POCUS: Review
1/131
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Why is gel needed on the probe to scan?
prevent air from showing up on image
What is included in the FAST exam?
RUQ + R pleural space (long axis)
LUQ + L pleural space (long axis)
Pericardial space (subxiphoid)
Pelvis (long & short axis)
How does fluid appear on US?
anechoic
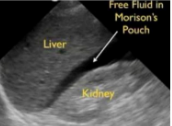
Where is Morrison’s pouch?
*common spot for blood to accumulate
R side btw liver & kidney
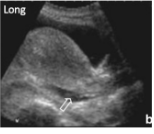
Where is the Pouch of Douglas?
*common spot for blood to accumulate in F
btwn uterus & rectum
What are normal lung artifacts?
A-line (bat sign), mirror image air artifact (liver/diaphragm), lung sliding (b mode → no air), seashore sign (m mode → no air), curtain sign (shadow of ribs)
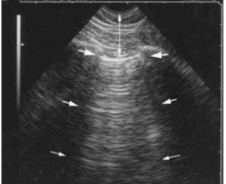
What are A-lines (“bat sign”)?
Normal, reverberation artifact → aerated lung
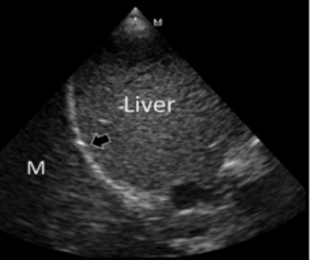
What is the Mirror Image artifact?
Normal, reverberation artifact → aerated lung
*liver & diaphragm MC
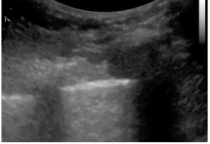
What is lung sliding (B mode)?
Normal, sliding present = NO AIR btwn visceral & parietal pleura → NO pneumothorax
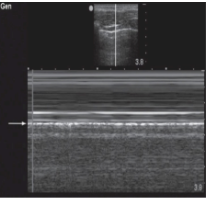
What is the Seashore sign (M mode)?
Normal, sliding present = NO AIR btwn visceral & parietal pleura → NO pneumothorax
*smooth lines “waves” → no movement, hyperechoic lines → pleura, grainy area “sand” → air
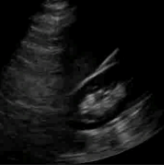
What is the Curtain sign?
Normal, shadow of rib moves like a curtain → aerated lung
What are pathological lung artifacts?
B lines, Shred sign, Barcode signs, PLAPS, Pleural effusion
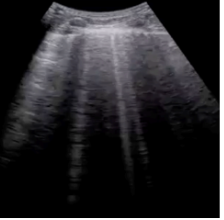
What do B lines indicate?
*more vertical, A-lines are horizontal
fluid in the interlobular space → PE, CHF, fluid overload
*3+ = pathological
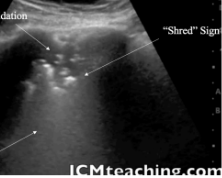
What does consolidation w/ the shred sign indicate?
lung is not air-filled in area of consolidation → PNA, atelectasis
How does pneumothorax appear on US?
absence of lung sliding (pleural layer is no longer present)
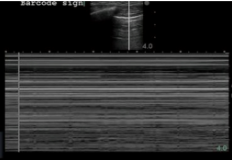
What does the Barcode sign indicate?
*seen in M-mode
No pluera movement → Pneumothorax (MC), pleurodesis, pleural adhesions
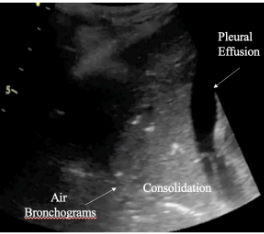
What does PLAPS indicate?
air bronchograms, consolidation, pleural effusion
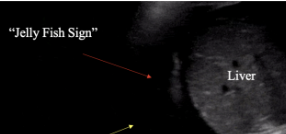
What is the Jellyfish Sign?
collapsed lung floating w/in fluid → pleural effusion
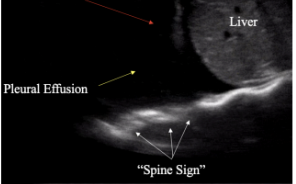
What is the spine sign?
