Psy 437: Marriage and In-Laws
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Identity the top 5 reasons people say they marry
love
making a lifelong commitment
companionship
having children
financial stability
Explain factors related to arrange marriages
elder wisdom: the older individuals in the family have a better sense of lifelong commitment to
lineage & family status
benefit: no rejection in dating
Explain what a common-law marriage is
a legal marriage without a formal ceremony or a license in which the couple plans to formally get married in the future but have certain aspects to prioritize such as finances and cohabitation
Explain legal factors that change after getting married
assets
- property
- retirement benefits
- “next of kin” inheritance
- alimony
taxes
- different rate brackets
- larger standard deduction
- none of spousal gifts
healthcare
- decision-making authority
- hospital visitation rights
- HIPPA helps spouse grant access to their spouse’s medical record
Explain what Financial Infidelity is
the idea of one partner using money in terms that were on agreed upon
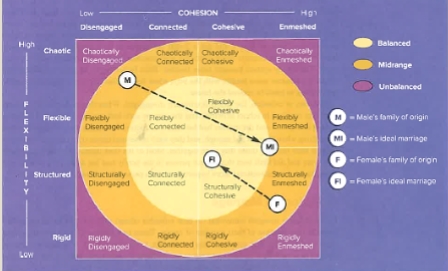
Differentiate between flexibility and cohesion in family type and how these relate to marriage
flexibility > could be very rigid/structured and chaotic
leadership, discipline roles
cohesion > together very disengaged/separate
interdependency, connected
Identify top 4 reasons people say they have children
finding the right partner to have children with
joy of children
adequate financial resources
spouse’s or partner’s wishes
Identify examples of the 4 reactions to finding out having children
planner partners: both spouses discussed it and want to have children
acceptance of fate: pleasant surprise
ambivalent partners: both partners don’t want to have children
yes-no partners: one partner says yes while the other says no
Identify examples of the 4 decision types of couples becoming “child-free”
accelerated consensus: both partners both agree that they don’t want to have kids early on in their relationship; both partners came into the relationship both not wanting to have children
mutual negotiation: both partners had not made a decision of wanting to have children, both communicate the pros and cons of having kids, experience times of uncertainty about wanting children
unilateral persuasion: one spouse is committed to being childfree and convinces the undecided partner to not have kids
bilateral persuasion: both partners disagree completely, one wants to have kids while the others doesn’t which causes heated communication and turmoil
Explain factors related to the “empty nest” period
feelings of malaise
feeling like there is a lack of purpose
or feeling that the nest is “spacious”
boomerang kids: kids move back in with their parents after moving out for a period of time
Identify factors related to changes in marital satisfaction
the honeymoon period: lovey-dovey period of intense levels of love
having their first child
having the second child
the last child leaves the home
retirement
Explain how in-law relationships are different than other relationships
secondhand self-disclosure: learning about the in-laws before meeting them and getting to know them
lack of choice with in-laws
mothers are name first then the father and after that the siblings
spilt between 50/50 for positive and negative relationship with in-laws
Explain what impacts relationship quality with in-laws
contact with the spouses
individual contact (so partner doesn’t have to reach out for them)
generally positive relationship with in-laws
complaints about the son or daughter in-law are due to the in-laws reporting that they are distant and inconsiderate
complaints about the mother or father-in-law typically lie in that they are meddlesome, critical or nagging about the marriage, and can be possessive in regard to their child or grandchildren