Applied Anatomy and Physiology
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
The Musculoskeletal system
The combined system of the skeletal system and the muscular system, that work together to provide movement
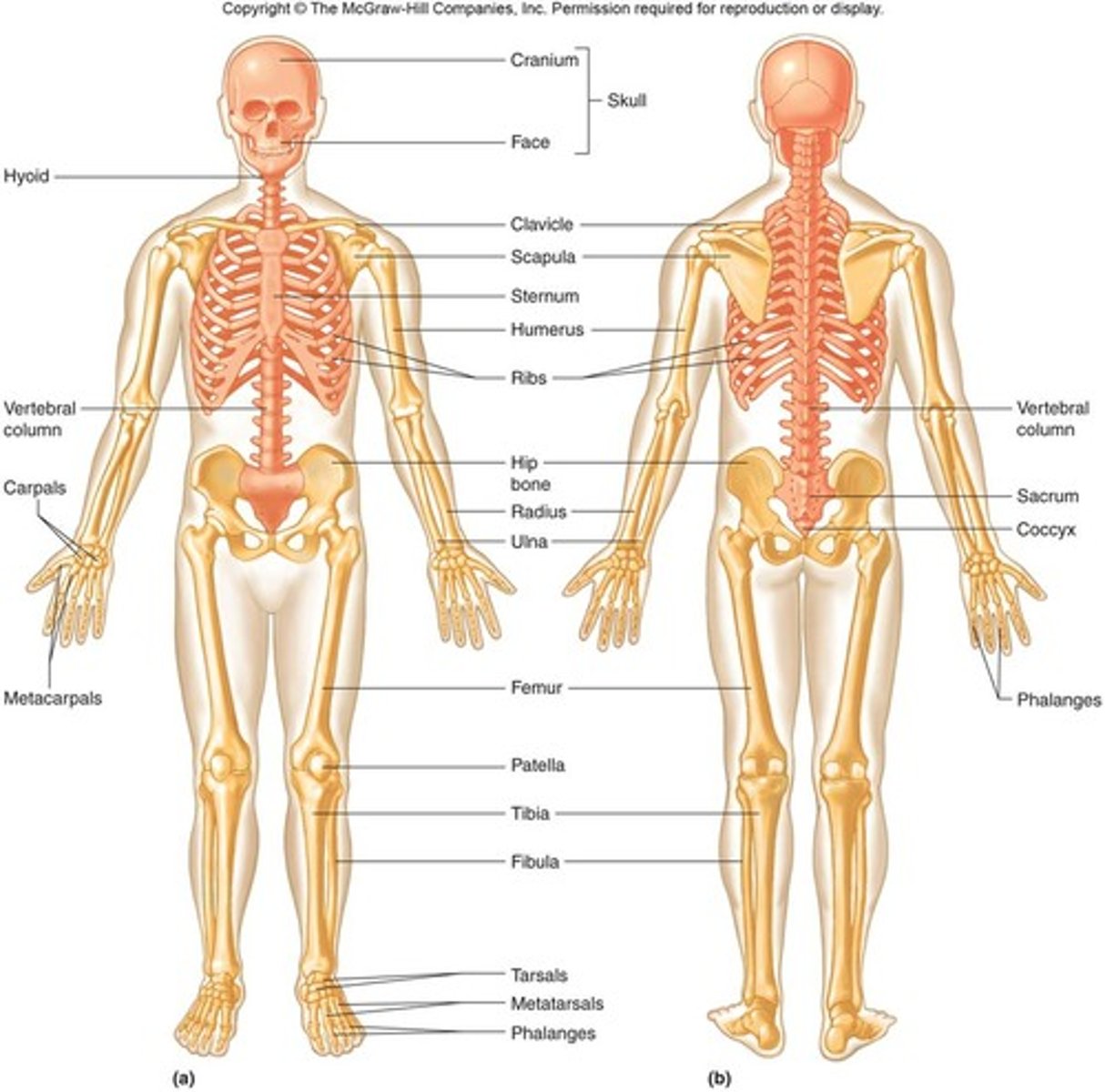
Flat bones
These bones are often quite large and protect vital organs
Long bones
These bones enable gross movement
Short bones
These enable finer, controlled movements
Irregular bones
These are specifically shaped to protect.
Articulating bones
These are bones that meet at a joint to enable movement
The shoulder
The scapula, clavicle and humerus are articulating bones that meet at which joint?

The elbow
The humerus, radius and ulna are articulating bones that meet at which joint?
The hip
The pelvis and femur are articulating bones that meet at which joint?
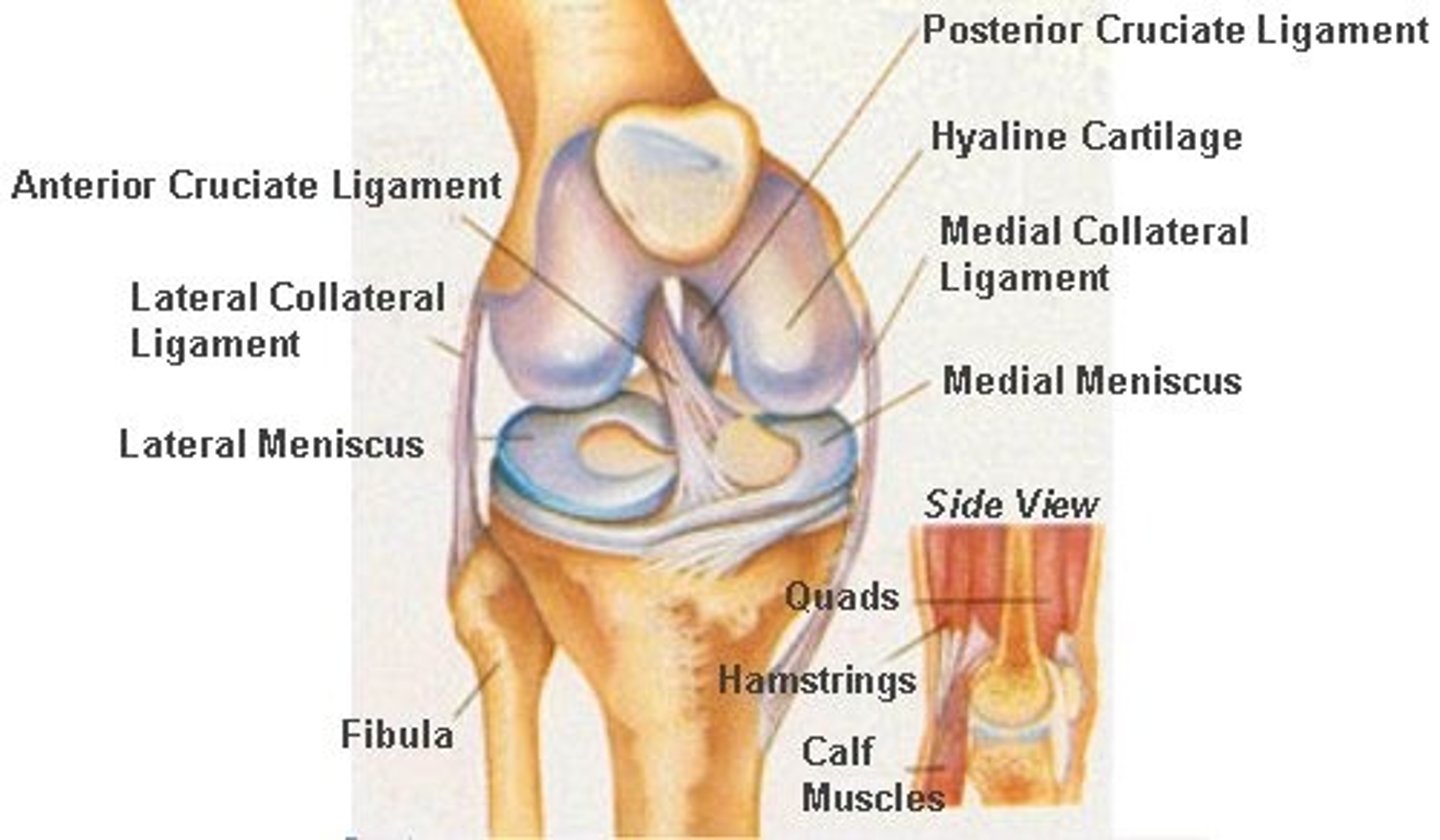
The knee
The femur, patella, fibula and tibia are articulating bones that meet at which joint?
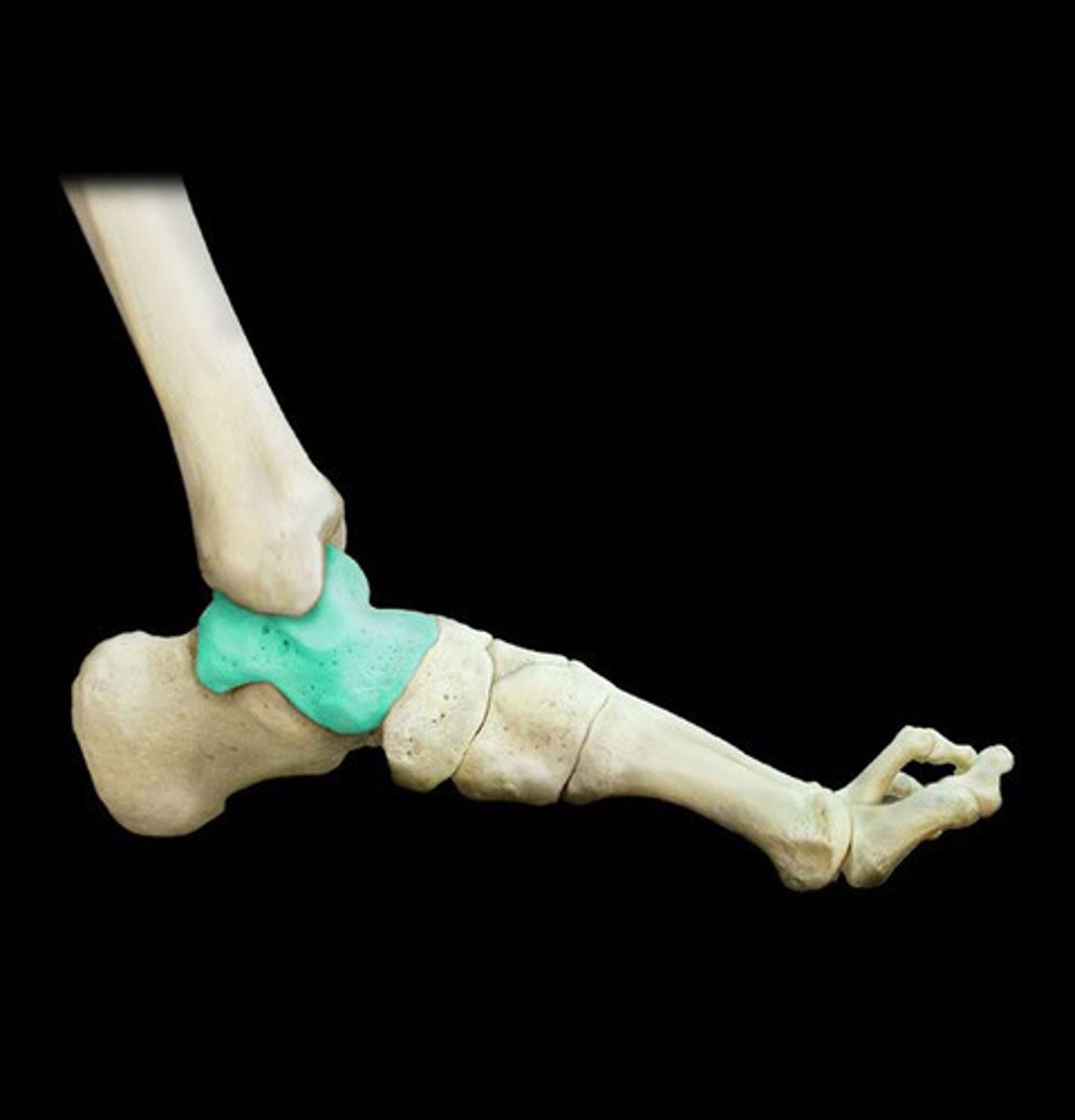
The ankle
The tibia, fibula and talus are articulating bones that meet at which joint?
