ap psych c4--biological bases of behavior
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
basic overview—genetic predisposition
genetic predisposition is the increased chance of developing a specific trait or condition because of our genetic code
twins are heavily studied because of their genetic code similarities
some people have extra chromosomes
what are neurons?
neurons are individual nerve cells that make up our entire nervous system (pg 23)
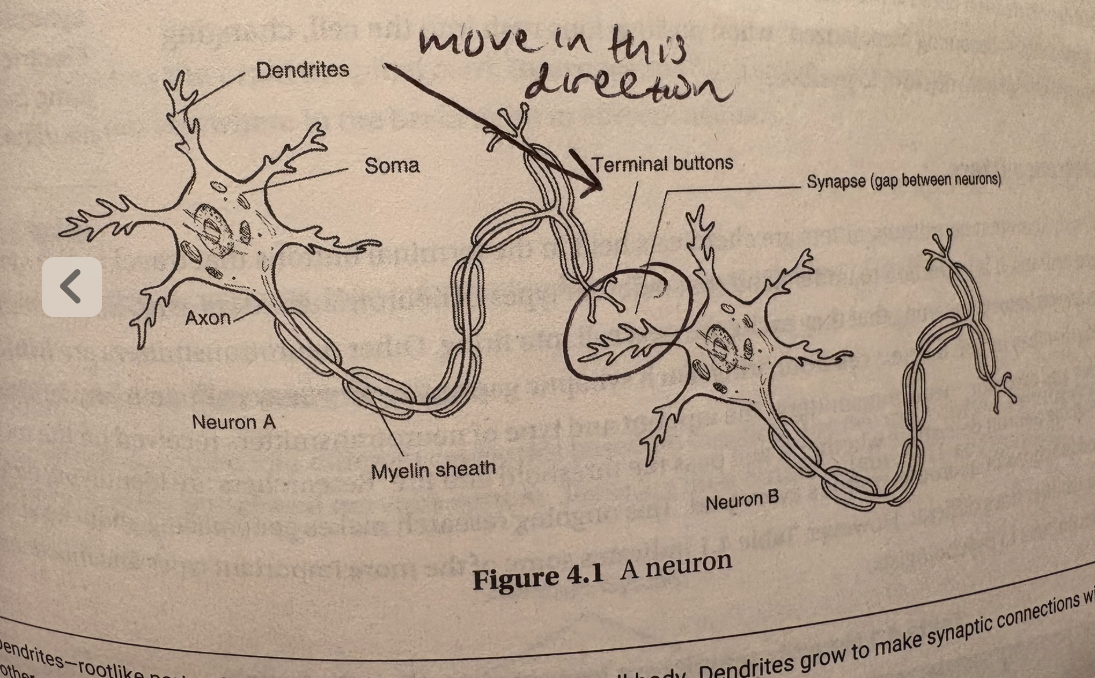
how does a neuron fire (buckle up)
neurons transmit messages through neural transmission
in resting stages (resting potential), neurons have slightly negative ions inside and positive outside which is regulated through selectively permeable material
one neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synapse (gap between neurons). once the other neuron has received enough and reaches a threshold, the charge in the second neuron rapidly changes (action potential)
neurons either fire completely or not at all (all or nothing principle)
firing is called depolarization because the cell fires due to the resting potential of the cell (its negative charge) which “depolarizes it” when the charge changes
excitatory neurons vs. inhibitory neurons
some neurotransmitters are excitatory (excite the next cell into firing) while others are inhibitory
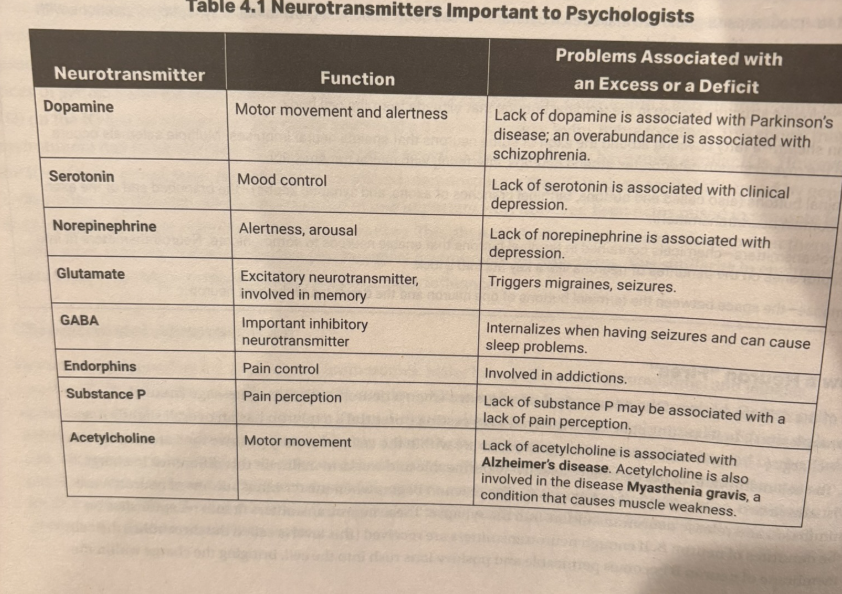
what are some important neurotransmitters?
