Chapter 8: Introduction to single entity accounts
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the objective of financial statements according to IAS 1?
What components make up a complete set of financial statements under IAS 1?
Does IAS 1 require specific titles for the financial statements?
What does IAS 1 require regarding comparative information?
Who is responsible for the preparation and presentation of financial statements under IAS 1?

What does IAS 1 para 15 state about fair presentation?
What four conditions must be met to achieve fair presentation under IAS 1?
When can an entity depart from an IFRS requirement to achieve fair presentation?
What must an entity disclose if it departs from an IFRS requirement for fair presentation?
What is the going concern assumption under IAS 1?
What does IAS 1 require regarding the accruals basis of accounting?

What does IAS 1 say about consistency in financial statements?
How does IAS 1 define materiality?
What is the guidance on aggregation and disaggregation under IAS 1?
What does IAS 1 say about off-setting?
What is the IAS 1 requirement for comparative information?
What are IAS 1’s requirements for the frequency and timeliness of financial statements?

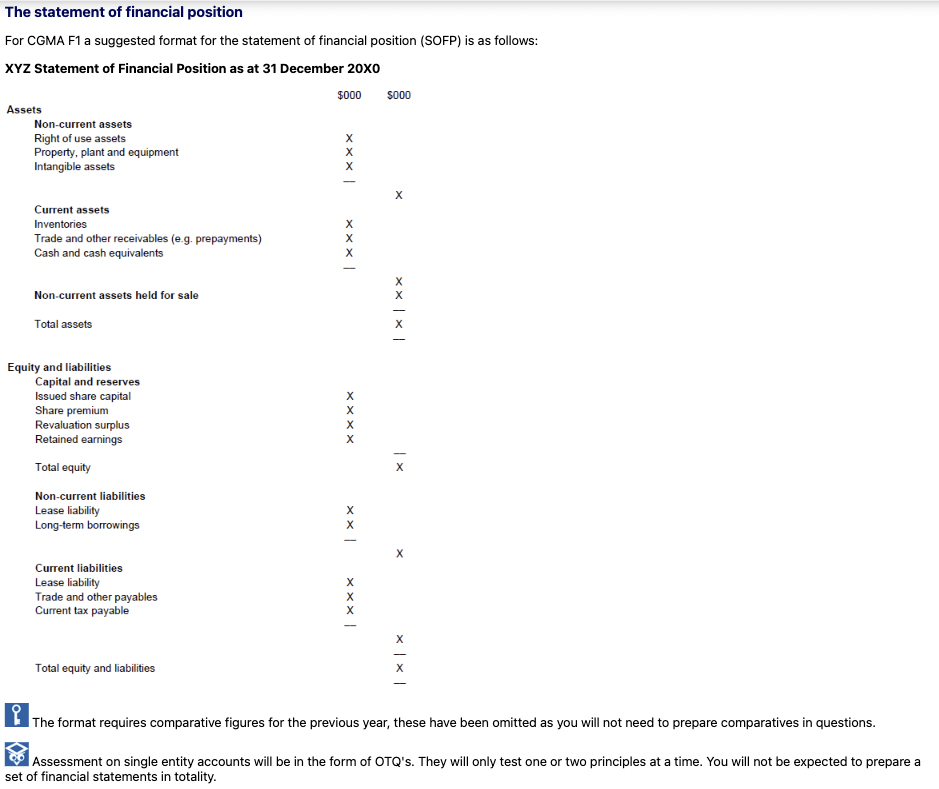
What are the two main sections of the Statement of Financial Position?
What are the categories under Non-current assets in the SOFP?
What are the categories under Current assets in the SOFP?
What type of assets are listed separately at the bottom of the asset section?
What are the components of Capital and reserves in the equity section?
What are examples of Non-current liabilities in the SOFP?
What are examples of Current liabilities in the SOFP?
What three factors should management consider when deciding to present additional line items in the SOFP?
Why might different assets or liabilities need separate presentation?

Where should further sub-classifications of line items be presented according to IAS 1?
What are examples of disclosures that may require sub-classification under IAS 1?

What disclosures are required by IAS 1 for each class of share capital?
What must IAS 1 disclose about reserves and dividends?

