enviro water test
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
why are wetlands important for water quality
reduce flooding and erosion because they absorb water and release it slowly
filter toxins from water
positive + negative impacts of dams
-supply electricity without releasing carbon
-sediment pollution, too much evaporation, alters habitats upstream and below stream, possibility of failure, expensive to construct
what is thermal pollution and what is it caused by
change in water temp by human activities
dams (release cold), nuclear power (warm)
remove shade trees
thermal pollution impact
warm water holds less 02, fish and aquatic species can’t handle the changed temp
what is toxic chemical pollution and what is it caused by
petroleum, pesticides, metals (Pb, As, Hg), caused by industry, mining sites, agriculture, homes, and businesses
toxic chemical pollution impact
poisons animals and plants, causes cancer and health problems for humans
what is pathogens and disease pollution and what is it caused by
bacteria (fecal coliform), protists, pathogenic viruses. caused by untreated sewage and animal feedlots
pathogens and disease pollution impact
human health problems (cholera, dysentry, typhoid fever)
what is nutrient pollution and what is it caused by
nitrogen and phosphorous, animal waste and fertilizers
nutrient pollution impacts
causes deadzones
what is biodegradable waste pollution and what is it caused by
human waste, paper pulp, yard waste,
animal farms, paper mills, yard waste
biodegradable waste pollution impact
dead zones
what is sediment pollution and what is it caused by
eroded soil,
clear cutting construction and agriculture
sediment pollution impact
kills fish, dramatically alters aquatic habitats
cultural eutrophication, and what is eutrophication
excess nutrients in waterway caused by human activities
too many nutrients - bacteria uses oxygen up processing these nutrients - not enough 02 for mammals and plants - algae blooms - dead zone
how do biodegradable wastes lead to hypoxic conditions
bacteria breaks down waste, uses up 02, and creates hypoxic or low 02 areas
wetland mitigation
creating new wetlands to make up for the wetland losses associated with development or land use changes
how are floodplains created
areas next to bodies of water that are periodically flooded at different points in time (rivers deposit eroded material in these plains)
why are floodplains important
-filter minerals and sediments out of the water
-great for farming (nutrient rich soil)
-gives wildlife habitat
-refill aquifers with water
drawbacks of aquaculture
disease (can be transferred to wild fish)
cross breeding, compeititon
waste water
rafts for invasive species
feed them other fish - goes against purpose
non point source pollution and examples
too many different sources, no clear cut source (runoff) - storm runoff from a parking lot
point source pollution and examples
identifiable source of pollution (discharge) chemicals from a factory into a stream
aquatic biomes with high biodiversity
coral reeds, estuaries, deep oceans: photic zone, pelagic zone, benthic zone
aquatic biomes with the lowest light
marine benthic zone, deep ocean
main uses for freshwater
agricultural, residential, agricultural
drinking water, laundry
what causes surface currents
winds near coastal areas and ocean oceans
thermohaline circulation
suns radiation is absorbed by the oceans
weather patterns are driven by these currents
thermohaline circulation - moves water, causes currents
driven by density differences in water due to temp and salinity in different parts of the ocean
affects climate
how do currents impact energy distribution
transfer heat energy from the tropics to polar regions, influencing climate
where does El Niño occur
Tradewinds weaken, which lets warm water in the Pacific Ocean to travel eastwards and build up near the South American coast
el nino factors
-warmer sea surface temperatures
more rainfall
upwelling weakens in pacific coast
fewer phytoplankton
what does the alkalinity of a river measure
ability to neutralize acids and bases and maintain a fairly stable ph (20 - 200 ppm)
cod near Newfoundland
overfishing of cod led to a ban- 82% gone- fisherman laid off+ fishing of other species
negative impacts of plastic on aquatic life
ingest - die
rafts can promote invasive species
caught in plastic debris
plastics infiltrate tissues of mammals
oil pollution
what happens on land goes to oceans, most oil comes from land
overfishes has lost
80% of fish stocks
lakes
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
fresh/salt
in land
varies
both
Lilly pads, fish
pollution, cultural eutrophication, agriculture, industrial, development
wetlands
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
freshwater
in land or coasts
varies
photic
ducks, frogs, trees
destruction (removal) over ½
filter toxins from water
streams and rivers
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
freshwater
in land
varies
photic
fish, algae, birds
pollution (agricultural and industrial), daming, development
transports material from land into oceans
estuaries
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
salt and fresh
shores, river meets ocean
varies
photic
grass, low biodiversity of plants , tons of animals
destruction, pollution, development
salt marshes- temperate, mangroves- tropical (filtrate toxins and absorb waves)
interdial zones
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
salt
coast with tides
varies
photic
crabs, kelp
pollution, coastal development
barriers and rocky beach
Ocean pelagic zone
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
salt
open ocean
varies
both
plankton
pollution, overfishing
Coral reefs
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
salt
shallow tropical seas
warm
P
coral starfish fish
destruction (T increase, pH), overfishing, soil erosion, UV up
high biodiversity, coral - poly p and zoozanthea
Marine benthic zone
location
temp
photic or autophotic
plants and animals
human impact
interesting facts
salt
bottom of the ocean
cold
a
worms, crabs
shipwrecks
cold dark, low nutrients
why are sources of freshwater unreliable for some and plentiful for others
unevenly distributed among earth. many high populated areas are poor in water
why do the Colorado, rio grande, nile, and yellow rivers now slow to trickle or dry before reaching their deltas
Irrigation for agriculture because the water is being used and is not being renewed.
