C6-The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
1
New cards
The rate of chemical reaction
How fast the reactants are changed into products.
(Rusting iron being one of the slowest reactions). As well as chemical weathering e.g. acid rain damage to limestone buildings
A moderate reaction could be metal magnesium reacting with an acid to produce a gentle stream of bubbles.
Burning is a fast reaction, but explosions are even faster and release a lot of gas. Explosive reactions are all over in a fraction of a second
(Rusting iron being one of the slowest reactions). As well as chemical weathering e.g. acid rain damage to limestone buildings
A moderate reaction could be metal magnesium reacting with an acid to produce a gentle stream of bubbles.
Burning is a fast reaction, but explosions are even faster and release a lot of gas. Explosive reactions are all over in a fraction of a second
2
New cards
Collision theory
In order for a reaction to occur particles need to have enough energy to collide successfully (activation energy)
3
New cards
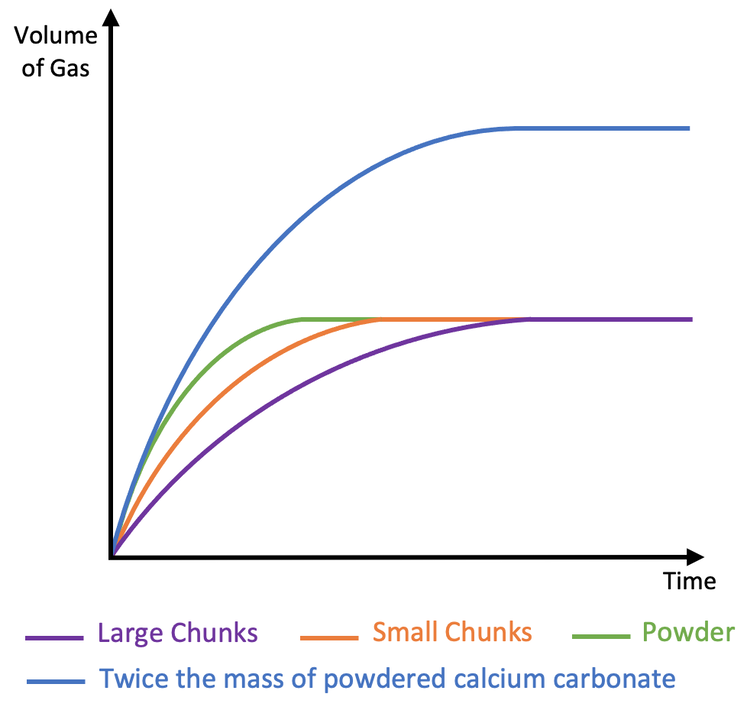
Rate of reaction graphs
higher the line evens out the more product produced and more reactants at the beginning hence the picture which shows how the highest line used more reactants before the reaction and the rest all had the same amount of products but each had a different rate of reaction
4
New cards
Factors affecting rate of reaction
all four methods increase the rate of successful collisions between the reacting particles
**Increasing temperature**
\-when the temperature is increased the particles move faster
\-If they move faster they are going to collide more frequently
\-the faster they move the more energy they have, so more collisions will have enough energy to make the reaction happen
**Increasing the Concentration or pressure**
\-If a solution is made more concentrated, it means there are more particles knocking about in the same volume of water (or other solvent)
-increasing pressure means there is a smaller space so particles are more likely to collide
\-this makes collisions between reactant particles more frequent
**Increasing surface area**
Increasing the surface area to volume ratio increases the rate of reaction as the particles have more area to collide with so collisions are more frequent
Using a catalyst
Lowers the activation energy without being used up
Enzymes are biological catalysts
**Increasing temperature**
\-when the temperature is increased the particles move faster
\-If they move faster they are going to collide more frequently
\-the faster they move the more energy they have, so more collisions will have enough energy to make the reaction happen
**Increasing the Concentration or pressure**
\-If a solution is made more concentrated, it means there are more particles knocking about in the same volume of water (or other solvent)
-increasing pressure means there is a smaller space so particles are more likely to collide
\-this makes collisions between reactant particles more frequent
**Increasing surface area**
Increasing the surface area to volume ratio increases the rate of reaction as the particles have more area to collide with so collisions are more frequent
Using a catalyst
Lowers the activation energy without being used up
Enzymes are biological catalysts
5
New cards
Measuring rate of reaction
rate of reaction = __Amount of reactant used or amount of product formed__
Time
Time
6
New cards
Measuring rates of reaction
1) precipitation and colour change
* you can record visual change if the solution is transparent and the product is a precipitate which clouds the solution
* You can observe a mark underneath the solution to see how fast it disappears. The faster it disappears the quicker the reaction
* However results are very subjective
2) Change in Mass (Usually Gas given off)
* Measuring the speed of a reaction that produces a gas can be carried out using a mass balance
* As the gas is released the mass disappearing is measured on the balance
* the quicker the reading on the balance drops the quicker the reaction
* You can plot a rate of reaction graph if you take readings at regular intervals
* This is most accurate although it does involve allowing the gas produced into the room
3) The volume of gas given out
* Involves using a gas syringe to measure the volume of gas given off
* The more gas given off in a timed interval , the faster the reaction
