edit RCIS 📚Practice Exam 2024 version
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
What is a complication associated with mechanical cardiac valves?
Thrombus formation
What is the most common complication while performing an endomyocardial biopsy?
Perforation
What imaging modality is used to confirm proper stent opposition?
IVUS
Immediate ED general treatment should include (MI) :
ASA, morphine, nitro, O2
What initial signs of a retroperitoneal bleed May a patient exhibit?
Hypotension, tachycardia, lower back pain, a falling hematocrit
Which of the listed signs and symptoms may indicate a vasovagal response?
Nausea, bradycardia, hypotension
Select the methods used to treat flow limiting dissections?
Stent, Angioplasty, Covered Stent
When using a rotational atherectomy device in the RCA, what else should you consider using?
Stiffer wire, guide with side holes, Temporary pacing wire
Which of the following pacing methods requires the use of external pacing pads?
Transcutaneous
Which of the following is the most commonly used drug for sedation during cardiac Cath?
Midazolam (Versed)
Which vascular closure device has a suture that is self-tightening?
Angioseal
Which of the following segments of the left ventricle would most likely be affected by a significant stenosis of the RCA?
Inferior LV wall
The device that converts X-rays into visible light is the:
image intensifier (II)
________ exposes the operator standing on the patient's right side to the highest dose of radiation.
LAO Cranial
The cephalic vein is located:
In the antecubital area on the inner side of the arm
Which atherectomy catheters shave and sand away plaque?
Orbital and directional
Prior to deploying a vascular closure device in the femoral artery, which angiographic view should be used to visualize the femoral artery bifurcation?
Anterior/Posterior
Which of the following hemodynamic abnormalities would be observed with mitral stenosis?
Large a wave in the LA
Large V-waves in the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) waveform traditionally indicate:
acute MR (e.g., ruptured chordae tendineae)
V-waves greater than twice the mean pulmonary capillary wedge pressures are suggestive of:
severe mitral regurgitation (MR)
Where are baroreceptors located?
Arch of aorta, internal carotid, external carotid
True/False- A wire is needed for both placement and removal of the Impella?
True
________catheter is the "Gold Standard" for LV Angiogram.
Angled Pigtail
The posterior tibial pulse is located:
near medial malleolus
The dorsal is pedal pulse is located:
On the anterior foot
A washer that is visualized on fluoroscopy is placed to mark the:
Proximal vein graft
What is the NYHA classification of a patient on a ventricular assist device?
IV- Severe limitation of activity; symptomatic at rest
What is an alternative to monitor heparin therapy if ACT is not available?
PT/PTT
What is the ACT needed for Impella placement?
150-250
Prior to mitral valvuloplasty a TEE is needed because of what absolute contraindication?
Atrial thrombus
What is regular rhythm combined with alternating strong and weak arterial pulse; usually indicative of left-sided heart failure
Pulsus alternans
When using the Rotablator where should the burr start rotating?
Proximal to the lesion
The drive to breath in a person with COPD is?
Decreased O2
RCA vessel diameter:
2.8 mm
Circumflex (CX) vessel diameter:
3.4 mm
Left Main (LM) vessel diameter:
4.5 mm
Which medication is most commonly given to a patient with SVT?
Adenosine
Heparin potentiates the action of:
Antithrombin
What is the formula for BP?
COxSVR
How do you determine Stroke volume (SV)?
EDV-ESV
Percentage calculation of how much blood the LV can eject with one contraction
Ejection Fraction (EF)
What is the EF formula?
SV/EDV x 100
How do you calculate Cardiac Output (CO)?
HRxSV/1000
What is the Cardiac index formula?
CO/BSA
What is Flamm's equation?
(3)SVC+(1)IVC/4
When calculating a L to R shunt occurring in the RA, what formula should be used for mixed venous saturation?
