Case 6: Maria Rossi
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS)
Narrowing of renal arteries or branches = Impair blood flow to kidneys
RAS: Epidemiology
Cause 1-10% of HTN cases
Risk Factors:
Depend on underlying cause
Smoking
RAS: Etiology
Atherosclerosis
Renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia
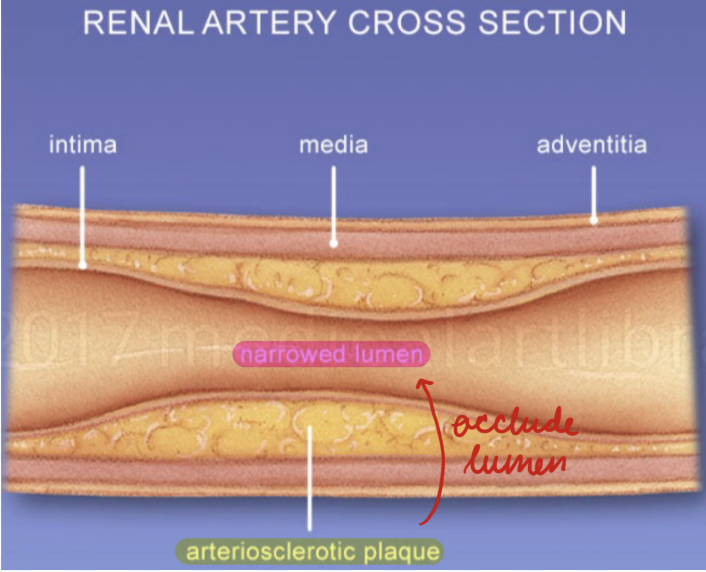
RAS: Atherosclerosis
90%
Mostly men > 50 years
Aterionephrosclerosis: Atherosclerotic plaques in renal arteries
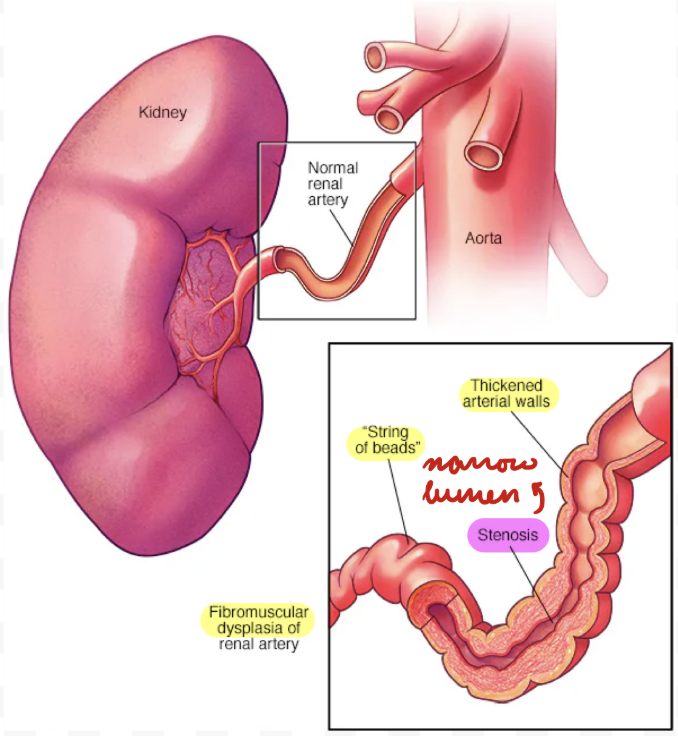
RAS: Renal Artery Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Renal artery stenosis from connective tissue and muscle fibre proliferation
10%
Mostly women < 50 years
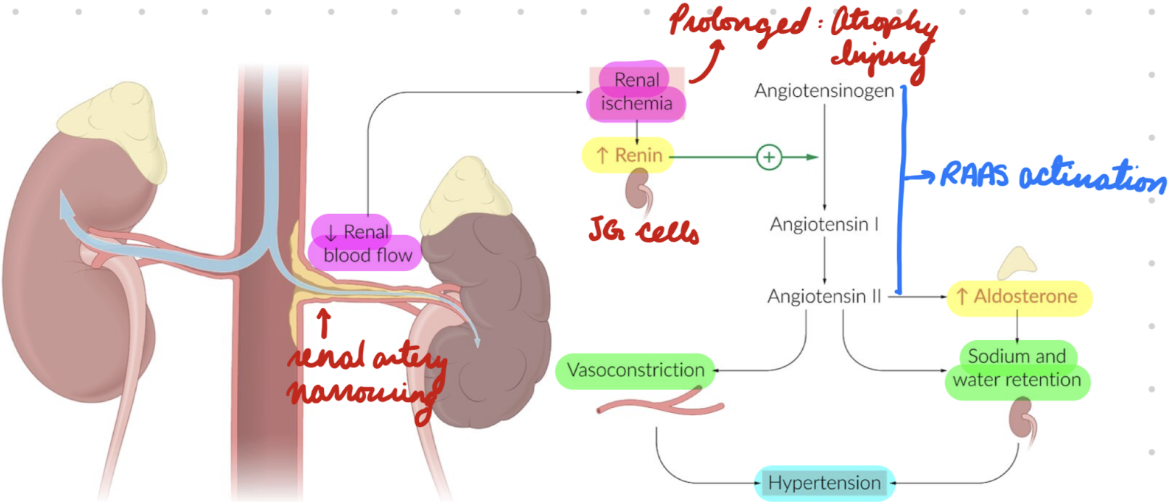
RAS: Pathophysiology
Cause dependent:
Arterionephrosclerosis: Sustained high BP = Endothelial injury = Hyaline deposition in arterial walls
Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Connective tissue and muscle tissue hyperplasia = Obstruct renal artery
Renal artery lumen narrowing = Decrease blood flow to kidneys = Ischemia
Prolonged ischemia = Renal injury + atrophy
Renal hypoperfusion = JG cells release renin = Activate RAAS = Increase aldosterone = Increase Na+ retention and vasoconstriction