The Cranium, clavicle, sternum, ribs and pelvis
Name 5 examples of flat bones
The humerus, radius, ulna, femur and tibia
Name 5 examples of long bones
The carpals and tarsals
Name 2 examples of short bones
The spine and the patella
Name 2 examples of irregular bones
The tarsals
These short bones sit between the lower leg and the top of the foot to allow for movement within the feet
The carpals
These short bones sit within the wrist, between the hand and forearm allowing for movement in the hand
The rib cage, scapula and sternum
These flat bones protects the heart and lungs
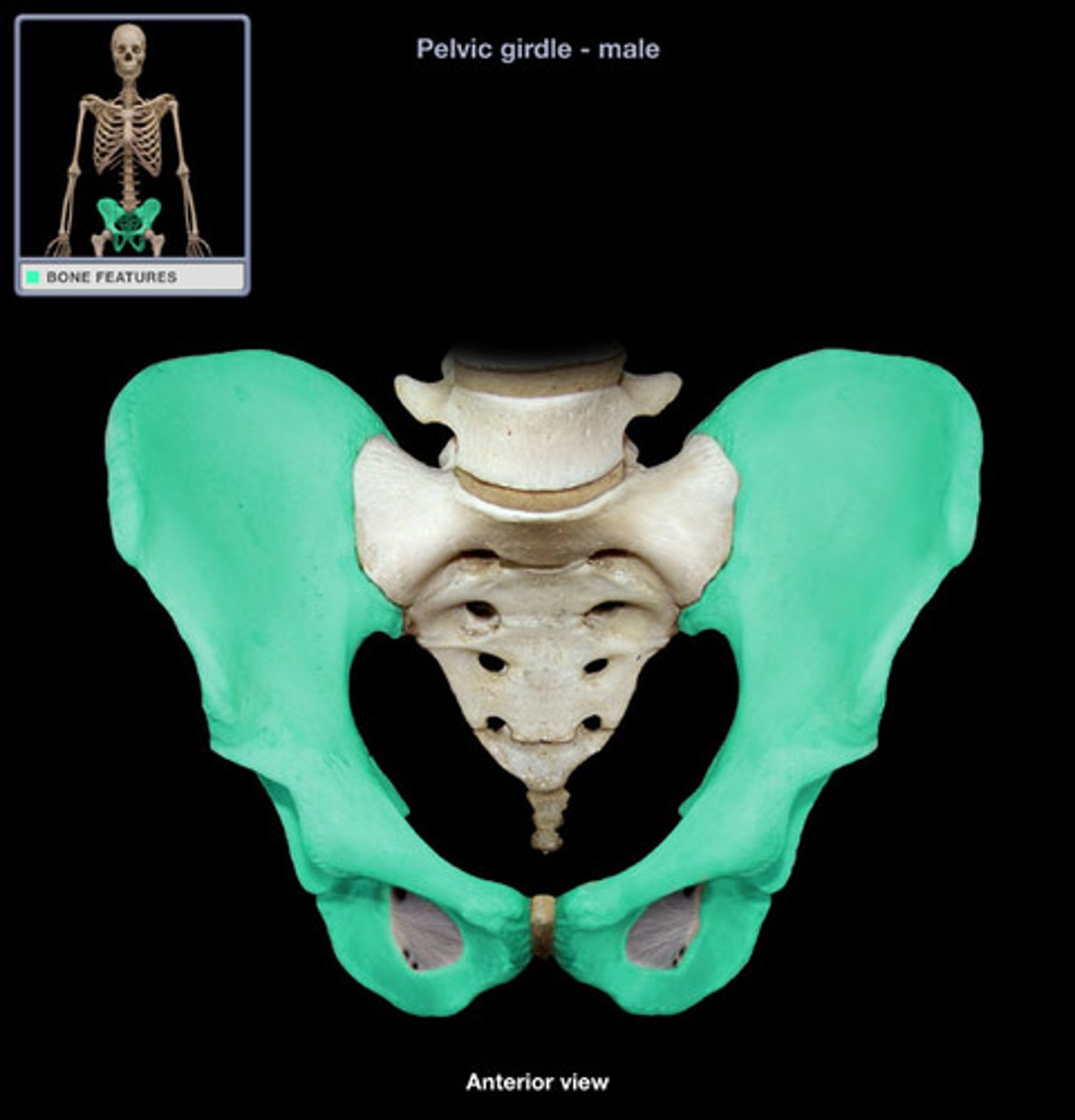
The pelvis and sacrum
These flat bones protect the reproductive organs and the bladder
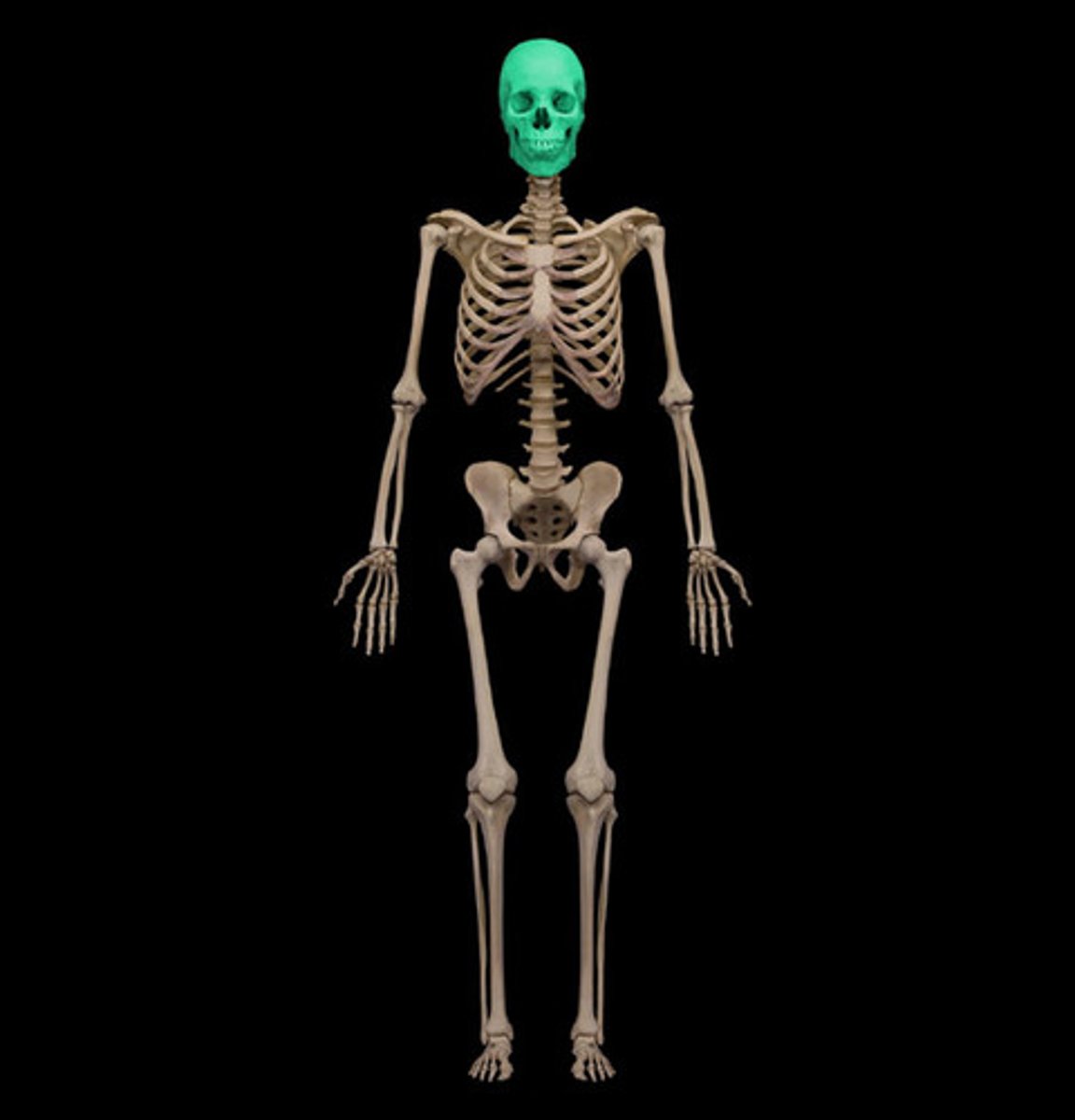
The cranium
This flat bone protects the brain
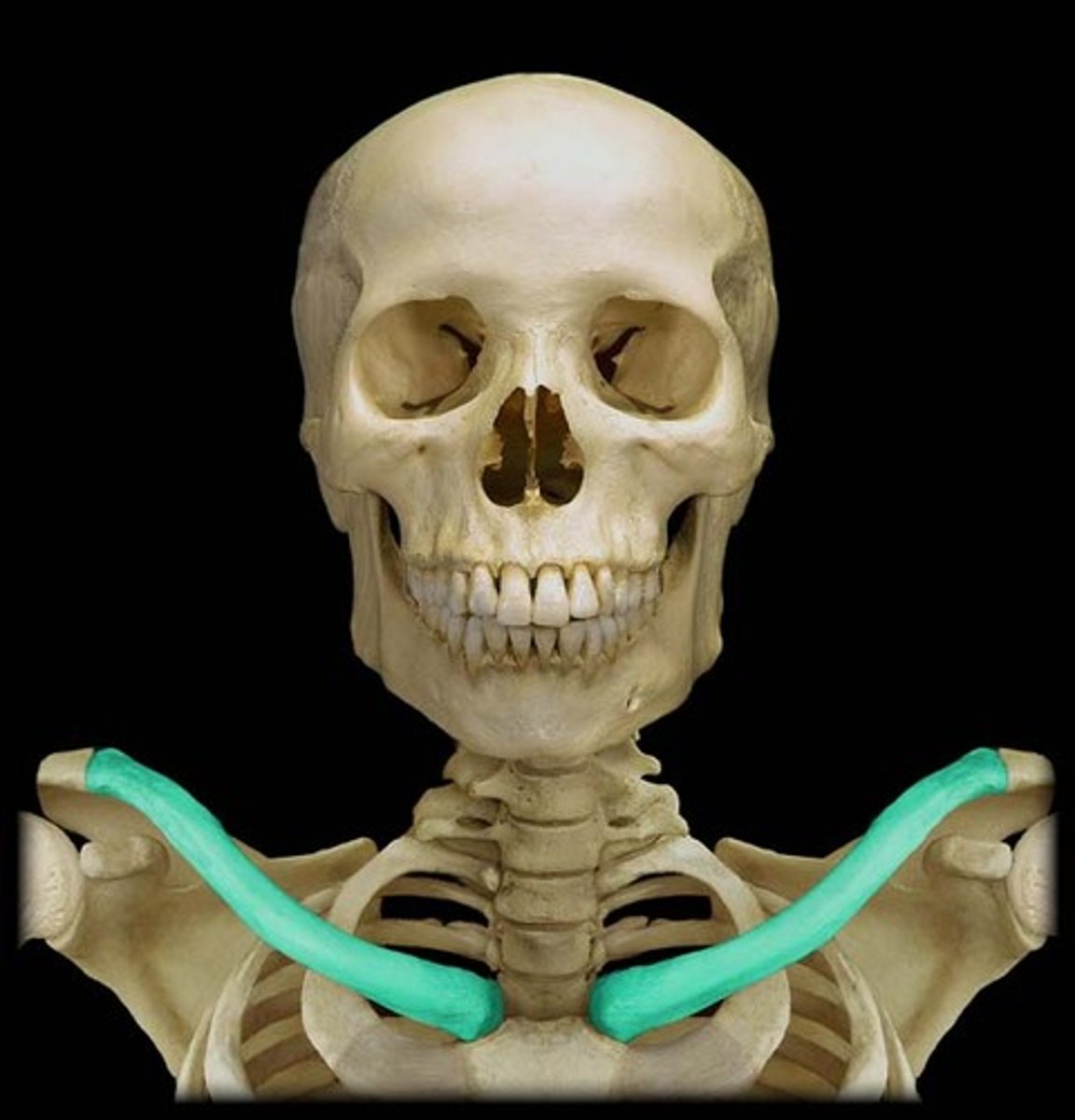
The clavicle
This flat bone protects the brain and the blood vessels to the neck
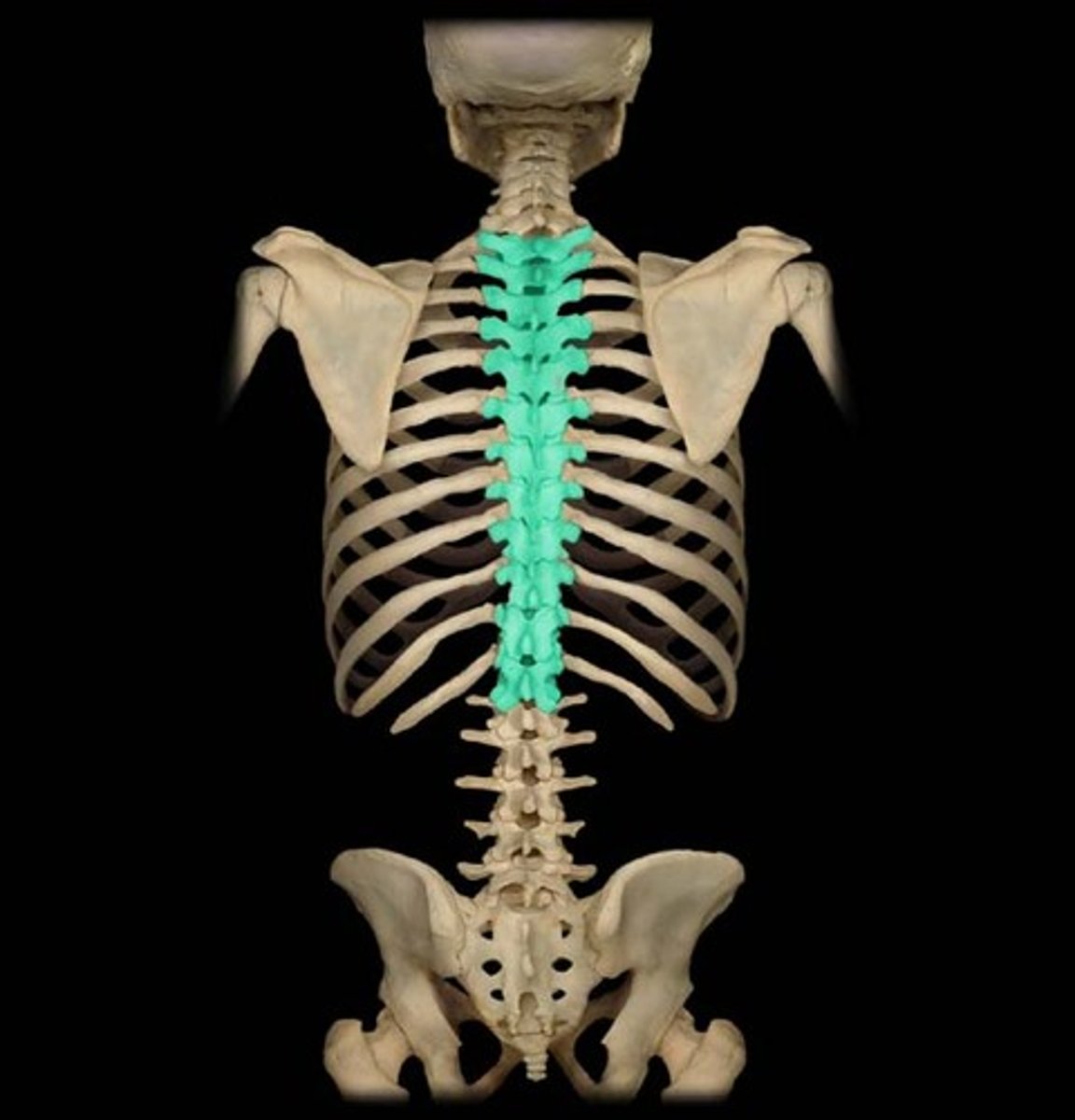
The vertebrae
These are irregular bones that protect the spinal cord
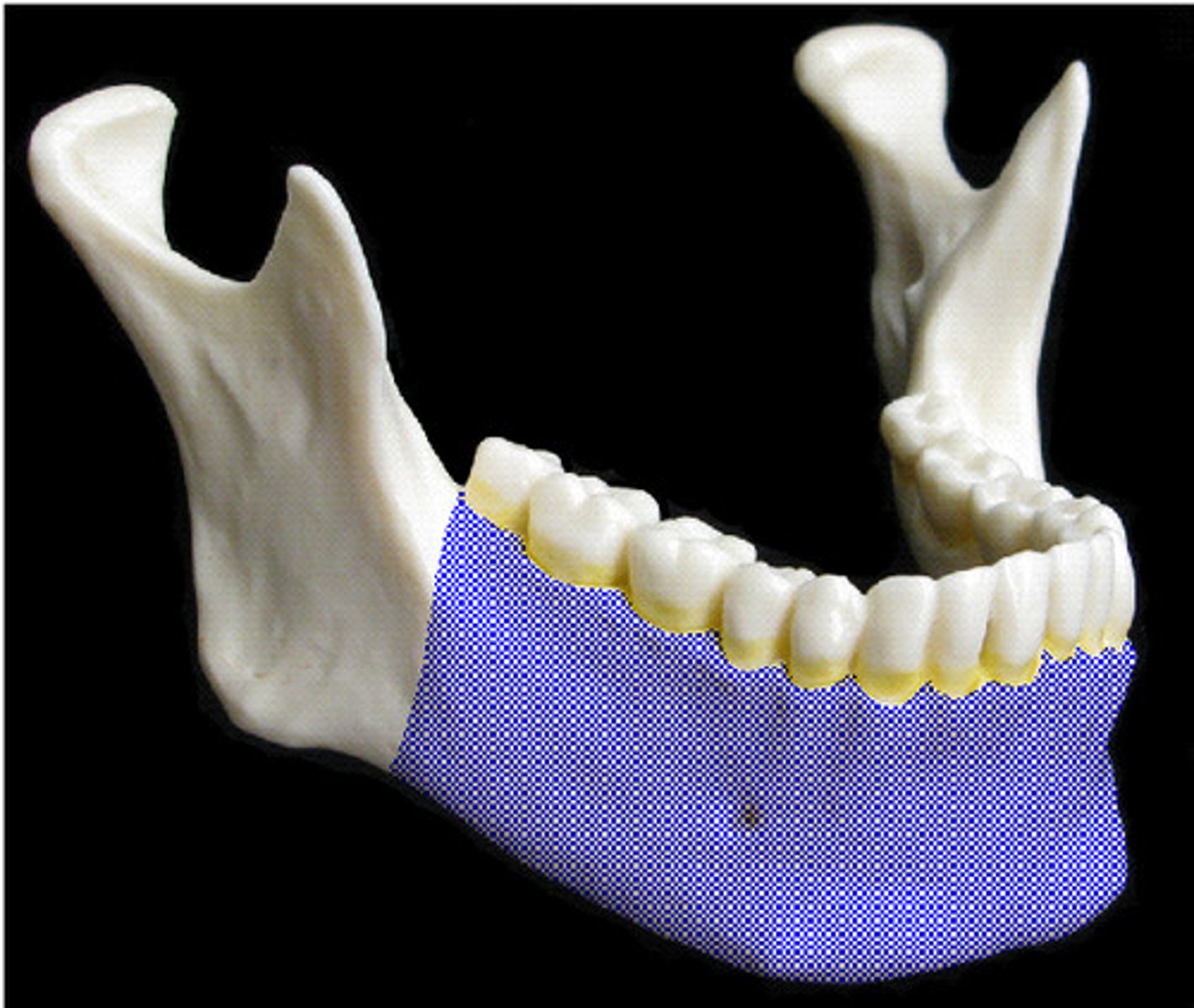
Mandible
