Human Anatomy and Physiology
5.0(2)Studied by 83 people
Card Sorting
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:13 AM on 12/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
1
New cards
Mechanical digestion
breaking food into smaller pieces
2
New cards
chemical digestion
breaking nutrients into small molecules
3
New cards
enzymes
(hydrolases) the speeding up of action in digestive system chemically
4
New cards
Hydrolysis
the process by splitting molecules by adding water.
5
New cards
Anus
one of the two opening that allows you to defecate
6
New cards
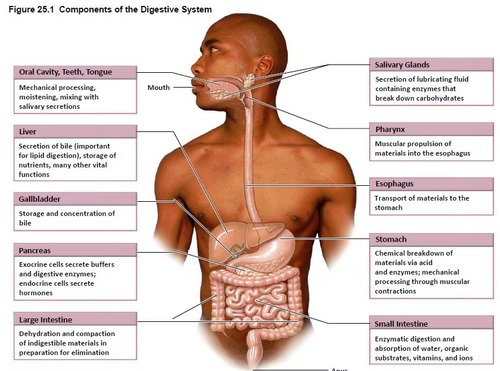
Alimaentary canal
Carries out specific phases of digestive process ex. mechanical and chemical digestion and absorption
* anus and mouth canal
* has specialized processes for digestion.
* anus and mouth canal
* has specialized processes for digestion.
7
New cards
Accessory organs
liver, gallbladder and pancreaas
8
New cards
surface area
makes food easier to swallow and digest
9
New cards
salivary glands
food stimulates a part of your mouth to release saliva which contains enzyme amylase
10
New cards
Amylase
breaks down starch into smaller carbohydrates molecules (monosaccharides and disaccharides)
11
New cards
Pharynx
when food is swallowed in gets pushes down by the tongue into the throat.
* Throat
* Throat
12
New cards
esophagus
food passes through here from throat
13
New cards
epiglottis
covers wind pipe when swallowing
14
New cards
Stomach
From esophagus the food is passed through there by muscular contractions
15
New cards
Peristalsis
muscular contractions
16
New cards
Gastric Juice
released by the lining of the stomach, and is made up of hydrochloric acid and protease
17
New cards
proteases
protein digesting enzymes
18
New cards
chyme
a liquid resulted from the smooth muscles mix partially digested food in the stomach
19
New cards
Small intestine
* chyme is released into the ………. in small portions through the pyloric sphincter
* most digestion takes place in the …..
* major site for absorption of of nutrients into the blood stream
* 6 meters long in humans
* most digestion takes place in the …..
* major site for absorption of of nutrients into the blood stream
* 6 meters long in humans
20
New cards
Pyloric Sphincter
chyme is released here through the …….. in small portions
21
New cards
Liver
produces bile that is stored in the gallbladder
22
New cards
Bile
helps break down fats
23
New cards
Gallbladder
stores bile,
24
New cards
Pancreas
supplies number of enzymes needed for digestion
25
New cards
villi
facilitates absorption \n - increases surface area for absorption of the end products of digestion into the blood and lymph.
26
New cards
large intestine/ colon
* undigested food is moved to the …….
* responsible for reabsorbing water that has entered the alimentary canal
* responsible for reabsorbing water that has entered the alimentary canal
27
New cards
rectum
feces stored here
28
New cards
Atrium
2 chambers of the heart that receive blood
29
New cards
Ventricles
2 chambers that pump blood to the body
30
New cards
atrioventricular valve
the valve in which blood passes from the atrium to the ventricle \n - purpose of valve to prevent back flow
31
New cards
pulmonary artery
the right ventricle pumps the blood through the semilunar valve into the …… \n - carries the blood to the lungs
32
New cards
deoxygenated
When the gas exchange occurs the blood is first……
33
New cards
oxygenated
\- blood receives air at the lungs, where gas exchange occurs.
34
New cards
pulmonary veins
\- newly oxygenated blood leaves the lungs through the ………which then returns blood to the left atrium
35
New cards
systole
When the heart contracts, the pressure increases
36
New cards
diastole
when the heart relaxes , the pressure is lowered
37
New cards
coronary circulation
The circulation of blood to the heart
38
New cards
pulmonary circulation
The circulation of blood through the lungs
39
New cards
systemic circulation
circulation throughout the body
40
New cards
Blood
considered connective tissue that is made up of a variety of cells suspended in liquid called plasma
41
New cards
Plasma
variety of cells suspended in a liquid
* liquid part of blood
* About 55% of our blood
* liquid part of blood
* About 55% of our blood
42
New cards
hemoglobin
oxygen carrier
* iron-rich compound
* iron-rich compound
43
New cards
White blood cells/ leukocytes
involved in host immune defense
44
New cards
Platelets
found in plasma, pieces of cells that are important in blood clotting
45
New cards
lymph capillaries
* as blood passes through the vessels of the circulatory system , fluid and proteins can leak out
* the lost fluid diffuses into the …….
* the lost fluid diffuses into the …….
46
New cards
Lymph nodes
* are special pockets in the lymphatic system where the lymph is filtered
* white blood cells are present here to attack bacteria and viruses that may be present in the fluid
* white blood cells are present here to attack bacteria and viruses that may be present in the fluid
47
New cards
Arteries
transport blood away from the heart.
