CVA SENSORY
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
SENSORY receptor function
general term for cells that detect info about env.
SENSORY neurons
Specialized to transduce stimuli into action potentials
Chemoreceptors are sensitive to—
chemicals
Pheromones
chemical messages form 1 indv. to another
Fishes’ olfactory epithelium in—
paired nasal sacs and open @ ext. nares
Vomeronasal organ/ Jacobson’s organ location and function
Accessory olfactory system;
ass. w/ pheromones and prey detection; detecting non-volatile chemicals
Taste buds: epithelial struct. that holds chemoreceptors of taste are transmitted by—
CN VII + X + XII
Visible light is “visible” bc—
it’s detectable by human eyes
UV light is visible to many invert., fishes, birds, reptiles but very few—
mammals
In Infared lights, emanated from objects acc to their—
temperature
Rods are—
LOW light sensors
Cones are—
COLOR sensors
Free
“Naked” nerve endings; v sensitive for pain and temp
Encapsulated
Enclosed in struct that modifies transduction
Associated
Wrapped around another organ (ie hair follicles)
Fishes’ lens are—
nearly round + moved in/out to focus
Proprioception meaning
sense of body’s position in space
Vomeronasal organ is NOT found in—
fish, most turtles, archosaurs, and aquatic mammals
Where is the Vomeronasal organ in Amphibians?
in nasal cavity
Where is the Vomeronasal organ in Mammals?
in nasal cavity (when present)