This flat bone is the lower jaw
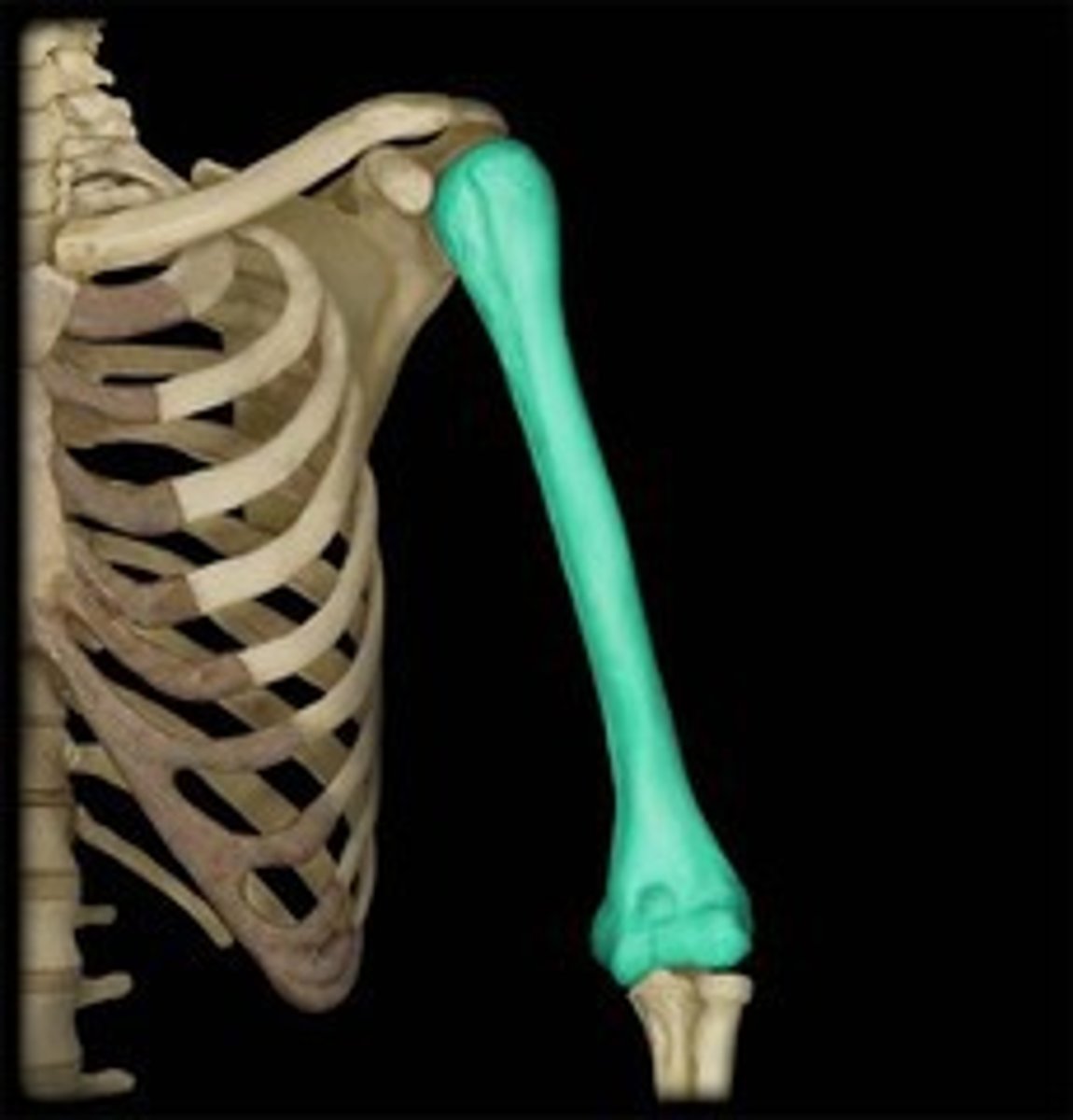
Humerus
This long bone is the upper arm bone
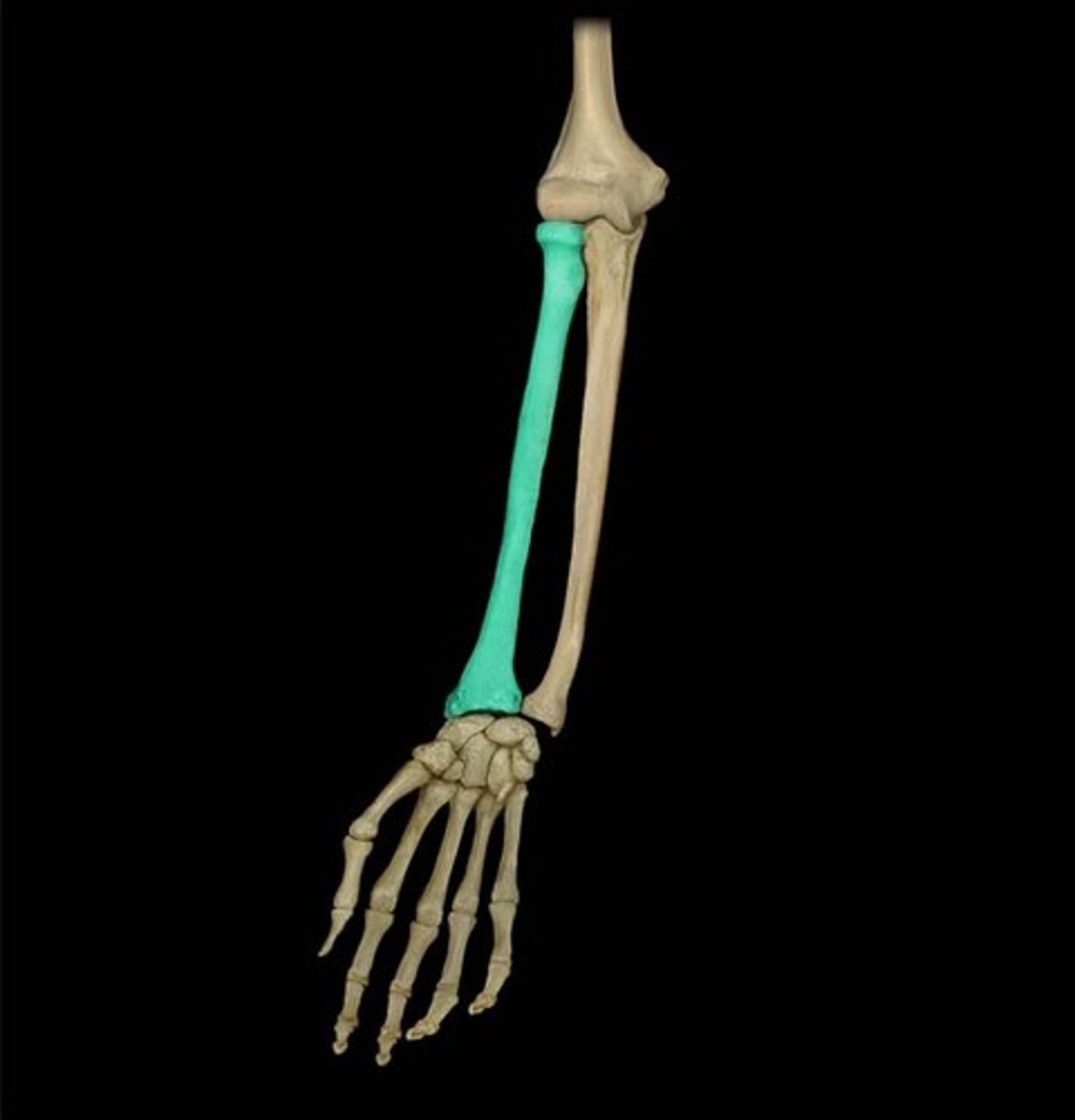
The radius
This long bone is in your lower arm and is on the thumb side
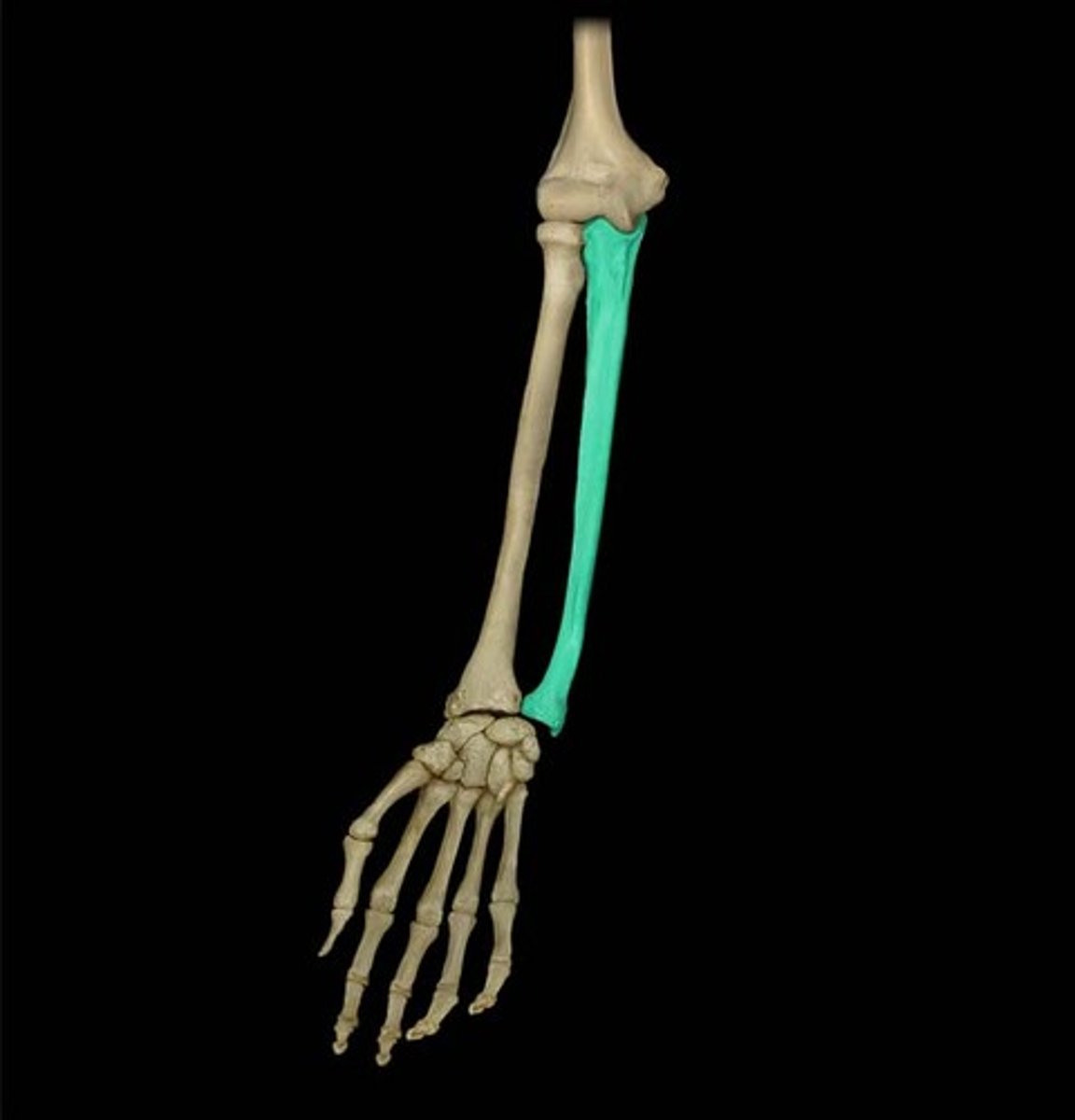
The Ulna
This long bone is in you lower arm on your pinkie side
The femur
This long bone is your thigh bone
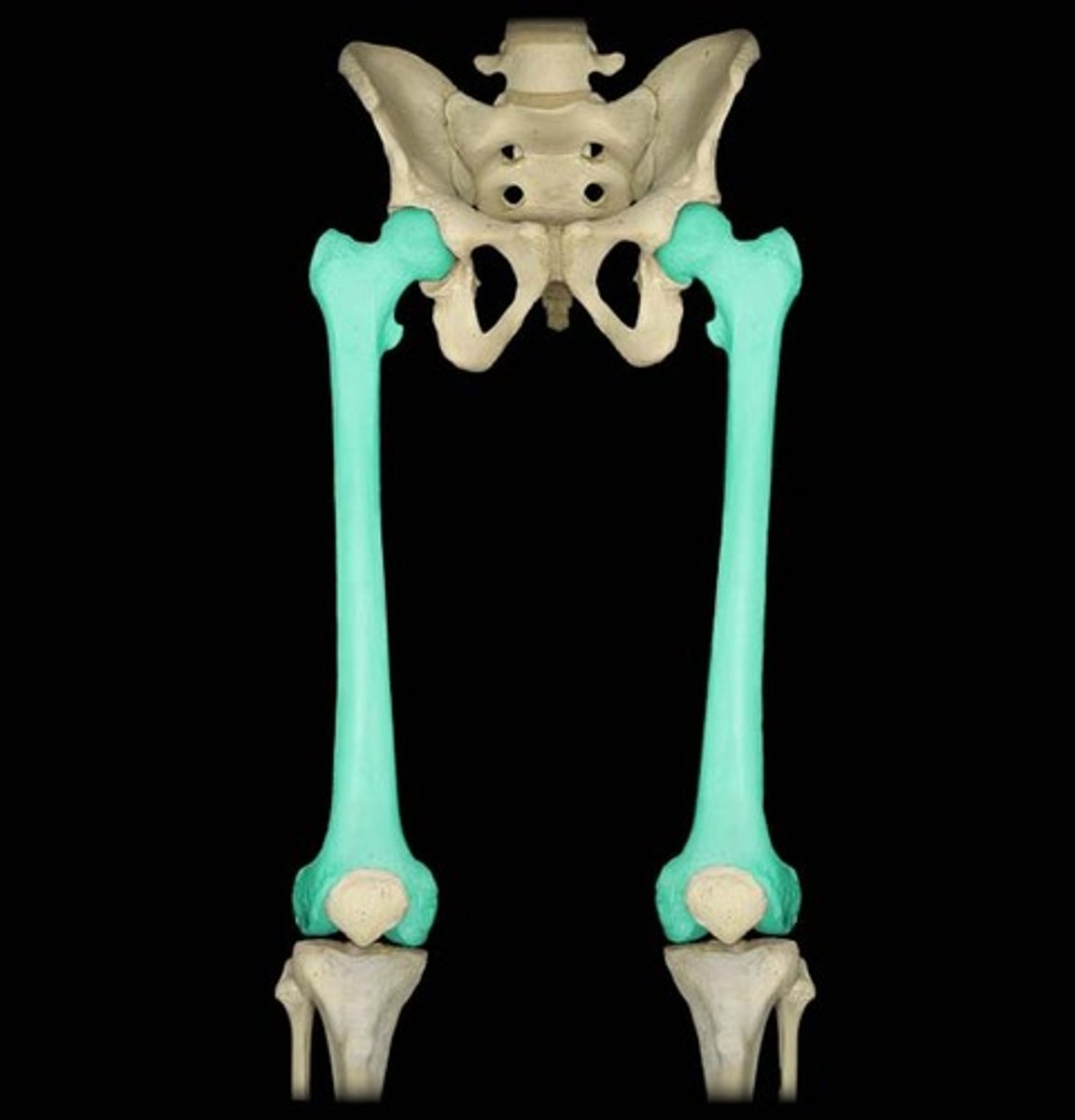
The tibia
This long bone is your shin bone
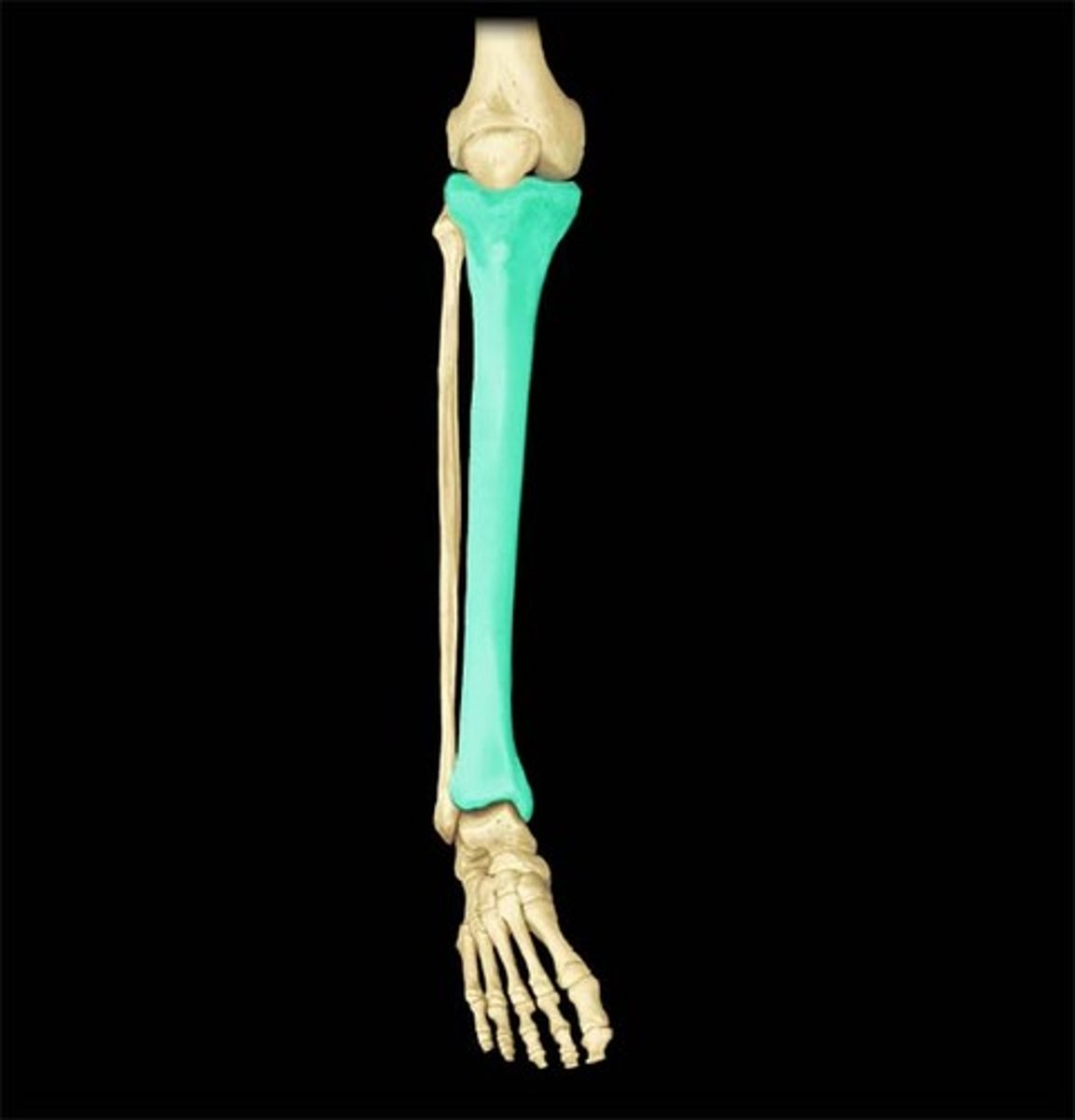
The fibula
This long bone is the calf bone
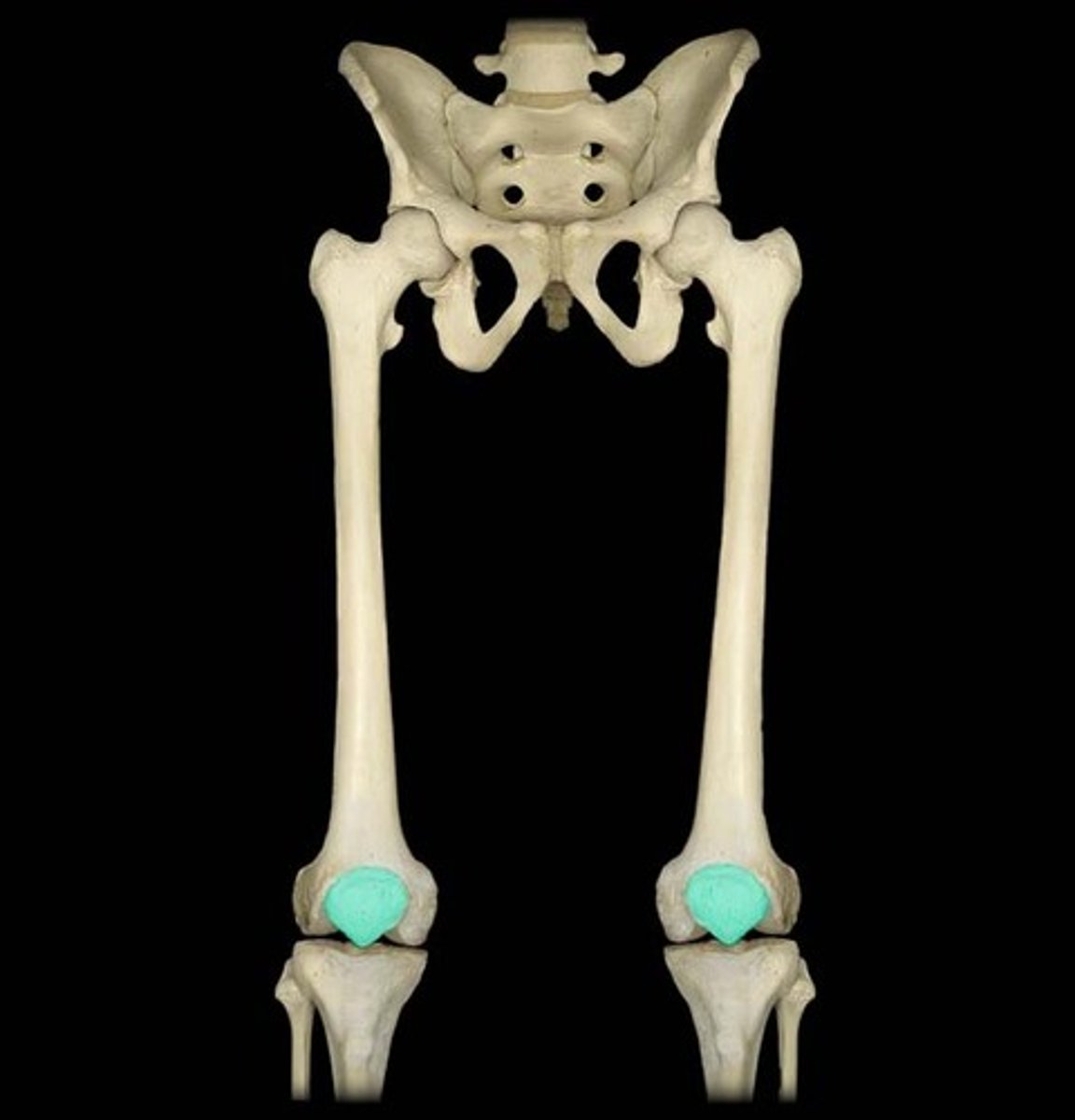
The patella
This irregular bone is your knee cap
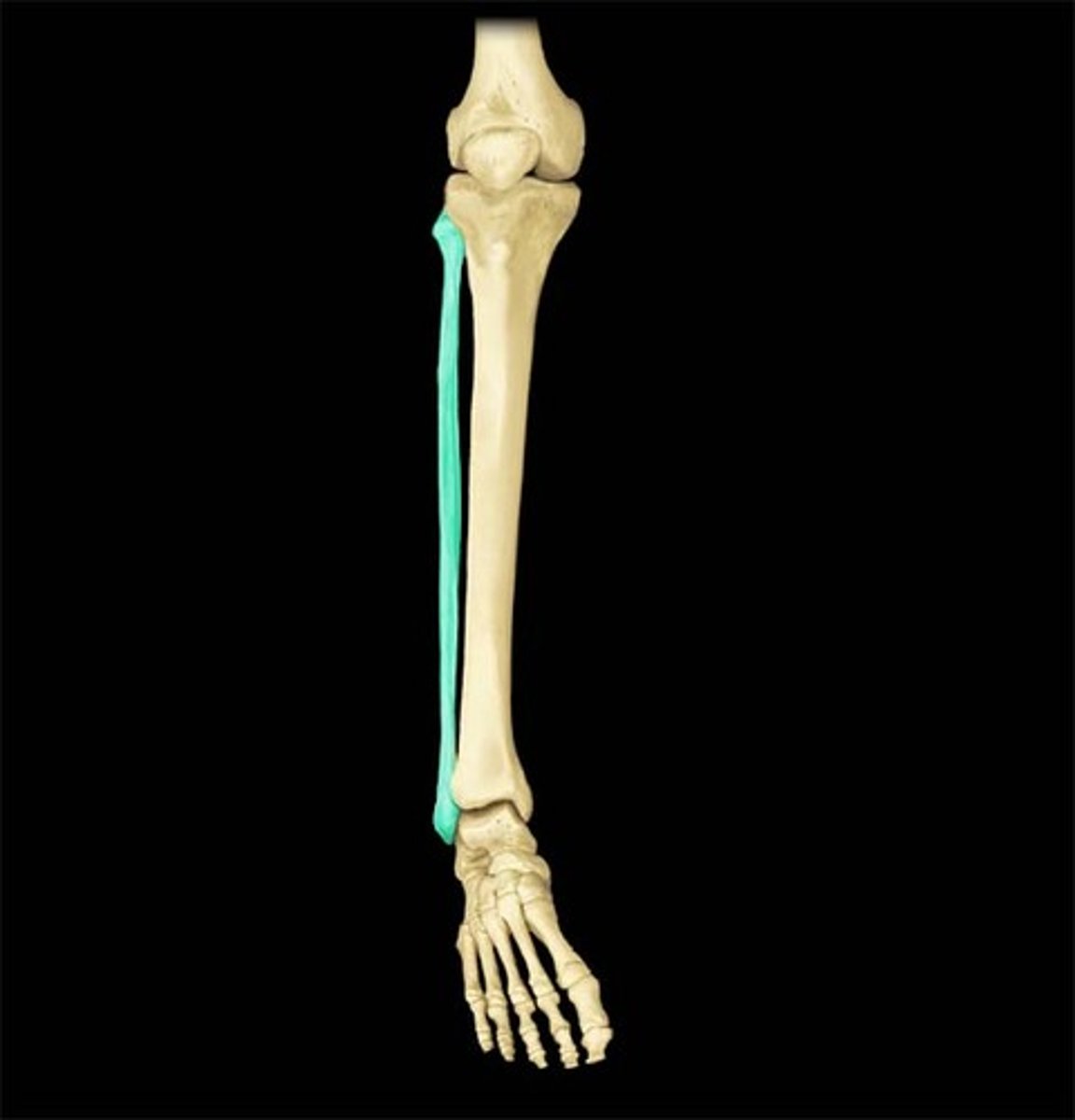
The talus
This is the ankle bone
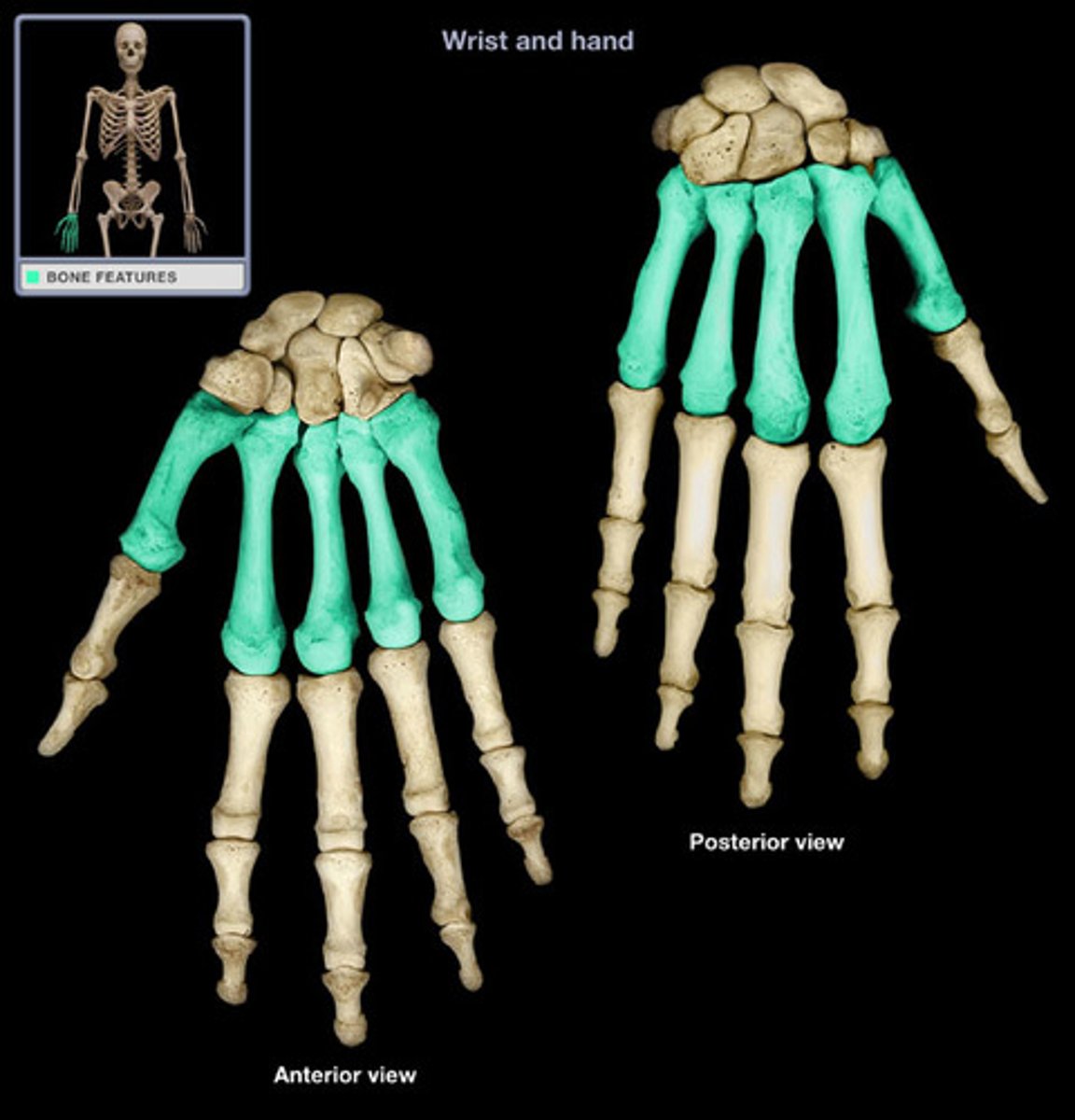
The metacarpals
These long bones form the top of the hand
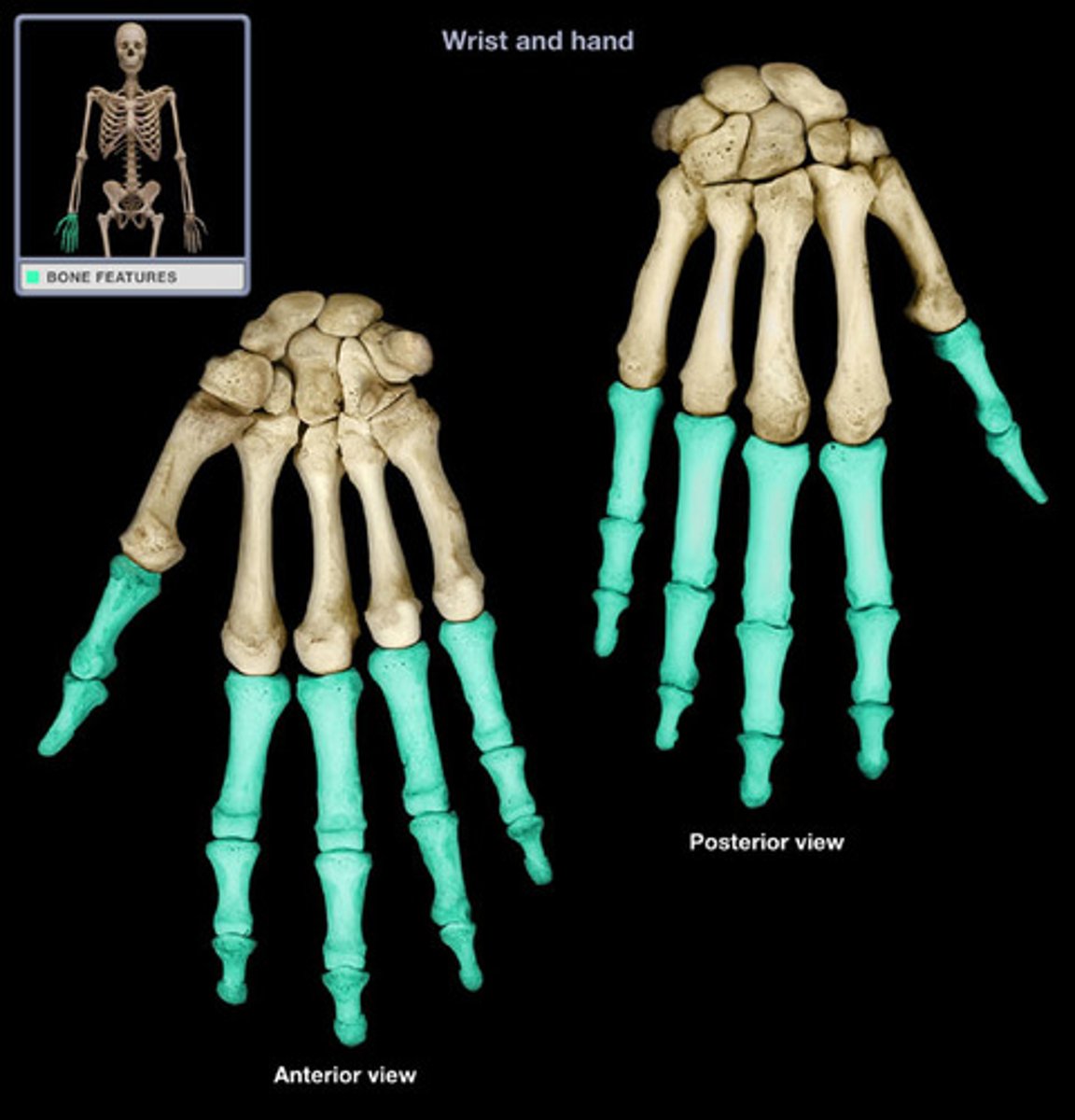
The phalanges
These long bones are your fingers and your toes
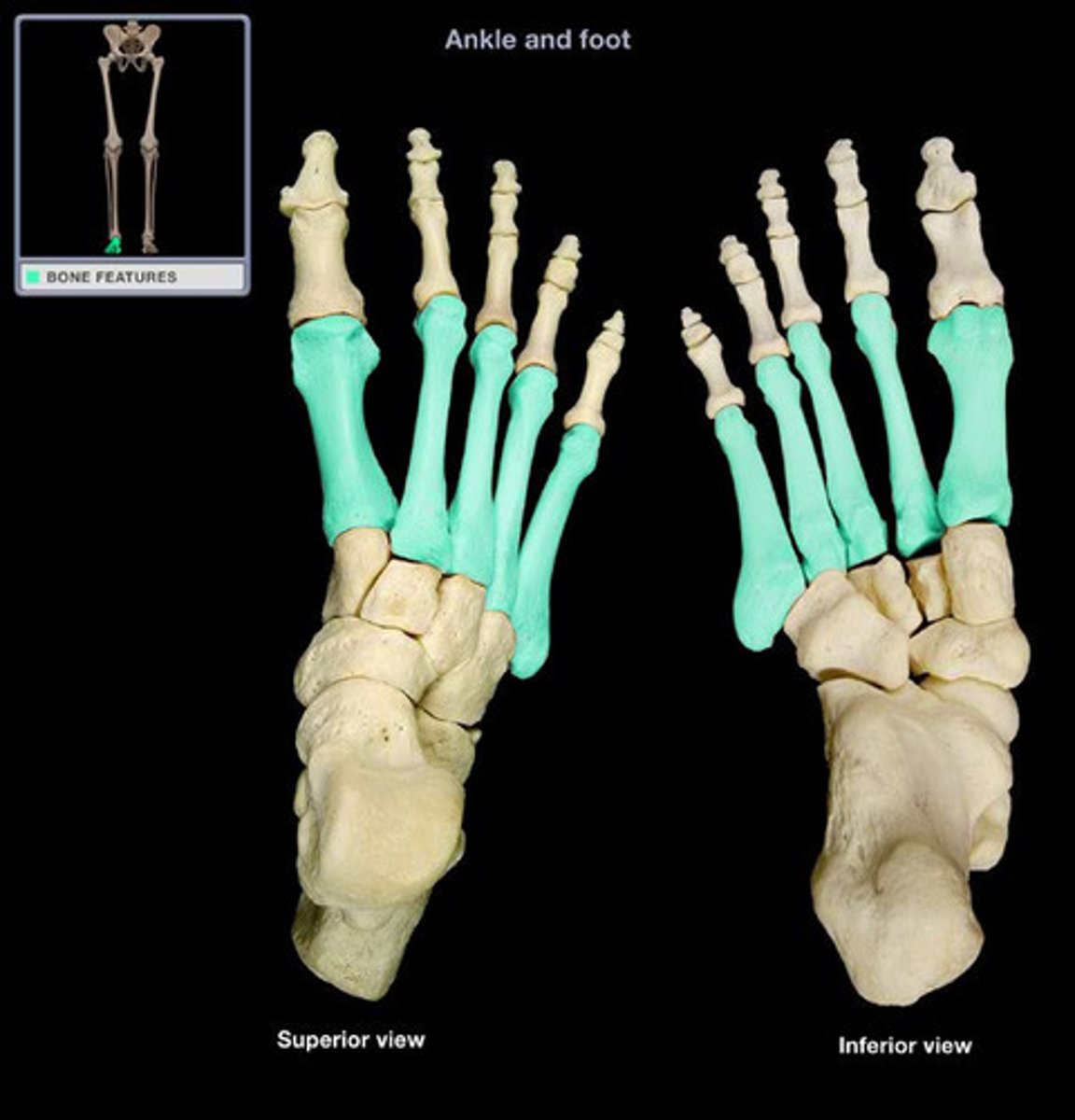
The metatarsals
These are the bones on the top of your foot
Tendons
These connect muscle to bone. They are very strong non-elastic cords.
