Bio Units 4/5 Study Cards
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the stages of interphase?
G1- growing, S- duplicating DNA, G2- finishes growing, checks
What are the parts of cell division?
PMAT and cytokinesis
What happens in meiosis?
The creation of 4 unique haploid cells (sperm or egg), it is PMAT times 2
What happens in Meiosis 1
PMAT occurs, the homologous pairs separate, ends with 23 chromosomes and 46 chromatids, still a diploid
What happens in meiosis 2?
PMAT times 2, sister chromatids separate, ends with 4 haploid daughter cells (23 chromosomes and 23 chromatids)
PMAT 1
Prophase 1- chromosomes pair up, form tetrads, and cross over
Metaphase 1- pairs randomly line up in cell center, 23 chromosomes on each side
Anaphase 1- pairs separate to opposite ends, chromatids remain together, independent assortment occurs
Telophase 1- membrane reforms, creates two cells w/ unique combo of parents
Diagram
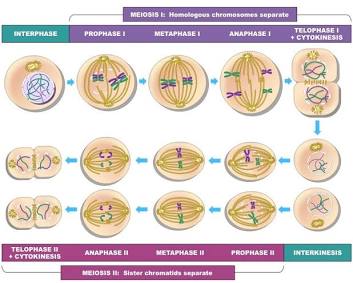
PMAT2
Prophase 2- membrane breaks down, spindle fibers assemble
Metaphase 2- spindle fibers align 23 chromosomes along equator
Anaphase 2- sister chromatids pulled apart/move to opposing sides
Telophase 2- membrane reforms, left with 4 unique haploid cells
Homologous chromosomes
A pair of chromosomes, one from each parent, code for same genes
Gametes
Sex cells
Haploid
a cell with one half genetic info
Diploid
A cell with full genetic info
How is genetic variation occurring?
Crossing over and independent assortment
Lactose
Sugar (disaccharide) found only in milk
Lactase
An enzyme that turns lactose into glucose and galactose
If you are lactose tolerant
Blood sugar spikes after drinking milk
Lactose tolerance is a
Selective advantage, which developed due to adaption to the consumption of milk
Genotype
The exact gene such as Gg or AA
Phenotype
the thing the gene codes for, such as Aa is brown hair
Homozygous
Homozygous dominant and recessive describe AA or aa
Heterozygous
Describes a gene such as Aa or Ss
Nondisjunction
When the homologous chromosomes fail to separate in anaphase of meiosis
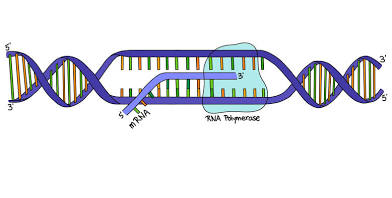
Transcription
In the nucleus, DNA code turns into mRNA, uses RNA polymerase to separate the strands
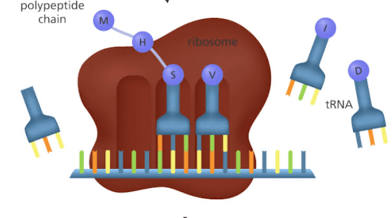
Translation
In cytoplasm, at ribosomes, mRNA code is translated into amino acids, tRNA brings the correct amino acid to build the protein
Transcription and translation model
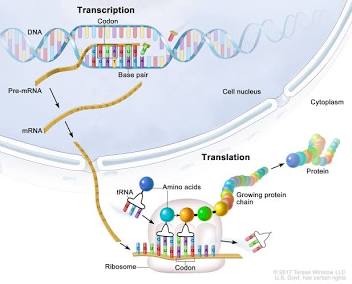
How do the letters in transcription and translation work?
