WGU - D427 - Data Management - Applications - PreAssessment
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
San Francisco, CA 94110
USA
How many attributes are present in the address fragment?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4
The Package table has the following columns:
Weight—decimal
Description—optional variable length string
LastChangedDate—date
TrackingNumber—integer
Which column should be designated the primary key for the Package table?
- Weight
- Description
- LastChangedDate
- TrackingNumber
Tracking Number
Which data type will store "2022-01-10 14:22:12" as a temporal value without loss of information?
- DATE
- DATETIME
- DECIMAL
- BIGINT
DATETIME
Which SQL command is an example of data definition language (DDL)?
- UPDATE
- ALTER
- SELECT
- DELETE
CREATE, ALTER, OR DROP
How would a database engine process an update that violates a RESTRICT referential integrity constraint?
- The offending value would be set to the database default.
- The update would be rejected by the database.
- The offending value would be changed to NULL.
- The updated value would flow to the primary key.
The update would be rejected by the database.
Which restriction applies when using a materialized view?
- The users of the view must provide search terms.
- The underlying data must be periodically refreshed.
- The tables referenced in the view must be indexed.
- The rows in the table must be compressed.
The underlying data must be periodically refreshed.
Which query illustrates performing an outer join of the Movie table with a different table?
- SELECT M.Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M, Actor A
WHERE M.ActorID = A.ID
- SELECT M.Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M
LEFT JOIN Movie MB ON M.ID, Actor A
- SELECT M.Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M
RIGHT JOIN Actor A ON M.ActorID = A.Id
- SELECT M.Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M
INNER JOIN Actor A ON M.ActorID = A.ID
SELECT M.Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M
LEFT JOIN Movie MB ON M.ID Actor A
Assume there are two tables, A and B.
Which rows will always be included in the result set if Table A is inner joined with Table B?
- Only rows in Tables A and B that share the join condition
- all rows in Table B
- All rows in Table A
- Only rows in Tables A and B that do not share the join condition
Only rows in Table A and B that share the join condition
1. Portland, OR 97212
How many attributes are present in the address fragment?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3
2. The Patient table has the following columns:
first_name varchar(20)
last_name varchar (30)
birthdate date
patient_id int
Which column should be designated as the primary key for the Patient table?
- first_name
- last_name
- birthdate
- patient_id
patient_id
3. The Exam table has the following columns:
exam_id int
exam_date date
exam_reason varchar(100)
patient_number int
Which column should be designated as the foreign key for the Exam table?
- exam_id
- exam_date
- exam_reason
- patient_id
patient_id
4. Which data type represents numbers with fractional values:
- varchar
- integer
- binary
- decimal
decimal
5. Which of the following is a DDL (Data Definition Language) command?
- INSERT
- SELECT
- CREATE INDEX
- UPDATE
CREATE INDEX
CREATE, ALTER, DROP
6. Which of the following is a DML (Data Manipulation Language) command?
- CREATE VIEW
- CREATE TABLE
- INSERT
- ALTER INDEX
INSERT
7. Patient Table
PK patient id
first name
last name
birthdate
Exam Table
PK exam id
exam date
exam reason
FK patient id
CREATE TABLE Exam (
exam_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
exam_date DATE NOT NULL,
exam_reason VARCHAR(100),
patient_id INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (exam_id),
FOREIGN KEY (patient_id) REFERENCES Patient (patient_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);
What would happen to exams in the Exam table that are linked to a patient if that patient is deleted?
- Those exams would remain in the database
- Those exams would be deleted also
- The Patient ID for those exams would be changed to NULL
- Nothing would happen
Those exams would be deleted also
8. Patient Table
PK patient id
first name
last name
birthdate
Exam Table
PK exam id
exam date
exam reason
FK patient id
CREATE TABLE Exam (
exam_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
exam_date DATE NOT NULL,
exam_reason VARCHAR(100),
patient_id INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (exam_id),
FOREIGN KEY (patient_id) REFERENCES Patient (patient_id) ON DELETE RESTRICT
);
What would happen to exams in the Exam table that are linked to a patient if that patient is deleted.
- Those invoices would remain in the database
- Those invoices would be deleted also
- The Customer ID for those invoices would be changed to NULL
- The delete of the Customer would not be allowed
The delete of the Customer would not be allowed
9.