Where is the Vomeronasal organ in Reptiles?
in mouth
Sclera is the
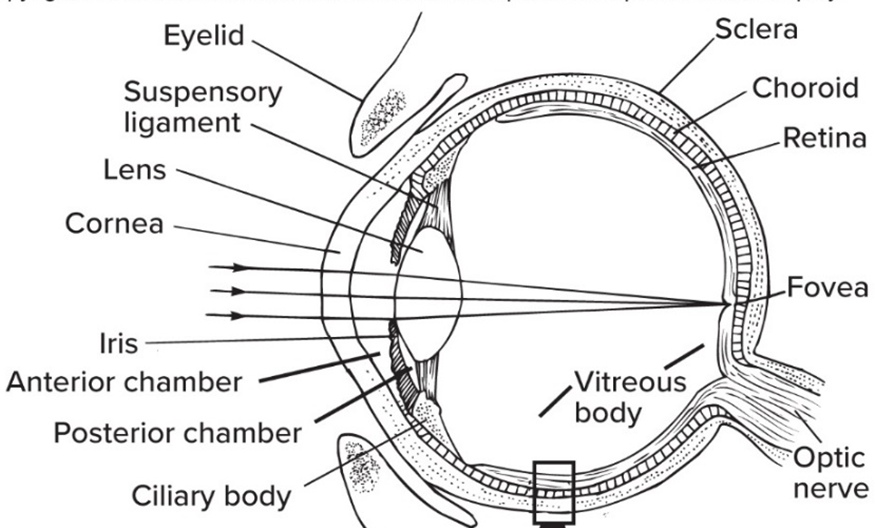
tough outer layer of the eye
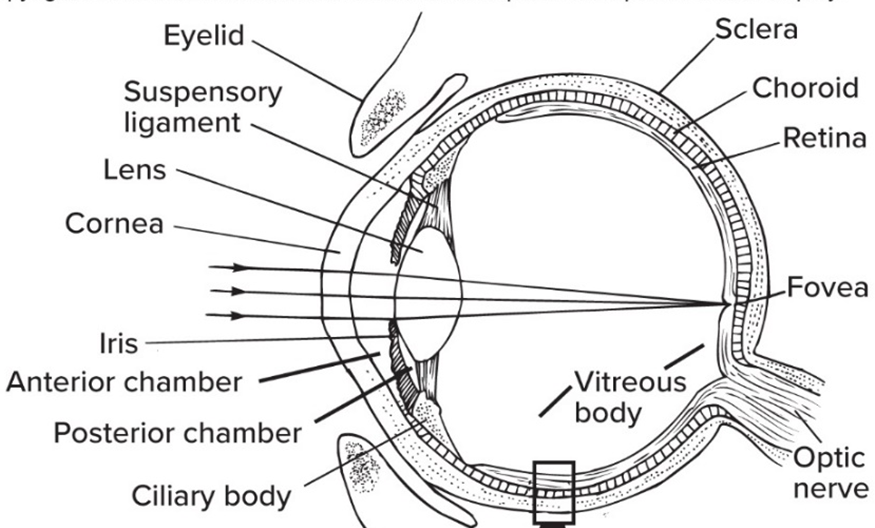
Cornea is the—
clear front area of the sclera
Tapetum lucidum is the—
reflective layer in nocturnal species; “eye shine”
Ciliary body
circle of smooth muscle that focuses lens
Lens’ function
focuses light on retina
Iris’ function
muscle that opens/ closes pupil
Retina is the—
inner layer w/ photoreceptors
Fovea is the “pit” in the retina with the—
highest density of cones (highest focus)
The Optic never (CN II) is not really a nerve but rather—
an extension of the brain
Fishes’ eyeball(s) often supported by—