During transcription, the original letters, A and T, which go together, and G and C, continue to the cytoplasm, but T turns into U
Central dogma
Flow of genetic info in cells- dna and rna
Nucleotide
4 types of nucleotides GCAT
mRNA
a vital type of RNA molecule that carries genetic instructions from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized
tRNA
a small RNA molecule that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by acting as an adapter between messenger RNA (mRNA) and amino acids
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a key structural component of ribosomes, the organelles that synthesize proteins
Diagram different types of RNA
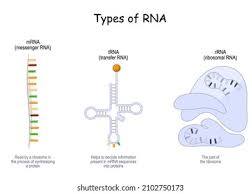
Codon
Sequence of 3 nucleotides
Point mutation
A change in a single base pair within a dna sequence (this includes insertion, substitution, deletion, etc)
Substitution mutation
One nucleotide base replaced with another
Insertion mutation
A nucleotide is added to the sequence, drastically changing it
Deletion mutation
A nucleotide is taken out of the sequence, changing it drastically
Silent mutation
When a mutation occurs in one mutation but doesn’t change the amino acid
Missense mutation
one nucleotide is replaced, causing a changed amino acid
Nonsense mutation
An early stop codon occurs
Frame shift mutation
One nucleotide is changed in the sequence, affecting the whole, and causing severe change to each amino acid
Melanin
Pigment produced in the skin, helps protect from UV radiation
Epidermis
Topmost layer of skin
Eumelanin
Black/brown form of melanin (found in larger amounts in darker skin)
Pheomelanin
Red/yellow form of melanin (found in larger amounts in lighter skin)
Melanocytes
Create melanin, which is packaged into melanosomes.
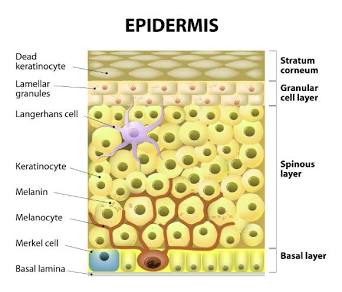
Melanosomes
Melanin is packaged into them by melanocytes, and they travel to keratinocytes and protect their nuclei
Vitamin D
UV rays help produce vitamin d, which is necessary for absorbing calcium
Folate
A chemical that is necessary in pregnant women to prevent birth defects. Without melanin protecting it, it will be broken down by UV.
Why did skin evolve over time?
To be balanced to protect folate and synthesize vitamin D based on levels of UV radiation in the area
Polygenic traits
Traits produced by two or more genes
5 Factors of Evolutionary change
Natural selection, mutation, gene flow, genetic drift, non-random mating (NMGGM)
Hardy Weinberg
Hypothetical, non-evolving population
Describes and measures how a population might change
P
Dominant allele frequency
Q
Recessive allele frequency
Equations
P + q = 1 (determines how many alleles)
P² + 2pq + q² = 1 (determines how many individuals)
Cancer and the cell cycle
Mutations in genes that regulate the cell cycle, such as oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, can disrupt normal cell cycle control and contribute to cancer development
Telomerase
Cancer cells often activate telomerase, an enzyme that repairs the ends of chromosomes (telomeres), allowing them to continue dividing indefinitely
Checkpoints
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by checkpoints that monitor DNA damage, replication errors, and other factors. Cancer cells often lose control of these checkpoints, allowing them to divide even with damaged DNA or other abnormalities
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death. It is used during early development to eliminate unwanted cells; for example, those between the fingers of a developing hand. In adults, apoptosis is used to rid the body of cells that have been damaged beyond repair. Apoptosis also plays a role in preventing cancer.
Contact inhibition
Contact inhibition is a process where cell growth and migration are halted due to contact with other cells
Hayflick limit
The Hayflick Limit is a biological concept that describes the limited number of times a normal human cell can divide before it enters a state of senescence, a process of cell aging and eventual death.
How do viruses infect/harm our cells?
They attach to the surface of the cell. Then, they insert their dna, which replaces the host dna. They then, through translation/transcription, copy this dna and create viral proteins. These proteins are finally released to begin to infect other cells.