Comprehensive Review of Learning Theories, Conditioning, and Behavior Analysis in Psychology
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Learning
Permanent change in behavior resulting from experiences/acquisition of knowledge.
Evolution
Change across generations resulting in differential reproduction from existing variation.
Darwin and Artificial selection
Specific trait selected by breeder to be present in next generation.
Natural selection
Survival of the fittest/most adaptable to change.
Observation 1 of Natural selection
Organisms have more offspring than can survive to adulthood.
Observation 2 of Natural selection
Offspring aren't identical (variation in size/appearance etc).
Inference of Natural selection
Organisms better adapted to environment have greater likelihood of surviving + passing characteristics to offspring.
Requirements for Natural selection
Genetic variation, heritability, differential reproductive success.
Lamarckism
Things don't change because organisms want/need them to.
Latent learning
Form of learning not immediately expressed.
Elicited behaviors
Learning not required.
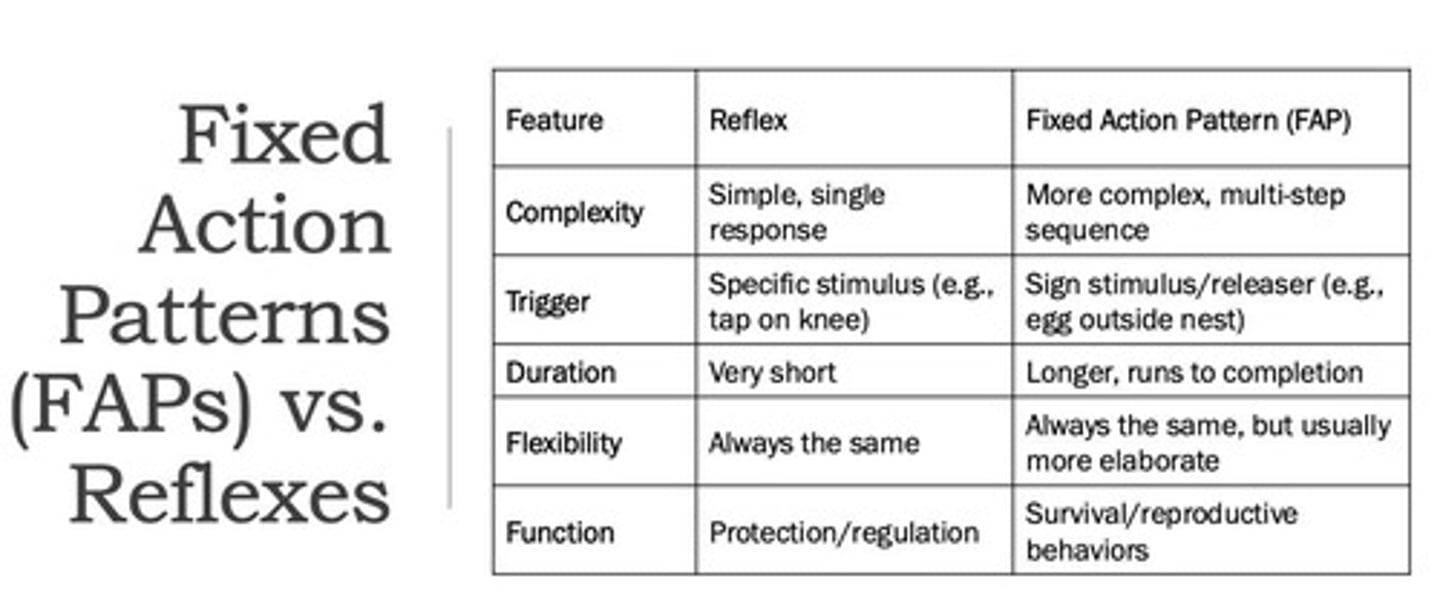
Reflexes
Involuntary response from stimulus.
Fixed action patterns
Species-specific behaviors that must be completed.
Non-associative learning
Organisms' behavior towards specific stimulus changes over time from repetition of stimuli.