Patient Table
PK patient id
first name
last name
birthdate
Exam Table
PK exam id
exam date
exam reason
FK patient id
CREATE TABLE Exam (
exam_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
exam_date DATE NOT NULL,
exam_reason VARCHAR (100),
patient_id INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (exam_id),
FOREIGN KEY (patient_id) REFERENCES Patient (patient _id) ON DELETE SET TO NULL );
what would happen to exams in the Exam table that are linked to a patient if that patient is deleted.
Those invoices would remain in the database.
Those invoices would be deleted also.
The Customer ID for those invoices would be changed to NULL.
The delete of the Customer would not be allowed.
The Customer ID for those invoices would be changed to NULL
10.
Which of the following are true about materialized view (Choose 2)?
- It is a base table.
- It is stored.
- It must be refreshed whenever the base table changes.
- The results are stored as a temporary table.
It is stored
It must be refreshed whenever the base table changes
11. The Student table will have the following columns:
StudentID—positive integer
FirstName—variable-length string with up to 50 characters
MiddleInitial—fixed-length string with 1 character
LastName—variable-length string with up to 50 characters
DateOfBirth—date
AccountBalance—positive decimal value representing a balance of up to $24,999, with 2 digits for cents
Write a SQL statement to create the Student table.
Do not add any additional constraints to any column beyond what is stated.
CREATE TABLE Student(
StudentID INT UNSIGNED,
FirstName VARCHAR(50),
MiddleInitial CHAR(1),
LastName VARCHAR(50),
DateOfBirth DATE,
AccountBalance DECIMAL(7,2) UNSIGNED
);
12. The Classification table has the following columns:
ClassificationCode—integer, primary key
ClassificationDescription—variable-length string
The Vehicle table should have the following columns:
Name—variable-length string, maximum 30 characters
ClassificationCode—integer
Write a SQL statement to create the Vehicle table. Designate the ClassificationCode column in
the Vehicle table as a foreign key to the ClassificationCode column in the Classification table.
CREATE TABLE Vehicle (
Name VARCHAR(30),
ClassificationCode INT,
FOREIGN KEY (ClassificationCode) REFERENCES Classification(ClassificationCode)
);
13. The Vehicle table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key
Make—variable-length string
Model—variable-length string
Year—integer
A new column must be added to the Automobile table:
Column name: EngineSize
Data type: decimal (2,1)
Write a SQL statement to add the EngineSize column to the Vehicle table.
ALTER TABLE Vehicle
ADD EngineSize DECIMAL(2,1);
14. The Song table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
Write a SQL statement to create a view named MyMusic that contains the Title, Genre, and Year columns for all movies books. Ensure your result set returns the columns in the order
indicated.
CREATE VIEW MyMusic AS
SELECT Title, Genre, Year
FROM SONG;
15. A database has a view named MyMusic.
Write a SQL statement to delete the view named MyMusic from the database.
DROP VIEW MyMusic;
16. The Pet table has the following columns:
petID - integer, primary key
name - variable-length string
breed - variable-length string
birthdate - date
Write a SQL statement to modify the Pet table to make the petID column the primary key.
ALTER TABLE Pet
ADD PRIMARY KEY (petID);
17. The Dog table has the following columns:
dogID - integer, primary key
name - variable-length string
breedID - integer
birthdate - date
The Breed table has the following columns:
breedID—integer
breedDescription—varchar
Releases—integer
Write a SQL statement to designate the breedID column in the Dog table as a foreign key to the breedID column in the Breed table.
ALTER TABLE Dog
ADD FOREIGN KEY (breedID) REFERENCES Breed (breedID);
18. The Song table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
Write a SQL statement to create an index named idx_year on the Year column of the Song table.
CREATE INDEX idx_year
ON Song(Year);
19. The Podcast table has the following columns:
podcastID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Speaker—variable-length string
Minutes—integer
The following data needs to be added to the Podcast table:
Title Speaker Minutes
Rock Painting, Kecia McDonald, 25
Write a SQL statement to insert the indicated data into the Podcast table.
INSERT INTO Podcast (Title, Speaker, Minutes)
VALUES ('Rock Painting', ' Kecia McDonald', 25);
20. The Podcast table has the following columns:
podcastID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Speaker—variable-length string
Minutes—integer
Write a SQL statement to delete the row with the ID value of 33 from the Podcast table.