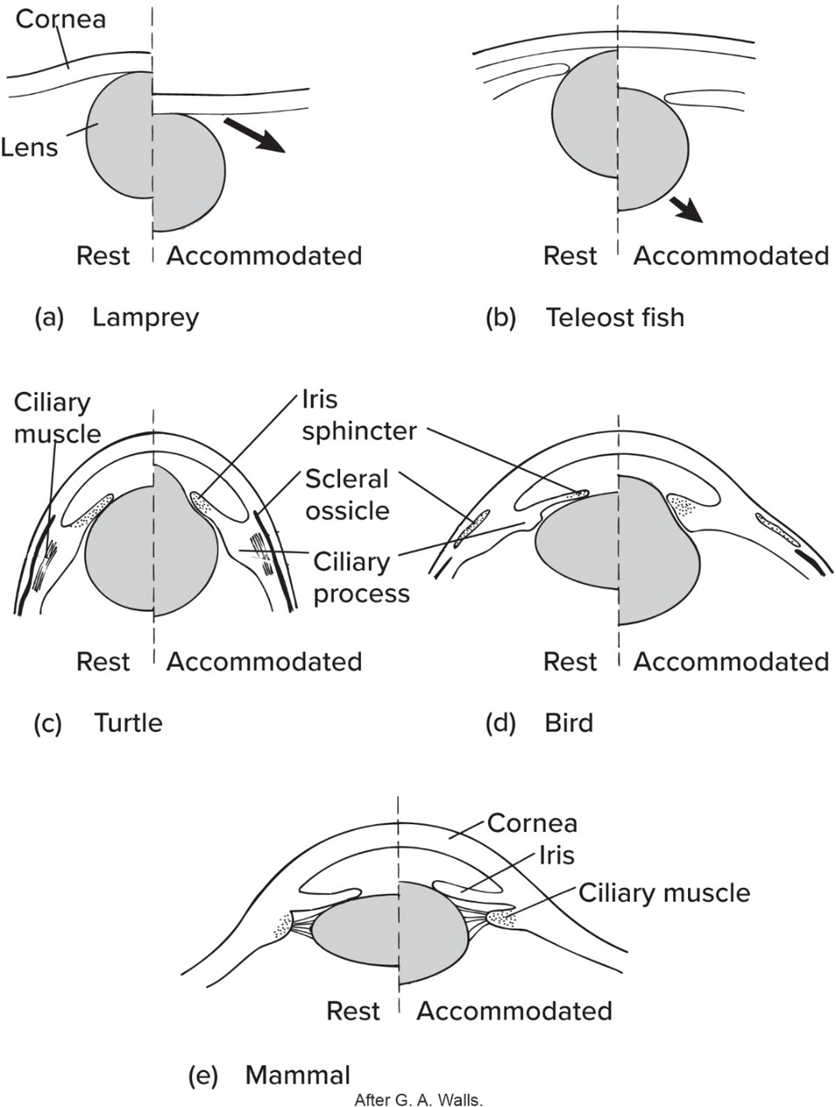
scleral ossicles or cartilages
Amphibians’ have no—
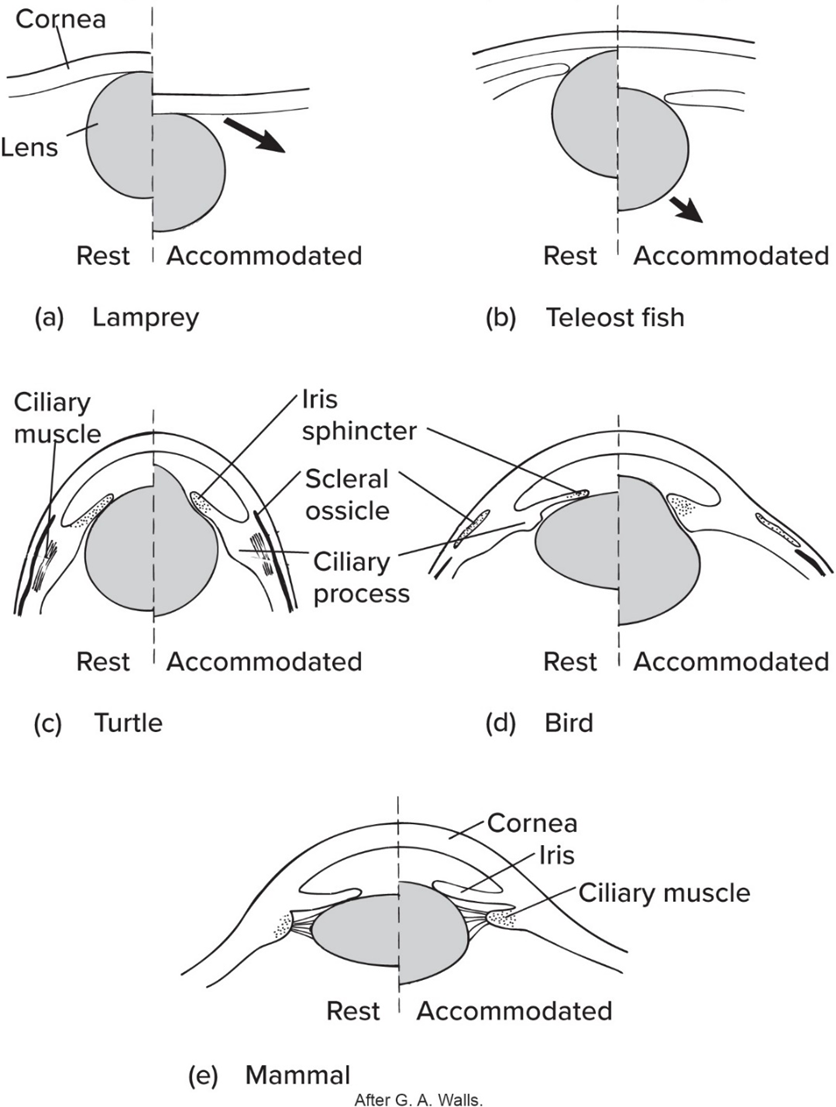
scleral ossicle but sometimes cartilages
Like fishes’ eye phylogeny, amphibian lens—
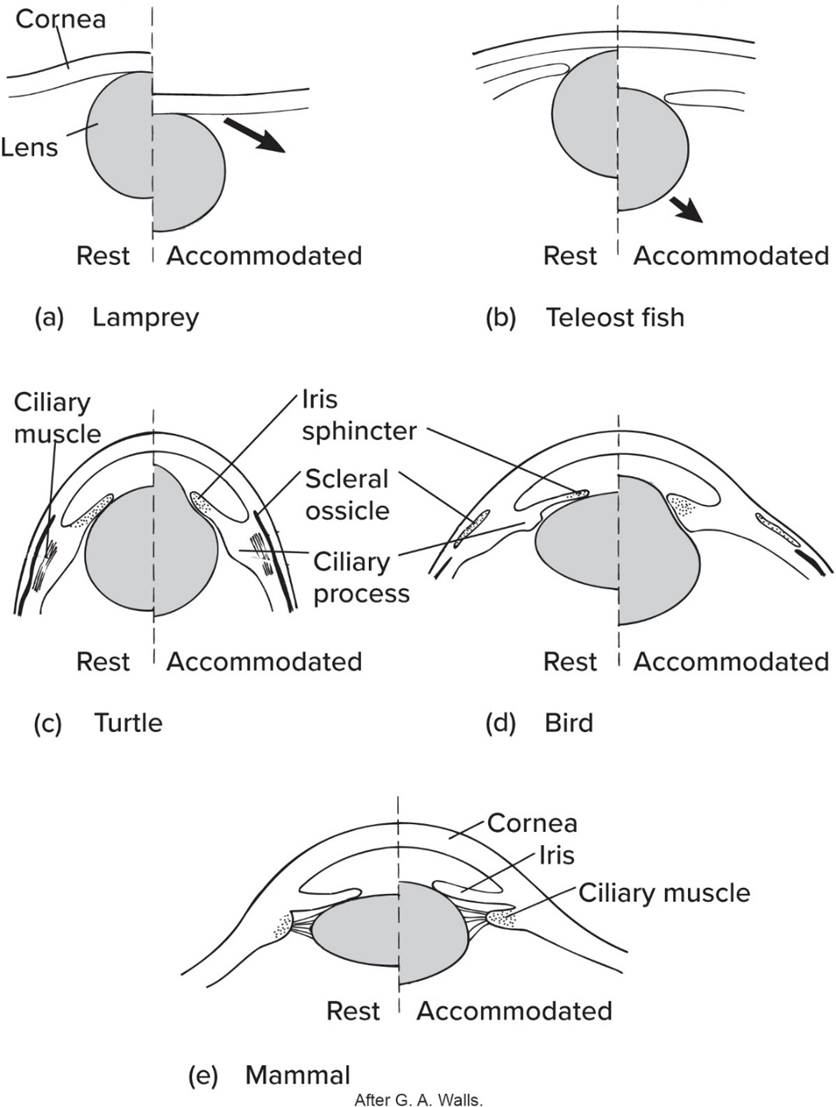
moved in/out to focus
Amphibian’s lens usually—
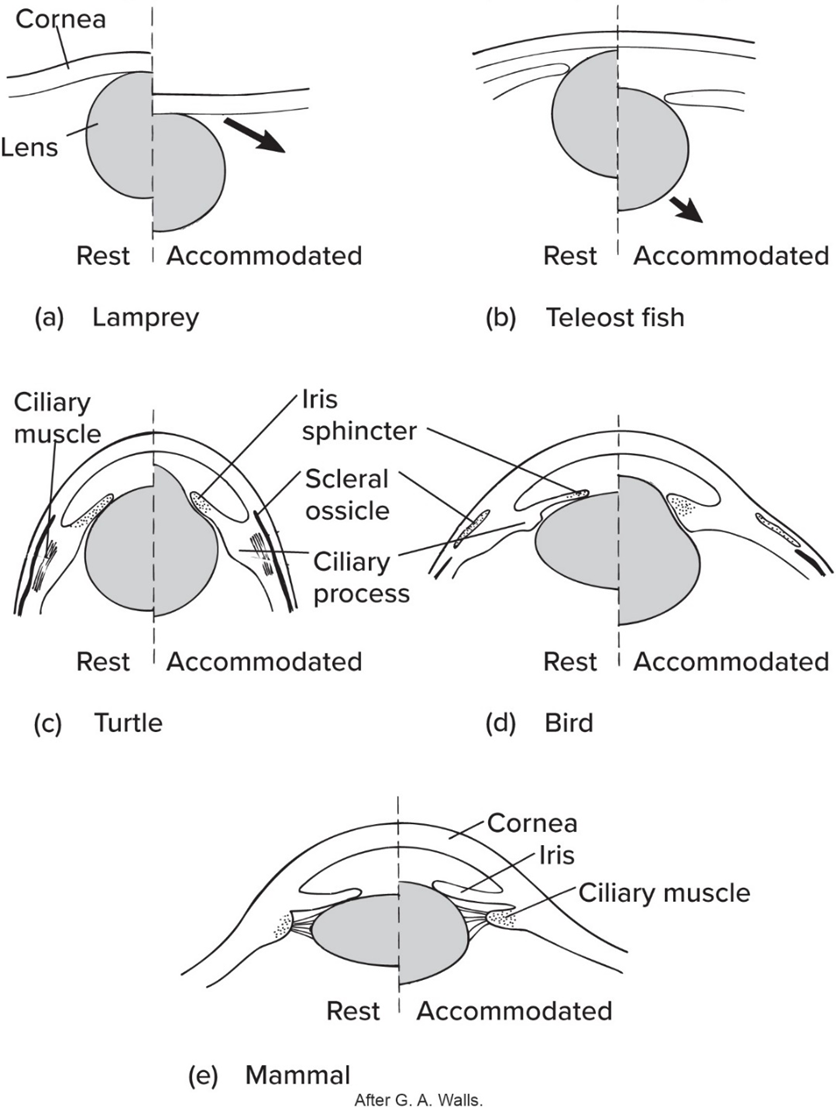
focused on distant objects
Compared to fishes and amphibians, Amniotes’ lens—
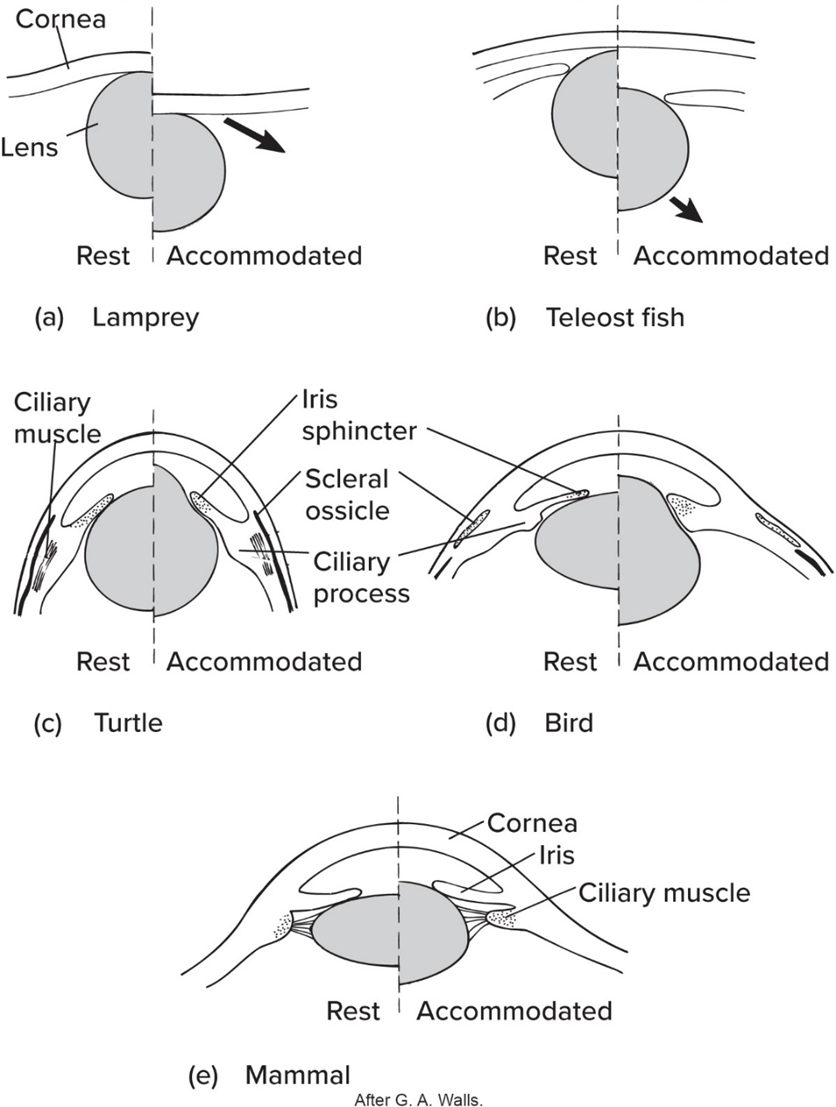
changes shape to focus (except for snakes)
No mammals possess—
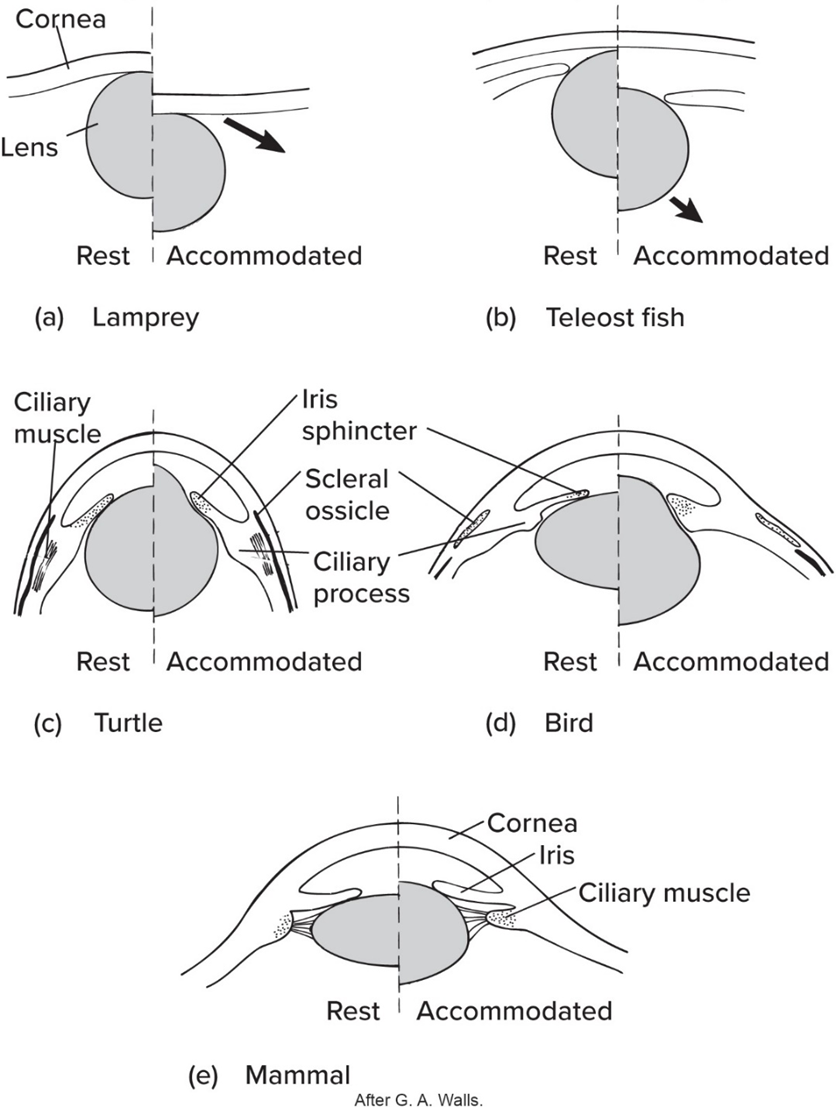
scleral ossicles
All vertebrates possess rods, but not all vertebrates possess—
cones nor every known cone
Does visual range shorten in water than in air?