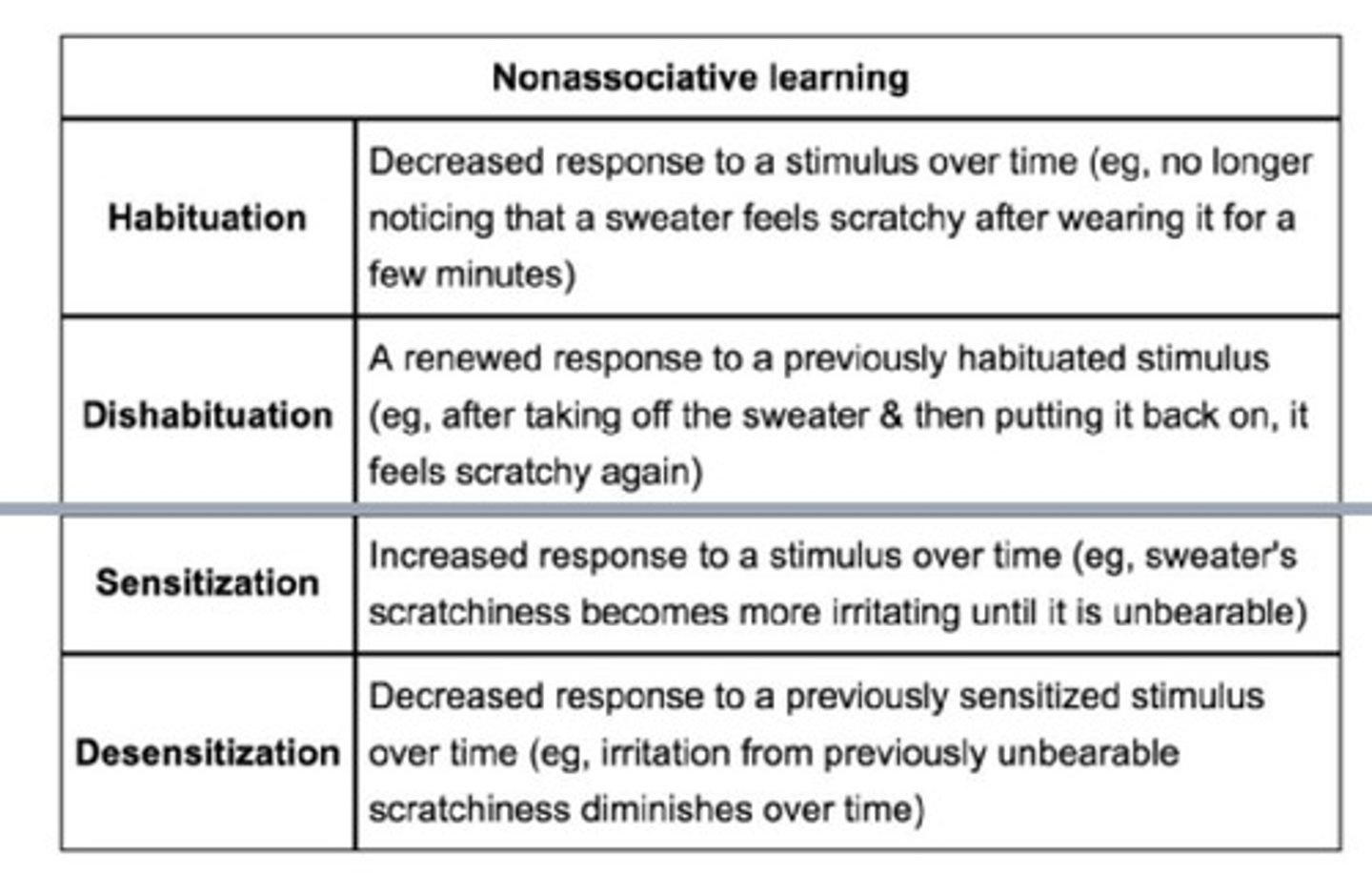
Habituation
Decrease in response within nervous system, helps ignore irrelevant stimuli saving energy.