dopamine for movement, too much causes schizophrenia
serotonin helps with mood
norepinephrine is for alertness
glutamate for memory
GABA for an inhibitory
endorphins control pain
substance P helps you feel pain
acetylcholine for movement
what do sensory neurons do?
sensory neurons take info from senses to brain
what to interneurons do?
interneurons take messages to other places in the brain or to motor neurons
what do motor neurons do?
take info from brain to other parts of the body
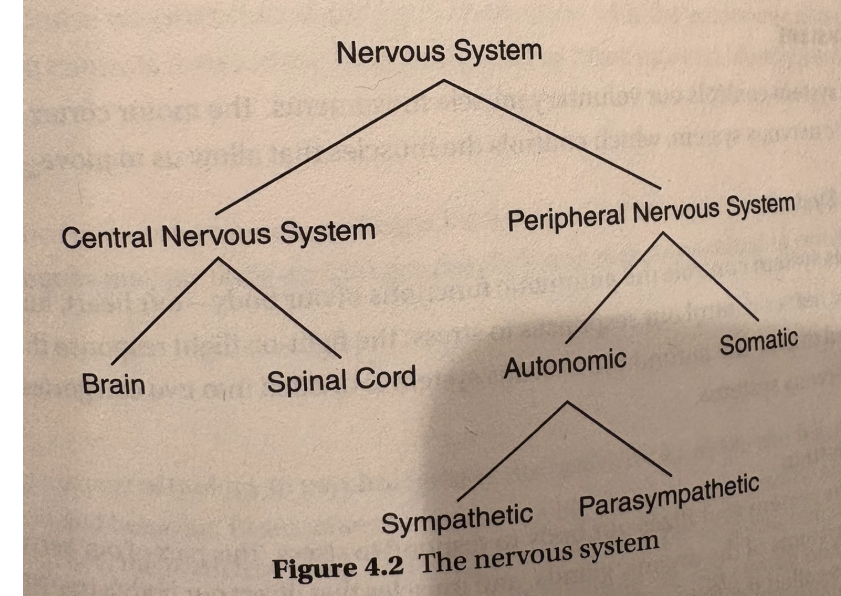
central nervous system
our central nervous system has our spinal chord, which has a bunch of nerves and is inside the spine, and brain
NOTE: some reflexes to do not follow the “i pass things down through the spinal chord” idea. some are called reflex arcs and our spine immediately processes information before the brain realizes it
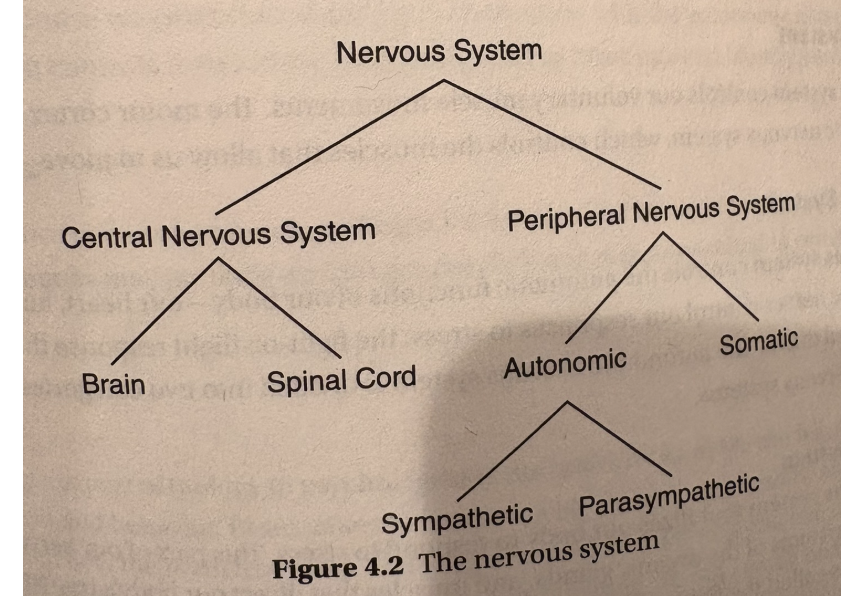
peripheral nervous system (somatic, autonomic, sympathetic, parasympathetic)
anything not encased in bone
endocrine system
endocrine system helps secrete hormones that affect many processes in our bodies
some important hormones/body parts found in the endocrine system
adrenaline for fight or flight, produced by adrenal glands
ovaries and testes for sex hormones
leptin to regulate weight and eating
ghrelin to increase eating
melatonin for sleep
oxytocin for good feelings like trust
lesioning
taking off a part of the brain which is done if patients maybe have a tumor or another problem, we can see the before and after