JG hyperplasia
Secondary HTN
RAS: Clinical Presentation
Severe/early-onset HTN
Abdominal bruit
Pulmonary edema
Atherosclerosis symptoms
CAD
Carotid stenosis
RAS: Investigations
Imaging
Lab studies
RAS: Imaging
Diagnostic
First-Line:
Duplex ultrasonography
MR angiography
CT angiography
Second-Line: Catheter angiography
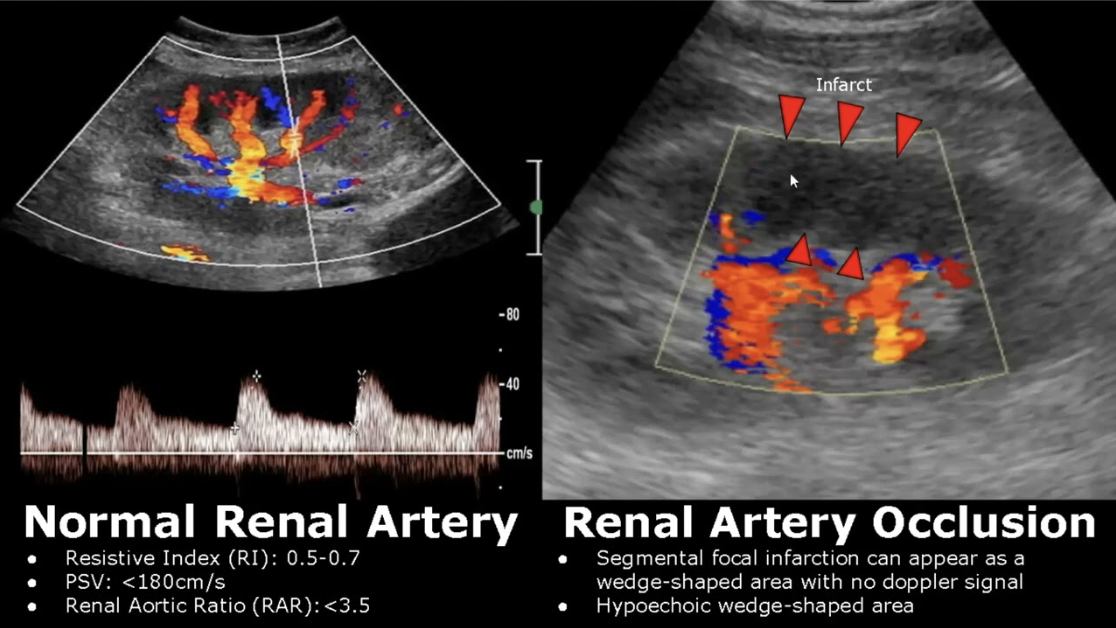
RAS Imaging: Duplex Ultrasonography
Ultrasound image + Doppler
Determine occlusion site + severity
RAS Imaging: MR Angiography
MRI for blood vessels
No contrast (kidney injury)
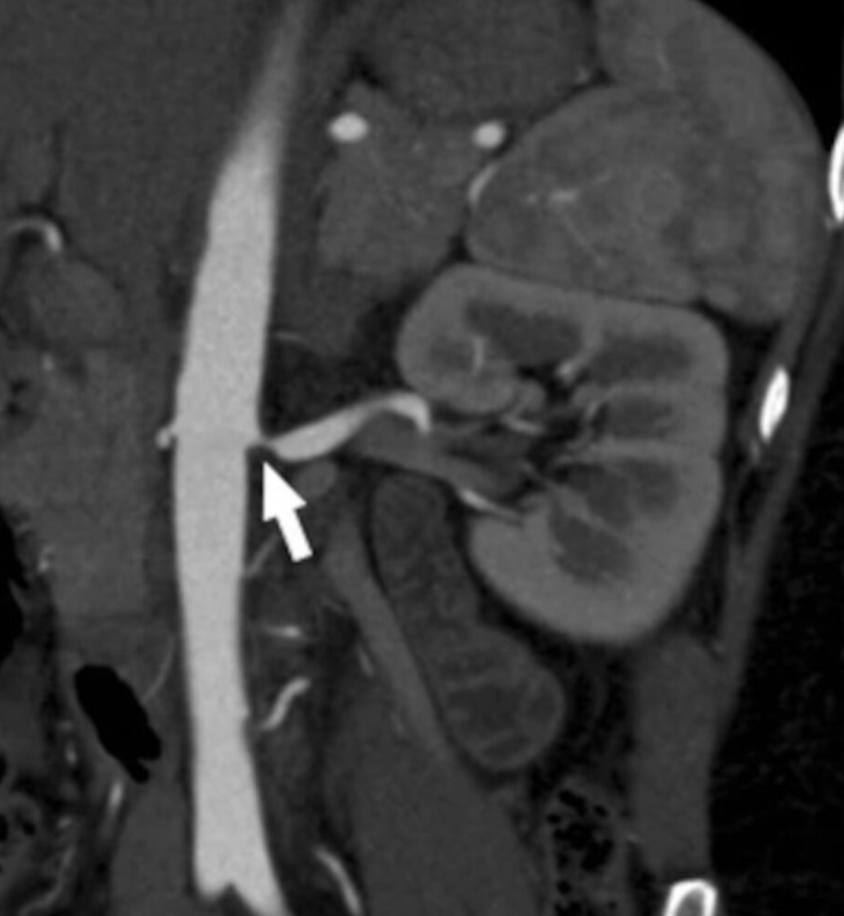
RAS Imaging: CT Angiography
Fibromuscular dysplasia
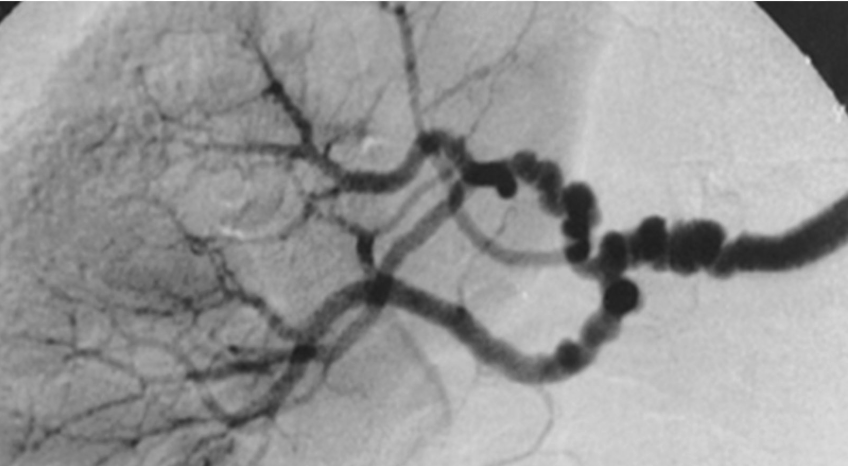
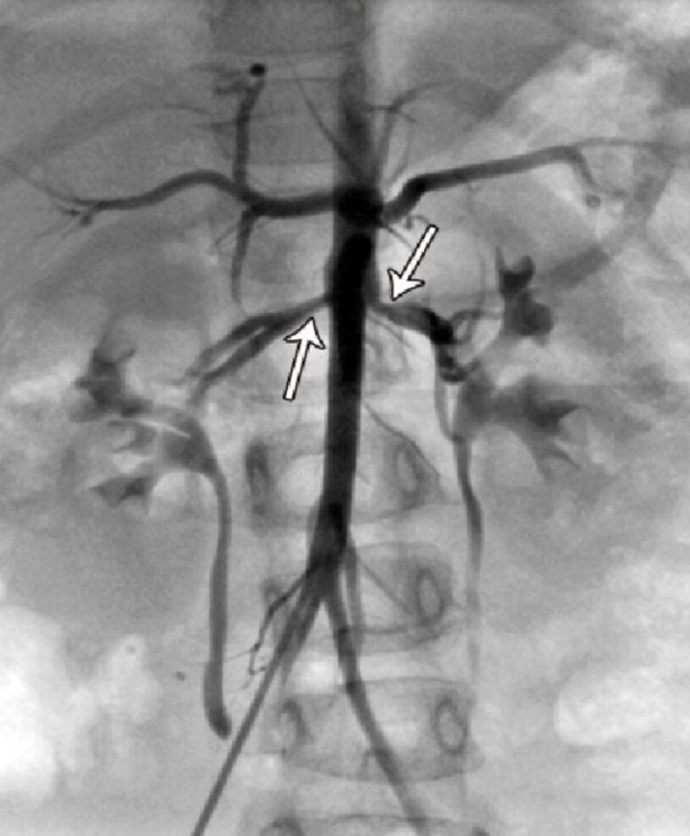
RAS Imaging: Catheter Angiography
Gold standard
Catheter + dye to visualize arteries
RAS: Lab Studies
Supportive
BMP:
Renal insufficiency
Hypokalemia (rare)
Urinalysis:
Proteinuria
RAS: Complications
CVD
Kidney disease
Progress to end-stage
Renal injury + atrophy
Renal artery dissection
Secondary HTN
Elevated BP (≥ 140/90 mmHg) caused by underlying condition
Secondary HTN: Etiology
RAS
Hyperaldosteronism
Thyroid dysfunction
Renal parenchymal disease
Secondary HTN: Pathogenesis
Depend on underlying cause
