Age at Death Estimation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
intrinsic factors
genetics
extrinsic factors
nutrition, stress, environment, disease status, activity, etc.
formative changes
modifications that occur during growth and development
subadult aging
dental formation and eruption
length of developing long bones
appearance and fusion of ossification centers
dental development
most accurate; narrow age ranges
sequence of tooth formation
sequence of tooth eruption
tooth formation
cusps → crown → root → closing of root apex
diaphyseal length
measurement of immature long bones without epiphyses
age can be estimated until epiphyses unite
appearance/fusion of ossification centers
primary and secondary centers appear roughly according to a schedule
epiphyseal union
process by which primary and secondary ossification centers unite
normally correlated with chronological age
most fusion occurs between 15-23
first → elbow region
last → medial clavical
degenerative changes
modifications that occur as a result of normal age-related changes, wear and tear, disease, etc., less reliable, age estimates cannot be as narrow
symphyseal face
key anatomical features:
symphyseal rim
ventral rampart/border
dorsal plateau/aspect
upper/lower extremities
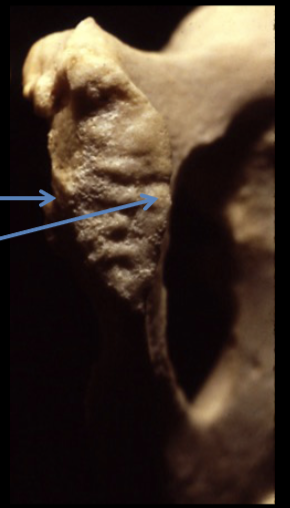
younger age ranges
pubic symphysis has prominent ridges and furrows (billowing)
upper and lower extremities become delimited
middle age ranges
lower rim complete dorsally; gap ventrally
oval outline complete; remnants of billowing
older age ranges
pubic symphysis face becomes depressed, porotic
rim breaks down, irregular in shape, lipping present
sternal rib ends
other rib morphology terms:
scalloping
central arc (females)
plaque deposits (females)
porosity within pit
window formation (gaps in ossifying cartilage)
older sternal rib ends
with age, a rim extends, thins, and becomes irregular
surface porosity increases
bone becomes ragged: “crab claw” appearance
auricular surface
secondary age estimation method:
age-related remodeling of the joint surface
pro: durable → likely to be preserved
con: methods difficult to apply