DELETE FROM Podcast
WHERE ID = 33;
21. The Book table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
Write a SQL statement to update the Year value to be 2022 for all books with a Year value of 2020.
UPDATE Song
SET Year = 2022
WHERE Year = 2020;
22. Which query illustrates performing an outer join of the Movie table with a different table?
- SELECT M.Title, A.Name FROM Movie M, Actor A
WHERE M.ActorID = A.ActorID;
- SELECT M.Title, A.Name FROM Movie M, Actor A
WHERE M.ActorID = A.MovieID;
- SELECT M.Title, A.Name FROM Movie M RIGHT JOIN Actor A
ON M.ActorID = A.ActorID;
- SELECT M.Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M
INNER JOIN Actor A ON M.ActorID = A.ActorID
SELECT M.Title, A.Name
FROM Movie M
RIGHT JOIN Actor A ON M.ActorID = A.ActorID;
23. Assume there are two tables, A and B.
Which rows will always be included in the result set if Table A is inner joined with Table B?
a. Only rows in Tables A and B that share the join condition
b. All rows in Table B
c. All rows in Table A
d. Only rows in Tables A and B that do not share the join condition.
Only rows in Tables A and B that share the join condition
24. The database contains a table named Book.
Write a SQL query to return all data from the Book table without directly referencing any column names.
SELECT *
FROM Book;
25. The Book table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
Write a SQL query to retrieve the Title and Genre values for all records in the Book table with a Year value of 2020. Ensure your result set returns the columns in the order indicated.
SELECT Title, Genre
FROM Book
WHERE Year = 2020;
26. The Book table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
Write a SQL query to display all Title values in alphabetical order A-Z.
SELECT Title
FROM Book
ORDER BY Title ASC;
27. The Book table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
Write a SQL query to output the unique Genre values and the number of books with each genre value from the Book table as GenreCount. Sort the results by the Genre in alphabetical order A-Z. Ensure your result set returns the columns in the order indicated.
SELECT Genre, COUNT(*) AS GenreCount
FROM Book
GROUP BY Genre,
ORDER BY Genre ASC;
28. The Book table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
The YearSales table has the following columns:
Year—integer
TotalSales—bigint unsigned
Releases—integer
Write a SQL query to display both the Title and the TotalSales (if available) for all books. Ensureyour result set returns the columns in the order indicated.
SELECT Title, TotalSales
FROM Book
LEFT JOIN YearStats ON Book.Year = YearStats.Year;
29. The Book table has the following columns:
ID—integer, primary key, auto_increment
Title—variable-length string
Genre—variable-length string
Year—integer
Write a SQL query to return how many books have a Year value of 2019.
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM Book
WHERE Year = 2019;
30. A(n) _____ is a query that is embedded (or nested) inside another query.
- alias
- operator
- subquery
- view
subquery
31. All changes to a table structure are made using the _____ command, followed by a keyword that produces the specific changes a user wants to make.
- ALTER TABLE
- UPDATE TABLE
- COMMIT TABLE
- DELETE TABLE
ALTER TABLE
32. The SQL aggregate function that gives the number of rows containing non-null values for a given column is _____.
a. COUNT
b. MIN
c. MAX
d. SUM
COUNT
33. The _____ condition of a JOIN is generally composed of an equality comparison between the foreign key and the primary key of related tables.