electroencephalogram/EEG
detects brain waves, shows consciousness and sleep patterns
computerized axial tomography (CAT scans)
to get a picture of the structure of a brain
magnetic resonance imaging
CAT but more detailed, without radiation like a CAT scan
positron emission tomography (PET)
looks at what parts of the brain are active during certain tasks, which is coded for by different colors
functional MRIs
if PET and CAT scans had a baby
we can study the brain by looking at how people are…
before/after accidents
hindbrain—pons, medula, cerebellum (pg 29 for pic)
hindbrain is anything on top of the spinal chord
medulla is what controls blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing
pons connects the hindbrain with the midbrain and forebrain and is used for facial expressions
cerebellum is for muscle movements
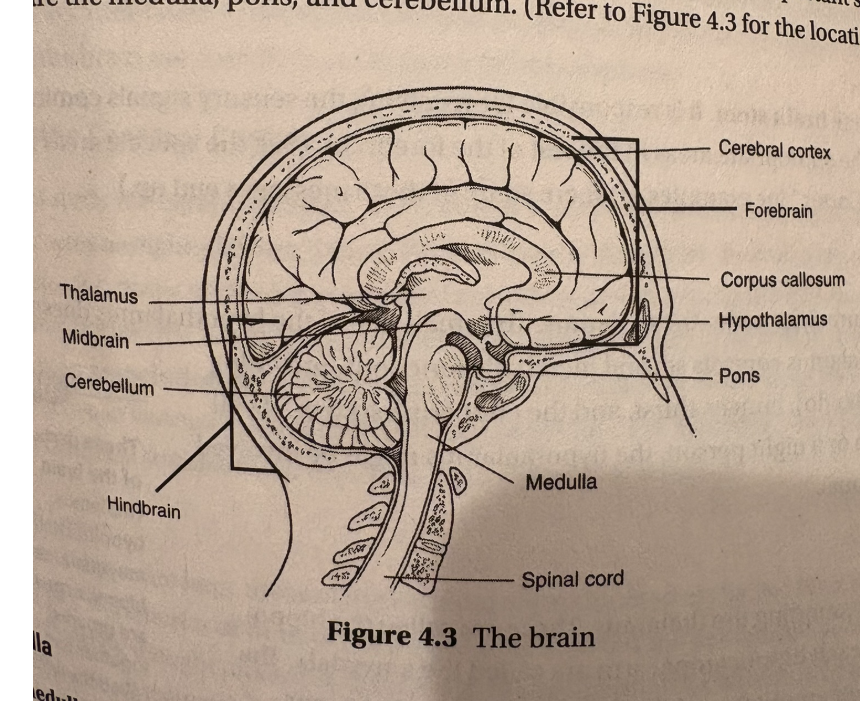
midbrain—reticular formation
midbrain helps your simple movements with sensory information (so your muscles in your eyes move to keep them focused on a book when you turn your head)
integrates sensory information and muscle movements
reticular formation is cells in the midbrain that keep us attentive and awake, otherwise we would be in a coma
forebrain—thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala/hippocampus
forebrain is thought and reason
thalamus is on top of the brain stem (which connects brain and spinal chord) and gets sensory signals and sends them to other places
hypothalamus is for body temp, hunger, thirst, etc.