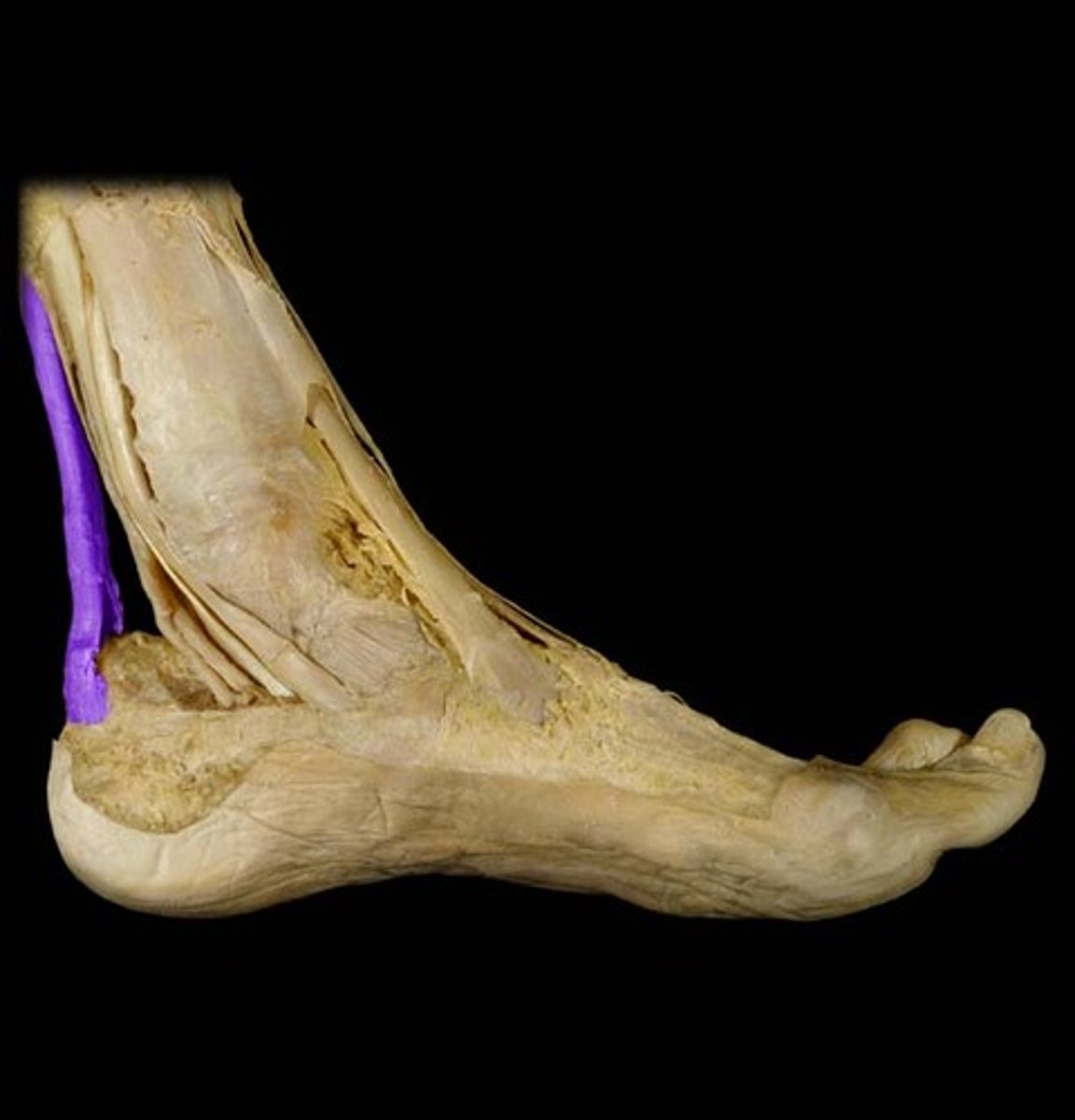
Ligaments
These connect bone to bone. They are bands of elastic fibre and keep the joint stable by restricting the amount of movement.
support, protection, movement, structure, mineral storage and blood cell production
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
It supports muscles and vital organs. Without the skeleton you wouldn't be able to move
How does the skeletal system support the body?
It protects vital organs. Protection is essential for physical activity and long term health and reduces the chance of injury
How does the skeletal system protect the body?
Movement occurs at the joints when muscles contract, pulling the bones in the desired direction
How does the skeletal system help the body move?
It provides something for the muscles to attach onto, which forms the body's basic structure
How does the skeletal system help structure the body?
Mineral storage is vital for all bodily functions, minerals are stored in the bone marrow.
How does the skeletal system help with mineral storage?
Blood cell production happens in the bone marrow. Red blood cells carry oxygen for aerobic respiration and white blood cells fight infection
How does the skeletal system help with blood cell production?
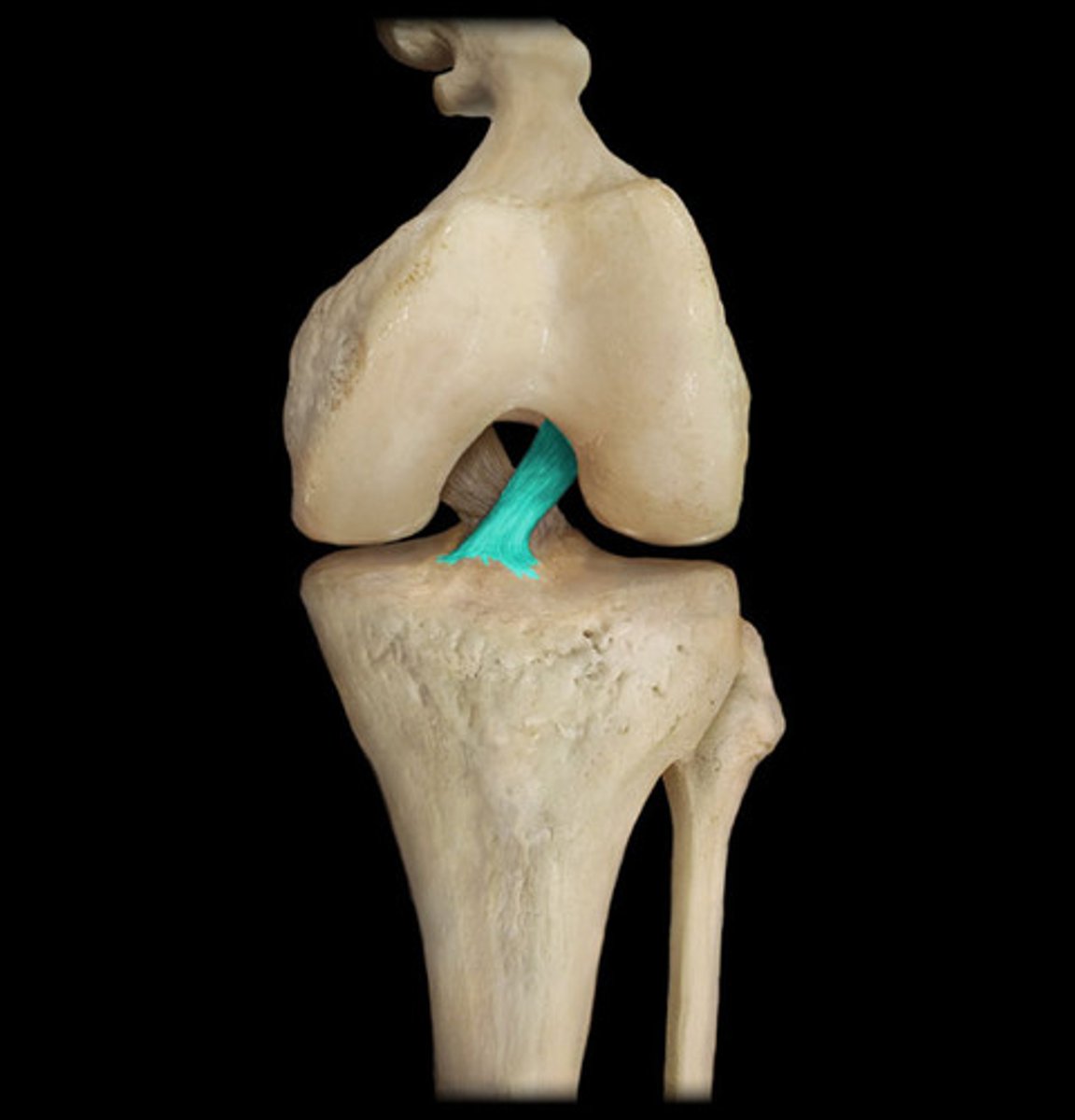
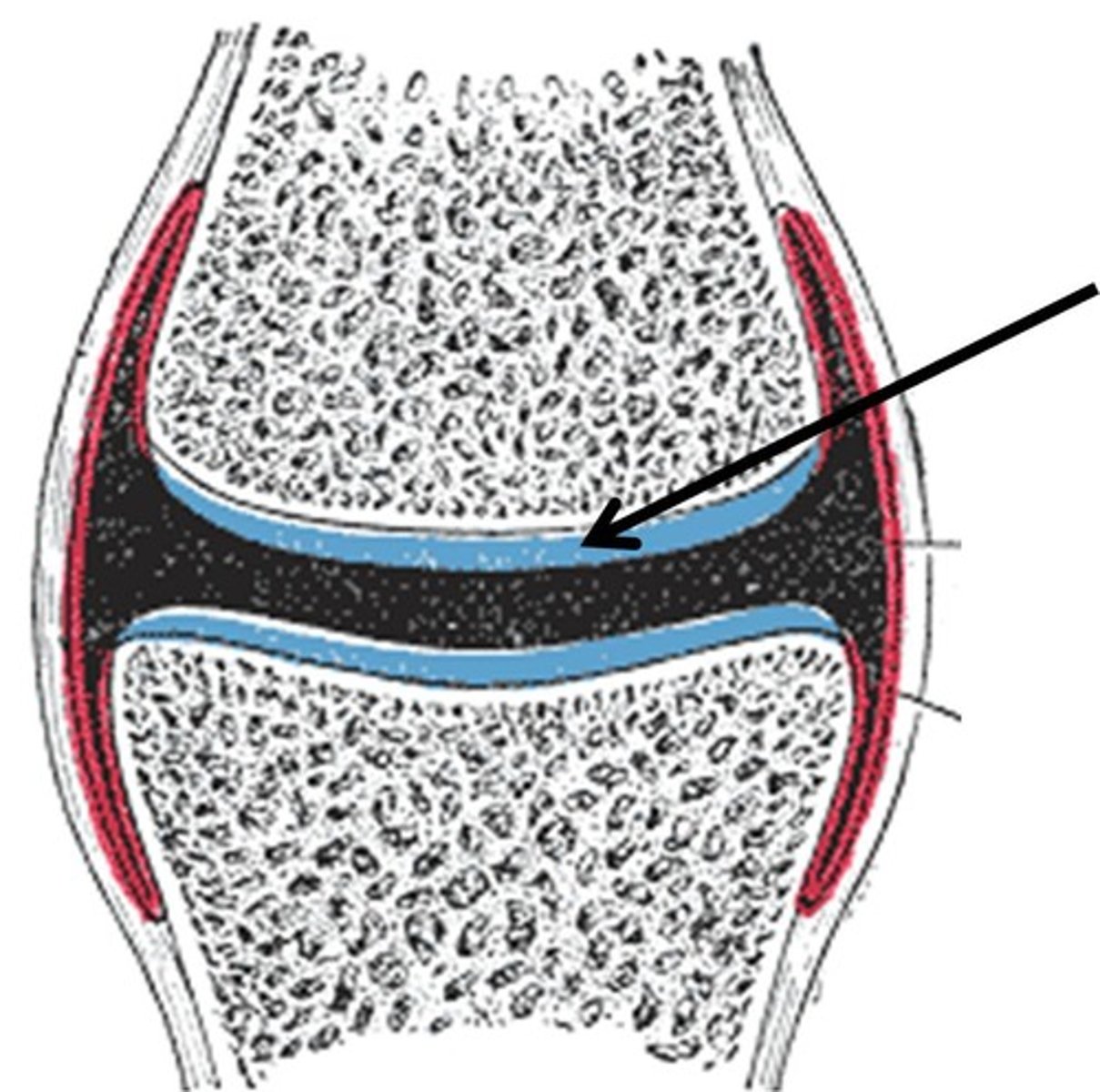
Synovial joints
These are freely moveable joints characterised by fluid filled spaces between cartilage and the joint capsule
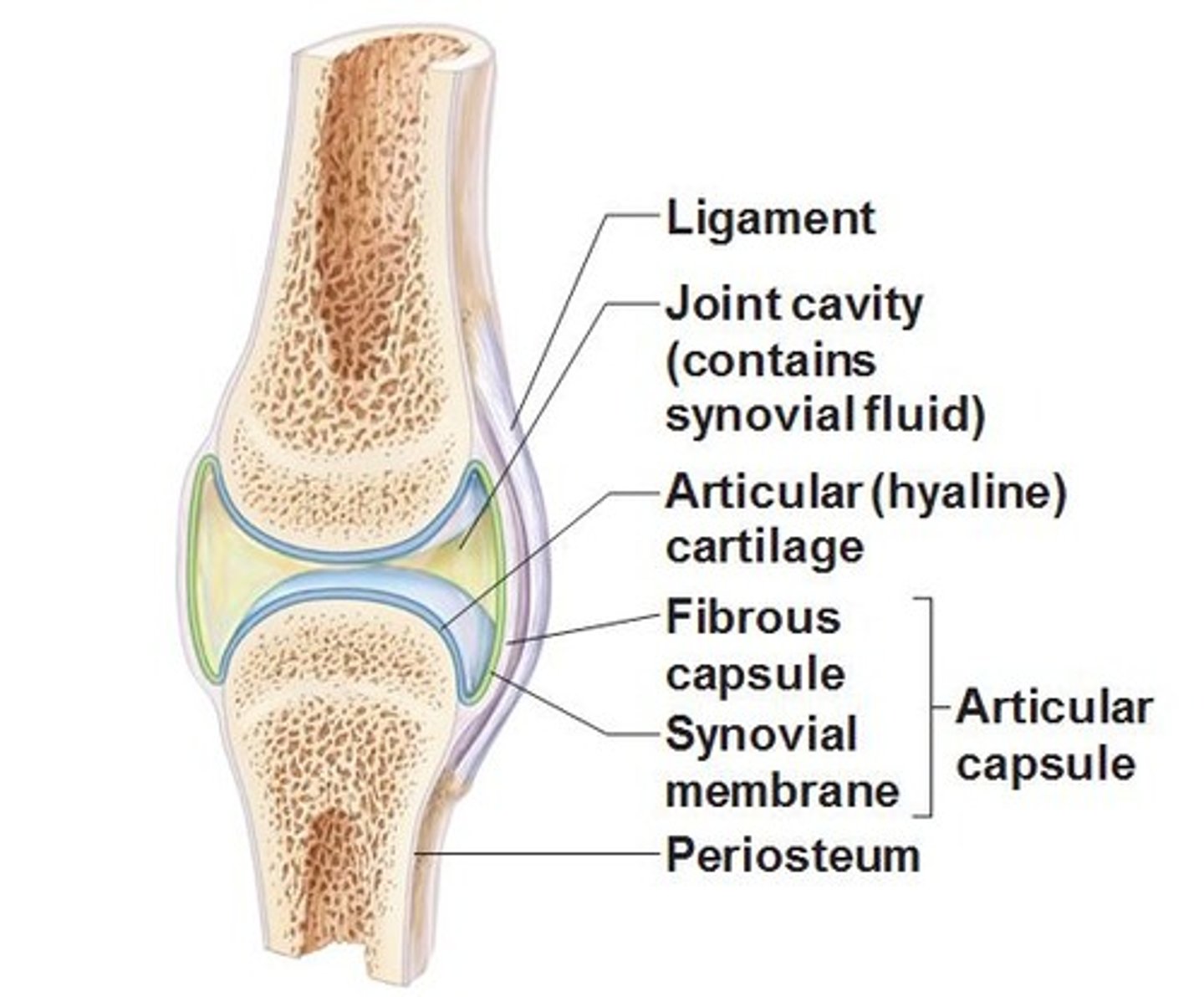
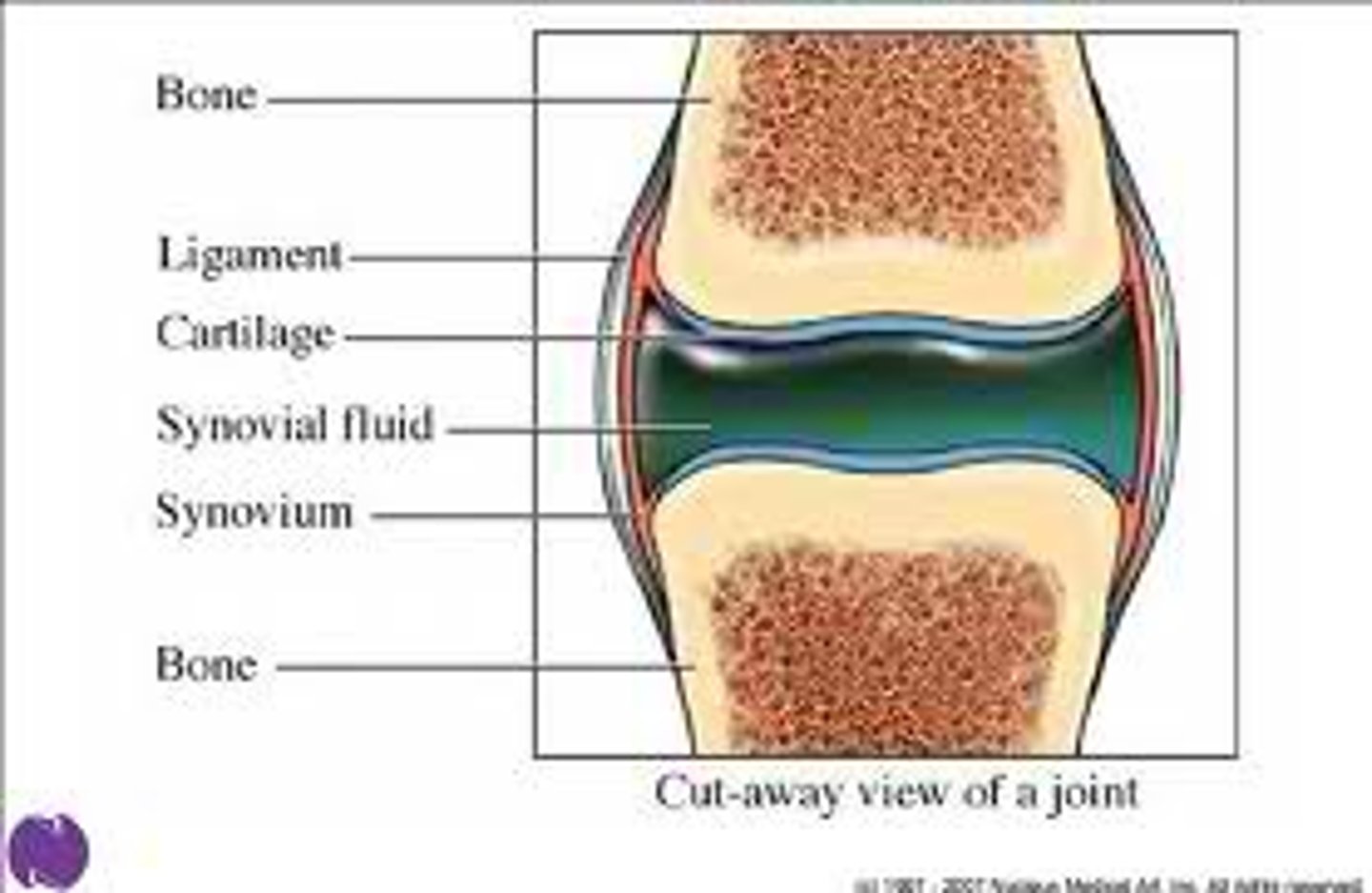
Synovial fluid
This is a viscous fluid that reduces friction that could occur against the cartilage. It is a clear slippery liquid that lubricates the joint.