ON
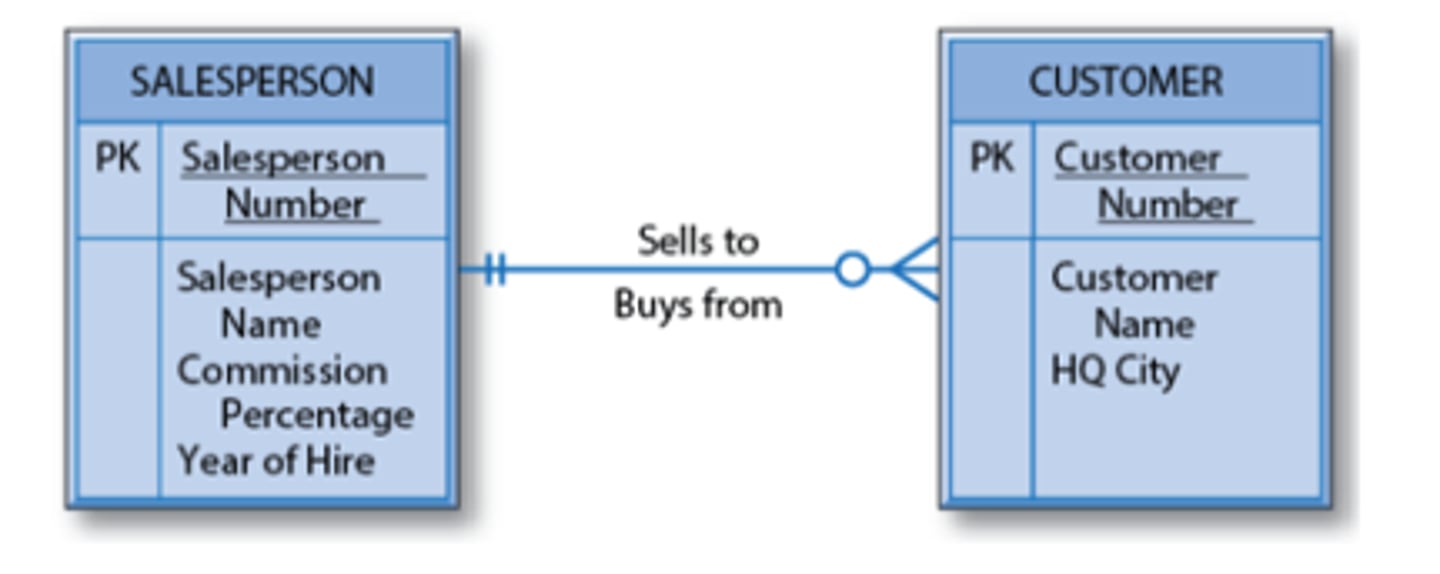
34. Which kind of relationship is displayed in the entity-relationship diagram below?
- Binary one-to-one
- Unary many-to-many
- Ternary one-to-one
- Binary one-to-many
- Unary one-to-one
Binary one-to-many
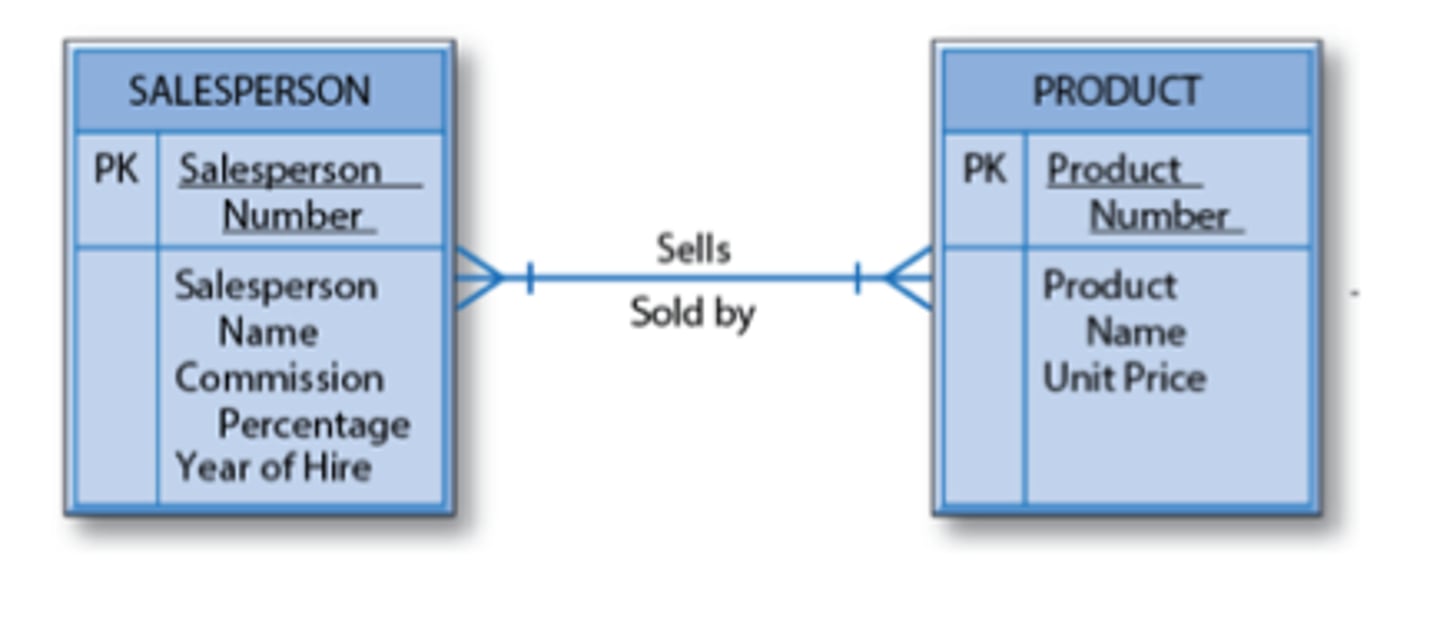
35. Which kind of relationship is displayed in the entity-relationship diagram below?
- Binary one-to-one
- Unary many-to-many
- Ternary one-to-one
- Binary one-to-many
- Unary one-to-one
Binary many-to-many
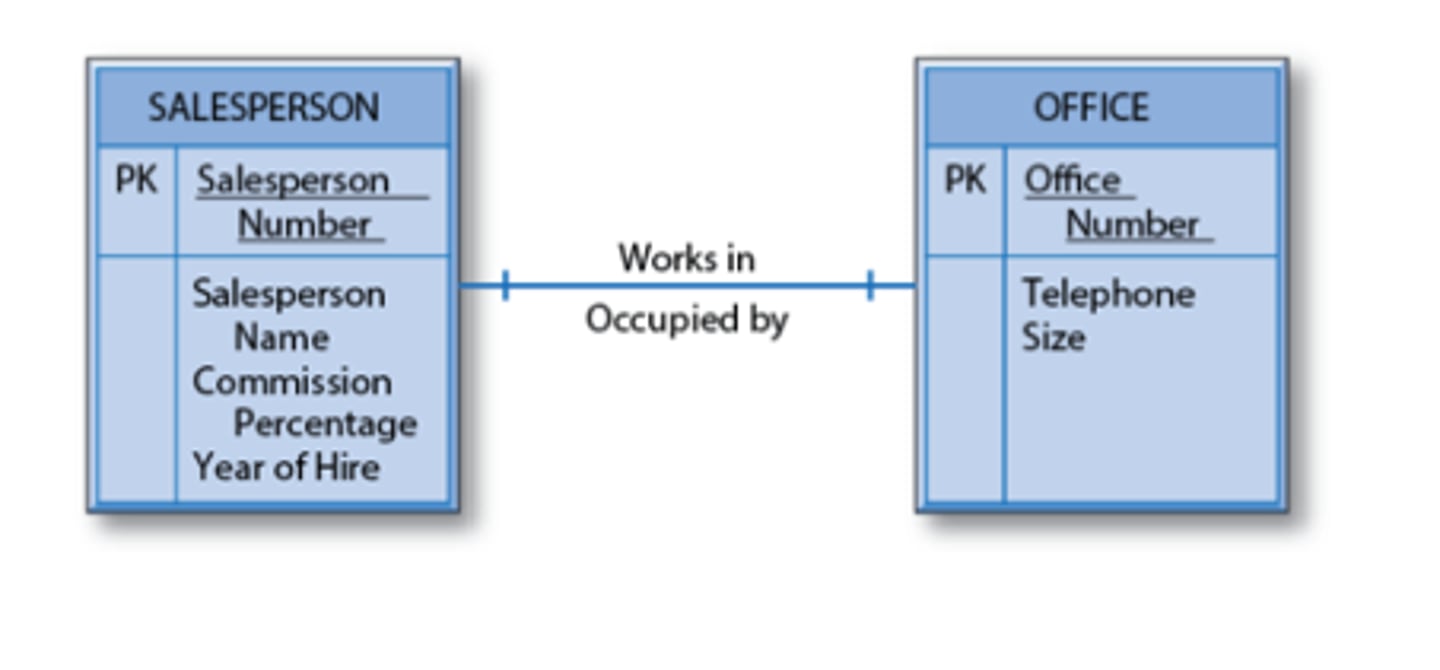
36. Which kind of relationship is displayed in the entity-relationship diagram below?
- Binary one-to-one
- Unary many-to-many
- Ternary one-to-one
- Binary one-to-many
- Unary one-to-one
Binary one-to-one
37. Which data type can be designated to allow for storage of dates
a. VARCHAR
b. INTEGER
c. DECIMAL
d. TIMESTAMP/DATE
TIMESTAMP/DATE
38. PATIENT TABLE
patient_id
first_name
last_name
birthdate
EXAM TABLE
exam_id
exam_date
exam_reason
patient_id
Which query would produce a result set that listed all of the patients, regardless of whether they had an appointment in the Exam table or not.