* can feel a pulse there
* can feel a pulse there
48
New cards
Capillaries
tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins
* materials leave and enter through the walls that are one cell thick
* materials leave and enter through the walls that are one cell thick
49
New cards
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
50
New cards
trachea
windpipe
51
New cards
larynx
voice box \n contains vocal cords
52
New cards
bronchi
The passages that branch from the trachea and direct air into the lungs
53
New cards
bronchioles
small subdivisions of the bronchi that are dead ends with tiny air sacks called alveoli at the end
* thin tubes
* thin tubes
54
New cards
alveolus (alveoli)
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
* the functional unit of the lung
* air sac
* the functional unit of the lung
* air sac
55
New cards
diaphragm
a sheet of muscle lining the bottom of the thoracic cavity
56
New cards
increasing diaphragm pressure
forces outside air into the lungs and increases the pressure forces exhaled air out of lungs
57
New cards
exhaled air has more ___ than inhaled air
carbon dioxide and water
58
New cards
how gas exchange occurs during respiration (for blood to become oxygenated)
capillaries surround alveoli \n gas exchange occurs across alveolar membrane via diffusion
59
New cards
diffusion during gas exchange between alveoli and capillaries
blood picks up the oxygen and carries it back to the heart \n carbon dioxide is exhaled
60
New cards
cellular respiration
process by which we get energy from the food that we eat \n - can be aerobic or anaerobic
61
New cards
aerobic respiration
occurs when oxygen is present and it is the opposite process to that of photosynthesis
62
New cards
aerobic respiration begins at the __ and ends at the __
cytoplasm and ends in the mitochondria
63
New cards
anaerobic respiration
Respiration in the absence of oxygen. This produces lactic acid \n \n less efficient
64
New cards
forumla for aerobic respiration
glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy
65
New cards
lactic acid
when a muscle continues to burn sugar but doesn't have enough oxygen to do it properly
* cause of sore muscles after strenuous exercise
* cause of sore muscles after strenuous exercise
66
New cards
neuron
functional unit of a nervous system
67
New cards
nervous system
regulates body function and responds to environmental stimuli
68
New cards
Sodium
an essential nutrient and is needed by the body in relatively small amounts
69
New cards
Potassium
an essential mineral that is needed by all tissues in the body.
70
New cards
impulse
the electrical discharge that travels along a nerve fiber
71
New cards
dendrites
extension of the cell body of a neuron that carries impulses from the environment or from other neurons toward the cell body \n \n receives impulse
72
New cards
Cell body
largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
73
New cards
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands.
74
New cards
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored.
75
New cards
neurotransmitters
chemical used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell
76
New cards
myelin sheath
help transmit impulses faster
77
New cards
synapses
location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell
78
New cards
sensory neurons
transmit impulses from sense organs and receptors
79
New cards
interneurons
make up the brain and spinal cord
80
New cards
motor neurons
carry impulses from interneurons to skeletal and visceral muscles and glands
81
New cards
Nerves
bundles of axons of sensory and motor neurons
82
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
includes brain and spinal cord
* responsible for processing info
* responsible for processing info
83
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
nerves and sense receptors
* responsible for transmitting info to and from CNS
* responsible for transmitting info to and from CNS
84
New cards
PNS divided into two branches
somatic and autonomic PNS
85
New cards
Somatic
external environment
* transmits signals from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles, and from receptors of external stimuli, thereby mediating sight, hearing, and touch.
* transmits signals from the central nervous system to skeletal muscles, and from receptors of external stimuli, thereby mediating sight, hearing, and touch.
86
New cards
Autonomic
internal environment
* Acting or occurring involuntarily, without conscious control.
* Acting or occurring involuntarily, without conscious control.
87
New cards
Spinal Cord
extends from the brain and downward and is enclosed by the bones of the vertebral column, or spine
* conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain
* acts as the center for reflex actions
* conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain
* acts as the center for reflex actions
88
New cards
Reflex Arc
carries out simple, quick, and automatic responses to certain stimuli
* commonly defensive and do not necessarily involve the brain
* commonly defensive and do not necessarily involve the brain
89
New cards
Brain
protected and enclosed within the cranium and is divided into three areas
90
New cards
cerebrum
makes up the largest portion of brain and the site for high level thinking
* conscious and voluntary actions controlled here
* conscious and voluntary actions controlled here
91
New cards
Cerebellum
the "little brain" attached to the rear of the brainstem; it helps coordinate voluntary movement/ coordination and balance
92
New cards
Brain Stem/ Medulla
controls basic homeostatic functions \n - body temps, Blood Pressure, breathing,
93
New cards
Homeostasis
process by which the body maintains a relatively stable internal environment by secretion from endocrine glands
94
New cards
Hormones
chemicals that act as messengers and that help control the important processes of growth, metabolism, reproduction, osmotic balance, and development
* bind to receptors and influencing the activity of the cell
* usually activated by a stimulus
* bind to receptors and influencing the activity of the cell
* usually activated by a stimulus
95
New cards
negative feedback mechanism
homeostatic control mechanism that reduces the output of the stimulus
96
New cards
positive feedback mechanism
homeostatic control mechanism that increases the stimulus to push the variable farther from its original value
97
New cards
where are blood cells made?
red marrow of long bones
98
New cards
pituitary gland (funct, hormones assoc.)
the endocrine system's most influential gland, controls other endocrine glands \n -growth stimulating hormone \n -thyroid stimulating hormone
99
New cards
thyroid gland (funct, hormones assoc.)
regulates metabolism \n -thyroxin
100
New cards
parathyroid gland (funct, hormones assoc.)
regulates calcium metabolism \n essential for proper bone formation \n -parathormone