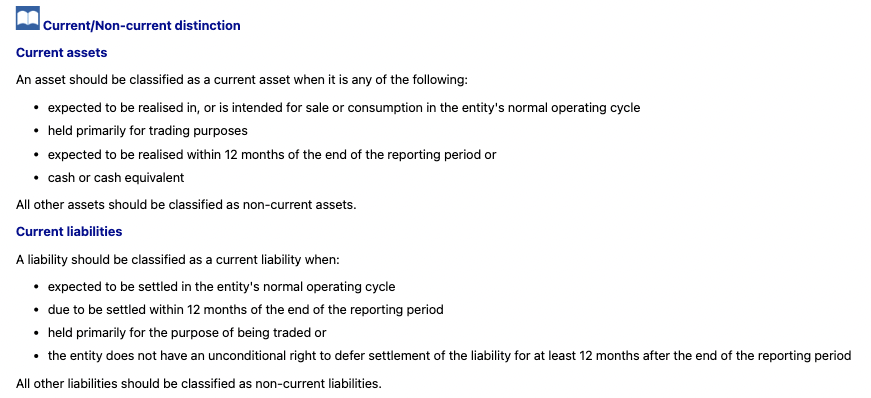
When should an asset be classified as a current asset?
When should a liability be classified as a current liability?
What does the Statement of Changes in Equity (SOCIE) show?
Why is the SOCIE useful to users of financial statements?

How are ordinary/equity shares and dividends treated in financial reporting?
What are preference shares?
What are the accounting entries for:
issuing shares above nominal value?
paying an ordinary dividend in cash?
dividends declared but not yet paid?
preference dividends when treated as equity and paid immediately?
What is the journal entry for preference dividends when treated as a liability and unpaid at year-end?
Ordinary Shareholders
Ordinary shareholders own a percentage of net assets and have voting rights. Dividends are declared by directors and paid per share; they are only accounted for when declared.
🟨 Preference Shares
Preference shareholders own part of the share capital but usually don’t have voting rights.
They typically receive a fixed dividend each year.
Dividends are accounted for on an accruals basis.
Depending on classification, dividends may be treated as equity or liability.
✅ Accounting for Share Issue:
| What happens: Company receives money from investors
| Accounts affected:
Cash/Bank (Asset) → Increasing → Debit (DEAD)
Share Capital (Equity) → Increasing → Credit (CLIC)
Share Premium (Equity) → Increasing → Credit (CLIC)
✅ Accounting for Dividend Payment (Ordinary Shares):
| What happens: Company distributes profit to shareholders
| Accounts affected:
Retained Earnings (Equity) → Decreasing → Debit (opposite of CLIC)
Cash/Bank (Asset) → Decreasing → Credit (DEAD)
✅ If Dividend Is Declared but Not Yet Paid:
| What happens: Company commits to a dividend but hasn’t paid it yet
| Accounts affected:
Retained Earnings (Equity) → Decreasing → Debit (opposite of CLIC)
Dividend Payable (Liability) → Increasing → Credit (CLIC)
✅ If Preference Shares = Equity Instruments
| Accounts affected:
Retained Earnings (Equity) → Decreasing → Debit (opposite of CLIC)
Cash/Bank (Asset) → Decreasing → Credit (DEAD)
✅ If Preference Shares = Liability Instruments
| Accounts affected:
Finance Cost (Expense) → Increasing → Debit (DEAD)
Accruals (Liability) → Increasing → Credit (CLIC)

What presentation options does IAS 1 allow for profit or loss and OCI?
What is total comprehensive income?
What is included in other comprehensive income (OCI)?

What format is used in the example Statement of Profit or Loss and OCI? (Tip: split into 4 sections: p/l from ops, invest/finance, tax, OCI)
Alternative to function method?
What does the total comprehensive income line include in the statement?

What does IAS 1 say about the treatment of material items of income or expense?
What are some examples of material items that require separate disclosure?

How does IAS 1 require other comprehensive income (OCI) to be split?

What key items must IAS 1 require to be presented in the statement of profit or loss (SPL)?

What three purposes do the notes to financial statements serve under IAS 1?
What is the typical order of content in the notes to financial statements under IAS 1?