- SELECT patient_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate, exam_date
FROM Patient
RIGHT JOIN EXAM ON Patient.patient_id = Exam.patient_id;
- SELECT patient_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate, exam_date
FROM Patient
INNER JOIN EXAM ON Patient.patient_id = Exam.patient_id;
- SELECT patient_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate, exam_date
FROM Patient
INNER JOIN EXAM ON Patient.patient_id = Exam.exam_id;
- SELECT patient_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate, exam_date
FROM Patient
LEFT JOIN EXAM ON Patient.patient_id = Exam.patient_id;
SELECT patient_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate, exam_date
FROM Patient
LEFT JOIN EXAM ON Patient.patient_id = Exam.patient_id;
39. MODELS TABLE
model_id
lname
birtdate
model_type_id
MODEL_TYPE
model_type_id
hourly_fee
Which query would produce a result set that listed all of the Model Types, regardless of whether a model was assigned to that type.
- SELECT model_id, lname, Models.model_type_id, hourly_fee
FROM Models
RIGHT JOIN Model_TypeON Models.model_type_id = Model_Type.model_type_id;
- SELECT model_id, lname, Models.model_type_id, hourly_fee
FROM Models
LEFT JOIN Model_TypeON Models.model_type_id = Model_Type.model_type_id;
- SELECT model_id, lname, Models.model_type_id, hourly_fee
FROM Models
INNER JOIN Model_TypeON Models.model_type_id = Model_Type.model_type_id;
- SELECT model_id, lname, Models.model_type_id, hourly_fee
FROM Models
NATURAL JOIN Model_TypeON Models.model_type_id = Model_Type.model_type_id;
SELECT model_id, lname, Models.model_type_id, hourly_fee
FROM Models
RIGHT JOIN Model_TypeON Models.model_type_id = Model_Type.model_type_id;
40. Write a query to list Models along with the model type they are assigned. Include all model information and the hourly fee.
SELECT model_id, lname, birthdate, Models.model_type_id, hourly_fee
FROM Models
INNER JOIN Model_Type ON Models(model_type_id) = Model_Type(model_type_id);
41. Customer Table
Customer_ID
First_Name
Last_Name
Address
City
State
Zip
Mobile_Phone
Write a query to delete Amy Lin from the Customer table show below.
DELETE FROM Customer
WHERE Customer_ID = 101;
42. Write a SQL statement to update Blanca Garcia's phone number in the Customer table below to 555-222-1234.
UPDATE Customer
SET Mobile_Phone = '555-222-1234'
WHERE Customer_ID = 104;
43. Write a SQL statement to retrieve all of the Customers from Seattle from the table below.
SELECT *
FROM Customer
WHERE City = 'Seattle';
44. PATIENT TABLE
PK patient_id
first name
last name
birthdate
EXAM TABLE
PK exam_id
exam date
exam reason
FK patient_id
Write the CREATE TABLE statement to create the Exam table below. Make sure to designate the primary key and foreign key of the table.
CREATE TABLE Exam (
exam_id INT,
exam_date DATE,
exam_reason VARCHAR(255),,
patient_id INT,
PRIMARY KEY (exam_id),
FOREIGN KEY (patient_id) REFERENCES Patient (patient_id)
);
45. Write a query to pull all of the data from the Bagel table below. Order the result set alphabetically by Bagel ID.
BAGEL TABLE
Bagel ID
Bagel Name
Bagel Description
Cost/Bagel
SELECT *
FROM Bagel
ORDER BY Bagel_ID ASC;
46. Write a query to count the number of customers in each city
CUSTOMER TABLE
Customer ID
First Name
Last Name
Address
City
State
Zip
SELECT City, COUNT (*)
FROM Customer
ORDER BY City;
47. Write a query that will return all of the cities from the Customer table above. Do not include duplicates -list each city only once.