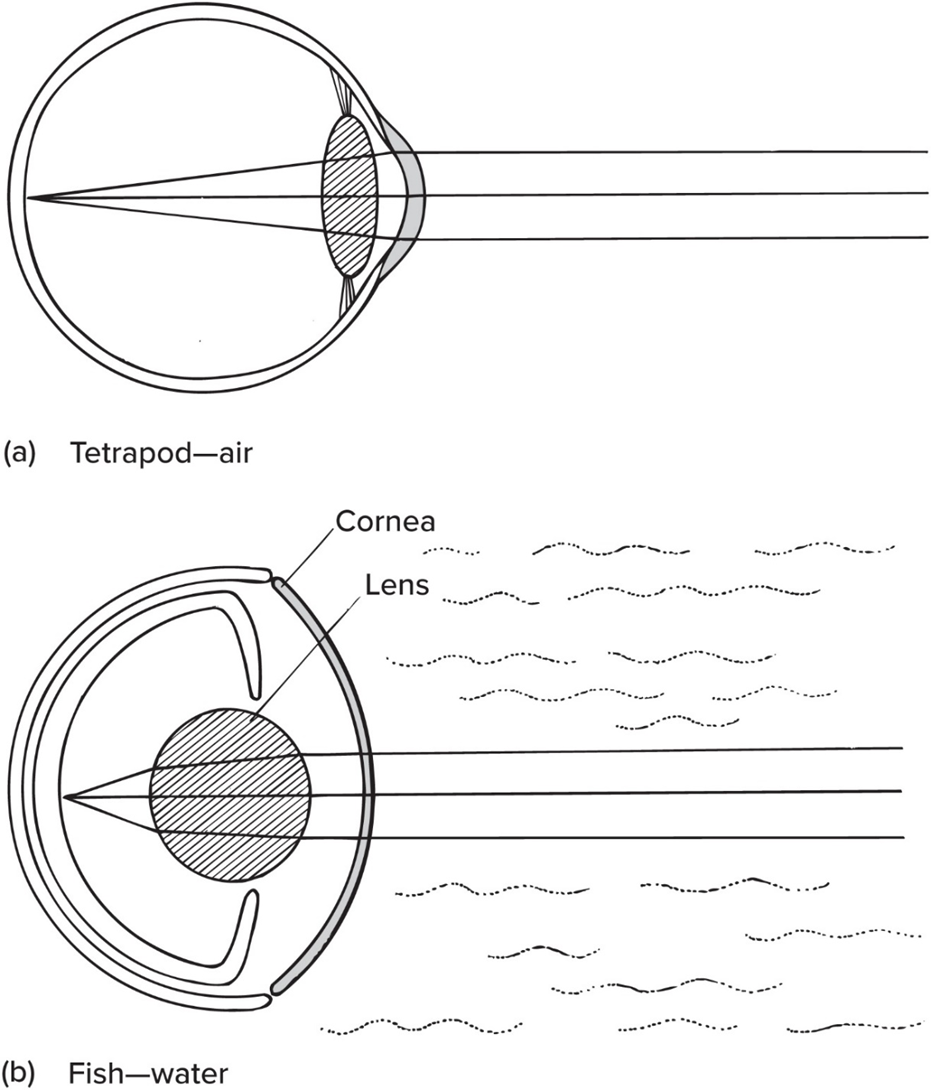
Yes
The earliest verts had—
tetrachromatic cones
Which does tetrachromatic cones consist of?
violet, blue, green, orange
What does trichromatic cones consist of?
blue, green, yellow
What does dichromatic cones consist of?
violet and orange
Which cone combo are most useful for nocturnal lifestyles?
Dichromatic
Monocular vision
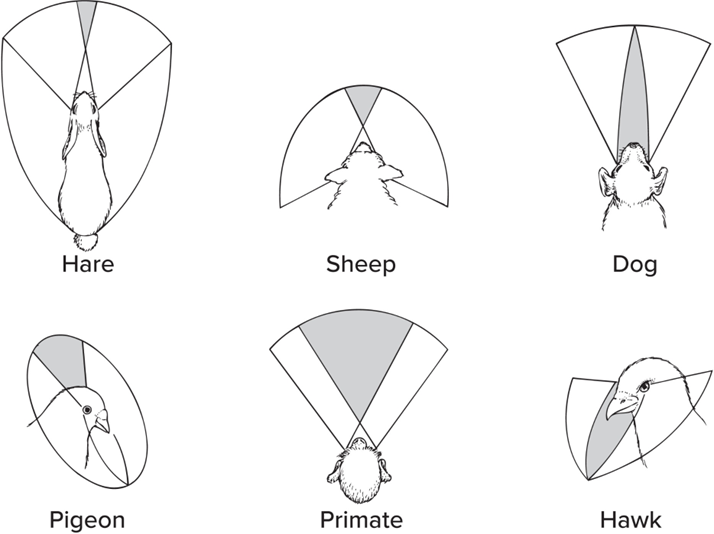
Visual fields do not overlap
Binocular vision
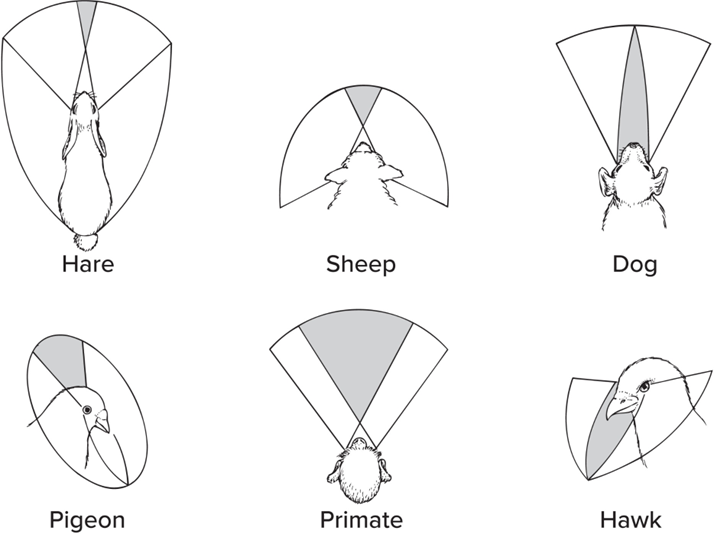
Visual fields overlap
Stereoscopic vision
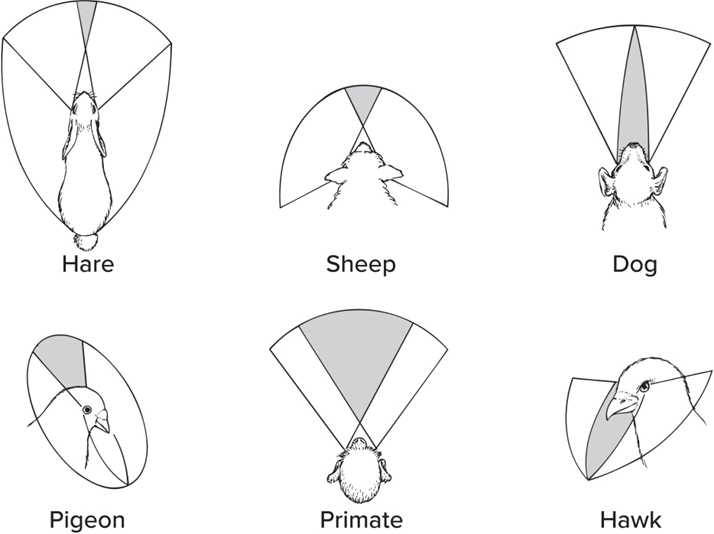
image w/in overlap of eyes
