Enzyme Activity-> Lysozyme
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Features of lysozome
small
Not easilt destroyed
Gram positive are more sensitive to it
have no outwer membrane to protect it
Can be found with specrophotomer see the light scattering→ apparent absorbance
Experiement
Assay lysozyme acitivty folloing the lysis of M.luteus
Check the light scattering properties of Micrococus lutes bacteria
cuvette add buffer
use as a blank for spectropphotomerer
Another one ass buffer and bacteria
mix well
Measure Apperent absoacne OD
Repeat with differen bacteria volumes
PLot a calibration curve
Relationship of the calibration curve
Should be linear
Lysozyme activity assay
At room temperature
ass buffer and bacteria
put in spectomephtor
take reading
Add lysozme WUICKLY and mix
Put into spectrophotomerter reed attenuance
Take readings every 10 seconds
Repeat
Plot OD vs time
Repeat assay with differen lyzosyme amounts
Is the decrease in OD600 linear or exponential? Suggest two reasons to explain this.
Yes
rate of reaction is proportional to the amount of intact walls present
BUT
as attached, disintergretes walls scatter into pieces less light then the original cells
Fragments could be substrates for lysozyme BUT further digestion would be invisibible→ so does not show rate of lysozome progress!
Is the initial rate of lysis a linear function of the amount of enzyme?
Must measure it from the linear part of the plot
Sometimes it is easier to find the log plot but this is not always the case
and this finds the first order rate constant!
Variation in the amount of enzyme used
Doubling the amount of enzyme DOES NOT quite double the rate of hydrolysis
But the curve is quite straight at lower enzyme concentrations
Shows an apprent approach towards satuation
Due to:
difficultires measring the initial rate when rates are very fast
unsual balance between enorcous substrate and tiny enzyme
not the usual case for how enzymes are used??
Activity of lysozme dependso n 2 amino acids
Glutamate 35
Asparatate 52
How to test effect of pH
Use different buffers
record control of bacteria at different buffers
Plot the initial rate of attenuance drop against pH of the assay
Conclusions
Optimum pH is 6
relevant values for these dissociation pKa being 6 and 4.6 for Glu and Asp
Affect of temperature
Incubate in sifferent water baths
use marble as a stoppper
wait for test tube to cool down
plot intitial rate of attenuance drop against temperautre
What is the effect of heating on lysozyme activity?
80 degrees→ lost half of its activity
someties precipate formed at hiest tmepratures
If lsozyme was mixed with the assay buffer BEFORE heating
survived higher tmepraures better
therfore: stability can depend strongly on pH
Because enzymes with their cofactors or substrate boud→ more stable and less easily denatured
How is lysozyme so stable?
small→ less to go wrong
constian 4 SS bridges
Adding DTT to the enzyme
broke the SS bridges
which are needed for heat stability
How to test lysozyeme activity from tears
Dilute tears ten fold
use as assay as before
How much lysozyme activity did the bodily fluid include?
Tears have lots of lysozyme activity, equivalent to about 2 mg/ml of the purified enzyme we supplied
Egg white has about 3 mg/ml lysozyme
Sweat usually has up to 0.2 mg/ml lysozyme and saliva 0.1 mg/ml lysozyme.
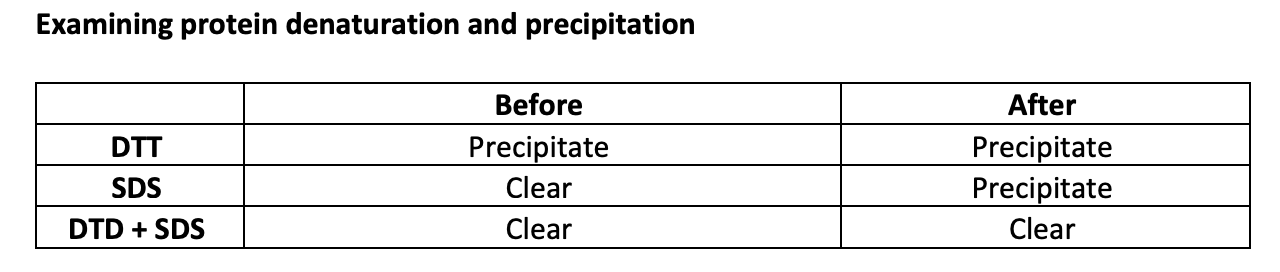
Why does the activity of lysozyme not return upon cooling?→ Test eg white with SDS and/DTT
Results show before and after boiling
DTT + SDS→ DTT reduces the disulphides, SDS reversvres aggregation and gets the precipitated protein back into solution
Once denaturation starts
makes it much easier to carry on
A small change in conditions can cause an enormousus increase in rate of denaturation
Can be due to
pH, temperaure, change of solvent
Why is denaturation irreveerible?