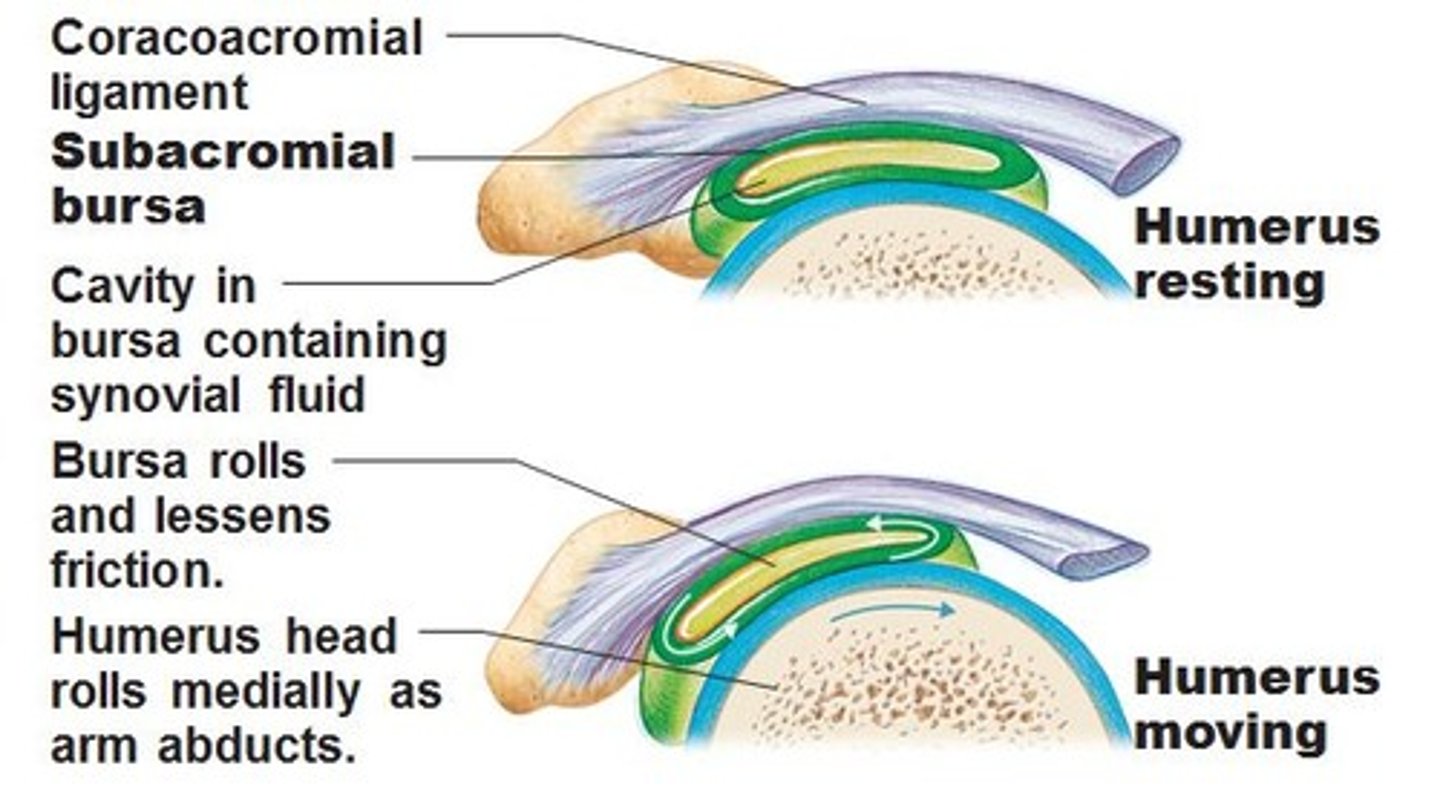
The Bursae
This is a sac filled with fluid that reduces friction between tendons and bones
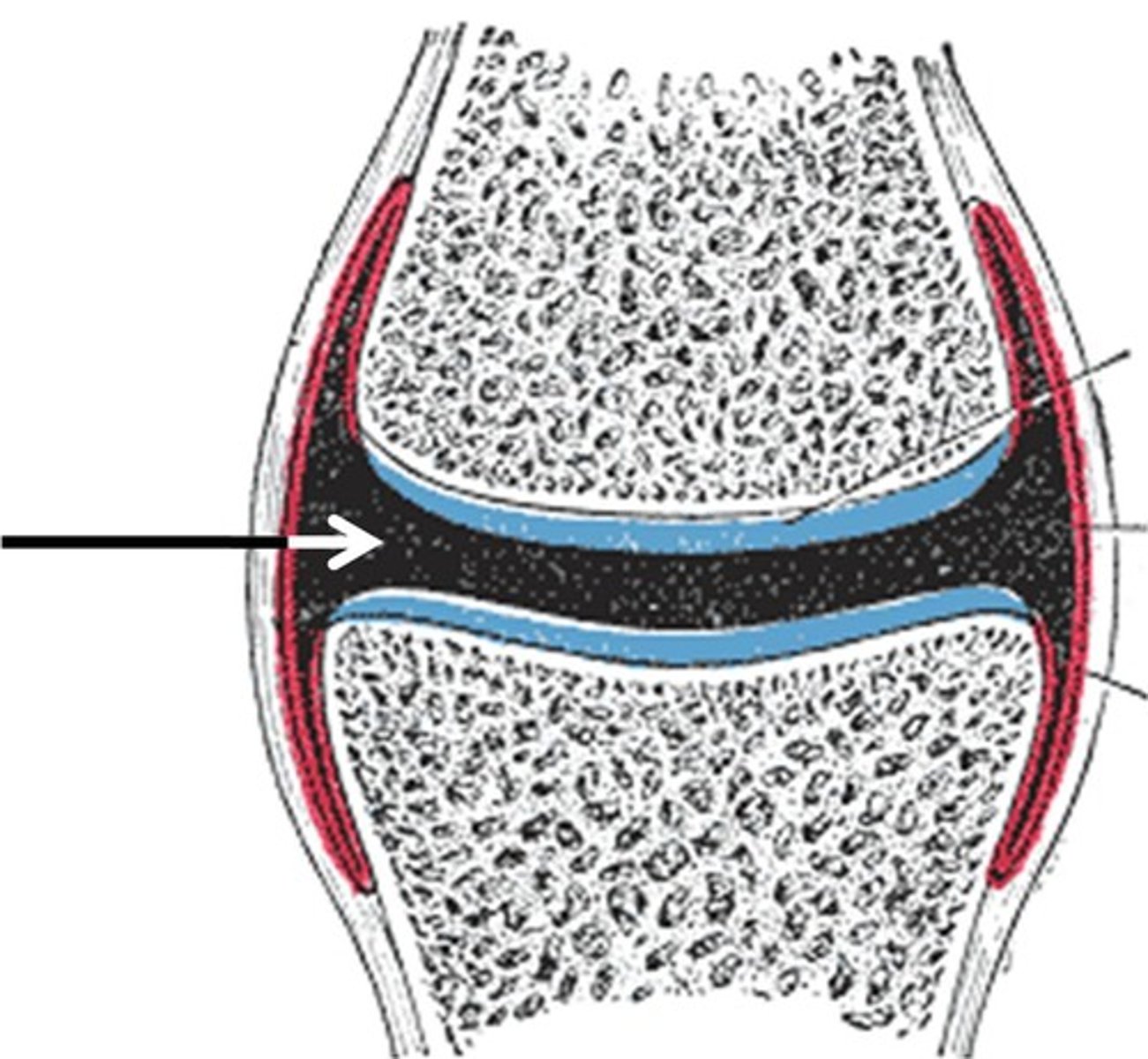
The joint cavity
This is filled with synovial fluid which prevents bones rubbing against each other
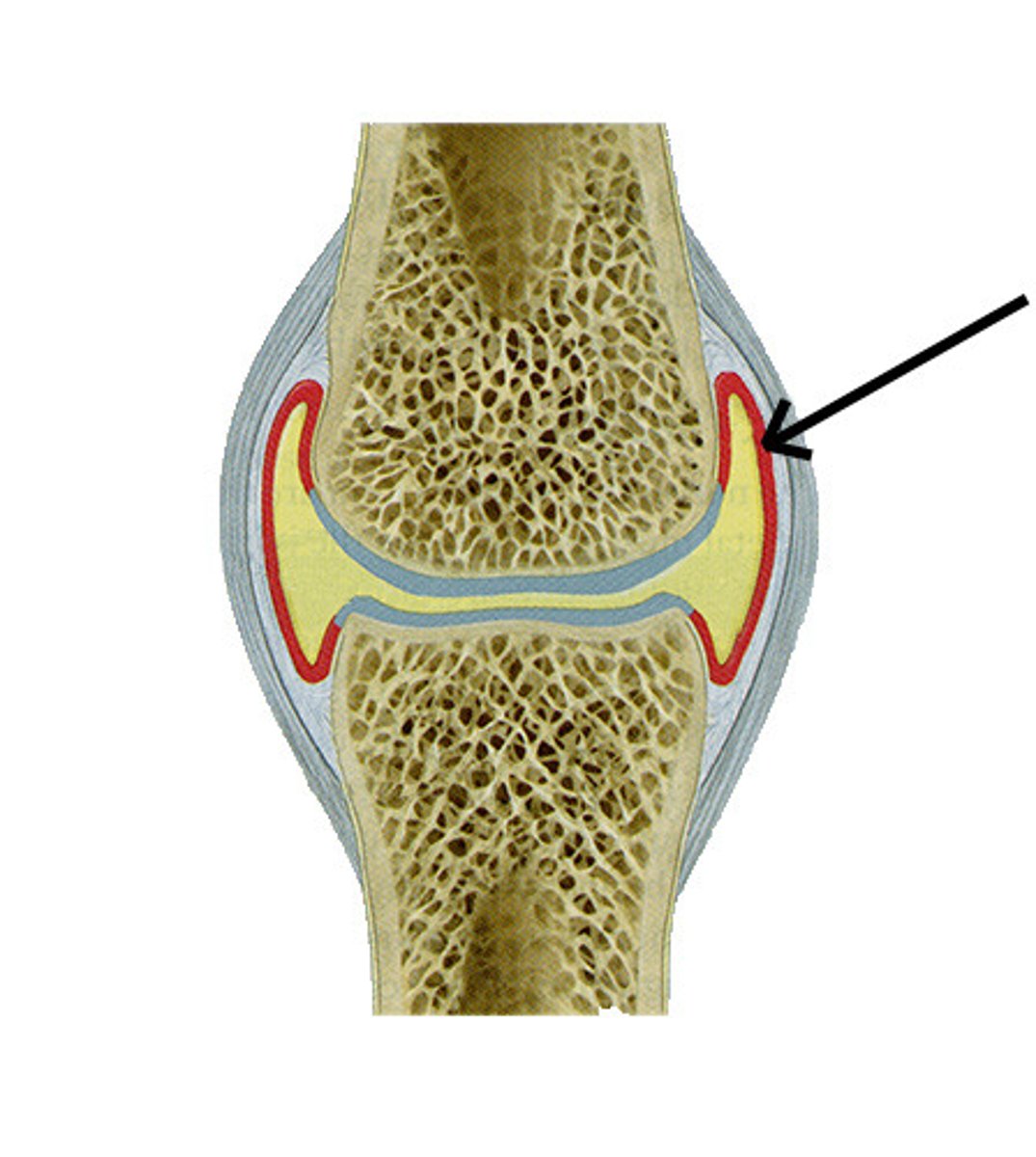
synovial membrane
This is the lining inside the joint capsule that helps to maintain the synovial fluid, releasing it into the joint
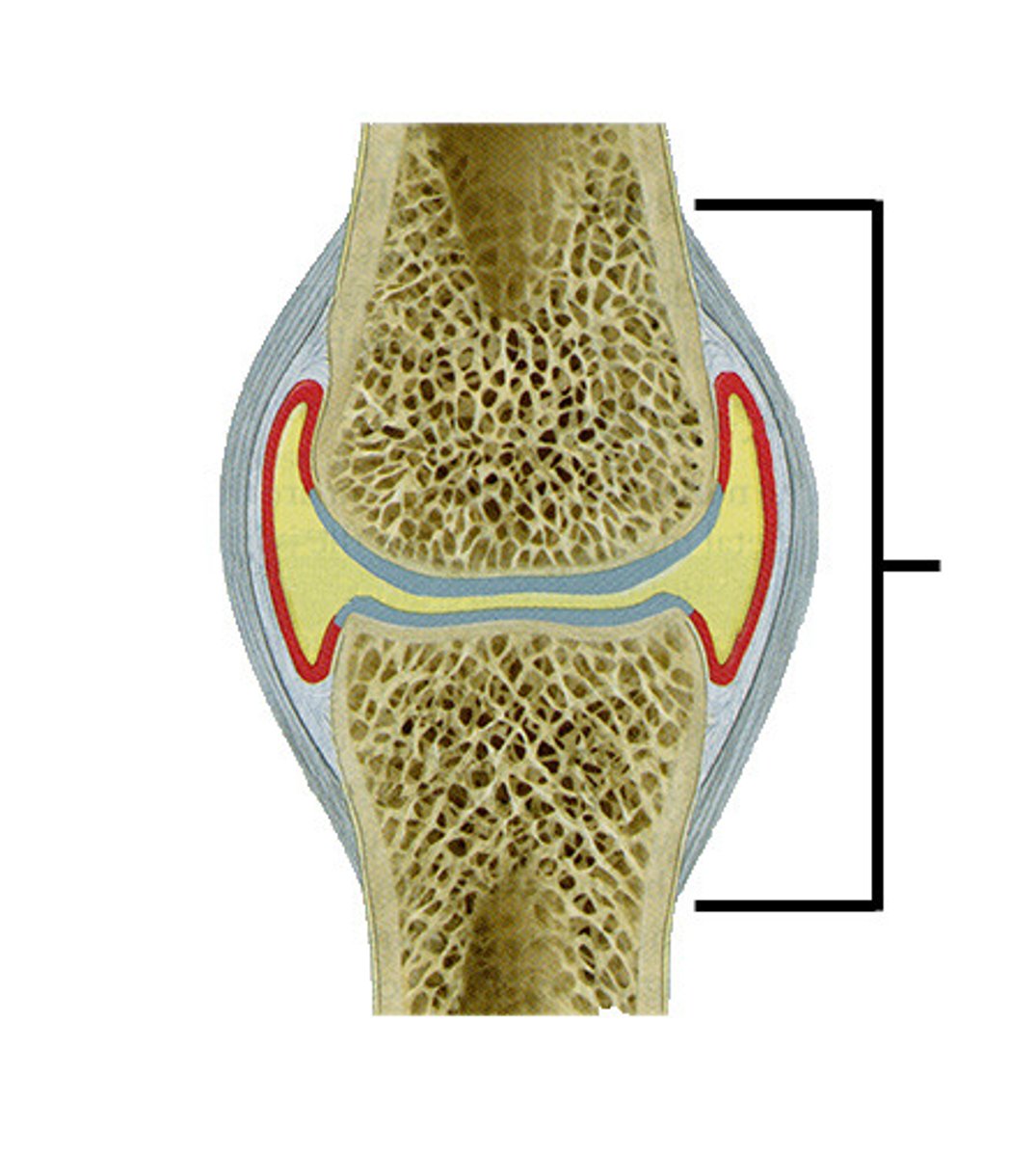
The Joint capsule
This is a piece of tissue around the joint that stops the synovial fluid from escaping. It encloses, supports and holds the joint together
Cartalige
This is a tough, flexible tissue that covers the end of bones, providing a smooth, friction-free surface
Ball and socket joint
This is a joint that allows for rotation, circumduction, adduction, abduction as well as flexion and extension.
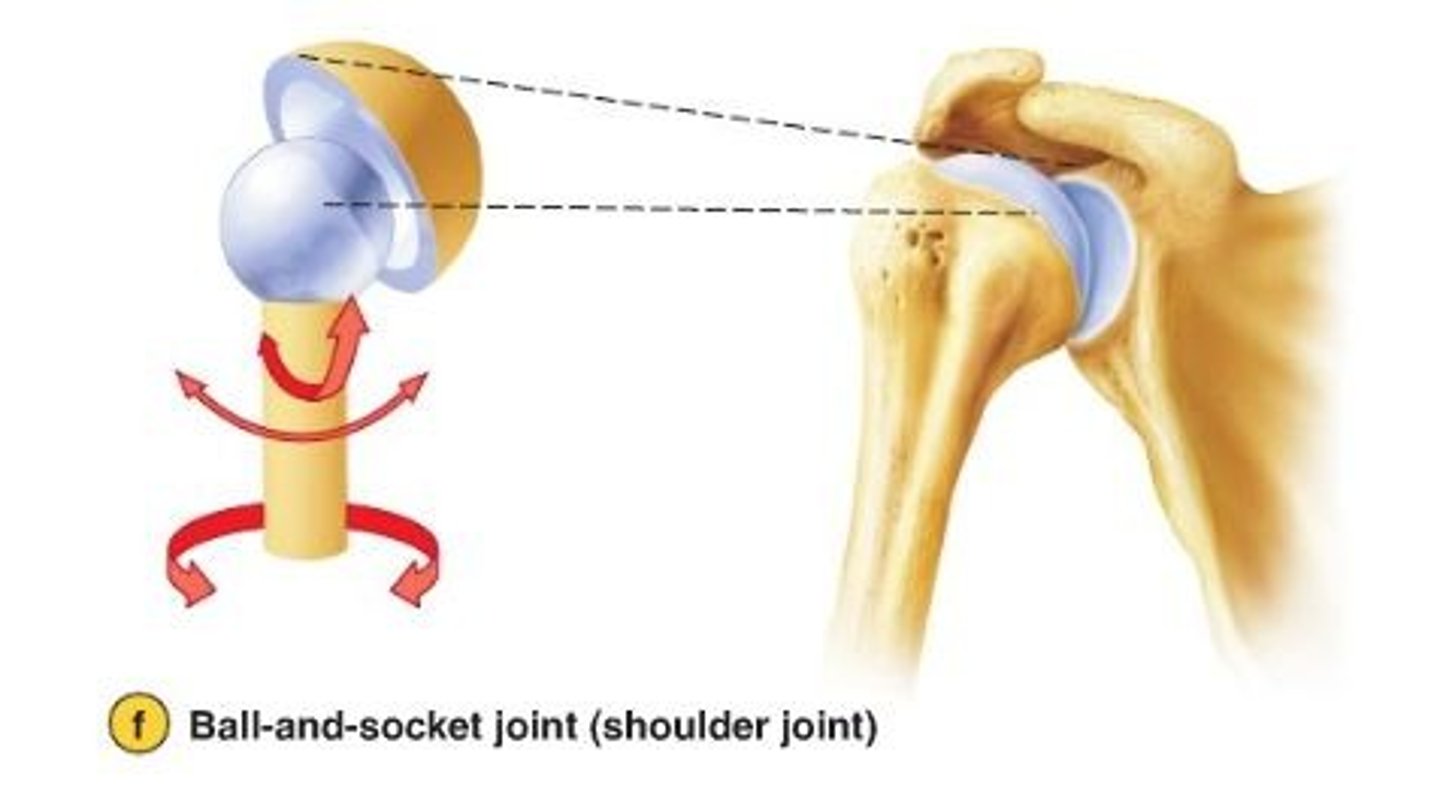
The shoulder and the hip
Name 2 examples of a ball and socket joint
Hinge joints
These are joints that allow for flexion and extension (at your knee and elbow), flexion and extension (at your ankle)
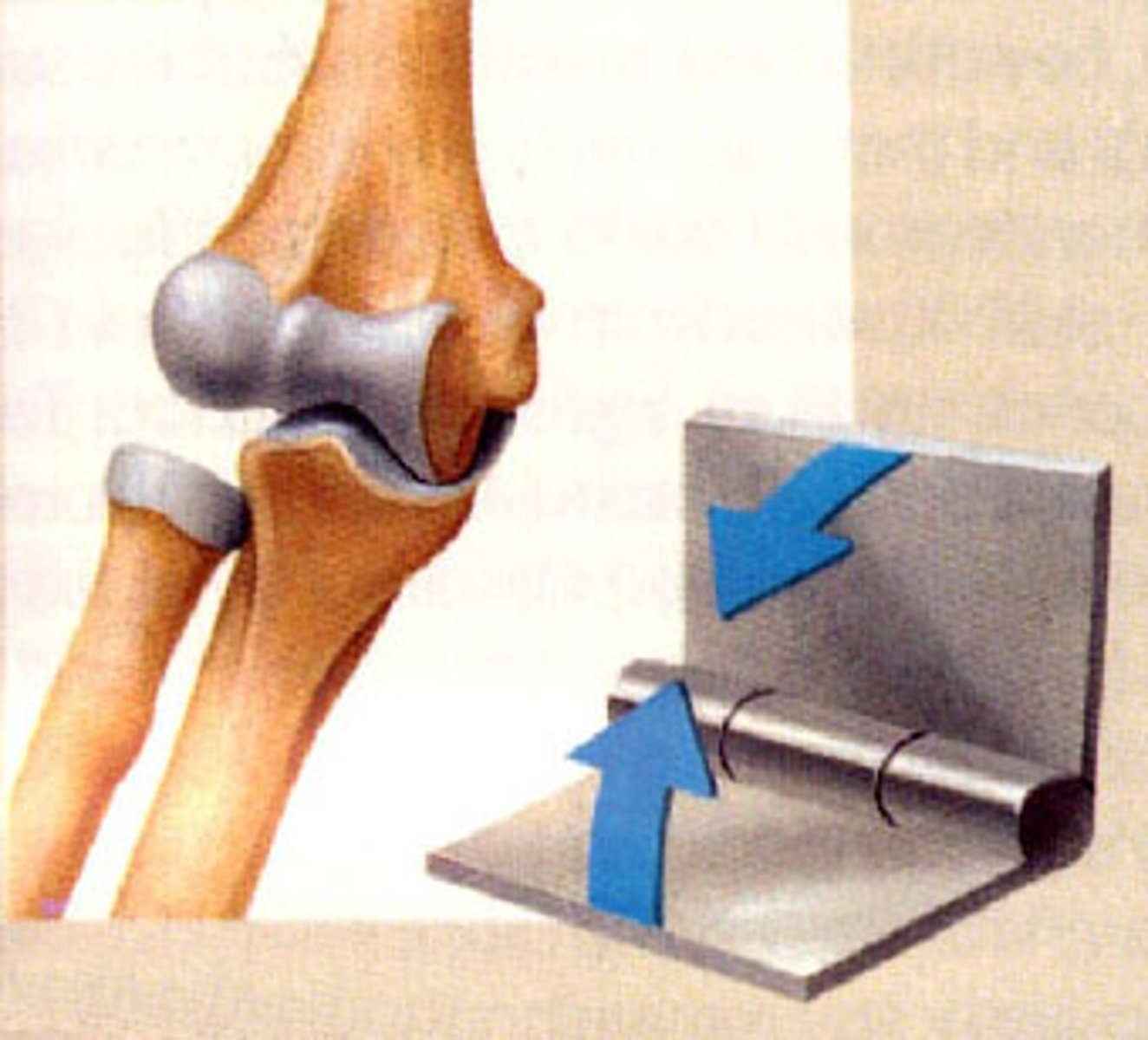
Knee, elbow and ankle
Name 3 examples of a hinge joint
Extension
The increase in the angle of bones at a joint
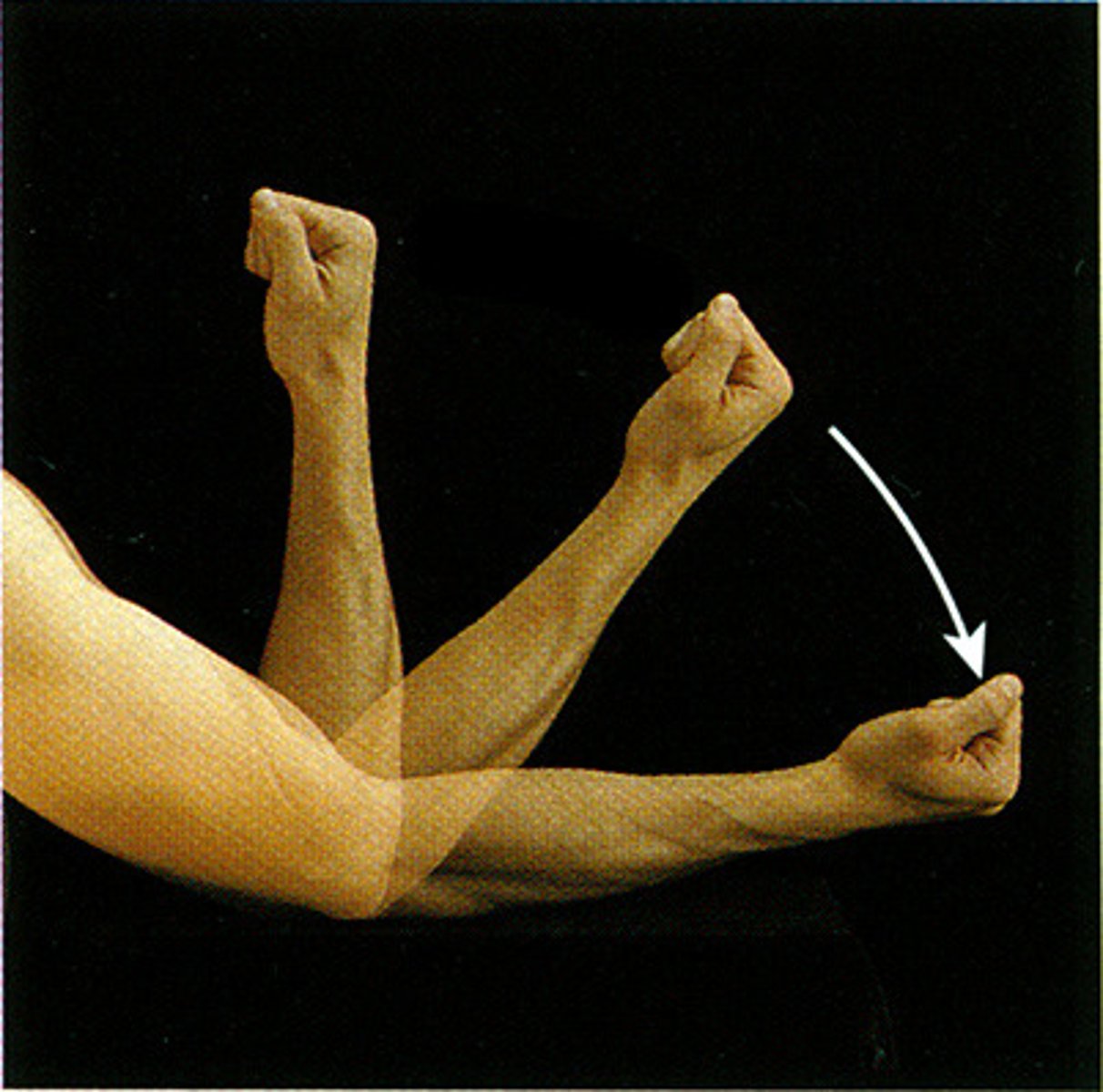
Flexion
The decrease in the angle of bones at a joint