In binocular vision, signals from both eyes cross in optic chiasm, so—
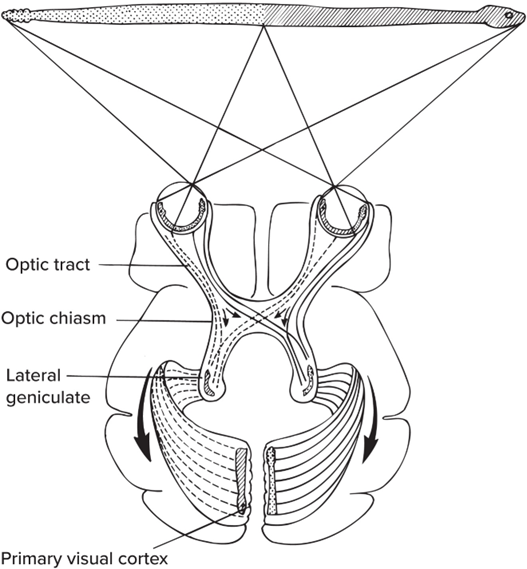
both sides of brain process both eyes’ input
Parietal eye aka pineal eye aka 3rd eye is a—

Photoreceptive extension of epithalamus
IR emitted by anything warmer than—
absolute 0
With IR sight, visible light only seen when it—
reflects off of something
Mechanoreceptors respond to—
movement
Hair cell(s) is a common type of
mechanoreceptor
Neuromast are a—
collection of hair cells and supporting/assisting cells
Mechanoreception forms senses of—
touch, hearing, balance/equilibrium
