Form 4 Unit 22 Physics: Waves
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What are the two types of waves?
Longitudinal and transverse
What are three levels of transparency?
Opaque, translucent, transparent
What are luminous objects?
objects that make their own light
Why can we see light?
Light rays travels from the light source to an object, and then reflects or passes through an object and into our eyes
How do transverse wave travel?
The direction of vibration of fields in the waves is at 90° to the direction that the light travels
How do shadows form(not persona ones)?
when an object blocks light, in which the object is opaque or translucent
What are the two types of shadows(non persona ones)?
Umbra and Penumbra
What is the speed of light in air?
299,702,547m/s
What is an Umbra?
the fully shaded inner region of a shadow cast by an opaque object
What is an penumbra?
a space of partial illumination
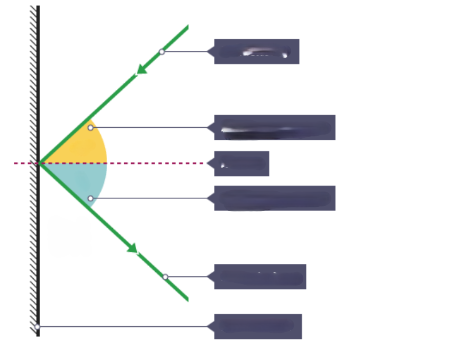
What is the ray that is hitting the surface?
Incident ray
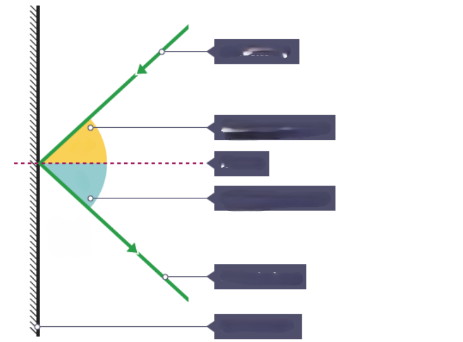
What is the ray that is leaving the surface
Reflected ray
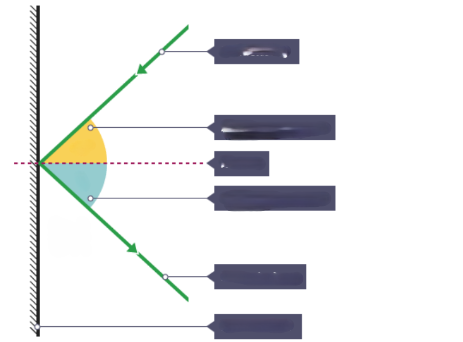
What is the dotted line?
Normal
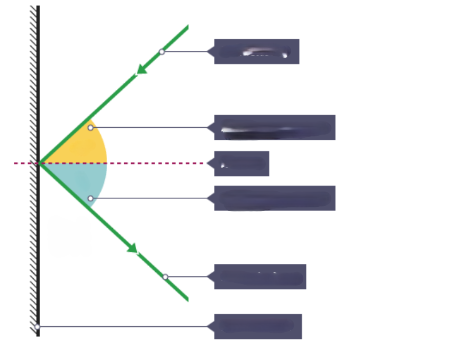
What is the yellow angle?
Angle of incidence
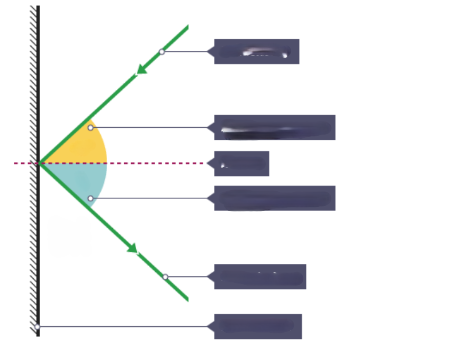
What is the blue angle?
Angle of reflection
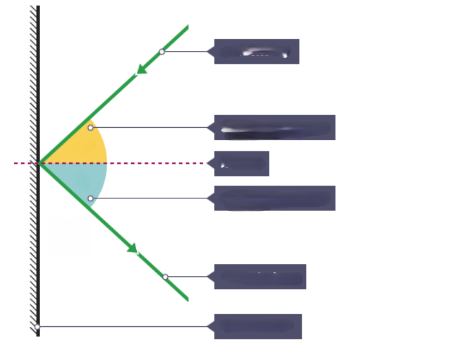
What is the surface that the rays are reflecting from?