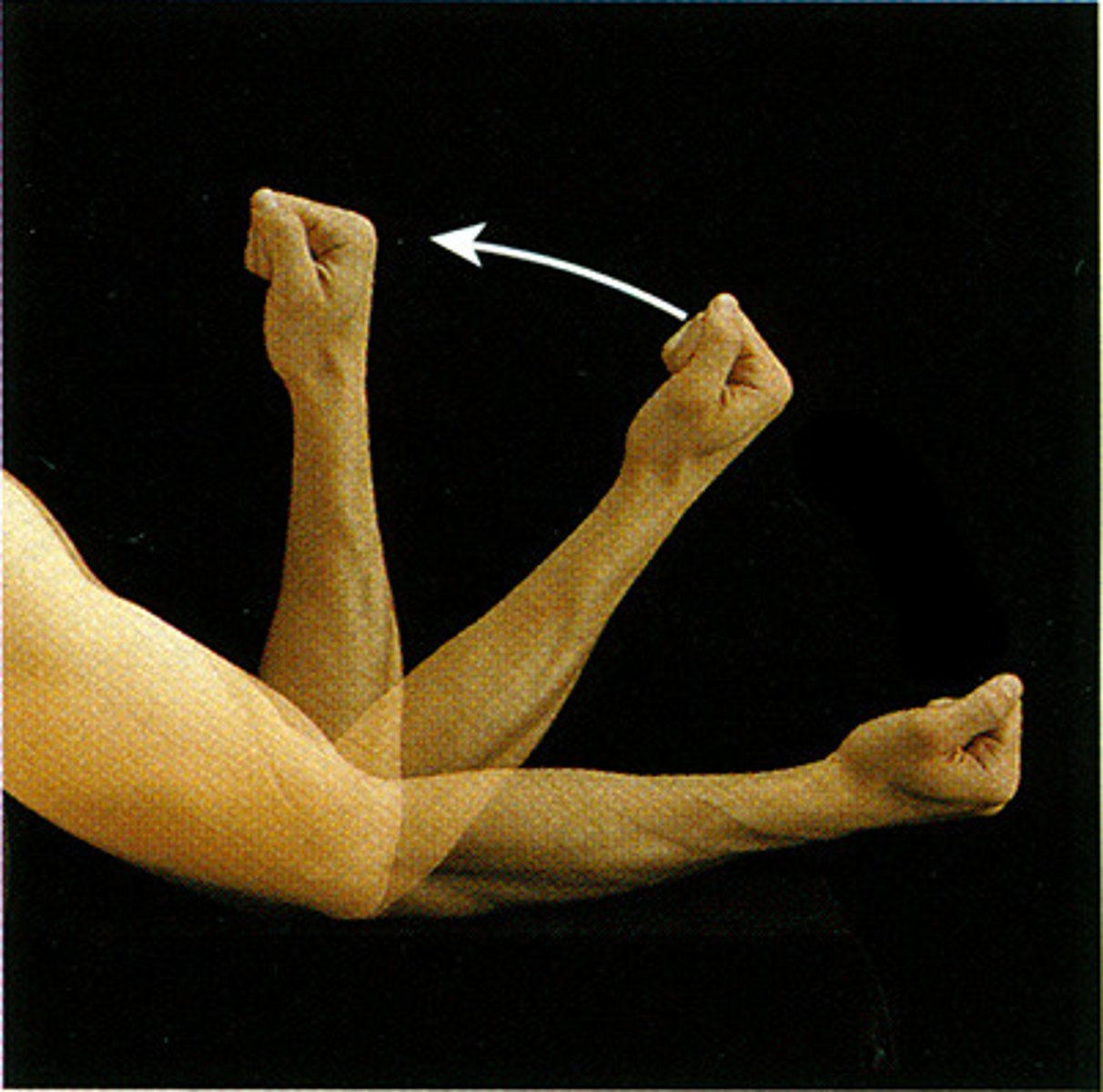
Abduction
The movement of a bone or limb away from the midline of the body
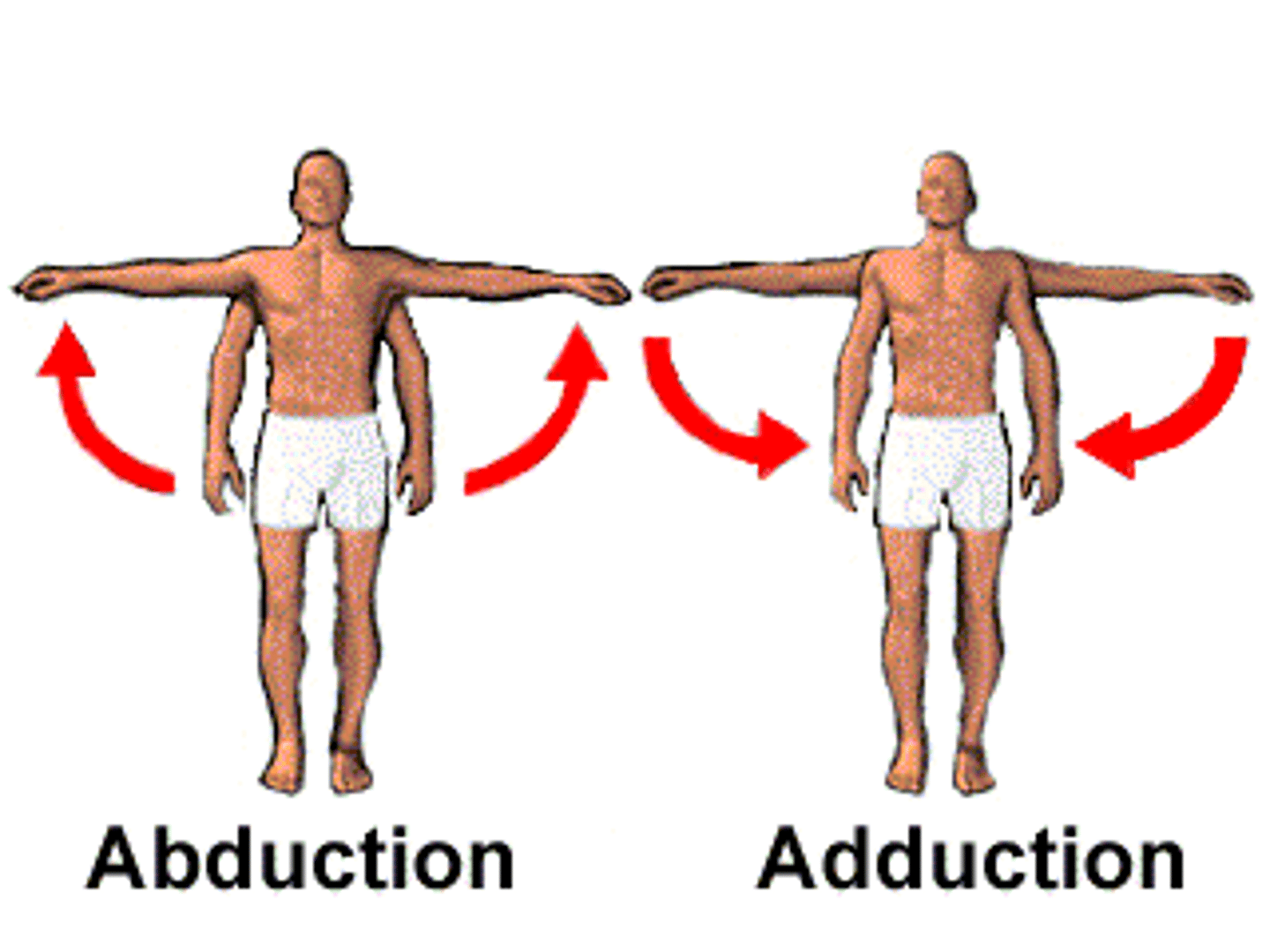
Adduction
The movement of a bone or limb towards the midline of the body
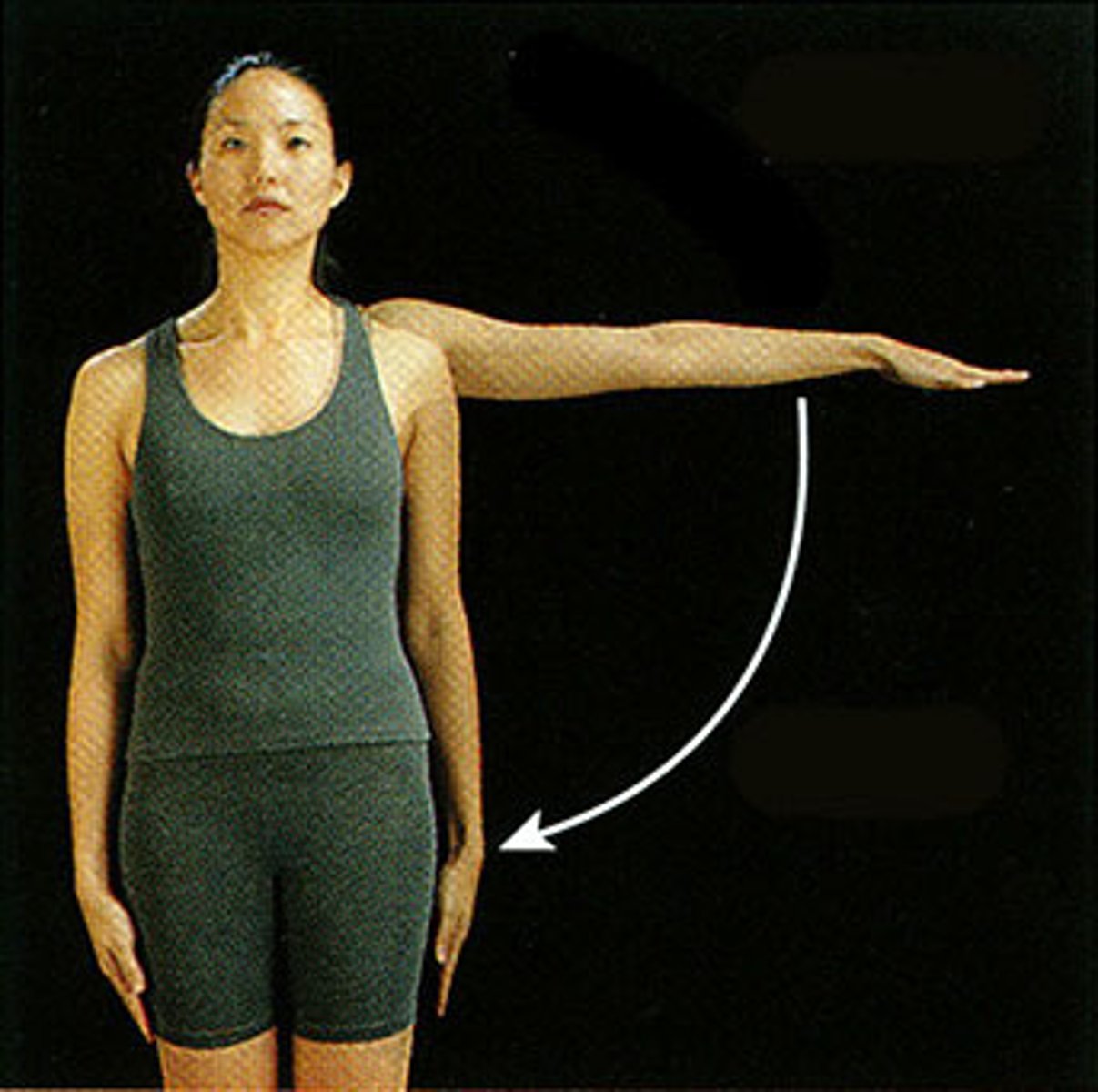

Rotation
A circular movement around a joint
Plantar flexion
A movement at an ankle joint that points the toes and increases the angle at the joint
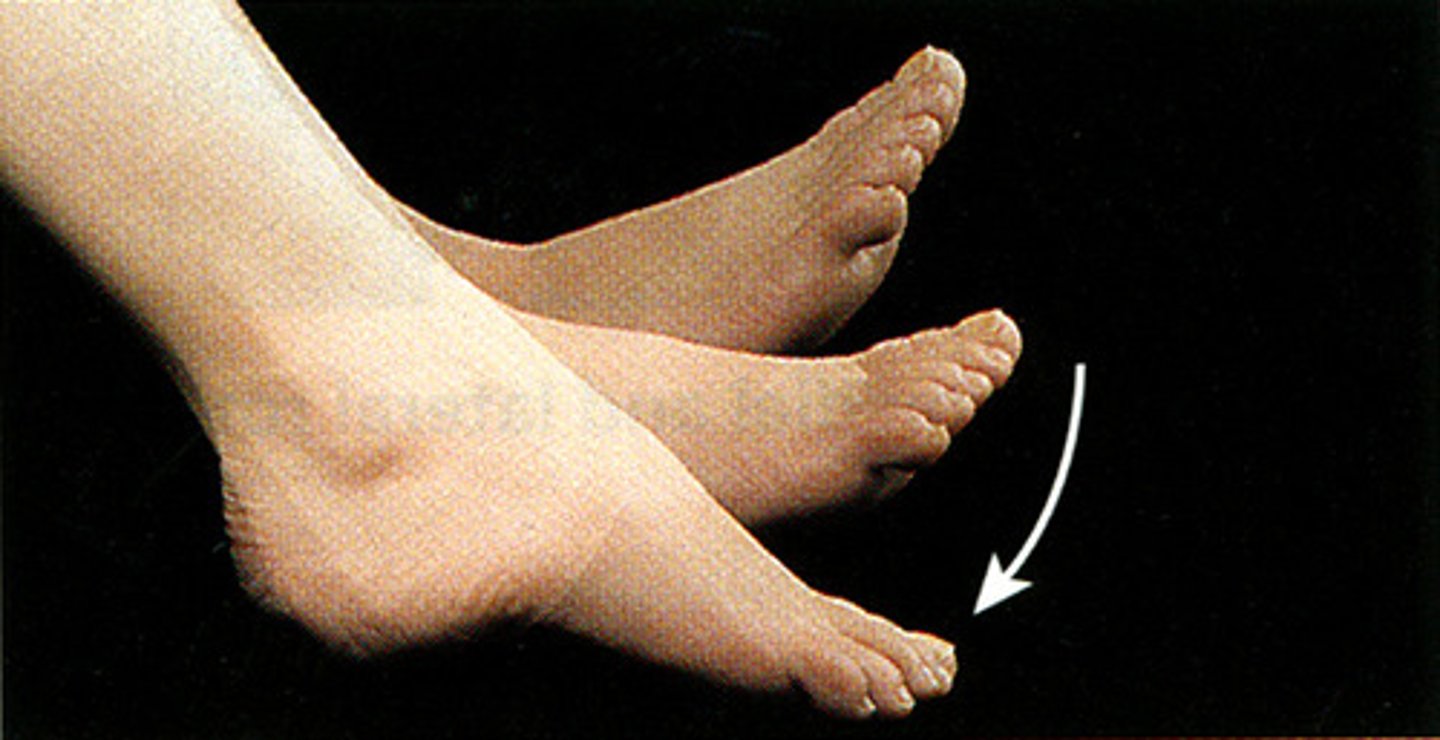
Dorsiflexion
A movement at an ankle joint that flexes the foot upwards and decreases the angle at a joint
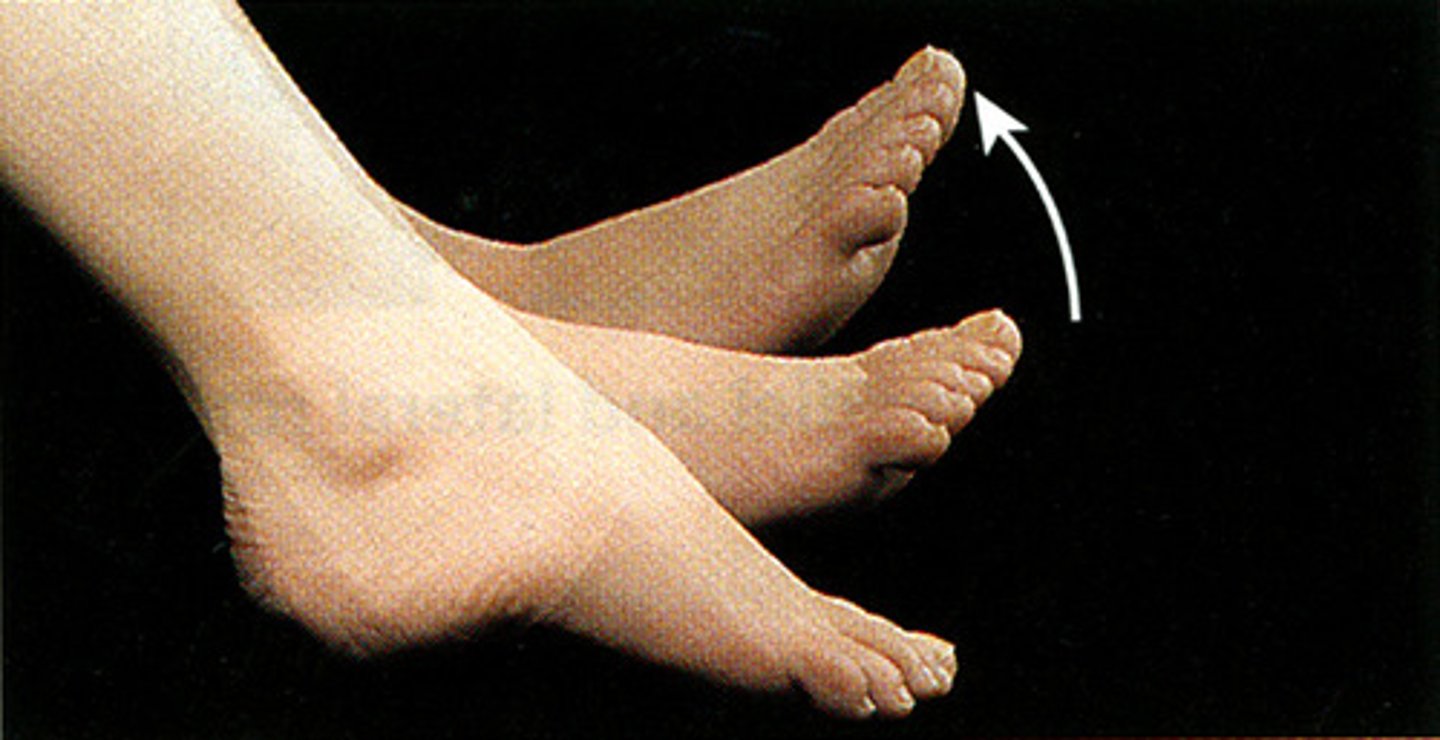
Circumduction
A circular rotation around a joint. It is a combination of flexion, extension, adduction and abduction
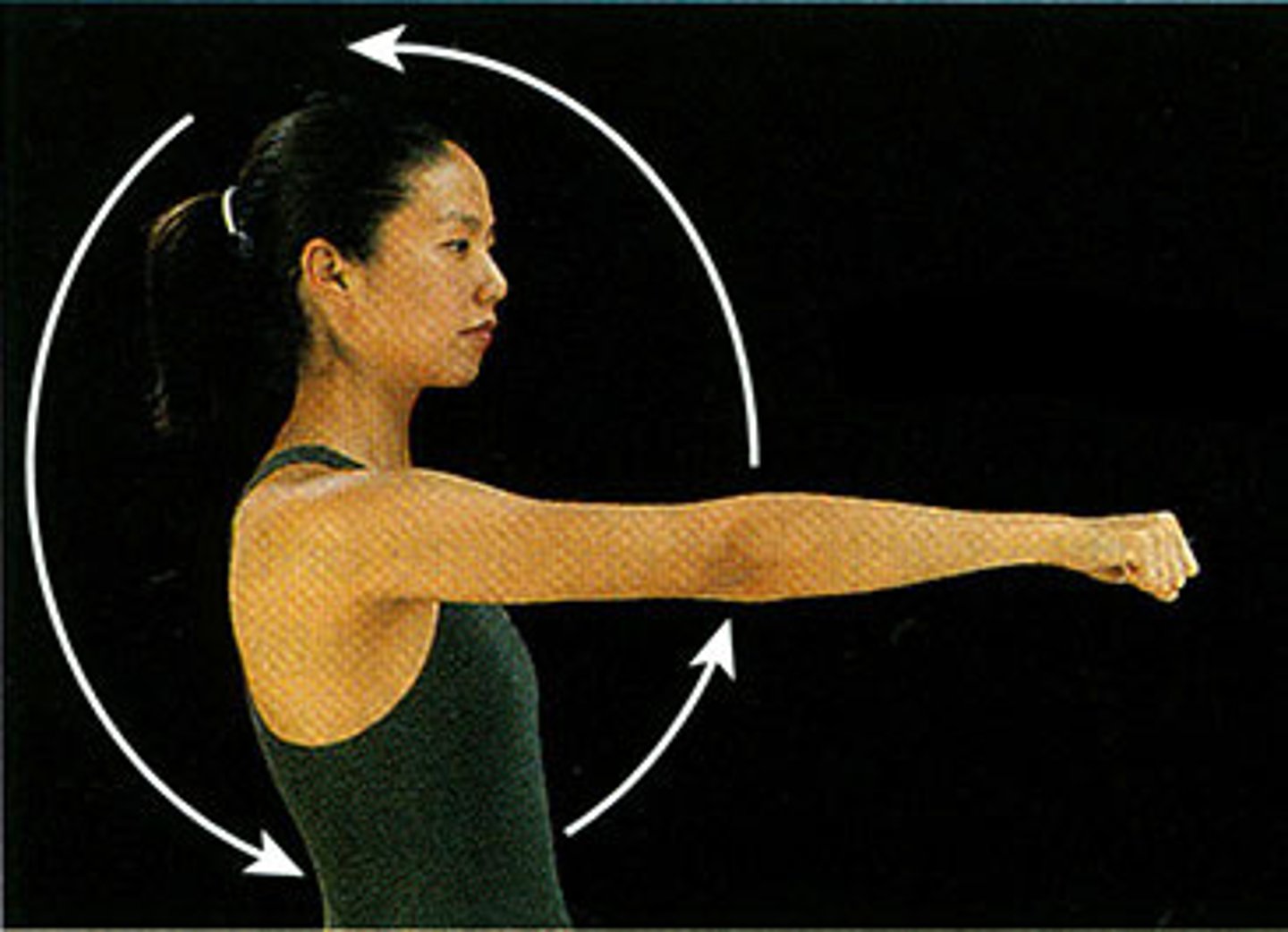
Aerobic exercise
Working at a low to moderate intensity so that the body has time to use oxygen for energy production and can work for a long period of time
glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + energy
What is the equation for aerobic respiration?
It comes from the break down of carbohydrates which forms glucose. This is then used in respiration to produce energy
Where does energy come from?
Anaerobic exercise
Working for short periods of time at a high intensity without oxygen for energy production
Glucose --> energy + lactic acid
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration?