Lateral line system is a—
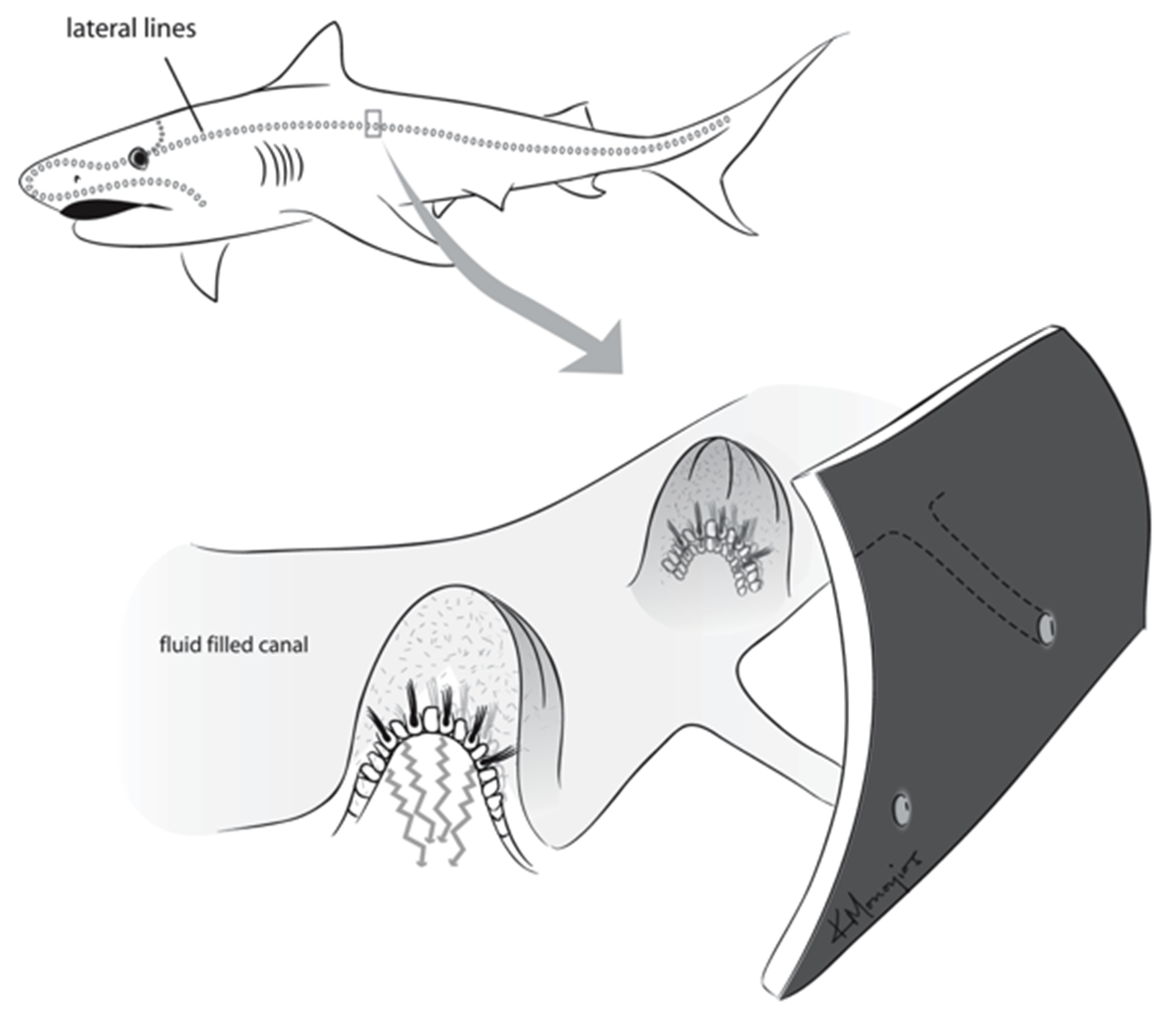
mechanoreception sys for detecting water currents
“Distant touch” functions
Many fishes can detect nearby objects w/out actually touching

Low-f sounds function
Sound waves may be detected (same physical stimulus)
Lateral line sys are absent in—
terrestrial vertebrates
Derived from lateral line sys, the Vestibular apparatus—
senses motion, balance, and orientation w/ Fluid-filled spaces w/ hair cells that detect
Macula
Organs that detect orientation due to gravity
Lagena aka cochlea
Enlargement of sacculus specialized for hearing