Sensitization
Increase in response after repeated exposure, preparation to respond stronger to threats.
Classical conditioning
Pavlov - salivation in dogs studying digestion.
2nd order conditioning
Adding neutral stimulus to conditioned stimulus to produce conditioned response.
Anecdotal research
Personal experience (confirmation bias), cherry picking.
Case study
Study on one individual.
Descriptive research
Correlation with mean/standard deviation.
Experimental research
Causation with independent/dependent variable.
Anthropomorphism
Applying human characteristics to nonhumans.
Law of parsimony (Occam's Razor)
Inference to best explanation = simplest explanation with fewest assumptions is best.
Reasons for animal testing
Irreversible effects, control, neurobiological continuity, disease models.
NHP's in testing
Similar reproduction, maternal stress, extended life span, alloparenting, epigenetics, social cognition.
Ethics in animal research
Animals used for research are provided humane care/treatment.
3 R's of animal research
Reduction, Refinement, Replacement.
Institutional animal care and use committee (IACUC)
Oversees/approves all animal research, mandates specifics of training.
Stimulus generalization
Conditioned response occurs in response to objects similar to conditioned stimulus.
Stimulus discrimination
Conditioned response occurs in response to specific stimuli.
Counterconditioning
Conditioned to have positive response to stimulus, to treat phobias.
Strength of behavior
Depends on consequences.
Four key elements of behavior
Environment where behavior occurs, behavior that occurs, change in environment after behavior, probability of behavior in future based on consequence.
B.F. Skinner
Known for operant conditioning and the term 'operant behavior' in instrumental conditioning study.
Skinner box
Operant conditioning chamber that measures behavior without considering what the animal thinks or feels.
Operant
Animal emits behavior and there are consequences; the animal is active.
Reinforcement
Increases behavior.
Punishment
Decreases behavior.
Positive reinforcement
Adds stimulus that was absent prior to responding.
Negative reinforcement
Removes stimulus that was present prior to responding.
Stimulus control
Behavior occurs more often in presence than absence of a particular stimulus.
Behavior chain
Sequence of behaviors where each behavior serves as a cue for the next.
Back chaining
Teaching method that starts with the last behavior in a chain.
Interval
Refers to time; frequency refers to ratio.
Differential reinforcement low rates (DRL)
Reinforcement of low rates of behavior.
Differential reinforcement of high rates (DRH)
Reinforcement of high rates of behavior.
Extinction
Increases variability in behavior, increases frequency of emotional behavior, increases previously reinforced behavior.
Extinction burst
Sudden increase in rate of behavior during early stages of extinction.
Variables impacting rate of extinction
Interval between extinction sessions, number of times behavior was reinforced before extinction, effort, type and size of reinforcer, schedule of reinforcement.
Partial reinforcement effect
Behavior maintained on intermittent schedule is more resistant to extinction than on continuous reinforcement schedule.
Escape behavior
Performance of behavior terminates aversive stimulus.
Avoidance behavior
Performance of behavior prevents aversive stimulus from occurring.
1-factor theory
Avoidance is reinforced by decrease in rate of shock.
Learned helplessness
Repeated exposure to aversive events that are predictable but uncontrollable.
Masserman's Experimental Neurosis
Exposure to unpredictable events leads to neurotic-like symptoms.
Vicarious reinforcement
Increase in strength of observed behavior following reinforcement of that behavior in a model.
Vicarious punishment
Decrease in strength of observed behavior following punishment of that behavior in a model.
Social learning mechanisms
How learning occurs, what individuals attend to, specifics of the action they replicate.
Bandura's social cognitive theory components
Attention, Retention, Motor reproduction, Motivation.
Matching law
Predicts consistent relationship between proportion of reinforcers and proportion of responses emitted.
Differential reinforcement
Withholding and providing reinforcement.
Reacquisition
Return of previously reinforced operant behavior during extinction of alternative behavior.
Spontaneous recovery
Reappearance of extinguished behavior.