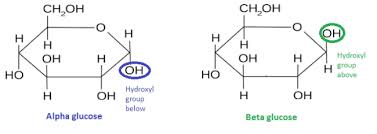
Disaccharide properties:
Soluble
Sweet tasting
Form crystals
Examples of disacharides
Glucose + glucose = maltose
Glucose + fructose = sucrose
Glucose + galactose = lactose
What is a condensation reaction?
Condensation reaction: two molecules are linked together and a water molecule is released.
Water is formed by removing a hydroxyl group (-OH) from one molecule and a hydrogen (-H) from the other. A bond is formed between the molecules as water is released.
Requires energy from ATP.
Formation of disaccharides (bonds)
Formed when two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond (covalent).
The reaction involves the formation of a water molecule (H2O)
The glycosidic bond forms at carbon 1 of the first glucose molecule, and carbon 4 of the second - called α -1,4 glycosidic bond.
Many of these 1-4 glycosidic bonds results in an unbranched chain.
What glycosidic bonds causes branching?
1,6 glycosidic bonds
Amylose, amylopectin, glucose and cellulose
Amylose consists of 1000’s of α -glucose molecules; all bonded together by 1,4 glycosidic bonds through condensation reactions. Unbranched, straight chains.
Consists of α –glucose molecules in a branched chain, bonded by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Polymer of α –glucose molecules (1,4 & 1,6 glycosidic bonds), Similar structure to starch, but shorter chains, Lots of branches, Found in animals
Polysaccharide of b-glucose molecules bonded together by condensation reactions (1,4, links). The chains are straight and long (unlike chains of a-glucose molecules which are coiled and often branched). The chains are strong, and called cellulose. Structural function
Roles of lipids:
Energy source
Excellent store of energy in animals and plants seeds
Being insoluble not leached from the cell
Insulation
Protection
Waterproofing
Buoyancy
Cell membranes
Glycerol is one of the building blocks in lipids. Draw glycerol.
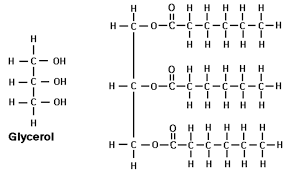
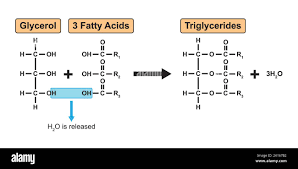
Triglycerides:
Triglycerides are formed by condensation reactions between a glycerol and 3 fatty acids.
These reactions form ester bonds.
They are insoluble in water
Completely hydrophobic.
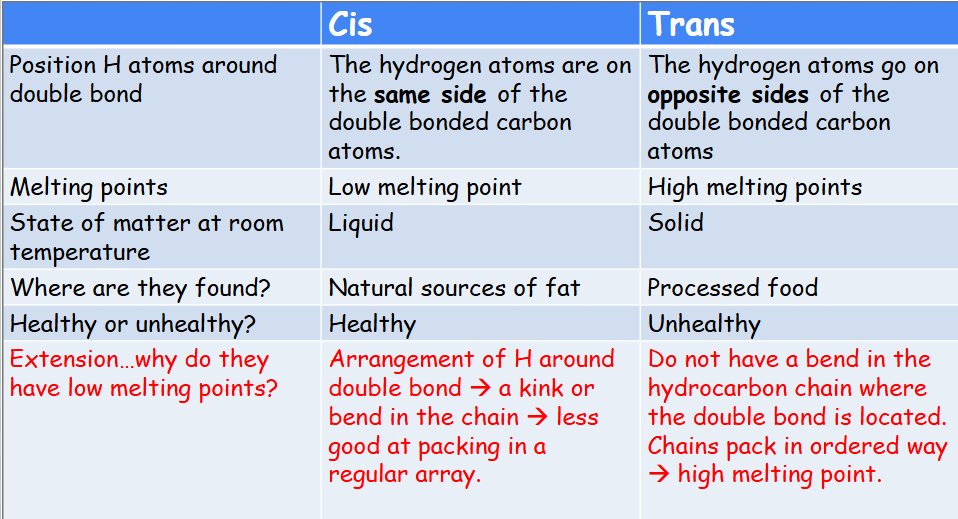
Saturated vs Unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds. They tend to be solid at normal temperatures.
If one double bond – mono-unsaturated
More than one double bond present – polyunsaturated
Unsaturated fatty acids tend to have a low melting points and so tend to be liquid at normal temperatures.
Cis vs Trans fats
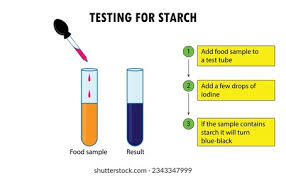
Starch test:
Starch test
Reagent: Iodine
Positive colour: blue/black
Negative colour: orange/brown
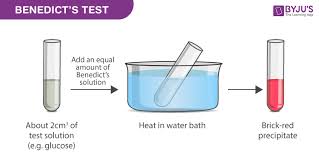
Testing for reducing sugars:
Reducing sugar
Reagent: Benedict’s reagent
Positive colour: brick red
Negative colour: blue
Testing for non-reducing sugars:
?