The Lagena is derived from—
the Vestibular apparatus
Ext. ears are absent in—
fishes and amphibians
Pinna
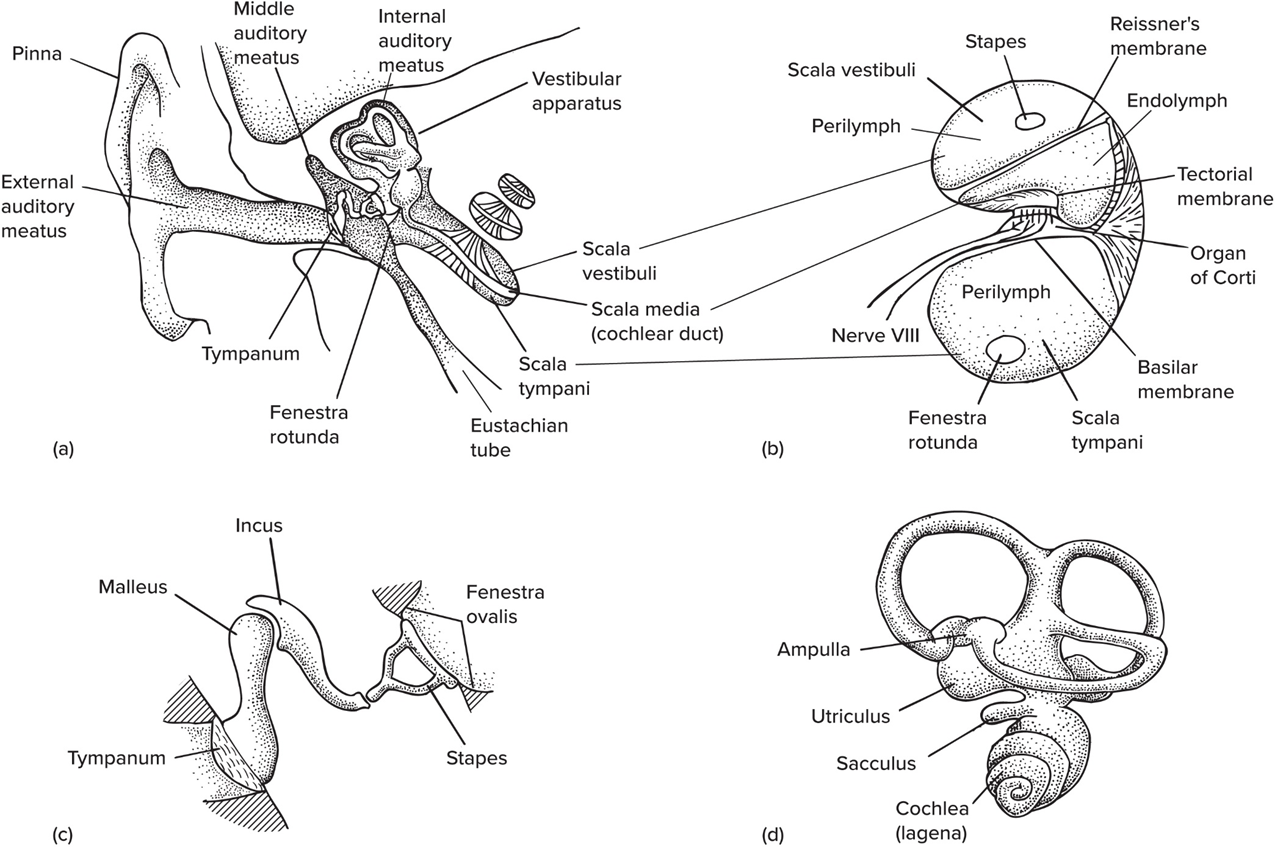
Ext. flap on mammals
The ext. auditory meatus is also known as—
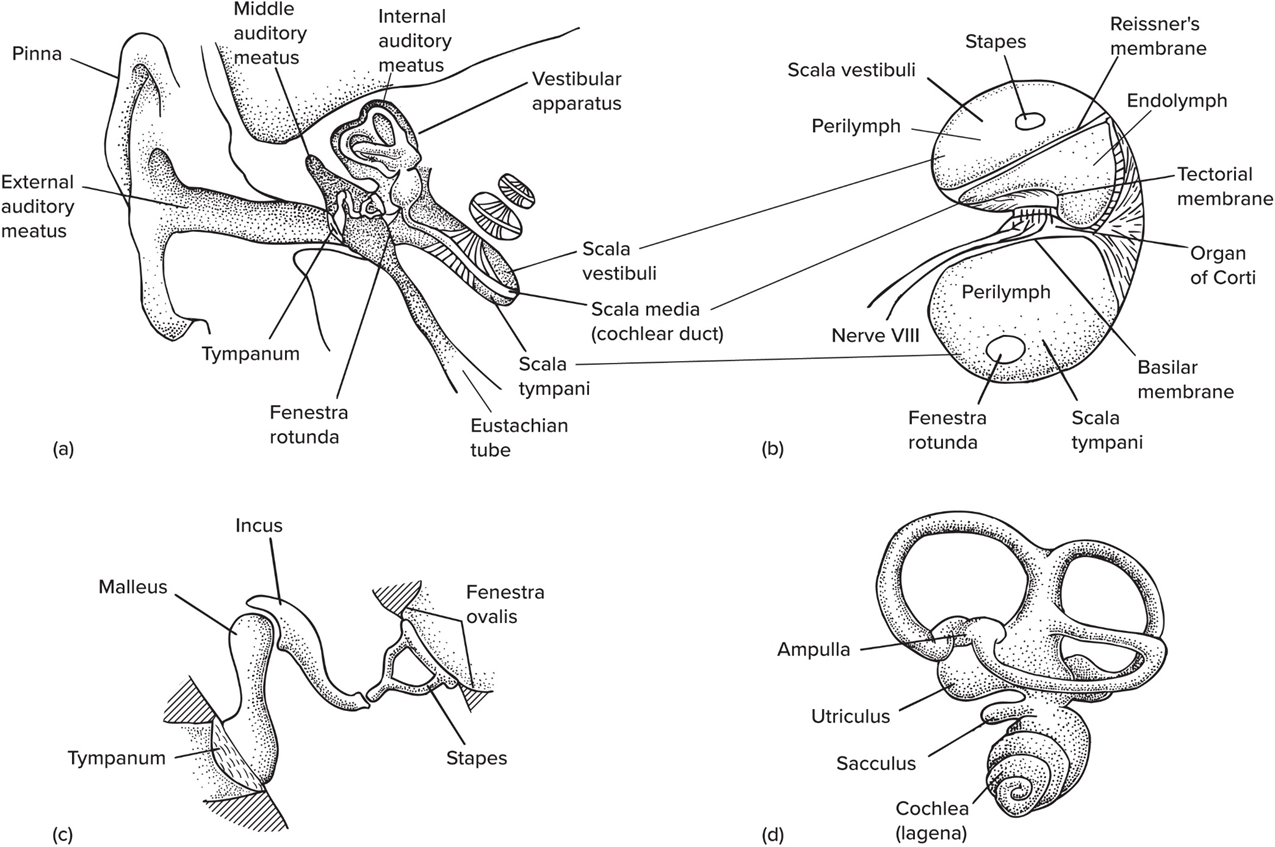
the Ear canal
Ossicles
Tiny bones that transmit sound to inner ear
Mammals, in number of ossicles, contain—
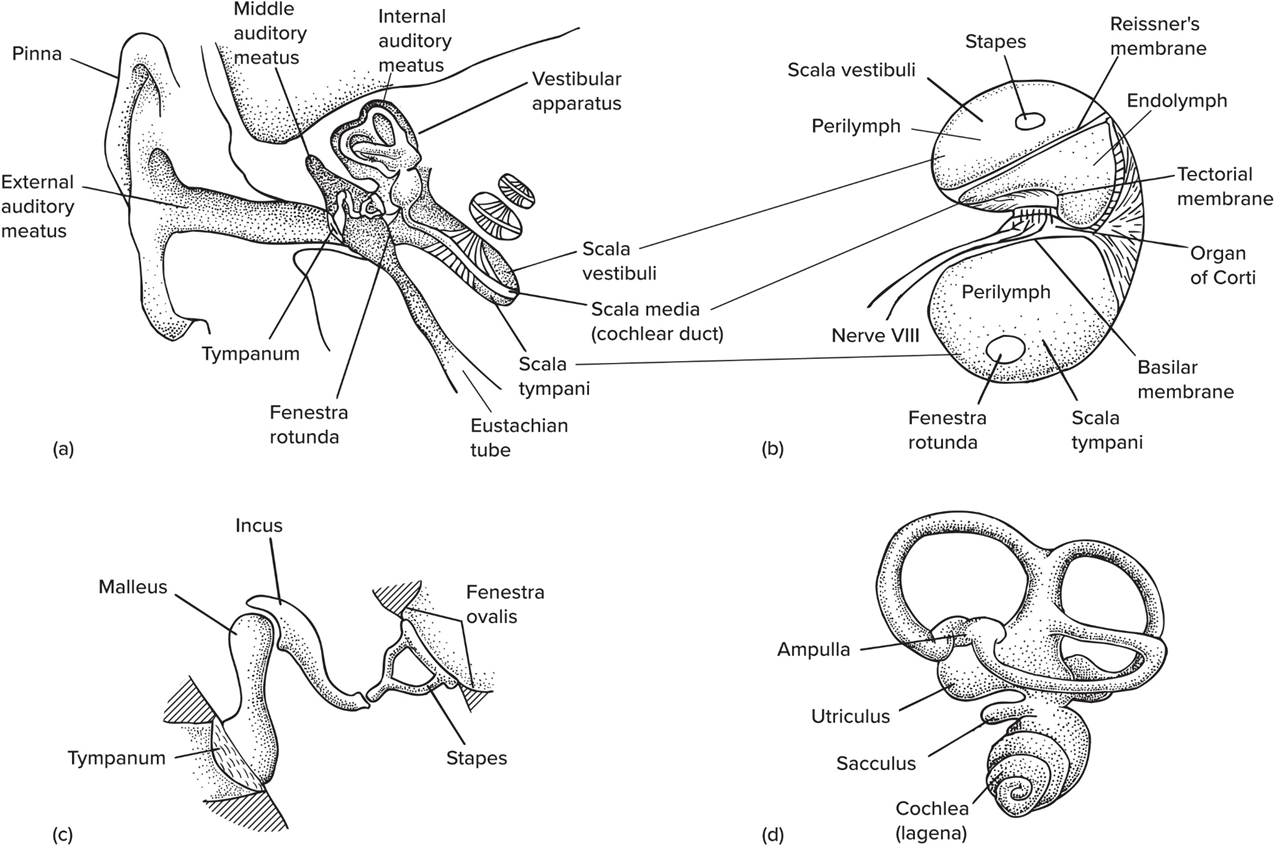
3 bones: malleus (articular), incus (quadrate), stapes (columella)
Electroreceptors detect—
electric fields
Ampullae of Lorenzini
Electroreceptors in sharks used in find prey