Spine visible posterior to fluid collection → pleural effusion
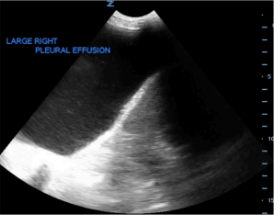
What is Plankton sign?
swirling echogenic material w/in effusion → exudative pleural effusion
What does fibrinous tissue w/in the anechoic free fluid indicate?
pleural effusion exdudate
Which way does the indicator point in short axis?
towards pts right
*probe is perpendicular to structure being scanned
Which way does the indicator point in long axis?
towards pts head
*probe is parallel to structure being scanned
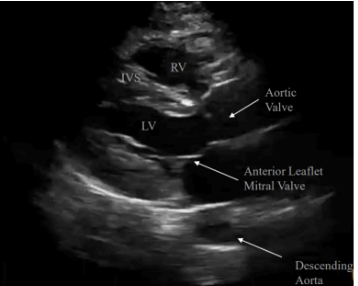
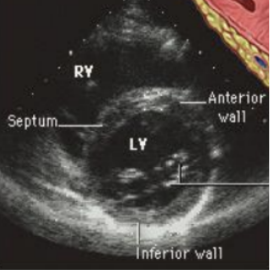
Which axis is this?
Long axis
What axis is this?
Short axis
What axis is this?
Short axis

What axis is this?
Long axis
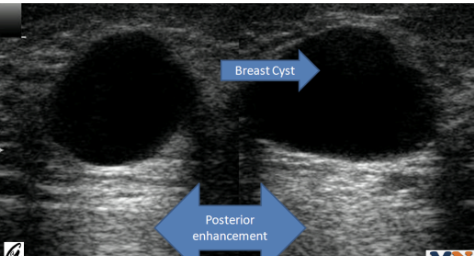
What is posterior enhancement?
hyperechoic area posterior to fluid (NORMAL)
*seen distal to fluid structures, result of low-attenuation (sound waves do not dissipate well in fluid)
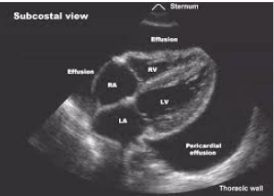
What does pericardial effusion look like on US?
anechoic fluid collection btwn visceral & parietal pericardium → heart appears to be floating
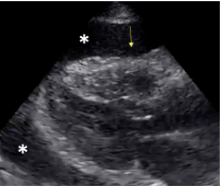
What sign is pathological for Cardiac Tamponade?
Trampoline sign = beat to beat collapse of RV
What is optimization?
changes made in the gain/depth in an image
What is gain?
brightness/darkness → amplification of echoes
*errors = preset is incorrect
What is depth?
how deep the scan area is in cm
What preset is used to look at the heart?
Abdomen
*dec gain to enhance hyperchoic structures, reduce depth so only heart fills screen (must include descending aorta posteriorly)
Where is the probe placed to obtain the Parasternal Long Axis (PSLAX) view?
left parasternal border near nipple
*if lung interference → have pt breathe in & hold their breath after expiration
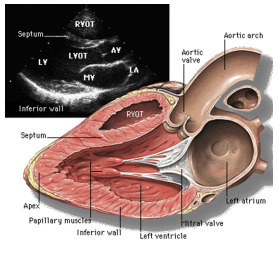
What is the PSLAX view used to see?
best view of anterior leaflet to look at mitral valve
*used to estimate EF
Where is the probe placed to obtain the Parasternal Short Axis (PSAX) view?
PSLAX position → rotate 90 degrees
*once in 8 o’clock position, fan probe to bring LV (doughnut) into view
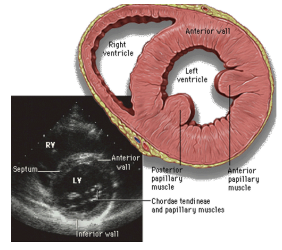
What is the PSAX view used to see?
best view to look for the D sign of PE & LV wall motion abnormalities
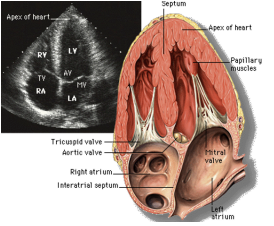
What does the Apical 4 Chamber view show?
shows all 4 chambers -RV narrower and comes to point (gnomes hat), LV wider (shoe print)
Where is the probe placed to obtain the Apical 4 Chamber (A4C) view?
probe facing apex of heart toward pt’s R
*cant find apex → start in PLAX & slide down to nipple → rotate 90 clockwise → fan anteriorly to see all chambers
How should pt be positioned to obtain A4C?
