Econ- chapter 1: what is economics?
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
scarcity
the condition that results from society not having enough resources to produce all the things people would like to have
economics
the study of how people try to satisfy seemingly unlimited and competing wants through the careful use of relatively scarce resources
need
a basic requirement for survival (food, clothing, shelter, etc.)
want
something we would like to have, but is not necessary for survival
TINSTAAFL
there is no such thing as a free lunch
TINSTAAFL
the idea that, although something is marketed as free, there is always someone who has to pay for the resources that produced the product (ex: bogo)
what, how, and for whom to produce
What are the three basic questions asked when producing a good?
factors of production
resources required to produce things we would like to have
land, capital, labor, and entrepreneurs
The factors of production are…
land
“gifts of nature,” or natural resources not created by people
fixed
Do economists think of “land” as being fixed or unfixed? (limited or unlimited?)
capital
the result of production
capital goods
manufactured goods that are used to produce other goods and services, such as tools, equipment, machinery, and factories
labor
people with all their efforts, abilities, and skills
birthrates, immigration, famine, war, and disease
What factors have historically had an impact on the quality and/or quantity of labor?
entrepreneur
a risk taker in search of profits who does something new with existing resources
they are the people who start new businesses or bring new products to the market
Why are entrepreneurs thought to be the driving force in an economy?
description, analysis, explanation, and prediction
What are the four key elements to the study of the social science of economics?
GDP
gross domestic product
gross domestic product (GDP)
the dollar value of all final goods, services, and structures produced within a country’s borders in a 12-month period
gross domestic product
What is the most comprehensive measure of a country’s total output and a key measure of a nation’s economic health?
the economic activity that it describes
What does economics analyze?
jobs, prices, trade, taxes, and government spending
What does economics describe?
good
a useful, tangible item, such as a book, car, or compact disc player, that satisfies a want
consumer goods
goods intended for final use by individuals
durable good
any good that lasts three years or more when used on a regular basis
nondurable good
and item that lasts for fewer that three years when used on a regular basis
service
work that is performed for someone
value
a worth that can be expressed in dollars and cents
paradox of value
scarcity was necessary for something to have value, yet, scarcity by itself could not fully explain how value is determined (diamonds valued higher that water, although water is a necessity and diamonds are not)
utility
the capacity to be useful and provide satisfaction (not measurable, and may vary from one person to the next)
is must be scarce and have utility
What are the requirements for something to have monetary value?
wealth
the accumulation of products that are tangible, scarce, useful, and transferable from one person to another
no- they are intangible
Are services counted as wealth?
market
a location or other mechanism that allows buyers and sellers to exchange a specific product
factor market
where the factors of production are bought and sold
factor markets
Where do individuals earn their incomes?
product markets
where producers sell their goods and services
the circular flow of economic activity
the continuous exchange of goods, services, and money between businesses, product markets, individuals, and factors markets
economic growth
when a nation’s total output of goods and services increases over time
productivity
What is the most important factor contributing to economic growth?
productivity
a measure of the amount of goods and services produced with a given amount of resources in a specific period of time
human capital
the sum of people’s skills, abilities, health, knowledge, and motivation
by providing education and healthcare
What are some ways governments can invest in human capital?
division of labor
a way of organizing work so that each individual worker completes a separate part of the work (more efficient for a worker to do one task many times than to do many tasks in the same period of time)
specialization
when factors of production perform only tasks they can do better or more efficiently than others
the division of labor
What makes specialization possible?
economic interdependence
we rely on others, and others rely on us, to provide most of the goods and services we consume, meaning events in one part of the world often have a dramatic impact elsewhere
the U.S. economy
What economy has a remarkable degree of economic interdependence?
trade-offs
What is present in every decision we make?
opportunity cost
the cost of the next-best alternative
production possibilities frontier
a diagram representing various combinations of goods and services and economy can produce when all its resources are in use
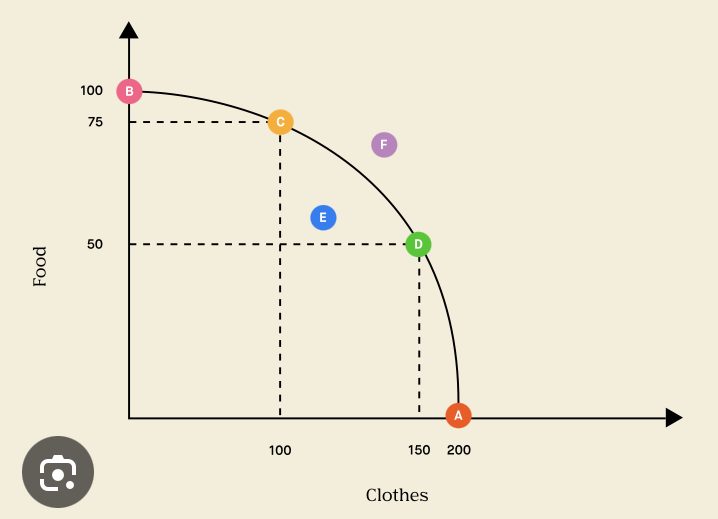
economic model
simplified equation, graph, or figure showing how something works
cost-benefit analysis
a way of comparing the costs of an action to the benefits received
free enterprise economy
an economy in which consumers and privately owned businesses, rather than the government, make the majority of the what, how, and for whom decisions
standard of living
the quality of life based on the ownership of the necessities and luxuries that make life easier