physics - topic 4: magnetism
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is a magnetic field?
The region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet/magnetic material.
What are the three magnetic materials?
Iron, nickel, and cobalt.
What do magnetic field lines show, and what do spread-out lines mean?
The size and direction of magnetic fields. If the field lines are far apart, the magnetic field is weak.
What are the two rules when drawing magnetic field lines?
Lines must not cross.
Must point from N to S.
The magnetic field is strongest at the //
Poles.
What is a uniform magnetic field?
A region where the magnetic field has the same strength and direction at every single point.
What are the two methods of investigating field lines?
Iron Filings - Place the magnet under a piece of paper and scatter the filings on top. They will align themselves with the magnetic field lines of the magnet.
Plotting compass - Put the magnet on a piece of paper along with a compass at one of the poles. Draw a dot where the needle points, and move the compass so that the tail end is on the previous dot. Continue this process until the magnetic field lines are drawn out, and join the dots together.
Which method for investigating field lines is better and why? (2 points)
Compass needle:
Iron filings are messy to work with.
Drawing will remain, even when the magnet is removed.
What proves that the Earth has a magnetic core?
Compasses will always point North, even when they aren’t near a magnet.
What is the difference between a permanent and induced magnet?
A permanent magnet produces its own magnetic field and’ll never lose it’s magnetism, while an induced magnet is only temporarily magnetic.
How can we calculate the direction of magnetic field lines?
The right-hand rule: thumb points in direction of current, and grip shows the way the field lines move.
When drawing 2D diagrams, what does a dot and cross mean in the middle of magnetic field lines?
Dot - Current is flowing out.
Cross - Current is flowing in.
What do the field lines around a solenoid look like?
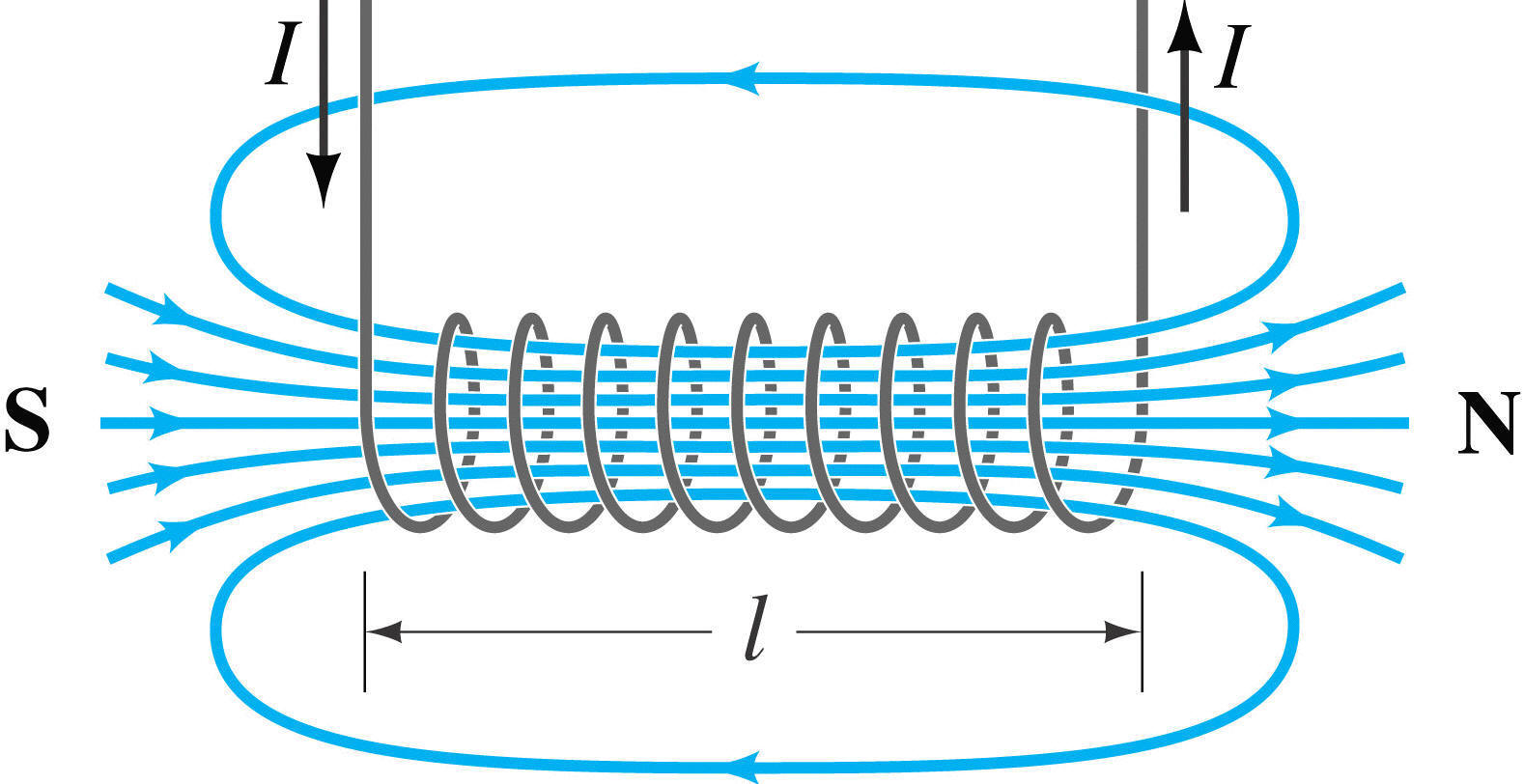
How can you increase magnetic flux density? (4 ways)
Use an iron core.