LLD w/ arm over head
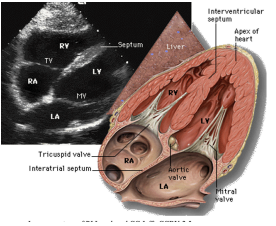
What does the subxiphoid view show?
all 4 chambers, BEST view to see PE & cardiac standstill
Where is the probe placed to obtain the Subxiphoid view?
10 degree angle at subxiphoid, inc depth ~20 cm
What position can help obtain a better Subxiphoid view?
supine w/ arms to side, have them bend legs to relax rectus muscles, get more depth, take breath in and hold it, dec gain
What probe is HIGH frequency, attenuates quickly, and is good for superficial structures & soft tissues?
Linear
-vessels (DVT), thyroid, LN, skin, pleura
What probe is good for deep structures, is LOW frequency, and attenuates slowly?
Curvilinear
-abdominal exams
What probe is good for cardiac imaging, is LOW frequency, and penetrates deeper than curvilinear?
Phased array
-small scan head → can fit btw ribs
What is a sliding movement?
Long axis → move probe cranially or caudally along Y axis
What is a sweeping movement?
Short axis → move probe cranially or caudally along X axis
What is a compression movement?
can be in long or short axis → apply downward force along Z axis
When is compression used?
DVT & appendicitis (both are non-compressible)
What is a fanning movement?
Short axis → angling probe from 90 to 45 degrees cranially or caudally
What is the POCUS criteria for dx a DVT?
non-compressibility of a deep vein + leg swelling + stasis
What veins are the deep veins to assess for a DVT?
common femoral, large saphenous, deep femoral, superficial femoral, popliteal
How should the probe be positioned to assess for DVT?
indicator points to pts right (short axis)
-veins are medial
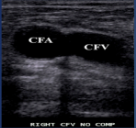
What is site 1 for a DVT?
Common Femoral Artery & Vein
*drape pt and gather drape & put probe right in inguinal line
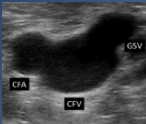
What is site 2 for a DVT?
Saphenofemoral junction
What is the Mickey Mouse sign associated with?
Saphenofemoral junction
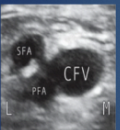
What is site 3 of a DVT?
bifurcation of common femoral artery
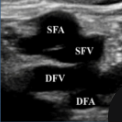
What is site 4 of a DVT?
bifurcation of the common femoral vein
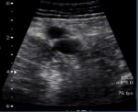
What is site 5 of a DVT?
lower superficial femoral vein
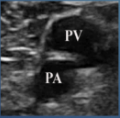
What is site 6 of a DVT?
popliteal artery & vein
(vein on top)
What is the tx for a DVT?
anticoagulant
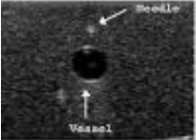
What is a common needle placement error that can cause the wire to not to advance in the vessel when placing a central line under US guidance?
too steep of an angle→ hits back wall of vessel → wire cant make the turn
What are the 2 access windows to place a needle in a structure under US guidance?
Long & Short axis
*biggest concern is introducing air → prevent by flushing all lines
What are the steps of the Seldinger technique?
US guided: utilizes a guidewire
1- Needle insertion
2- guidewire
3- take needle out
4- insert dilator over guidewire, then catheter
What technical term describes weak reflectors?
*ex: fluid
Anechoic (black)
-causes posterior enhancement
What technical term describes strong reflectors?
*ex: bone/air
Hyperechoic (white)
-causes posterior shadowing
What technical term describes mixed reflectors?
*ex: soft tissue
Hypoechoic (gray)
What is another technical term for mixed reflectors?
Isoechoic
Which mode is the default?
B-mode (Brightness mode)
What mode is good for pneumothorax and lung sliding?
M-mode (Motion mode)
What mode shows vascular flow?
Color Doppler mode
*Blue away (venous), Red towards (artery)
What helps visualize the kidney when rib shadow interfere with the image?