why are water tables dropping around the world. what are some negative impacts of falling water tables
We are making more withdrawals than deposits, the balance is shrinking. Subsidence and sinkholes can occur when tables drop
groundwater. why do many scientists consider groundwater pollution a greater problem than surface water pollution.
Groundwater is more difficult to manage because it contains less dissolved oxygen, microbes, minerals, and organic matter than surface water or soil water.
How does a septic system work?
designed to hold wastewater long enough to allow solids to settle to the bottom
how much of earths surface is covered by oceans
71%, 97% of earths water
average salinity of ocean water
3.5 %
how are density, salinity, and temp related in each layer of ocean water
warm water is less dense than cold water
most productive areas of the ocean
photic zone, pelagic zone, benthic zone
how are coral reefs valuable? how are they being degraded?
provide food and shelter for fish and other creatures
coral bleaching - depriving nutrition because of warm sea surface temps, pollutants, and bottom trawling
what is causing the disappearance of mangrove forest and salt marshes
shrimp farming. people developing coastal areas
overfishing harms
extinction of species
harms endangered fish
fish that are caught are smaller and younger
three industrial fishing practices
purse seining + drift netting captures mammals that end up drowning or dying of exposure on a ship
bottom trawling destroys entire benthic ecosystems
upwelling
process in which deep, cold water rises toward the surface
marine reserve differs from a marine protected area how
no fishing, MPAS allow fishing
scientists say these reserves can serve as production factories for fish in surrounding areas
bycatch
ontarget species of marine life that are scooped up in fishing nets or on hooks in addition to the target fish
water quality indicators - nitrate
nitrogen is needed for plant growth
less than 5 ppm
too much= excess plant growth + decay - low oxygen levels
water quality indicators - phosphate
high levels- overgrowth, decreased o2
2 ppm
sources- human and animal waste, industrial pollution, agricultural runoff
water quality indicators - fecal coliform
a reliable indicator of sewage or fecal contamination
water quality indicators - turbidity
measure of water clarity
turbid water is caused by suspended colloidal matter (sediments and organic matter)
soil erosion, urban runoff, algae blooms
0-40 jtu
water quality indicators - ph
6.5 -8.2
most organisms have adapted to specific ph levels
affected by industrial waste, agricultural runoff, mine drainage
water quality indicators - temperature
the amount of DO in the water
the rate of photosynthesis, sensitivity of organisms to toxic wastes, parasites, diease
caused by thermal pollution, industrial, and removal of streams
water quality indicators - DO
areas with high levels of Do- healthy +stable
10 ppm
high levels of bacteria are bad for DO
water quality indicators -species diversity
healthy rivers have a variety of species
water quality indicators - hardness
presence of dissolved solids (Mg+Ca)
121-180
water quality indicators - conductivity
ability to pass electric current
150-500
high conductivity can be caused by dissolved solids or chemicals
water quality indicators - BOD
measure of the quantity of DO used by bacteria to break down organic wastes,
dead zones
waste water treatment steps
series of screens and settling tanks separate large solid objects and oils that are less dense
-solids are called sludge and turns into fertilizer or goes to landfill
bacteria is added to digest organic matter
air is added to give bacteria oxygen
water is disinfected with chlorine or UV light, sometimes filtered with coal and sand
flow rate of water
the volume of fluid flowing through an area each second
groundwater recharge
occurs as precipitation falls on the land surface, infiltrates into soils, and moves through pore spaces down to the water table
most to least water runoff
concrete, gravel, pavers, greenspace
infiltration
the downward entry of water into the soil
Evapotranspiration
water is transferred from land to atmosphere
watershed
an area of land that drains or “sheds” water into a specific waterbody
warmer oceans can
dissolve gases from the atmosphere
oceans are
carbon sinks. the colder the ocean = better its ability to dissolve gases.
ocean acidification
co2 reacts with water to create carbonic acid which decreases the pH of the ocean
difficult of animals to make shells (bicarbonate ions react with carbonic acid)
current gyres
large system of circular ocean currents formed by global wind patterns and forces created by Earth's rotation. The movement of the world's major ocean gyres helps drive the “ocean conveyor belt.