Plane mirror
What is the relationship between Angle of incidence and Angle of reflection?
i = r
What is the image formed called when looking into a mirror?
Virtual image
What makes refraction occur?
When a ray reaches a substance with a different optical density from a substance it came from
What does the ray do when it reaches a denser substance?
the light slows down going into a denser substance, and the ray bends towards the normal
What does the ray do when it reaches a less dense substance?
the ray speeds up, and the ray bends away from the normal
What is the critical angle?
48.8 degrees
What happens to the ray after it passes the critical angle?
It reflects back inside the medium
What is the name of the ray reflecting back inside the medium?
Total internal reflection
What are the three primary colours in light?
Red, Green, Blue
What happens if a yellow light ray hits a yellow ball?
It gets reflected, making us see the colour yellow
What happens if a red light ray hits a yellow ball?
The light ray gets absorbed by the ball and we cannot see the ball
What is the order of the EM Waves?
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X-rays
Gamma rays
What types EMR can penetrate earth’s atmosphere?
Radio, Visable
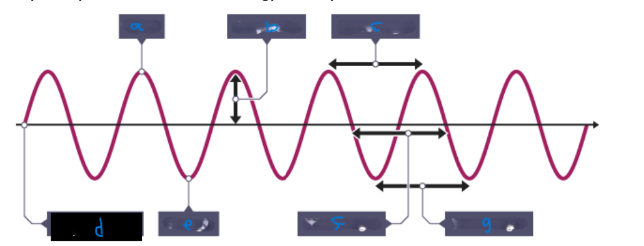
What is A ?
Peak
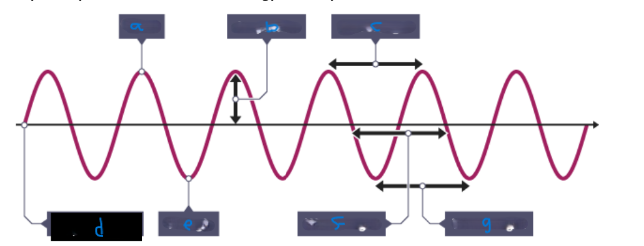
What is B?
Amplitude (amp)
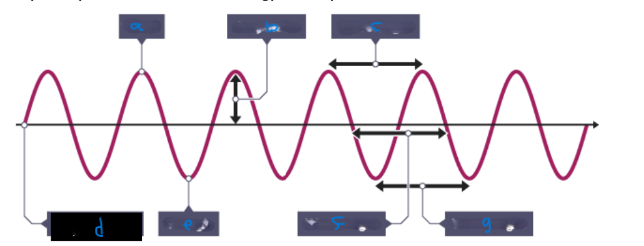
What is C?
Wavelength
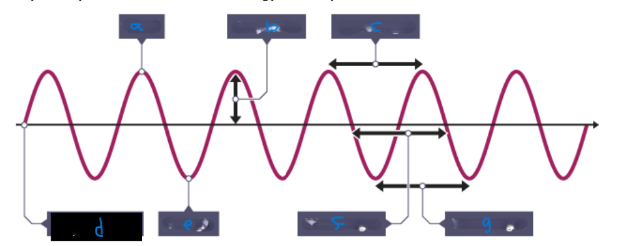
What is D?
Equilibrium
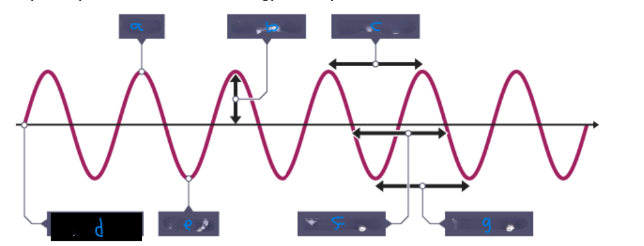
What is E?
Trough
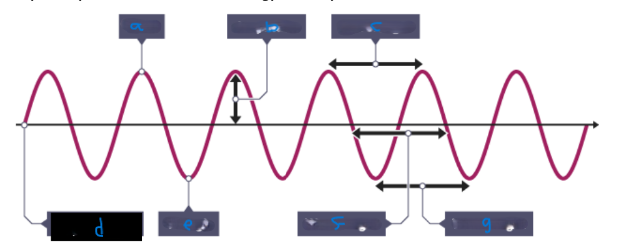
What is F?
Wavelength
What is the time period?
the time taken for a full cycle of the wave,