Slide down past kidney & fan up; Inhale and hold it to move kidney down → avoid shadowing
-L kidney: knuckles are on bed and you are scanning P→A (can roll pt into R lateral decubitus)
-R kidney: if you only see liver, fan probe posteriorly
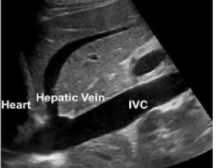
How would the IVC appear in the case of euvolemia?
normal
*will see respiratory variation (IVC collapses as pt breathes)
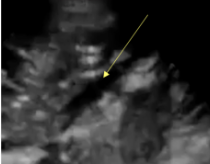
How would the IVC appear in the case of hypovolemia?
*hypovolemic or distributive shock
flat
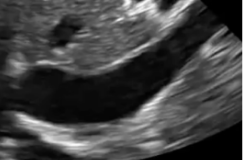
How would the IVC appear in the case of fluid overload?
*cardiogenic or obstructive shock
distended
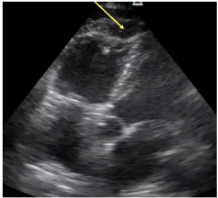
What is McConnel’s sign?
*for R. heart strain → PE; A4C
RV free wall akinesis w/ sparing of the apex
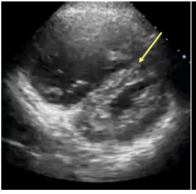
What is PSAX D sign?
*for R. heart strain → PE
dilation of RV causes bowing of the septum into the LV
What are the expected lung US findings if a PE is present?
lungs are NORMAL (bc they’re vascular), won’t see B lines, consolidation, or air bronchograms
ONLY see A lines
What interferes with seeing the aorta on US the most?
bowel gas→ jiggle probe, press harder, scan from below
What anatomical landmark is used to locate the aorta in transverse?
1st vertebral body to locate aorta (aorta will be anterior to it)
What are the two main causes of shock?
pump issue (cardiogenic & obstructive)
volume issue (hypovolemic & distrubutive)
According to RUSH protocol what is the most useful way to identify the type of shock?
assess the heart
What are causes of cardiogenic shock?
acute MI, valve defects, rhythm disturbances
What US findings are associated w/ cardiogenic shock?
hypodynamic heart, dilated LV, poor squeeze, abn rhythm, B lines
What are causes of obstructive shock?
PE, tamponade, tension pneumothorax
What US findings are associated w/ obstructive shock?
distended IVC, hyperdynamic heart, McConnel’s sign, D shaped septum, effusion, absent lung sliding, Trampoline sign
What causes hypovolemic shock?
bleeding d/t trauma, ruptured large vessel, ruptured viscus
What US findings are associated w/ hypovolemic shock?
Flat IVC & + FAST exam
*look for fluid in Morrison’s pouch, around spleen, pouch of douglas, if the uterus is floating in blood
What are causes of distributive shock?
sepsis, anaphylaxis, TSS, SIRS, neurogenic
What US findings are associated w/ distributive shock?
Flat IVC, - FAST exam, normal aorta
Using RUSH protocol what are you looking for when you exam the heart, IVC, and lung?
looking for dysfunction or obstruction
Using RUSH protocol what are you looking for when you exam the aorta and DVT?
supporting details to narrow ddx
Using RUSH protocol what are you looking for w/ E-FAST?
looking for volume loss or maldistribution
What is step 1 of RUSH protocol?
PUMP: heart + IVC and lungs
What is step 2 of RUSH protocol?
Volume: E-FAST
What is step 3 of RUSH?
Pipes: Aorta & DVT
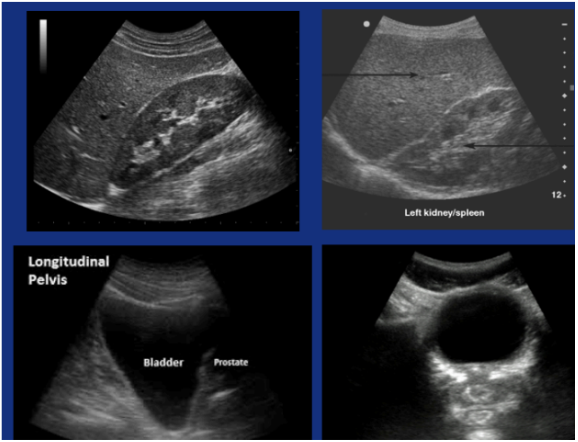
Normal FAST exam
:)
What does a normal gallbladder look like in Long Axis?
Anechoic, pear shaped w/ neck, body, and fundus; exclamation point when seen w/ portal vein