La Niña
Tradewinds strengthen, pushing warm water away from South America towards Australia. this allows cold water to spread westward (opposite of El Niño)

El Niño
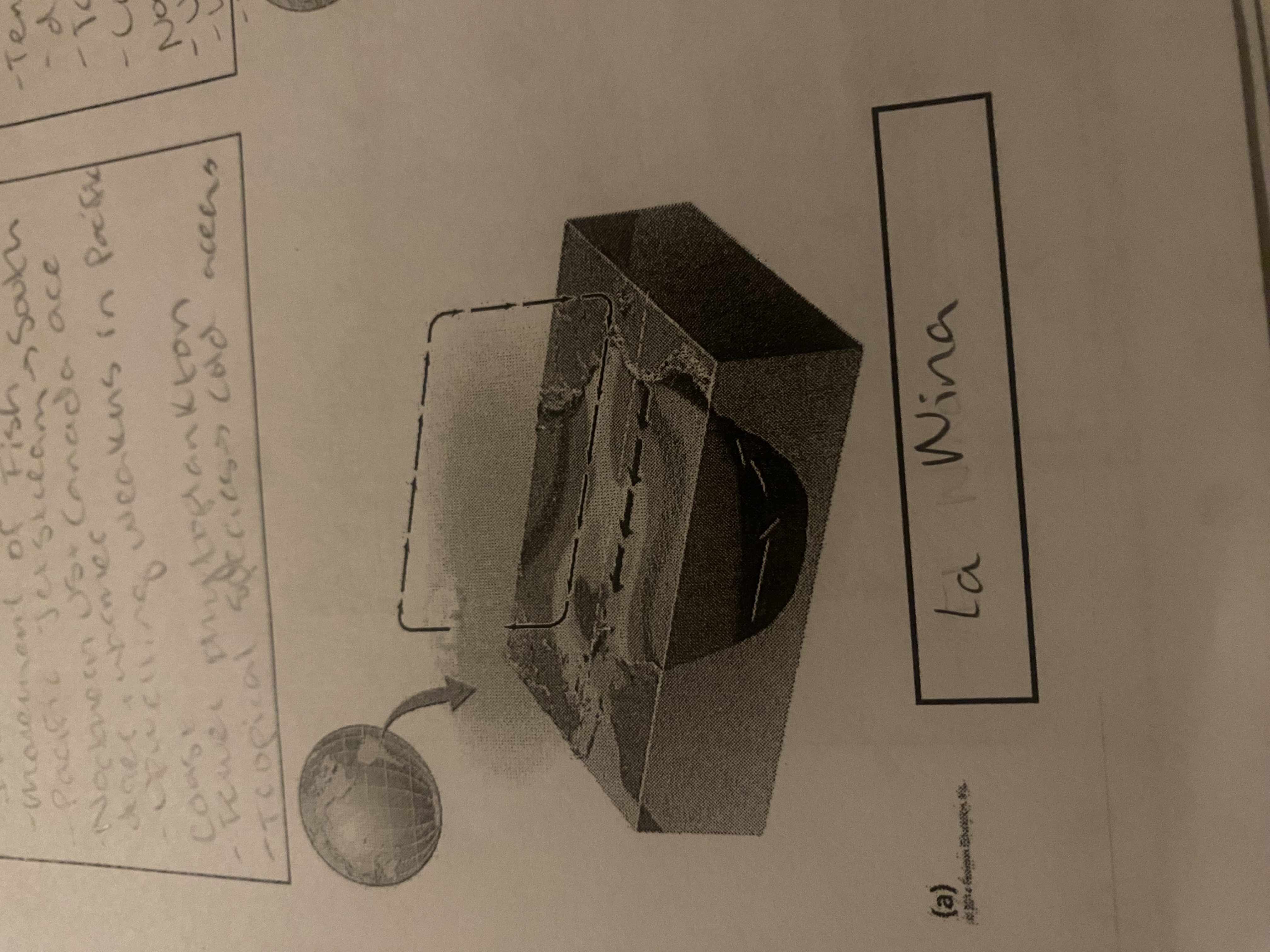
La Niña