Chemical changes taken place
other amino acids are potentially unstable:
Amides→ turn into acids (asparatic etc)
Methionine→ oxidised into methionin sulphoxide
SDS
detergent
helps protein binding→ gives them strong negative charge
needed for eggs to stop denaturation
Also wraps begative charge around→ for SDS polyacrylimide gel electrophoresis
DTT
reducing agent
helps to stop deanturation
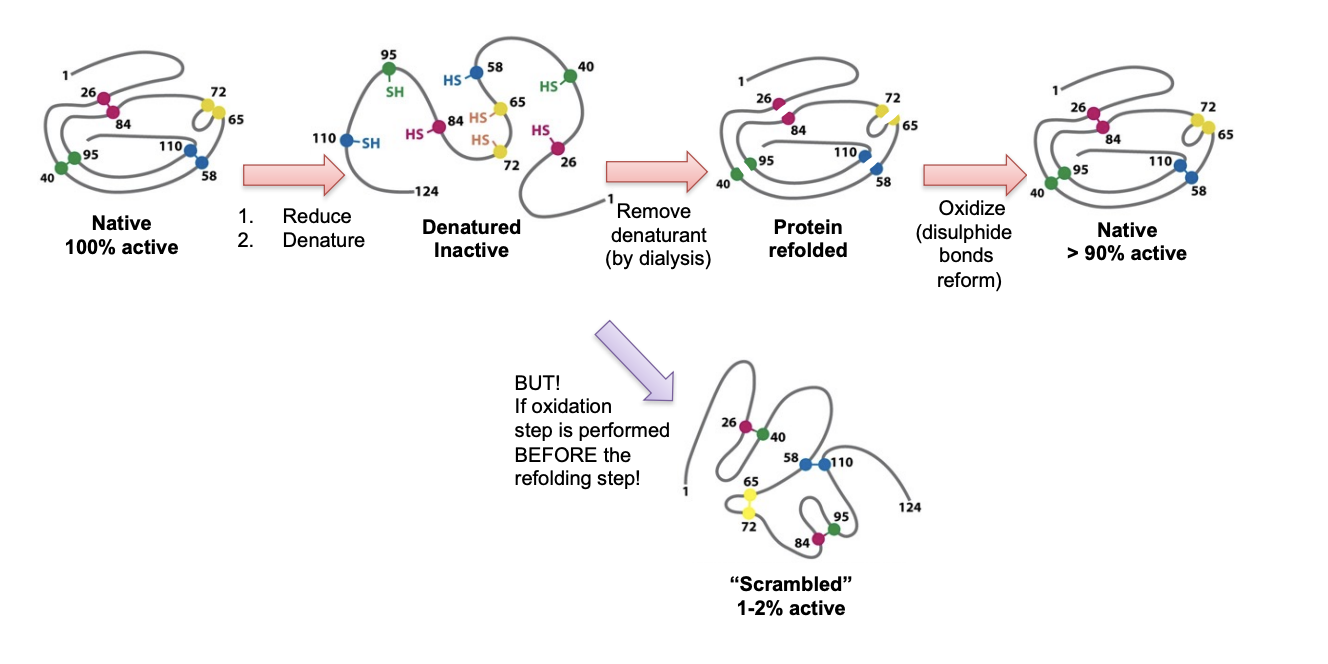
Afinsen’s experiment
Added Urea and DTT upon catlytic activity of ribonucluase
Lost all activity
Dialysed the Urea out first→ refolded correctly
Oxidised the DTT out→ reformed 90% of intitial activity
If oxidised first and then urea out→ only 1-2% of activity
this is because illegitmatie random disulphide bonds were able to form when the protein was unfolded prior to urea removal!