Vasoconstriction + Na+/water retention = Increase ECF (intravascular) = Increase BP
Secondary HTN: Clinical Presentation
Usually asymptomatic
Nonspecific symptoms
Same as primary HTN
Severe symptoms
Treatment-resistant HTN
Organ damage disproportionate to HTN degree
Unusual onset
Abrupt
< 30 years
Hypokalemia
Secondary HTN: Investigations
Same as primary HTN
BP measurements
Lab studies
ECG
Physical exam
Secondary HTN: Lab Studies
Blood test
Fasting glucose or Hb A1c
CBC
Lipid profile
Serum creatinine
Electrolytes
TSH
Urinalysis
Albumin:Creatinine
Secondary HTN: ECG
Abnormal → Echo
Secondary HTN: Treatment/Management
Same as primary HTN
Treat underlying cause
Pharmacotherapy (ACE inhibitors, ARBs)
Secondary HTN Pharm Adverse Effects: ACE Inhibitors
Increased bradykinin (inflammatory mediator) = Vasodilation + bronchoconstriction
C: Dry Cough
A: Angioedema (deep skin swelling)
P: Pemphigus vulgaris (autoimmune skin blistering)
T: Teratogenicity
O: HypOtension
P: Hyperkalemia (Potassium)
R: Renal failure (proteinuira)
I: Increased creatinine
L: Low GFR → AKI
Switch to ARBs
Secondary HTN Pharm Adverse Effects: ARBs
Angioedema
Hyperkalemia
Teratogenicity
Low GFR + High creatinine → AKI
Secondary HTN Pharm: Pregnant and Breastfeeding
