Acids, Bases, and Buffers
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
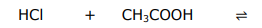
Complete the equilibrium and label the conjugate acid-base pairs.


Write balanced full equations and ionic equations for the following acid reaction
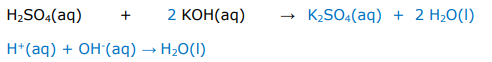
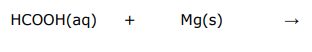
Write balanced full equations and ionic equations for the following acid reaction
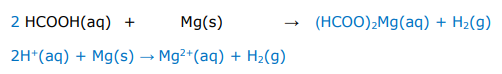

Write balanced full equations and ionic equations for the following acid reaction
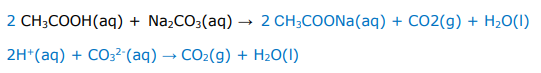
Strong Acids equations
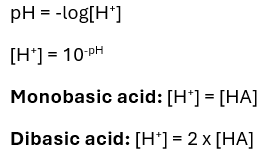
When calculating the pH of strong monobasic acids, what assumptions do you make?
That the acid is full dissociated, so [H+] = [HA]
That water dissociation is negligible
Weak Acids equations

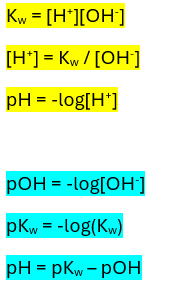
What’s the expression for the ionic product of water?
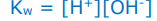
Strong Bases equations
Pure Water equations
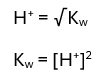
Diluted Acid equations

Diluted Base equations
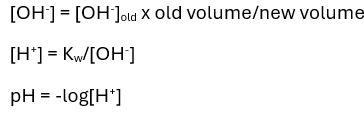
State two approximations used in the calculation of pH of weak acids.
Acid dissociation is neglible
Water dissociation is neglible
Buffer Solutions equations
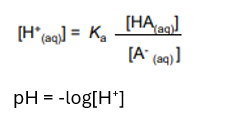
Making a buffer by adding a salt solution
Calculate the moles of both solutions
-
Insert into equation:
[H+] = Ka x ([HA]/[A-])
where HA is the acid and A is the salt solution.
-
Then calculate pH using the [H+]
Calculate the pH of a buffer made from 45 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid and 50cm3 of 0.15 mol dm-3 sodium ethanoate (Ka = 1.7 x 10-5)
Making a buffer by adding a solid salt
Calculate the moles of salt and the moles of the solution
-
Insert into equation:
[H+] = Ka x ([HA]/[A-])
where HA is the acid and A is the salt.
-
Then calculate pH using the [H+]
Making a buffer by adding NaOH to partially neutralise a weak acid
Calculate the moles of NaOH and the moles of the solution
-
Calculate the moles in excess. Minus the smaller number of moles from the bigger number of moles.
-
Insert into formula:
[HA] = Moles excess/Total volume (dm3)
[A-] = Moles OH- added/Total volume (dm3)
[H+] = Ka x ([HA]/[A-])
-
Then calculate pH using the [H+]
55cm3 of 0.50 mol dm-3 CH3COOH is reacted with 25cm3 of 0.35 mol dm-3 NaOH.
Calculate the pH of the resulting buffer solution.
Ka = 1.7 × 10-5 mol dm-3
N of CH3COOH = 0.0275mol
N of NaOH = 0.00875mol
0.0275-0.00875 = 0.01875
[CH3COOH] = 0.01875/80dm3 = 0.234 mol dm-3
[CH3COO-] = 0.00875/0.08 = 0.109 mol dm-3
[H+] = 1.7×10-5 × (0.234/0.109)
[H+] = 3.64 × 10-5
pH = -log[3.64 × 10-5]
pH = 4.44
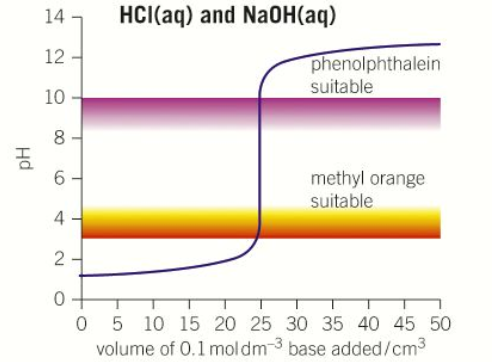
Vertical parts of strong acid and strong base.
Strong acid steep between pH 4 – 7
Strong base steep between pH 7 – 10
No steep part for weak acid or base