amygdala/hippocampus: amygdala is for emotion, hippocampus is for memories
forebrain—cerebral cortex and its two hemispheres
cerebral cortex is the wrinkly layer on top. it has a bunch of neurons connected together. the reason it is wrinkly is because if it wasn’t it would have to be much more spread out
left hemisphere: sensory messages/ motor functions for right half of the body, right hemisphere is the opposite (this is contralateral hemispheric organization)
forebrain—hemispheric specialization and corpus callosum
hemispheric specialization: how function is specialized in each hemisphere
split brain patients have their corpus callosum, a nerve that connects the two, cut, and thus they behave differently
what are the four areas of the cerebral cortex? (lobes)
4 different lobes which are called frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. see pg 32
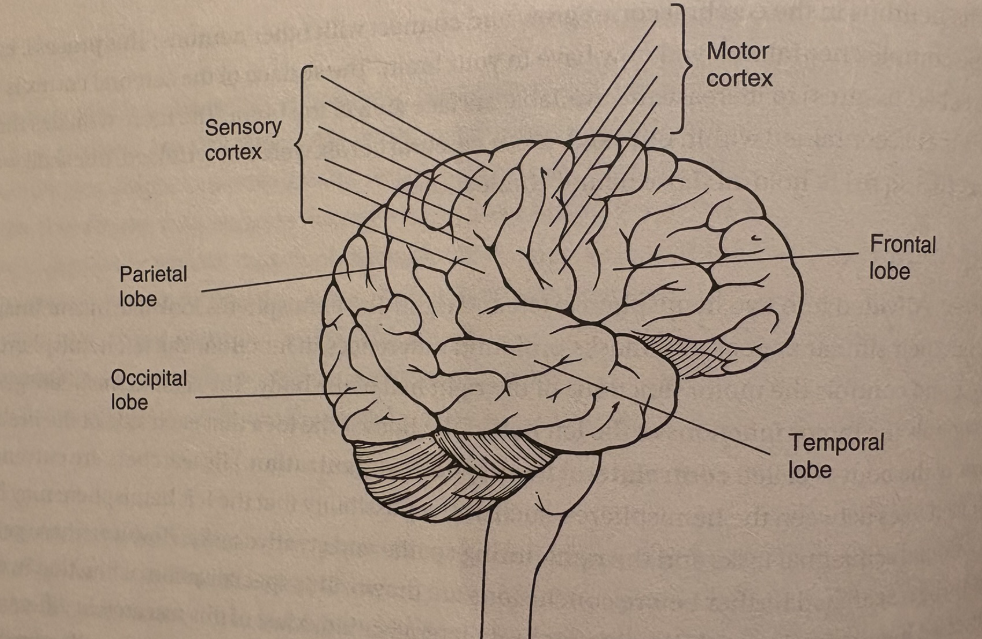
what are association areas, and how are they different from most parts of the brain?
association areas in the cerebral cortex do not receive sensory info or control muscles
frontal lobes—prefrontal cortex, broca’s area
prefrontal cortex to direct thinking processes, acts as the central executive of the brain to help pursue goals, predict consequences, etc.
broca’s area is in the frontal lobe in the left hemisphere and controls the muscles that help you talk, one of two areas for language processing
parietal lobes
somatosensory cortex/sensory cortex is right behind the motor cortex in the frontal lobe
phantom limb syndrome comes from this cortex
occipital lobes
process what our eyes see
temporal lobes
process sound
wernicke’s area is for linguistric processing, writing, and spoken speech
can we reform our brain? how?
our brains can have plasticity attributes so if a part of our brain is damaged we might be able to reform it