Lactic acid
A mild poison and a waste product of anaerobic respiration
EPOC
The amount of energy needed to recover from anaerobic exercise. It replenishes the body with oxygen to break down lactic acid. It's characterised by deeper and faster breathing
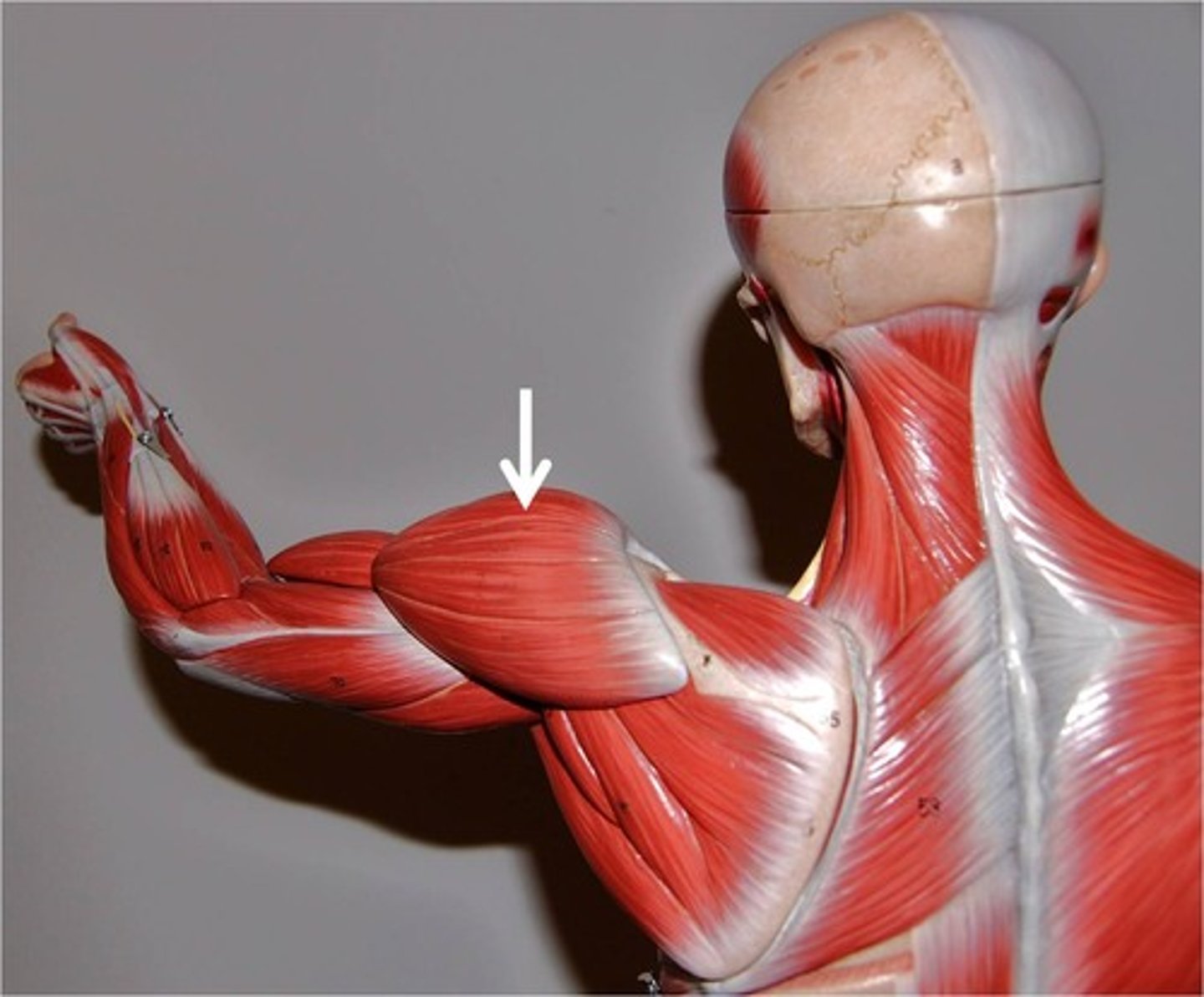
Deltoids
These create abduction at the shoulder and raise your arm sideways. They are at the top of your shoulder
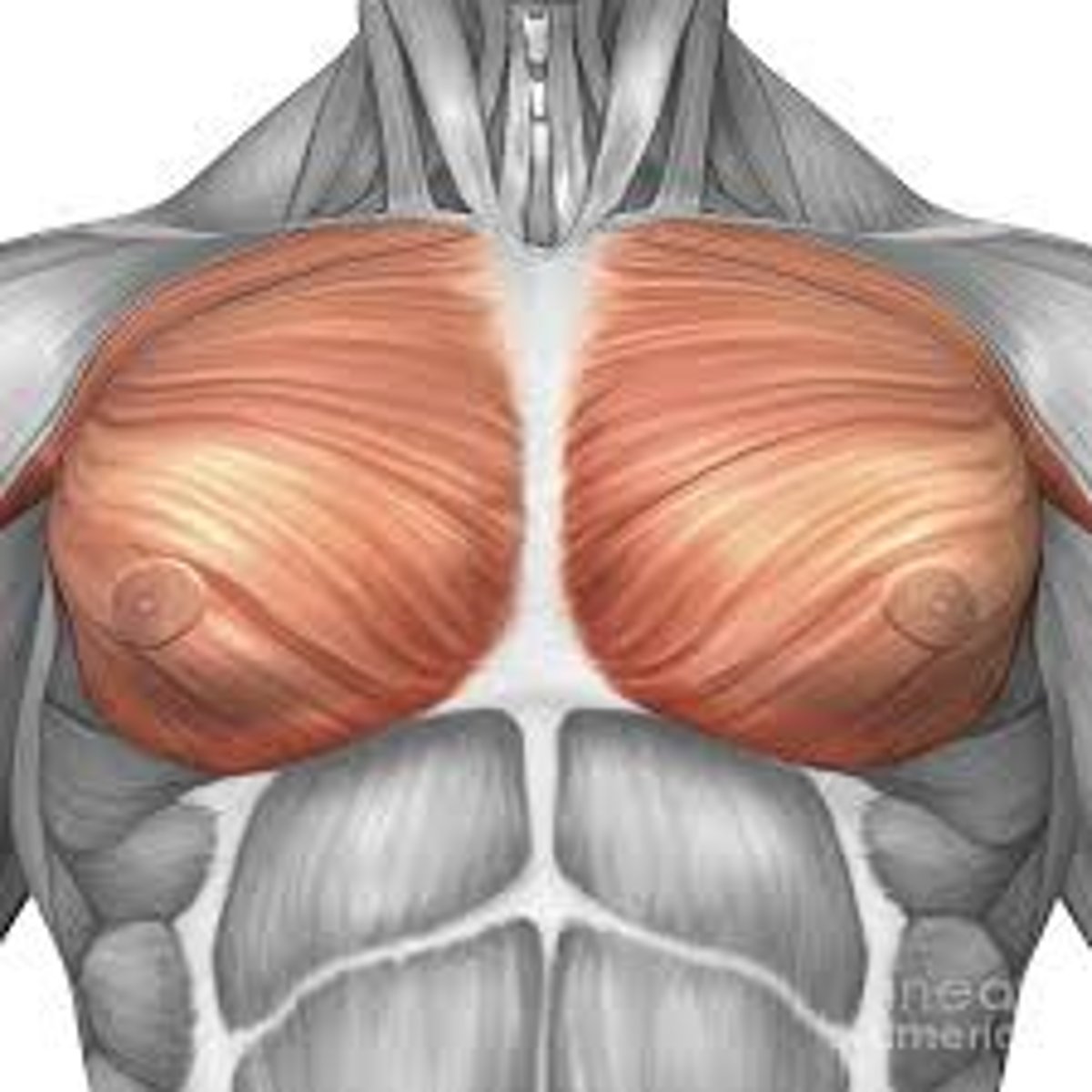
Pectorals
These are your chest muscles and they create adduction at the shoulder across the chest
Biceps
These are at the front of the upper arm and they cause flexion at the elbow
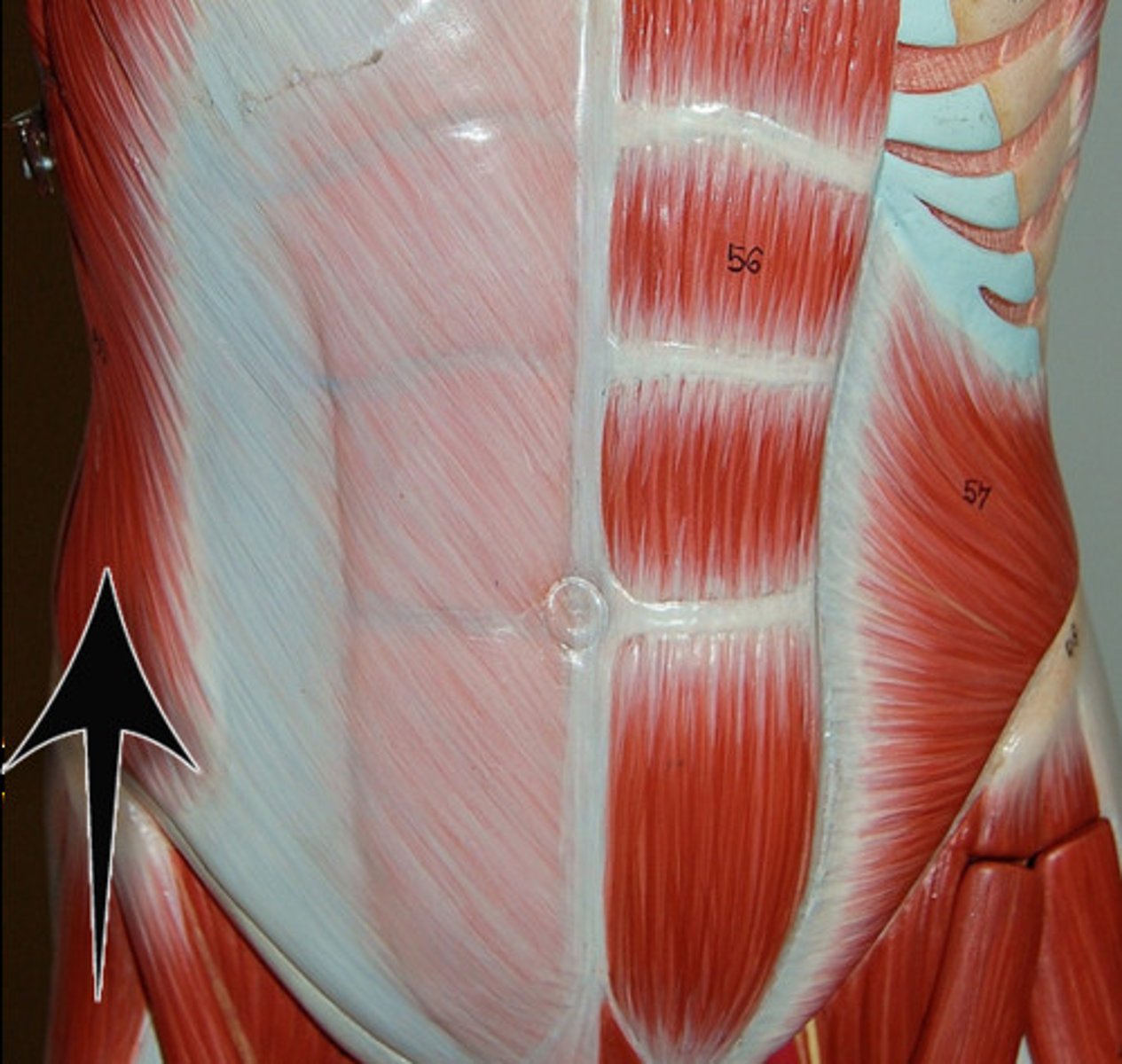
Abdominals
These are your stomach muscles and they allow you to flex your trunk
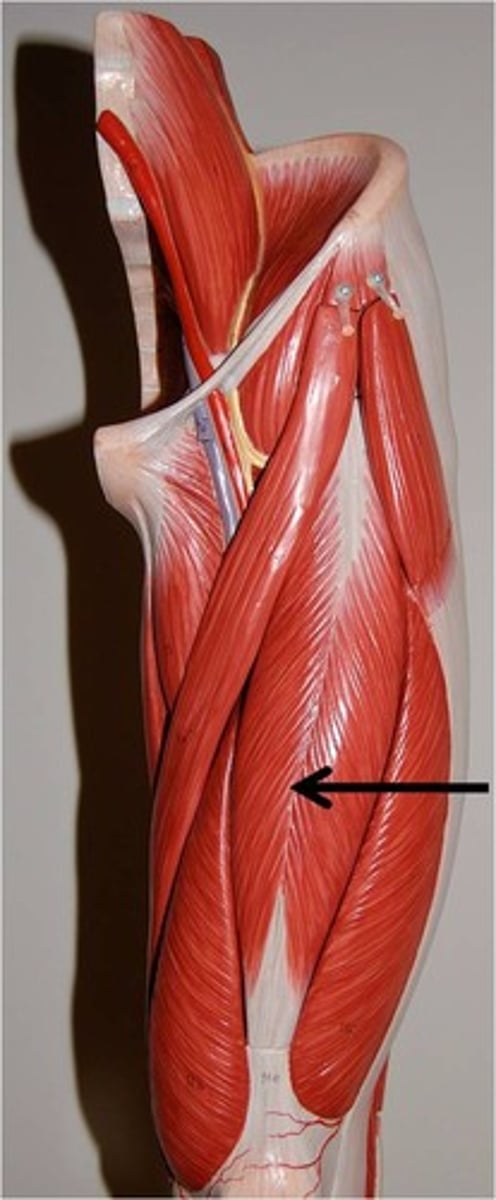
Quadriceps
These are your thigh muscles and they make extension
of the leg possible at the knee
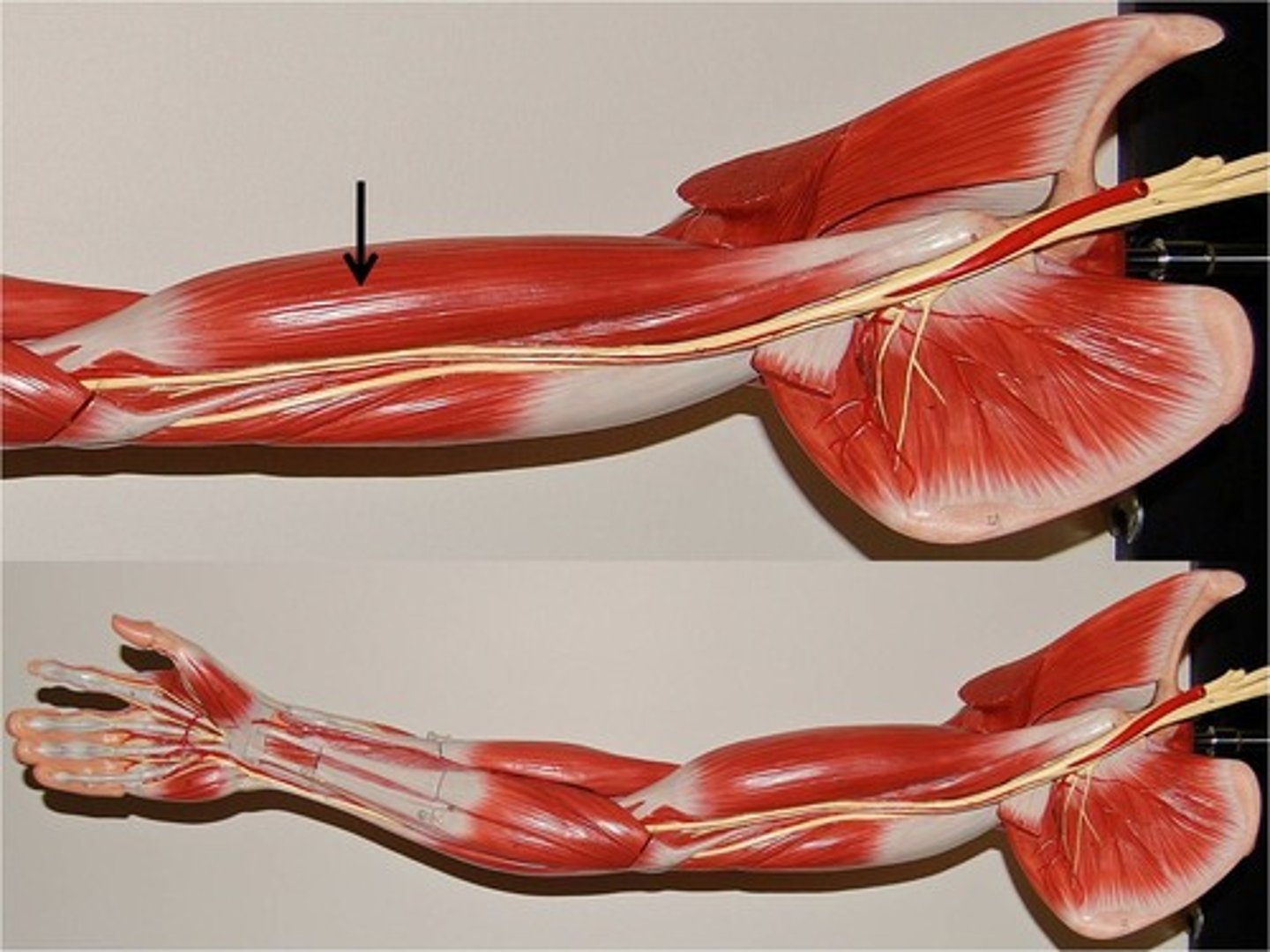
Triceps
These are located at the back of upper arm and create extension at the elbow
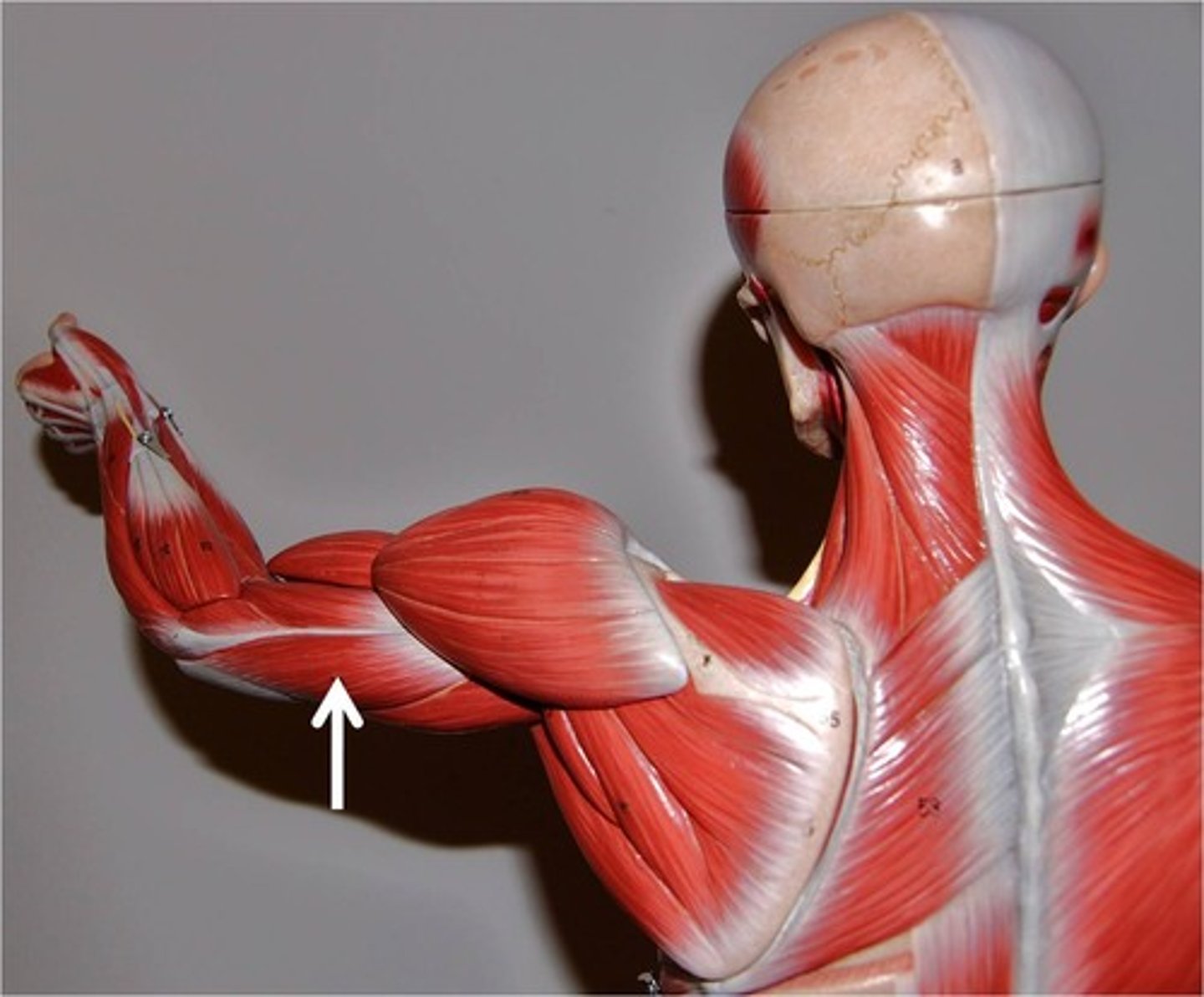
Gluteals
These allow extension,
abduction and adduction at the hip
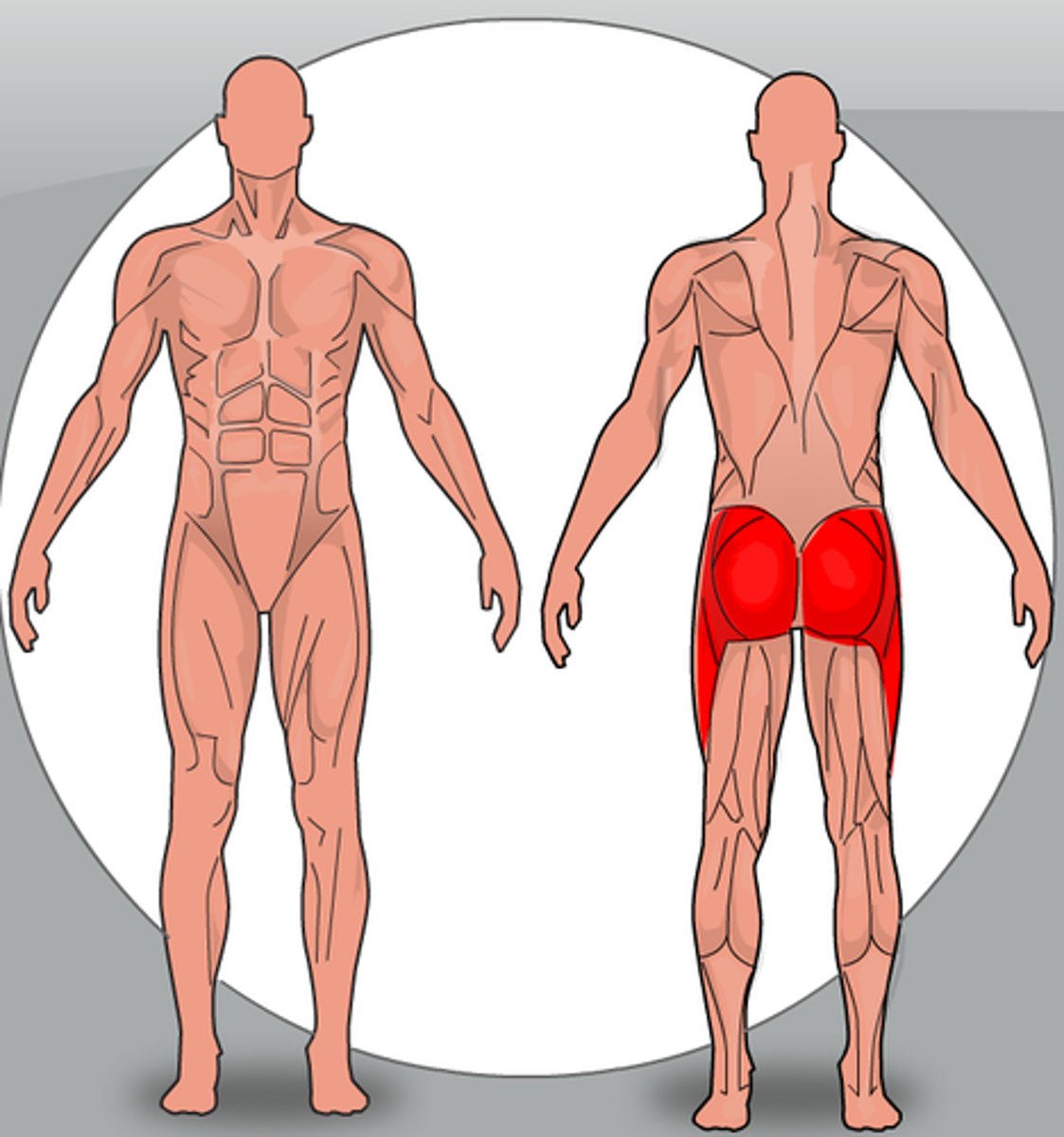
Hamstrings
These are on the back of your thigh and allow flexion of the leg at the knee
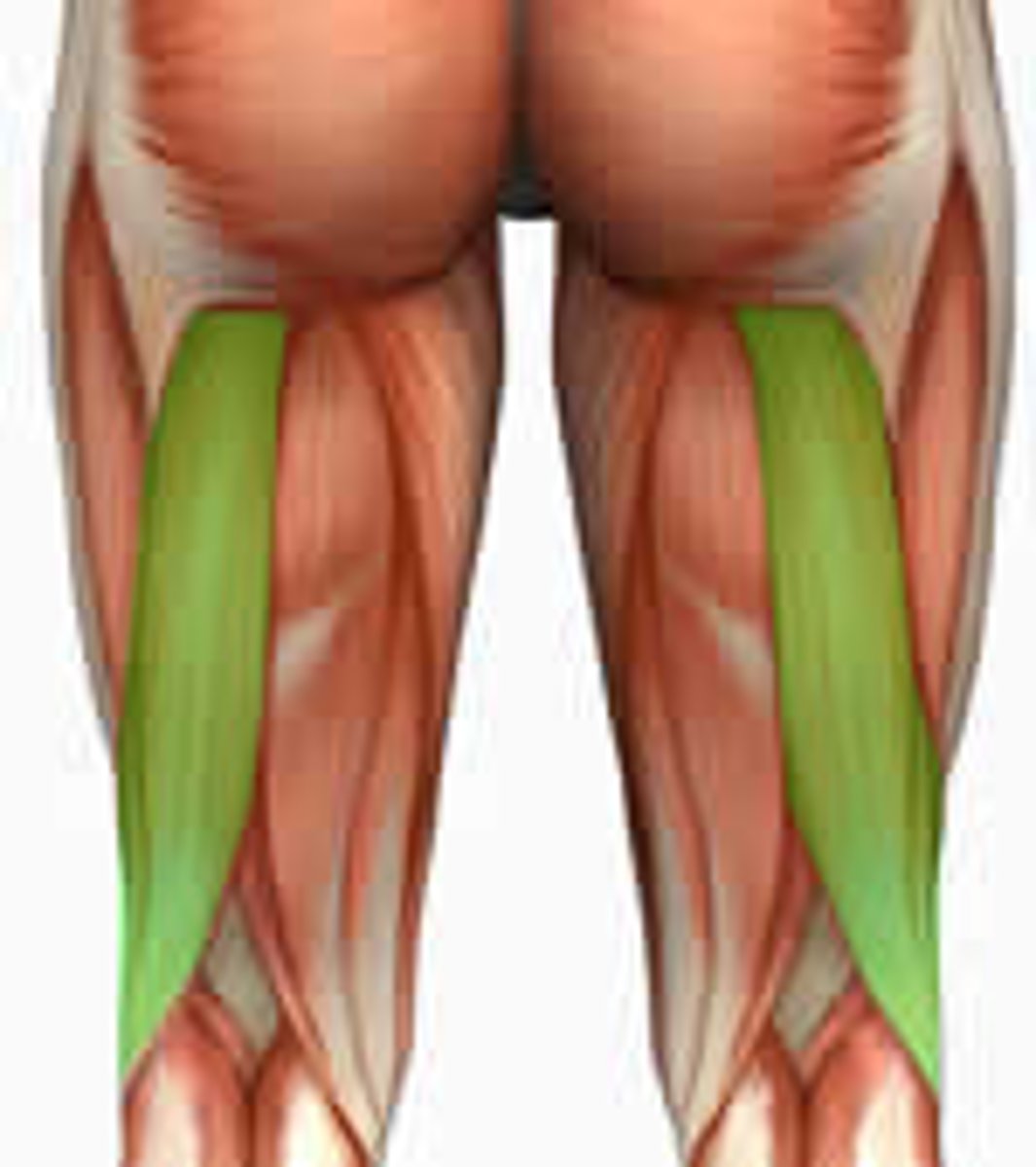
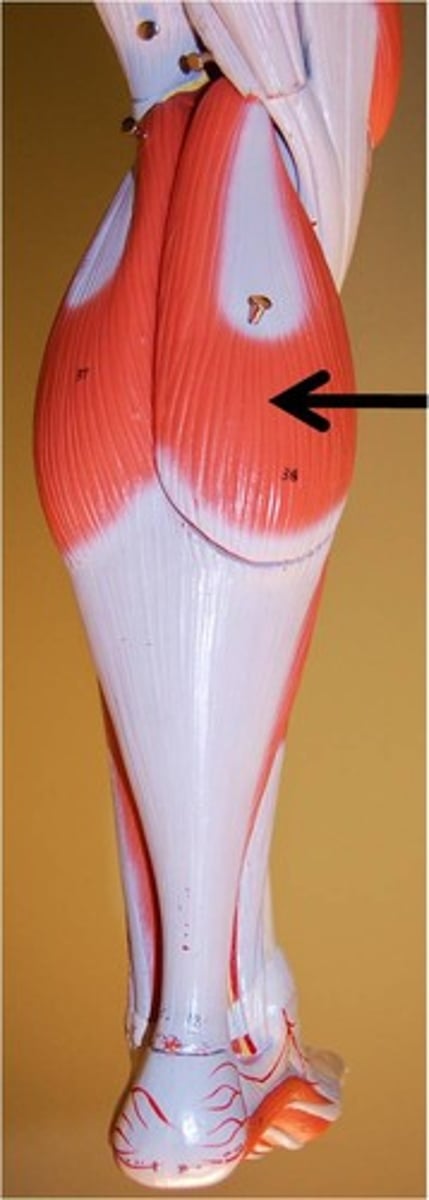
Gastrocnemius
This is your calf muscle and allows you to stand on tiptoes, by creating extension at the ankle
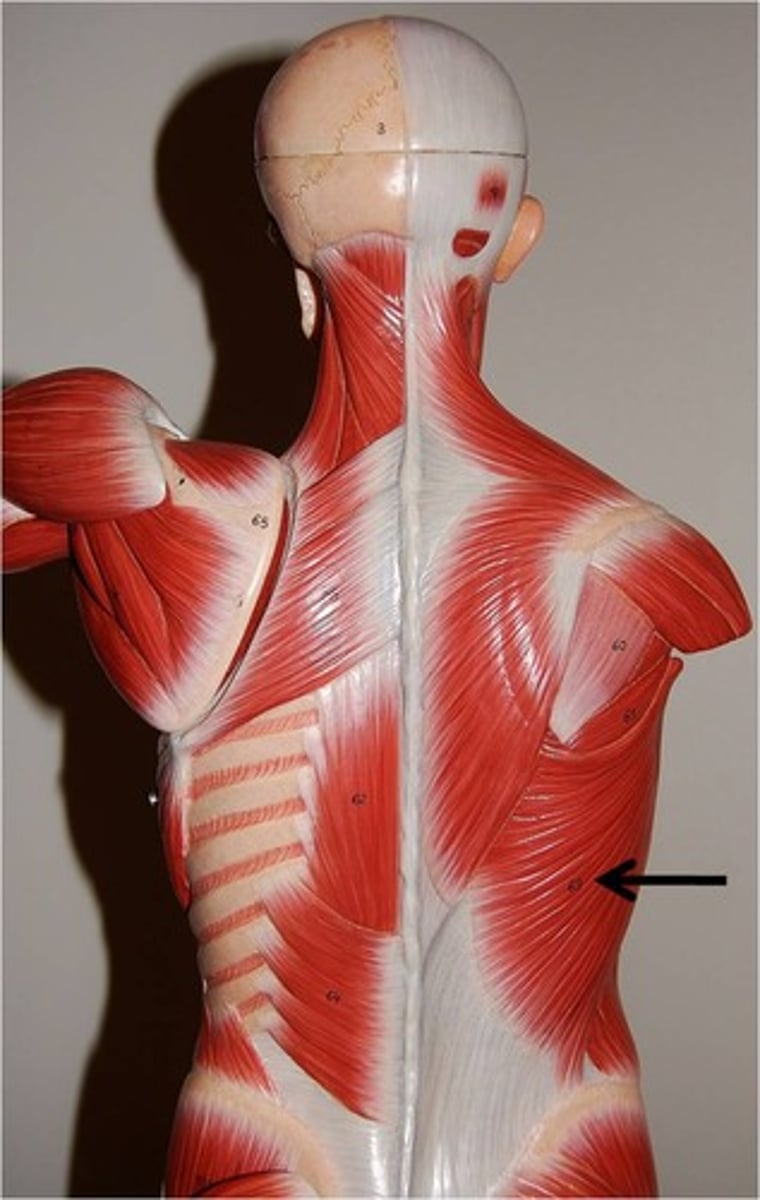
Latissimus dorsi
Extends, adducts, and rotates the arm; draws the shoulder downward and backward
Rotator cuffs
This is on the side of your shoulder
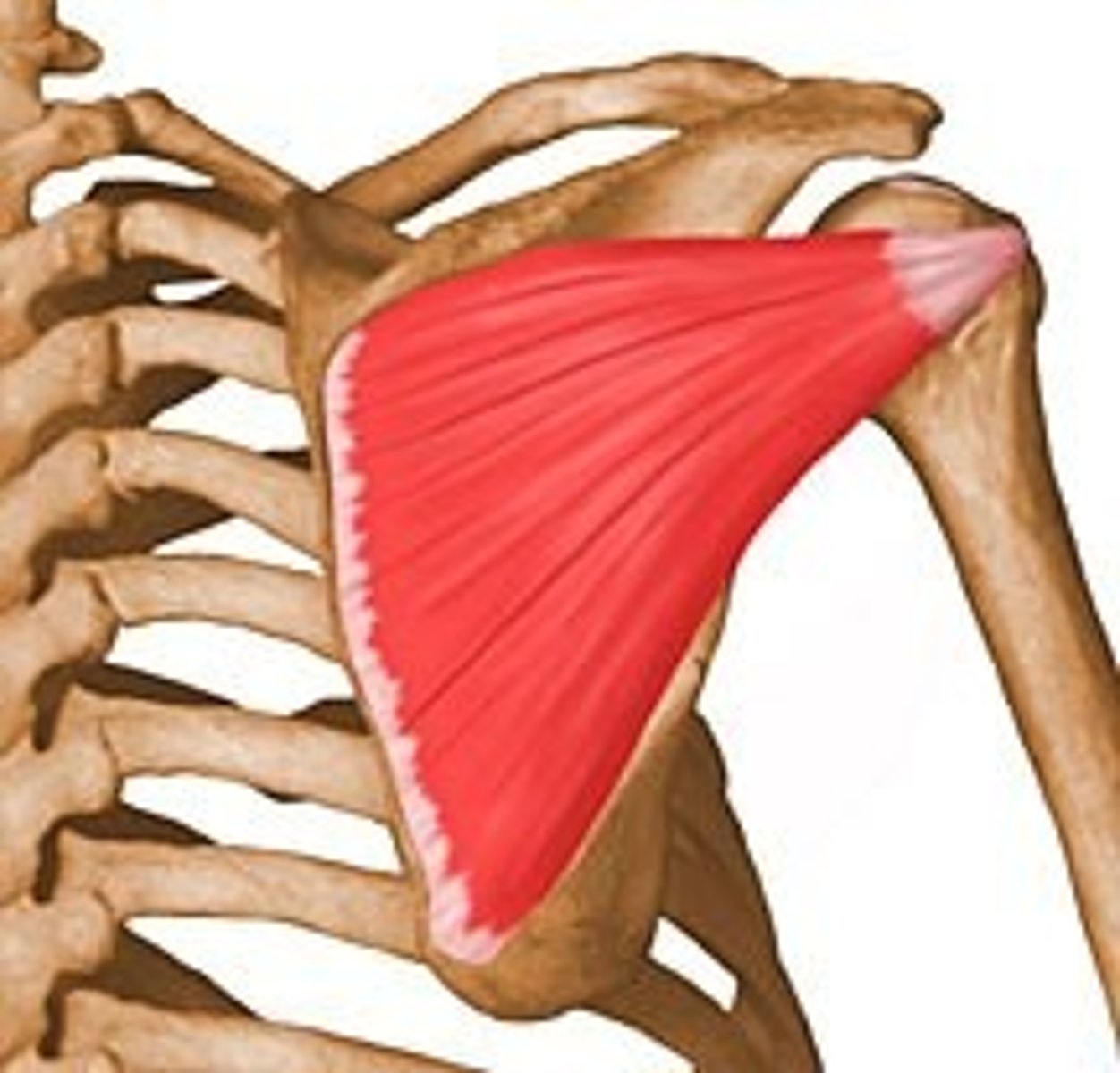
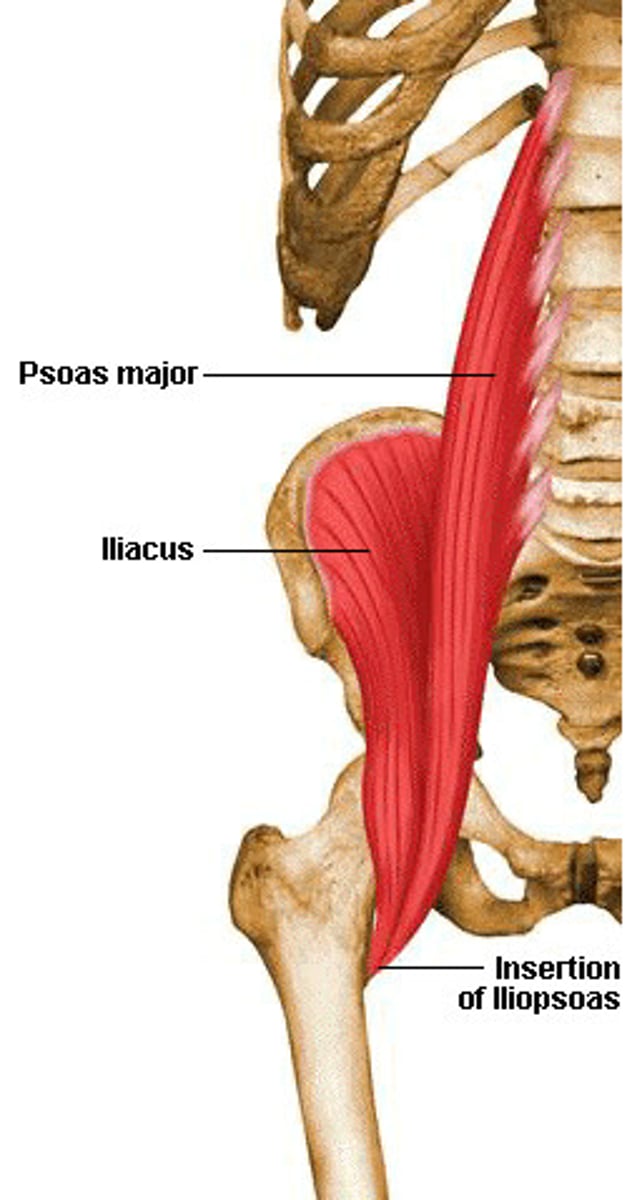
Hip flexors
A muscle group that aids in the flexion of the hip
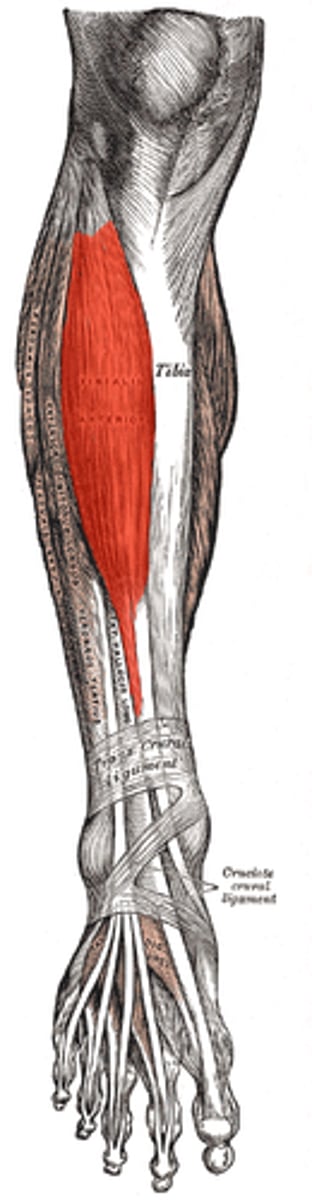
tibialis anterior
This is located on the side of your lower leg and creates dorsiflexion and plantar flexion at the ankle
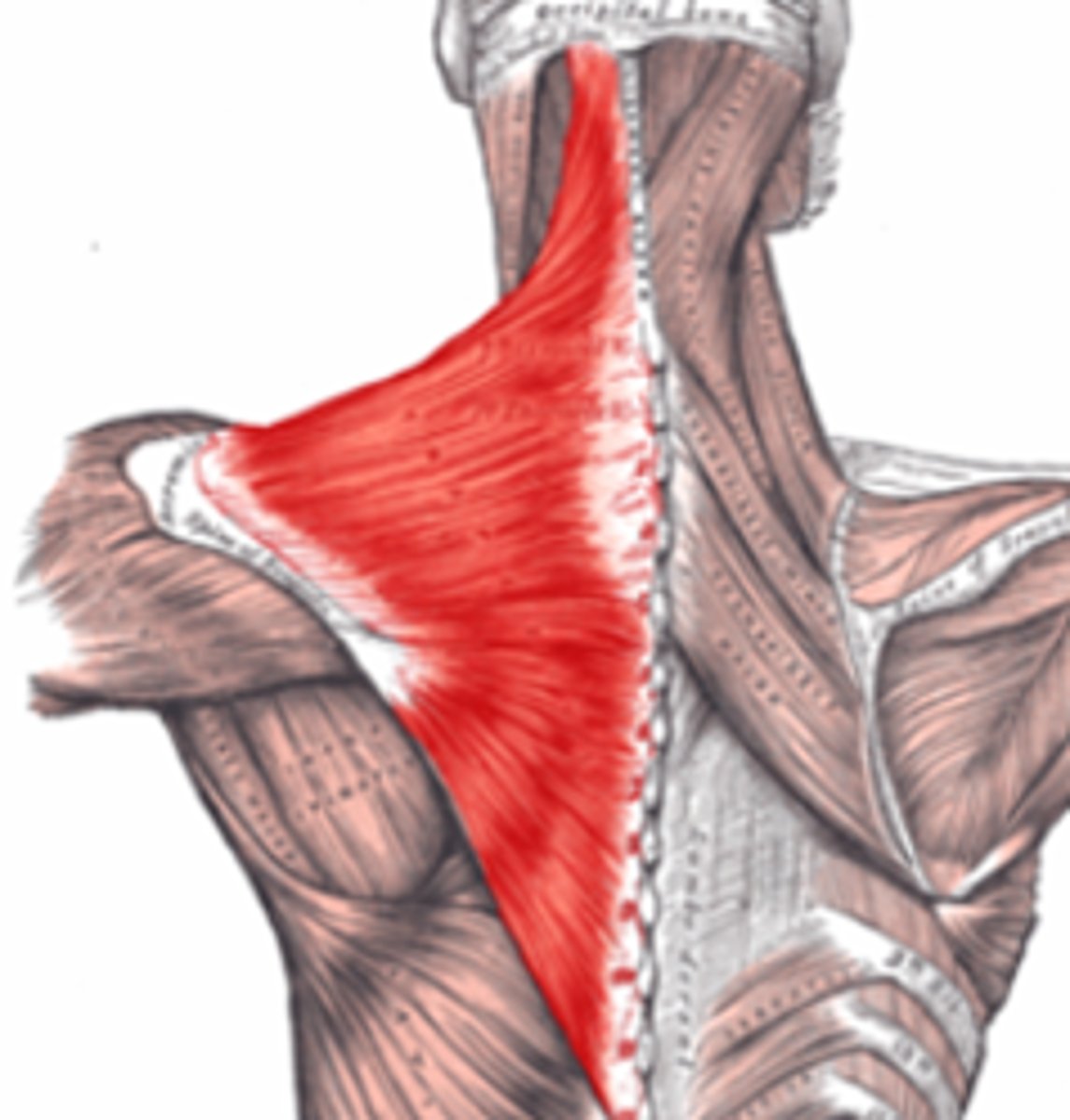
Trapezius
This rotates the arm and is located on the back of your shoulder