Flamm's Equation
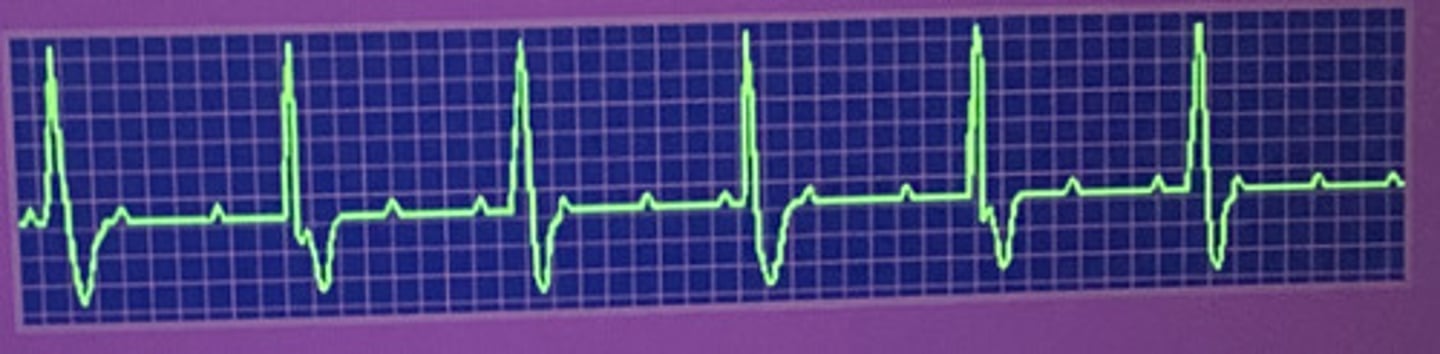
What type of heart block is this?
third degree
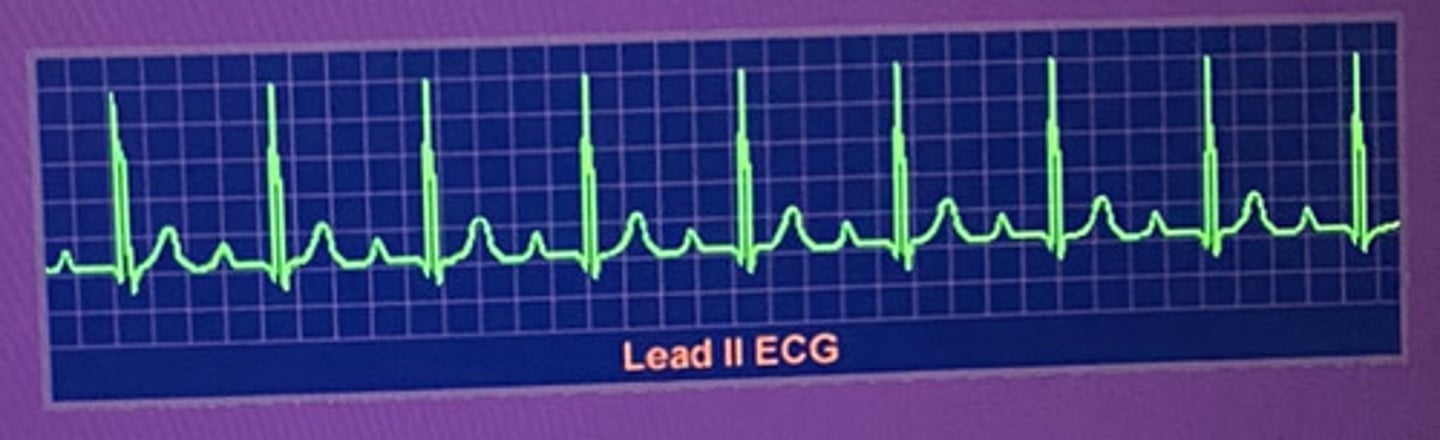
What type of heart block is this?
1st degree
Activated clotting time (ACT) is used to asses the effects of which medication?
Heparin
What French size is equal to a 1.5 mm rotational atherectomy burr?
4.50
Which of the following is associated with in-stent restenosis?
Poor stent apposition
In the AP projection, which of the following structures is the most posterior?
Left Atrium
What is used to reduce the cavitation effect and expanding gas bubbles inside the artery during laser atherectomy?
Rapid saline injection
What type of catheter is used for a thrombectomy?
Extraction
A "WAterhammer" pulse is caused by what valvular disease?