NO ACE inhibitors, ARBs, direct renin inhibitors, and atenolol (beta blocker)
Labetolol: Beta blocker
Nifedipine: Dihydropyridine CCB (extended release)
Methyldopal: Alpha-2 agonist
Secondary HTN: Complications
HTN crises
HTN Crisis
Acute severe HTN
Systolic BP ≥ 180 mmHg
Diastolic BP ≥ 120 mmHg
Hypertensive Urgency
Hypertensive Emergency
Hypertensive Urgency
Hypertensive crisis without symptoms or with nonspecific symptoms
No signs of acute organ damage
BP > 180/120 mmHg
Hypertensive Emergency
Hypertensive crisis with signs of acute end-organ damage
BP > 180/120 mmHg
End-Organ Damage:
Cardiovascular
HF
Pulmonary edema
MI
Aortic dissection
CNS
Cerebral edema
Stroke
Seizures
Altered mental status
Renal: Acute hypertensive nephrosclerosis (AKI)
Ophthalmic: Acute hypertensive retinopathy
Blurry vision
Retinal hemorrhages
HTN and Hypokalemia
Excess mineralocorticoids = Stimulate mineralocorticoid receptors = Increase Na+/water reabsorption + K+ excretion = HTN + Hypokalemia
Hyperaldosteronism
Cushing’s syndrome
Hyperaldosteronism
Increased aldosterone (mineralocorticoid) secretion from adrenal cortex = Stimulate ENaC in DCT
Cushing’s Syndrome
Increased cortisol (mineralocorticoid) secretion = Stimulate mineralocorticoid receptors