SELECT DISTINCT City
FROM Customer
48. Write a query to list customers from Chicago or Seattle.
SELECT *
FROM Customer
WHERE City = 'Chicago' OR City = 'Seattle';
49. Write a join statement that pulls the values listed from 3 of the tables below (Volunteer, Registration, and Activity Registration).
VolunteerID
LastName
Registration Date
ActivityID
VOLUNTEER TABLE
Volunteer ID PK
Last Name
First Name
REGISTRATION TABLE
Registration ID PK
Volunteer ID FK
ACTIVITY REGISTRATION TABLE
Registration ID (PK/FK)
Activity ID (PK/FK)
SELECT V.VolunteerID, V.LastName , R.Registration_Date, A.ActivityID
FROM Volunteer V
JOIN Registration R ON V.VolunteerID = R.VolunteerID,
JOIN Activity_Registration A ON R.Registration_ID = A.Registration_ID;
50. Write a join statement that pulls the values listed from 3 of the tables below (Customer, Invoice, and Invoice Item).
CustomerID InvoiceID Date ProductID
CUSTOMER TABLE
Customer ID PK
INVOICE TABLE
Invoice ID PK
Date
Customer ID FK
INVOICE ITEM TABLE
Invoice ID PK FK
Product ID PK FK
SELECT C.CustomerID, I.InvoiceID, Date, IN. ProductID
FROM Customer C
JOIN Invoice I ON C.CustomerID = I.CustomerID,
JOIN Invoice_Item IN ON I.InvoiceID = IN.InvoiceID;
51. Write a join statement that pulls the values listed from 3 of the tables below (Models, Model Types, Phone Numbers).
model_id
last_name
first_name
model_type_id
phone_number
MODELS TABLE
model_id
last_name
first_name
model_type_id
MODEL TYPES TABLE
model_type_id
PHONE NUMBERS TABLE
model_id
phone_number
SELECT M.model_id, M.last_name, M.first_name, T.model_type_id, phone_number
FROM Models M
JOIN Model_Types T ON M.model_type_id = T.model_type_id,
JOIN Phone_Numbers P ON M.model_id = P.model_id;
52. STUDENT_GRADES TABLE
studentID
lastName
grade
Refer to the given SELECT statement and the table above.
SELECT grade, COUNT(*) AS gradeCount
FROM student_grades
GROUP BY grade;
Which clause added to the statement finds grades with a count greater than 2?
a. WITH gradeCount <> DUPLICATE
b. NOT gradeCount = NULL
c. HAVING gradeCount > 2
d. INCLUDING gradeCount > 2
HAVING gradeCount > 2
53. Using the student_grades table listed above, write a query to count how many students have each grade (A, B, and C).
MODELS TABLE
model_id
SELECT grade, COUNT(*)
FROM student_grades
GROUP BY grade;
54. Using the Model_Types table in the E-R diagram above, write a query to find the highest model fee.
SELECT MAX(fee)
FROM Models;
55. Write a query to update the hourly_fee to 100.00 more for model types with an hourly_fee less than 600.00
UPDATE Model_Types
SET hourly_fee = hourly_fee+100.00
WHERE hourly_fee < 600.00;
56.Which query illustrates performing an outer equijoin of the Movie table with a different table?
a. SELECT M. Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M, Actor A WHERE M.ActorID = A.ID
b. SELECT M.Title, A.Actor FROM Movie MLEFT JOIN Movie MB ON M.ID = MB.ID, Actor A
c. SELECT M. Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M RIGHT JOIN Actor A ON M.ActorID = A.ID
d. SELECT M. Title, A.Actor FROM Movie M INNER JOIN Actor A ON M. ActorID = A.ID
Select M.Title, A.Actor
FROM MOVIE M
RIGHT JOIN Actor A ON M.ActorID = A.ID;
57. Which rows will always be included in the result set if Table A is right joined with Table B?
- Only rows in Tales A and B that share the join condition
- All rows in Table B
- All rows in Table A
- Only rows in Tables A and B that do not share the join condition
All rows in Table B
58. The Dog table has the following columns:
CREATE TABLE dog (
dogID INT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
breedID INT,
birthdate DATE
);
Modify the name column so that the variable length string has a maximum of 25 characters.
ALTER TABLE Dog
CHANGE name name VARCHAR(25);