Harvard Human Anatomy - Joints
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Joints (Articulations)
The unions between two or more bones or cartilages.
Abduction
Type of motion that occurs when a limb or limb segment moves away from the body midline.
Adduction
Type of motion that occurs when a limb or limb segment moves toward the body midline.
Bone congruence
The degree to which bone surfaces at joints are in contact.
Cartilage
A flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the human body.
Extension
Occurs when the angle between the bones meeting at a joint increases (becomes more obtuse).
Flexion
Occurs when the angle between the bones meeting at a joint decreases (becomes more acute).
Fibrous connective tissue
Unites bones meeting at fibrous joints and fills the spaces between them.
External rotation
Occurs when a limb or limb segment turns around its longitudinal axis away from the midline.
Internal rotation
Occurs when a limb or limb segment turns around its longitudinal axis toward the midline.
Synovial joints
Joints characterized by capsules surrounding articulating surfaces and lubricating fluid within those capsules. Their motion is determined by the shapes of the bone articular ends meeting at the joint and the ligaments and other structures limiting motion.
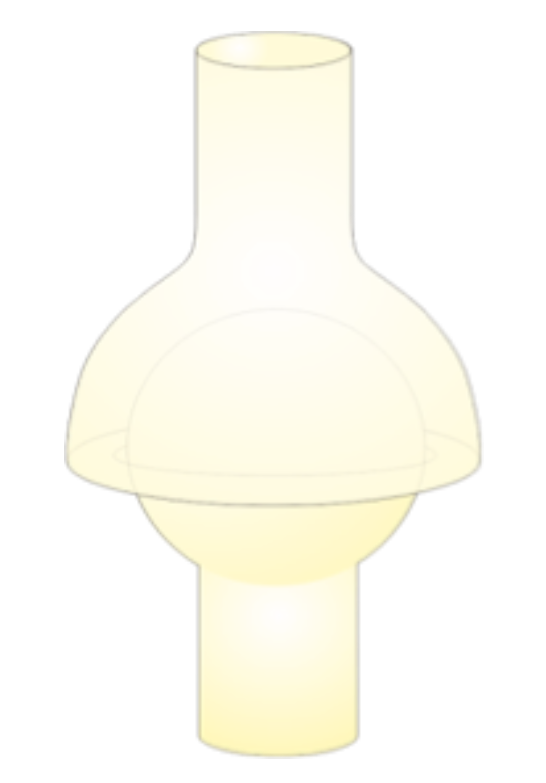
Ball and socket joint
A type of synovial joint permitting motion in three axes.
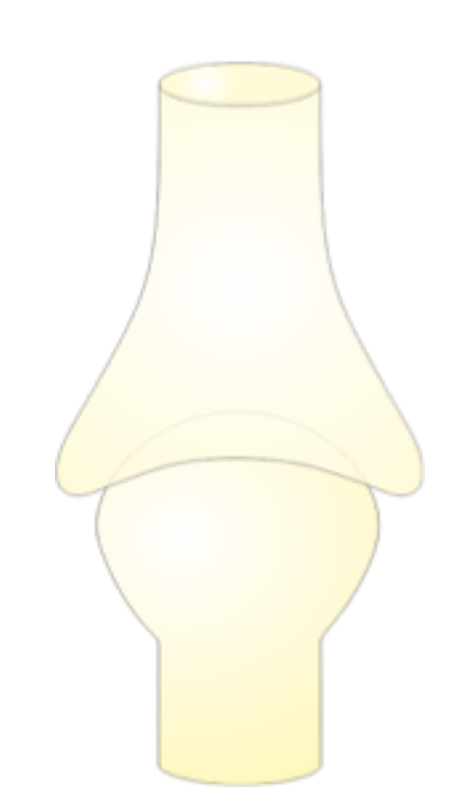
Condyloid joint
A type of synovial joint.
Hinge joint
A type of synovial joint permitting motion in one axis (flexion and extension).
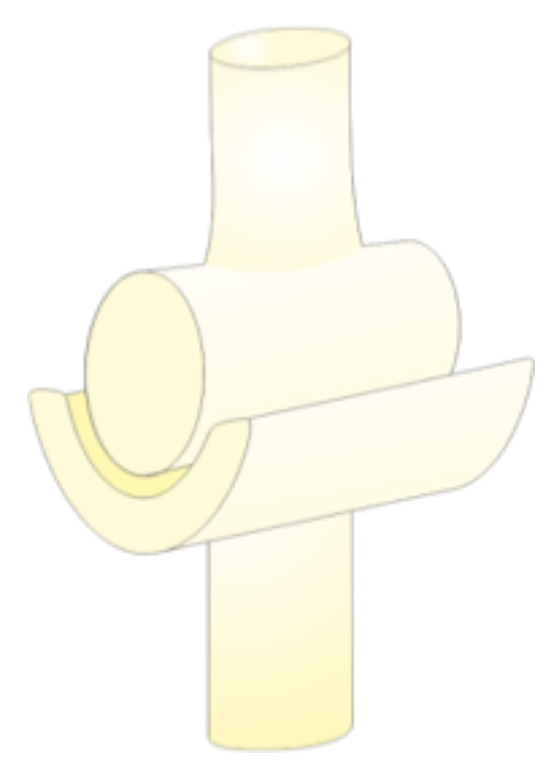
Pivot joint
A type of synovial joint.
Plane joint
A type of synovial joint permitting the gliding of structures.

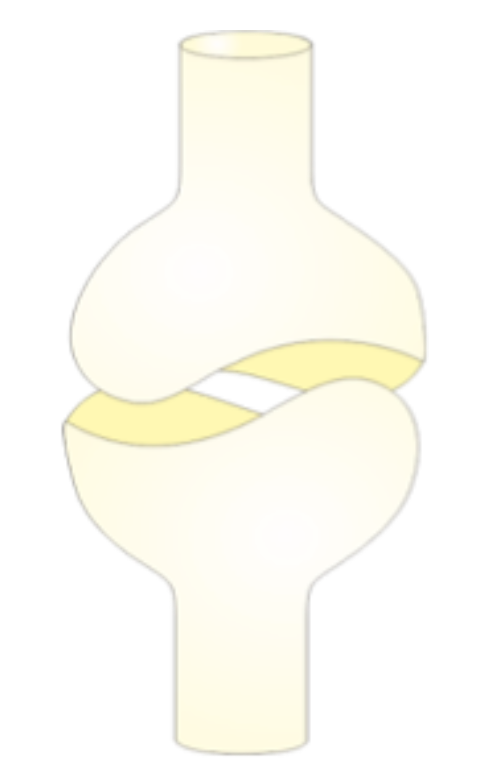
Saddle joint
A type of synovial joint.