Lecture 18 - Ocular I
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Cornea
Which part of the eye is a central collagen structure with an anterior squamous epithelium and posterior epithelium, which lacks keratinization and pigmentation? It consists of the epithelium, stroma, Descemet’s membrane, and endothelium, and is continuous with the sclera. It serves to protect the eye and provide a transparent entryway for light into the eye.
Sclera
Which part of the eye is an opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fibers?
Uvea
Which part of the eye is comprised of the iris, ciliary body, and choroid? There is a tapetum in the dorsal choroid (except in pigs), and these structures overall form part of the blood-eye barrier. It also consists of chambers and tunics (anterior/posterior), has zonular fibers arising from the ciliary processes, and allows outflow of aqueous primarily in the iridiocorneal angle/junction. It is the vascular tunic of the eye and produces the aqueous humor in the globe.
Pigs
Which animals do not have a tapetum in the dorsal choroid?
Lens
What part of the eye is an avascular, enclosed structure in a type IV collagen capsule, which maintains its position via zonular fibers, and uses anerobic glycolysis for metabolism?
IV
Which type of collagen forms the capsule around the lens?
Zonular
What type of fibers/ligaments hold the lens in position?
Retina
Which part of the eye is a ten-layered neural tissue with complex synaptic networks, has photoreceptors getting nutrition from the choroid, and gets nutrition for the inner layers by central blood vessels?
Vitreous body
Which part of the eye is a gel-like matrix of water, collagen, and hyaluronic acid, which anchors the lens and maintains ocular shape?
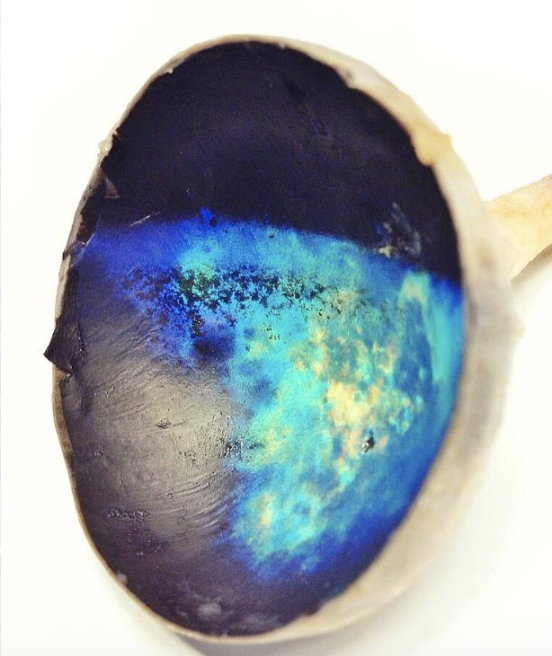
Tapetum lucidum
What structure/layer, found in the dorsal choroid, is shown in the image and is not seen in pigs?
Ciliary process
From what uveal structure do the zonular fibers arise?
Iris, ciliary body, choroid
What three structures together form the uvea/uveal tract?
Aqueous
What humor in the globe is produced by the uveal tract/uvea?
Iridocorneal
Aqueous humor flows out of the uveal tract at which angle/junction?
Retina
From exterior-interior, the retinal pigment epithelium, photoreceptor outer segments, outer nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, inner plexiform layer, ganglion cell layer, and nerve fiber layer together make up what part of the eye?
Panopthalmitis
What is the term for inflammation of all layers and structures of the eye?
Conjunctivitis
What is the term for inflammation of the mucous membrane covering the sclera/inside of the eyelids, the conjunctiva?
Blepharitis
What is the term for inflammation of the eyelid margins?
Keratitis
What is the term for inflammation of the cornea?
Keratoconjunctivitis
What is the term for inflammation of both the cornea and conjunctiva?
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca
What is the term for dry eye, or decreased tear production causing dryness and inflammation?
Corneal ulcer
What is the term for a defect or erosion of the corneal epithelium or stroma?
Uveitis
What is the term for inflammation of the uveal tract?
Iritis
What is the term for inflammation of the iris?
Cyclitis
What is the term for inflammation of the ciliary body?
Panuveitis
What is the term for inflammation of the entire uveal tract?
Glaucoma
What is the term for increased intraocular pressure leading to optic nerve damage and vision loss?
Cataract
What is the term for an opacity of the lens causing impaired vision?
Lens luxation
What is the term for displacement or partial displacement of the lens?
Retinitis
What is the term for inflammation of the retina?
Retinal detachment
What is the term for separation of the retina from the underlying choroid?
Optic neuritis
What is the term for inflammation of the optic nerve?
Phthisis bulbi
What is the term for a shrunken or non-functional eye due to severe or chronic disease?
Buphthalmos
What is the term for an enlarged globe, often due to chronic glaucoma?
Exopthalmos
What is the term for an abnormal protrusion of the eyeball?
Enopthalmos
What is the term for an abnormal sinking of the eyeball into the orbit?
Proptosis
What is the term for a forward displacement of the globe behind the eyelids, which is often traumatic?