Aortic insufficiency (Regurgitation)
Atherosclerosis begins when?
endothelial cells are damaged with fatty streak which is accumulation of lipids in the intimal layer of the artery.
myocardial ischemia stage:
ST depression
___________will cause metabolic alkalosis
An increase in sodium bicarbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate range
22-26
CO2 range in blood
35-45
Normal pH of blood
7.35-7.45
injury (MI)
ST elevation
An EKG demonstrates ST elevation in leads V5, V6, I & AVL. Which coronary artery is most likely occluded?
CX
When performing a myocardial biopsy post heart transplant, the biopsy is performed to evaluate?
Potential for rejection of the transplanted heart
When using a temporary pacer, where is the lead placed?
RV
Calcified lesions are best managed with which device?
Cutting/scoring balloon
An EKG demonstrates ST elevation in leads II, III & AVF what type of infarct would you suspect?
Inferior wall
A Fogarty balloon is commonly used to:
pull clot back into a vein
Vagal maneuvers:
Gagging, holding breath, bearing down, coughing, splash face with cold water (H2O)
What blood chemistry would be used to determine the amount of contrast used in an angiographic procedure?
Creatinine
An ABI measures the difference between the ________ and ________ pulses.
Left brachial, left pedal
An ABI reading of ________ indicates a flow limiting lesion.
0.7
Prior to deploying a vascular closure device in the femoral artery which view should be used to visualize the bifurcation?
Anterior/posterior (AP)
Cannulation of the femoral artery should be:
One finger breath below the inguinal fold
Pseudoaneurysm occurs most commonly when the puncture site is the:
SFA, External iliac artery, given inadequate compression time
Treatment of a Pseudoaneurysm includes:
Thrombin injection into the sac, ultrasound guided compression, surgical management
Physical signs of a Pseudoaneurysm may include:
palpable pulsatile mass, presence of a systolic bruit, significant site pain
What is a normal PR-interval?
.12-.20
PEG hydrogel plug:
Mynx
Suture mediated:
Perclose
Collagen & suture mediated closure device
Angio-Seal
Nitinol clip:
Starclose
What is the ACT necessary before a PCI is safely carried out?
250-350 seconds
For PCI non-emergent planned procedures warfarin is discontinued ________days prior.
4
For PCI anticoagulation therapy an ACT of 250-350 seconds is necessary before a PCI is safely carried out. ACT is checked within _________min of 1st dose then _________min throughout procedure.
5, 30
Signs & symptoms that may indicate a vasovagal response:
Nausea, bradycardia, hypotension
Buildup of fatty/fibrotic plaque on the vessel wall:
Atherosclerosis
The stiffening of the arterial wall due to calcification:
arteriosclerosis
The myocardial oxygen supply should equal myocardial oxygen demand. Mismatches in this relationship can lead to:
injury or ischemia
The myocardial oxygen supply is influenced by the:
Radius of the coronaries, coronary perfusion pressure, as well as oxygen & hemoglobin levels
Myocardial oxygen demand if influenced by:
Heart rate, preload, afterload, contractility
__________can decrease foward flow and pressure in the pulmonic circuit, and ultimately to the systemic circuit. Blood volume and pressure will initially increase in the right ventricle and can lead to a similar increase in the RA and systemic venous system
pulmonic valve stenosis
Results in decreased filling of the RV forward flow to the lungs, left heart, and systemic circuit. An increase in blood volume and pressure will initially occur in the RA and May ultimately be transmitted back to the systemic venous system, leading to venous congestion.
Tricuspid valve stenosis
When valves do not close all the way, they leak and are considered to be ___________.
Regurgitant or Insufficient
Regurgitant, or insufficient, valves can cause __________________. This can lead to congestion in the chamber before the valve and can decrease forward CO after it.
An increase in blood volume and pressure in the upstream chamber or vessel.
Blood flow to the LV is reduced, decreasing preload in the LV and the amount of blood flowing through the systemic circuit. It can also lead to an increase in blood volume and pressure in the Left Atrium and pulmonary circulation.
mitral valve stenosis
results in increased resistance during left ventricle ejection. The increase in Left ventricular blood volume and pressure can ultimately lead to similar increases in the LA and pulmonary circulation, resulting in pulmonary congestion. It is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality
aortic valve stenosis
Apex to your left, backbone to your right:
LAO
Apex to your right, backbone to your left:
RAO
Ribs tilt _______ toward apex
Down