Increase current.
Increase the number of turns (solenoid).
Increase the length (solenoid).
A wire must be // to the magnetic field to experience the full force.
Perpendicular
What rule can we use to find the direction of force?
Flemings Left Hand Rule:
Thumb - Force
First Finger - Magnetic field
Second finger - Current
What is the motor effect?
A current-carrying wire creates a magnetic field, which can interact with another magnetic field that causes a force that pushes the wire at a right-angle.
What does a simple d.c. motor consist of?
A current-carrying coil sat between two opposite poles of a magnet.
What does a split-ring commutator do?
Swaps the direction of current every half-turn so the forces on each side of the coil change direction.
What causes the coil to rotate in a d.c. motor?
The opposite forces.
How can you reverse a d.c. motor?
Swap the poles.
How can you speed up a d.c. motor? (3 ways)
Increase the current.
Add more turns to the coil.
Increase magnetic flux density (by using stronger magnets).
Motors convert // energy into // energy.
Electrical, Kinetic.
What is the generator effect/EM induction?
When there is relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field, potential difference (and current if its a full circuit) is induced.
What are the two types of generators and what do they do?
AC Generator/Alternator - Induces alternating current.
Dynamo - Induces direct current.
How can we increase the induced p.d? (3 points)
Increase strength of magnets
Move the wire faster
Increase number of coils
How does an AC generator work? (3 points)
Coil of wire rotates between magnets.
Wire is connected to slip rings and brushes.
Current changes direction every half-turn (if the wire moves up, it’s positive, and vice versa).
How does a dynamo work?
Coil of wire rotated between magnets.
Wire is connected to a split ring commutator.
Output current is switched every half-turn.
Current is never negative.
Generators convert // energy to // energy.
Kinetic, Electrical.
What is a transformer?
A device used to change the current and potential difference being transmitted.
Why does current need to be low across transmission lines?
To reduce heat loss.
Why does voltage need to be high across transmission lines?
Because of the loss of energy.
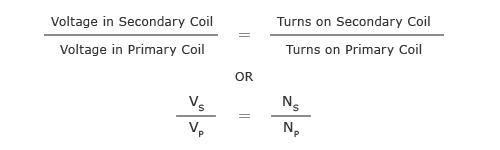
What is a step-up transformer? (3 points)
More turns on secondary coil
Increases output voltage
Decreases output current
What is a step-down transformer? (3 points)
More turns on primary coil
Decreases output voltage
Increases output current
What does a basic transformer consist of?
Primary coil, secondary coil iron core.
How does a transformer work?
A.c. is sent through the primary coil.
This induces an alternating magnetic field around the primary coil.
The iron core is easily magnetised, so the changing magnetic field passes through it. The magnetic field is alternating.
This cuts through the secondary coil and induces potential difference.
What is the transformer equation?
A microphone is a simple //
Generator
How does a microphone work? (3 points)
Pressure variations in the air causes the diaphragm (which is attached to a coil of wire) to move forwards and backwards.
Coil of wire moves within the magnetic field.
This induces alternating potential difference and therefore an alternating current.
How does a loudspeaker work? (4 points)
A.c. is passed through a wire which is wrapped around a cone.
The field of the wire interacts with the field of the permanent magnet, exerting a force on the coil (motor effect).
The force constantly changes direction due to the changing magnetic field, which causes the coil and cone to oscillate.
This makes the air oscillate, producing sound waves.
What does a microphone consist of?
Coil wrapped around a magnet with a diaphragm attached.
What does a loudspeaker consist of?
A coil of wire with a cone wrapped around a permanent magnet.
What does a microphone and loudspeaker do?
Microphone - Converts pressure variations into electrical signals/current.
Loudspeaker - Converts electrical signals/current to pressure variations.