* Quite accurate to the nearest cm cubed however if a vigorous reaction the plunger can fly off
* you can record visual change if the solution is transparent and the product is a precipitate which clouds the solution
* You can observe a mark underneath the solution to see how fast it disappears. The faster it disappears the quicker the reaction
* However results are very subjective
2) Change in Mass (Usually Gas given off)
* Measuring the speed of a reaction that produces a gas can be carried out using a mass balance
* As the gas is released the mass disappearing is measured on the balance
* the quicker the reading on the balance drops the quicker the reaction
* You can plot a rate of reaction graph if you take readings at regular intervals
* This is most accurate although it does involve allowing the gas produced into the room
3) The volume of gas given out
* Involves using a gas syringe to measure the volume of gas given off
* The more gas given off in a timed interval , the faster the reaction
* Quite accurate to the nearest cm cubed however if a vigorous reaction the plunger can fly off
7
New cards
Magnesium and HCL practical
1. Reacting magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
2. Use a measuring cylinder to place 50 cm³ of hydrochloric acid into a conical flask
3. Add a ribbon of magnesium to the acid and plug the flask with cotton wool
4. Start the stopwatch and record the mass on the balance. Take readings of the mass every 10 seconds
5. plot the results in a table and work out the mass lost and then plot the graph
6. Repeat the method but only change the concentration of acid. Volume of acid and amount of magnesium ribbon should be the same (controlled)
8
New cards
Sodium Thiosulfate solution and HCL practical
1. If we react Sodium thiosulfate solution and hydrochloric acid it produces a cloudy yellow sulfur (s)
2. Use a measuring cylinder to put 10 cm³ of sodium thiosulfate solution into a conical flask
3. Place the conical flask on a printed black cross
4. Next add 10 cm³ of hydrochloric acid into the conical flask
5. swirl solution and start the stop watch
6. look down through the top of the flask and stop the stop clock when the X is no longer visible
7. Repeat the experiment with lower concentrations of sodium thiosulfate
8. Then repeat the whole experiment and calculate mean values for each concentration of sodium thiosulfate solution.
9
New cards
Equilibrium
Both reactions are still happening but there is no overall effect (it’s a dynamic equilibrium). This means the concentrations of reactants and products have reached a balance and won’t change
\
Equilibrium can be right or left depending on whether the products or reactants have a higher concentration
The position of equilibrium depends on the following conditions
* the temperature - heating the reaction of ammonia and hydrogen chloride moves it to the right and cooling it moves it to the left creating more ammonium chloride
* the pressure(this only affects equilibria involving gases)
* The concentration of the reactants and products
\
\
Equilibrium can be right or left depending on whether the products or reactants have a higher concentration
The position of equilibrium depends on the following conditions
* the temperature - heating the reaction of ammonia and hydrogen chloride moves it to the right and cooling it moves it to the left creating more ammonium chloride
* the pressure(this only affects equilibria involving gases)
* The concentration of the reactants and products
\
10
New cards
Le Chatelier’s Principle
If you change the conditions of a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the system will try to counteract that change
11
New cards
Changes in temperature
All reactions are exothermic in one direction and endothermic in the other
if you decrease the temperature the equilibrium will shift to the exothermic side to produce more heat which means you will have more products for the exothermic reaction
if you decrease the temperature the equilibrium will shift to the exothermic side to produce more heat which means you will have more products for the exothermic reaction
12
New cards
Pressure
If you increase the pressure it will move to to the side with less molecules to try and reduce the pressure
13
New cards
Concentration
If either concentrations increased the products will be increased if it has an increase in reactants and if has more products it will reduce the amount of reactants