“Strong acid – Strong base” pH curve
pH = 1
pH = 13
pH = 7
Volume at neutralisation = 25cm3
Steep between pH 4-10

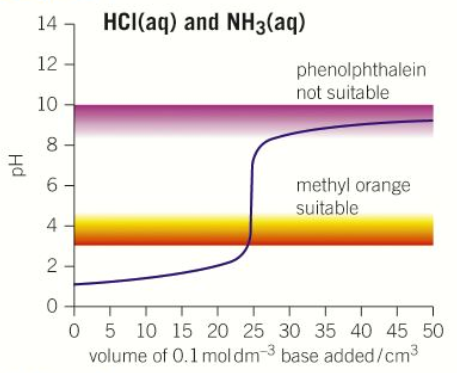
“Strong acid - Weak base” pH curve
pH = 1
pH = 9
pH = Less than 7
Volume at neutralisation = 25cm3
Steep between pH 4-7
Half Neutralisation Volume for Weak Acids
Half neutralisation volume is the point in a titration where half of the weak acid (HA) has been neutralised by the base (OH-)
At half the neutralisation volume, [HA] = [A-]
Ka = [H+][A-] / [HA]
Since [HA] = [A-], they cancel out.
Ka = [H+]
pKa = pH
If we know the Ka, we can then work out the pH at 1/2 V
If a pH curve is plotted, then the pH of a weak acid at half neutralisation (1/2 V) will equal the pKa.
![<p>Half neutralisation volume is the point in a titration where half of the weak acid (HA) has been neutralised by the base (OH-)</p><p>At half the neutralisation volume, [HA] = [A<sup>-</sup>]</p><p></p><p>Ka = [H<sup>+</sup>][A<sup>-</sup>] / [HA]</p><p>Since [HA] = [A<sup>-</sup>], they cancel out.</p><p>Ka = [H<sup>+</sup>]</p><p>pKa = pH</p><p></p><ul><li><p>If we know the Ka, we can then work out the pH at 1/2 V</p></li><li><p>If a pH curve is plotted, then the pH of a weak acid at half neutralisation (1/2 V) will equal the pKa.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/42bcc4bc-114d-4d3f-a43e-70298d5314d9.png)

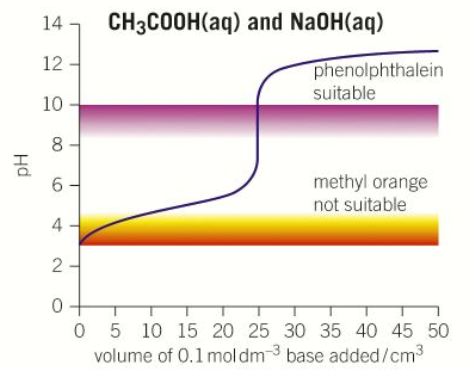
“Weak acid – Strong base” pH curve
pH = 3
pH = 13
pH = More than 7
Half neutralisation volume x2
Steep between pH 7-10

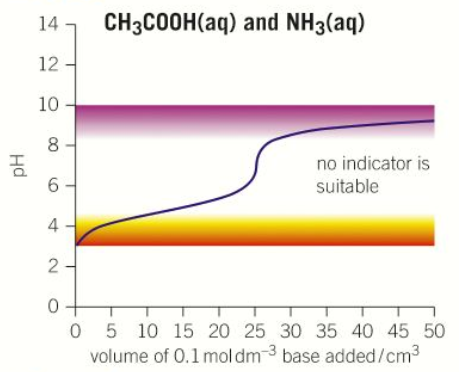
“Weak acid - Weak base” pH curve
pH = 3
pH = 9
No equivalence point
No volume at which equivalence occurs
No steep part of curve
Phenolphthalein
Only use in titrations with strong bases (NOT weak bases)
Colourless acid → pink alkali
Methyl orange
Only use in titrations with strong acids (NOT weak acids)
Red acid → yellow alkali