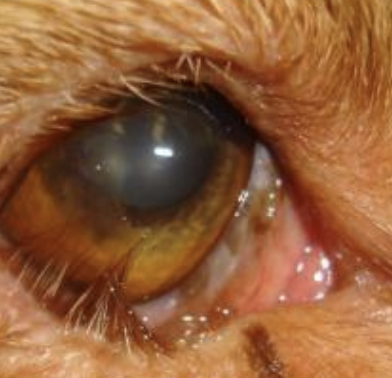
Entropion
What is the term for an inward eyelid margin, found in Chow-Chows, Shar-peis, and sheep?
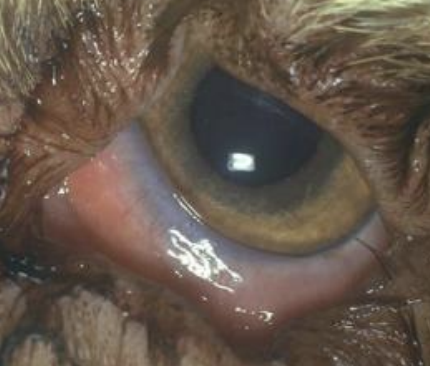
Ectropion
What is the term for an outward eyelid margin, found in Basset hounds and bloodhounds?
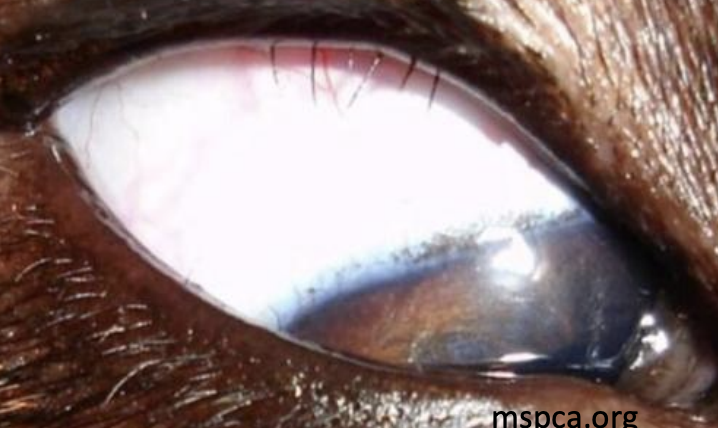
Distichiasis
What is the term, also called an ectopic cilia, which refers to abnormal eyelashes from the meibomian glands or the conjunctiva, found in cocker spaniels?
Eyelid coloboma
What is the term for a defect in the eyelid margin, found in collies and cats? It can be due to failure of closure of the optic fissure.
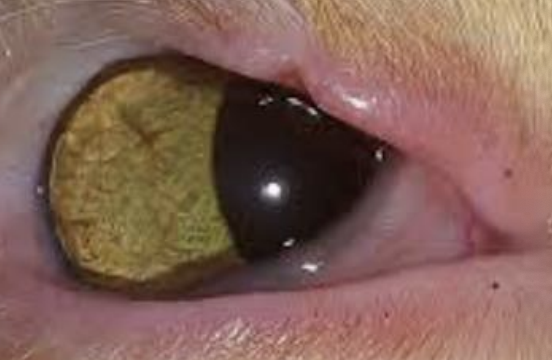
Ankyloblepharon peristens
What is the term for delayed eyelid separation in neonates?
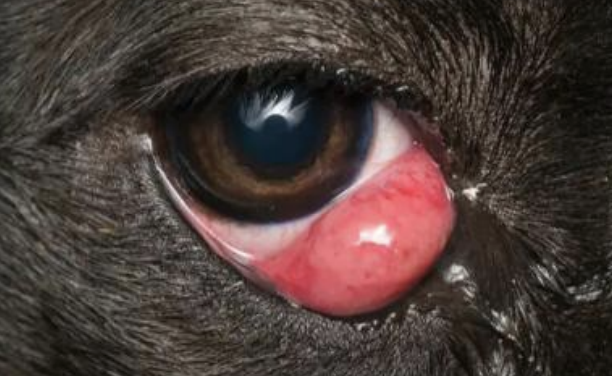
Cherry eye
A prolapse of the lacrimal gland is also called what, and is found in cocker spaniels and bulldogs? It can be due to weakness or rupture of the CT anchoring it to the periorbita, is often idiopathic, can be genetic, is more common in young dogs, and can also be found in Lhasa apsos, shih tzus, and brachycephalic breeds. It can be unilateral or bilateral, involve epiphora, mild irritation, conjunctival hyperemia, and can develop to KCS if the gland’s function is compromised.
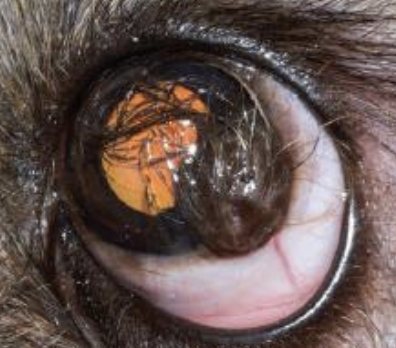
Dermoid
What is the term for a hairy skin-like patch on the conjunctiva/cornea found in dogs and cattle? It can be congenital.