primer mover (agonist)
The muscle or group of muscles that contract to create movement. This works in an antagonistic pair with the antagonist
Antagonist
The muscle or group of muscles that relax to allow a movement to take place. This works in an antagonistic pair with the agonist
antagonistic pairs
muscles that act on opposite sides of a joint
The biceps and triceps
Which muscles act at the elbow to create flexion and extension?
The hip flexors and gluteals
Which muscles act at the hip to create flexion and extension?
The hamstring group and quadricep group
Which muscle groups act at the knee to create flexion and extension?
The tibialis anterior and gastrocnemius
Which muscles act at the ankle to create dorsiflexion and plantar flexion?
Isotonic contraction
A muscle contraction where the muscle changes length when it contracts. There are two types of this.
Isotonic concentric contraction
When the muscle contracts and shortens
isotonic eccentric contraction
When the muscle contracts and lengthens
Isometric contraction
A muscle contraction where the length of the muscle does not change when it contracts
DOMS
delayed onset muscle soreness, muscle discomfort 24-36 hr after exercise
carbohydrate loading
the practice of greatly increasing carbohydrate intake and decreasing exercise on the days immediately before a competition. This boosts performance and limits the length and severity of the recovery period
Hypertropy
increase in the size of tissue, such as muscle
Protein
The intake of what is really important for power athletes whilst training? This provides the body with the nutrients it needs to heal the tears quickly and build muscle.
Ice baths
Treat both tissue swelling & soreness following hard exercise. It causes constriction (narrowing) of blood vessels surrounding muscles, squeezes blood and waste products away from muscles. After, blood rushes to muscles and fresh oxygenated blood & nutrients enter muscles.
Massage
This increases blood flow to a sore area, speeding up the healing process and reducing pain