Lacrimal
A cherry eye is caused by prolapse of what gland?
Stromal
What type of corneal dystrophy is seen in Siberian huskies?
Endothelial
What type of corneal dystrophy is seen in Boston terriers?
Yes
Are microcorneas and macrocorneas often seen alongside other abnormalities?
PPM
What condition refers to peristent pupillary membranes, and is seen in Basenjis and mastiffs, due to fetal iris vasculature being retained?
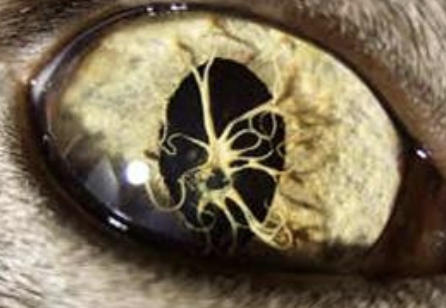
Collie eye anomaly
A uveal hypoplasia will be seen as part of what condition, abbreviated CEA? This is a congenital, inherited eye disorder in herding breeds, caused by a NHEJ1 gene mutation, is autosomal recessive, is found in rough/smooth collies, shetland sheepdogs, border collies, and australian shepherds, and involves choroidal hypoplasia, optic disc/posterior segment colobomas, retinal folds, retinal detachment, and hemorrhage. Signs can be variable and can involve blindness, it is usually non-progressive and present at birth, requires a opthalmic exam at 6-8 weeks, and supportive treatment and genetic screening before breeding.
NHEJ1
What gene’s mutation causes CEA?
Yes
Can cataracts be inherited in some dog breeds, and metabolic in other cases, like in calves?
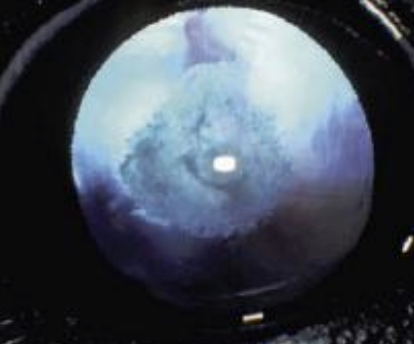
Microphakia
What is the term for a small lens? Aphakia refers to an absent one.
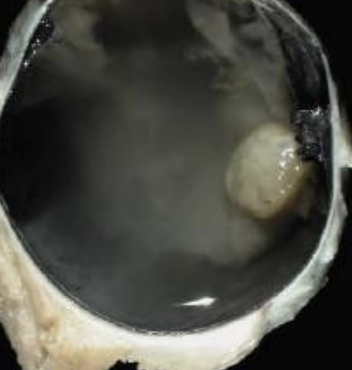
Lens
Lenticonus and lentiglobus refer to abnormal curvature of what eye structure?
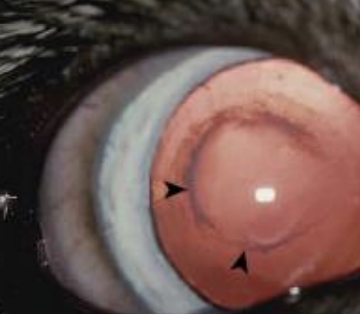
Yes
Does retinal dysplasia lead to retinal detachment?
PHPV
What condition in Dobermans and staffordshire bull terriers refers to peristent hyperplastic primary vitreous humor?
Photoreceptor
Progressive retinal atrophy, or PRA refers to degeneration of what cells and is found in many breeds?
Cattle
Retinal dysplasia in what animals includes folds and rosettes, and can be inherited or due to in utero infections like BVD and feline panleukopenia?
Yes
Is optic nerve hypoplasia a congenital defect?
Anopthalmia
What is the term for the absence of an eye, which is rare?
Micropthalmia
What is the term for a small globe, which can be inherited or infection-induced?
Buphthalmos
What is the term for an enlarged globe from congenital glaucoma?
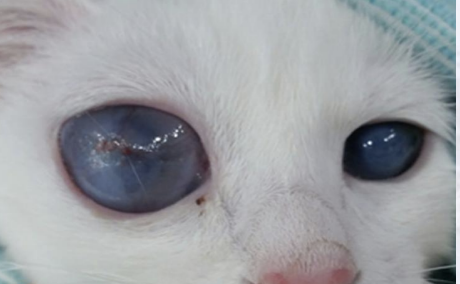
Congenital
What type of glaucoma is caused by a malformed iridocorneal angle, and is found in basset hounds and cocker spaniels?
Merle
Dogs with what coat pattern tend to show ocular dysgenesis, and includes microphthalmia, coloboma, cataracts, and retinal dysplasias?
Rocky Mountain
What horse breed has a silver gene which produces multiple congenital ocular anomalies, or MCOA? They tend to have cysts affecting the iris, ciliary body, or retina.
Albinism
What inherited skin condition involves hypopigmentation, photophobia, and nystagmus? This is due to a lack of melanin in the uveal tract and retinal pigment epithelium. This produces reduced visual acuity, a pale fundus without a tapetum, symmetrical/bilateral changes, and increased susceptibility to UV-related ocular disease.
