Eye physiology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What does the accessory structures of the eye include?
Eyelids, eyelashes, eyebrows, lacrimal apparatus and extrinsic eye muscles
What are the eyelids?
Sheets of voluntary muscle with the tarsal plate at the free edge
What does the tarsal plate contain in the eyelid?
Sebaceous glands that secrete the lipid layer of the tear film
What is the role of the sebaceous glands in the tarsal plates in the eyelid?
Delays evaporation of tears from the eyeball
What are the general properties of the eyelids?
Delays tear evaporation, upper eyelid more mobile than the lower, lined with a mucous membrane the conjunctiva
What are the roles of the eyebrows?
Direct sweat and other moisture away from the eye
What is the primary function of the eyelashes?
Protect the eyeballs from sunlight, sweat and foreign objects
What type of gland does each eyelash have?
Sebaceous gland
What is the function of the sebaceous ciliary glands?
Release fluid to lubricate the eyeball
What is included in the lacrimal apparatus?
Lacrimal gland, lacrimal duct, nasolacrimal duct, lacrimal sac, lacrimal punctum and lacrimal canals
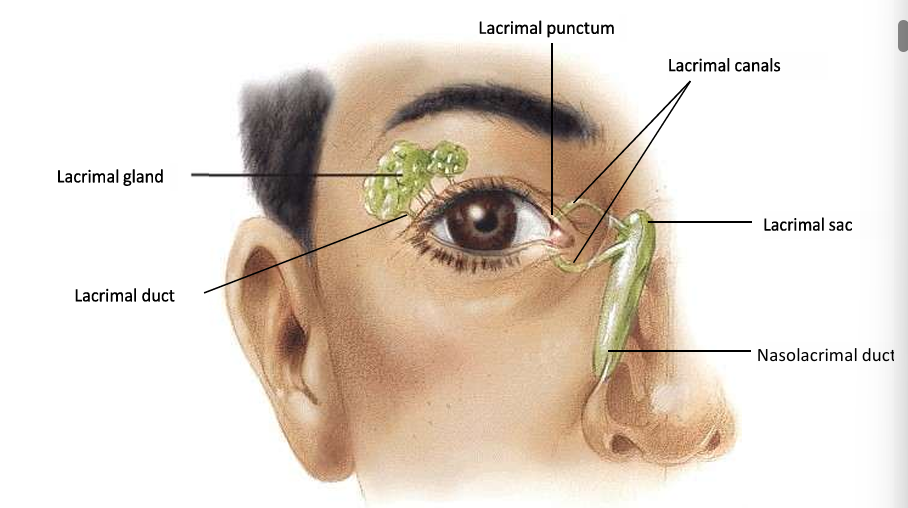
What is the role of the lacrimal apparatus?
Produce, distribute and drain tears
What is tear production stimulated by?
Parasympathetic fibres of the facial nerve in response to strong smells, irritants and emotion
Why do you get a runny nose when you cry?
Lacrimal overstimulation leads to the nasal cavity filling with fluid as the excess tears drain down the nasolacrimal duct
How many extrinsic eye muscles are there?
6
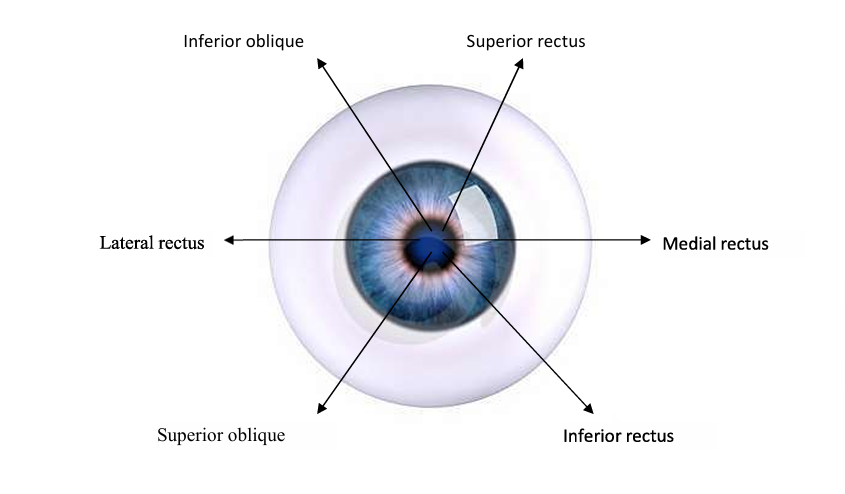
What are the extrinsic eye muscles?
Superior rectus, inferior rectus, lateral rectus, medial rectus. superior oblique and inferior oblique
What is the diagram showing direction of movement controlled by each of six extrinsic muscles?
Medial rectus adducts (moves towards nose), lateral rectus abducts (away from nose), superior rectus elevates and inferior rectus moves eye down, superior oblique rotates top of eye towards nose and inferior oblique extorts away from nose
How many regions are there in the eyeball?
3
What are the layers of the eyeball?
Fibrous layer, vascular layer and inner layer
What is the fibrous layer covered by?
Conjunctiva
What is the fibrous layer also known as?
Sclera
What is the sclera made up of?
Collagen fibres and fibroblasts - give shape and rigidity to eyeball and its white colour
What is the anterior sclera of the eye also known as?
Cornea
What does the cornea cover?
Iris
What structure is present at the junction of the sclera and cornea?
Canal of Schlemm
What is the function of the canal of schlemm?
Drains aqueous humour from the anterior chamber of the eye
What is the uvea?
Highly vascular choroid layer lining the sclera
What is the role of the uvea?
Provides nutrients to the retina and contains melanocytes
What do melanocytes do?
Produce melanin to absorb stray light that enters the eye and maintains sharpness on image of the retina
What does the choroid layer become in the anterior portion of the eyeball?
Ciliary body ending in ciliary processes
What do the ciliary processes do?
Contain capillaries that secrete aqueous humour into the anterior chamber of the eye
What do suspensory ligaments do in the uvea?
Hold the lens in place
What do the ciliary muscles do in the uvea?
Change the shape of the lens and hence the focus of the eye
What are the main structures in the uvea?
Melanocytes, choroid layer, ciliary body, ciliary processes, suspensory ligaments, ciliary muscle
What is the iris?
Coloured, doughnut shaped arrangement of circular and radial smooth muscle
Where is the iris attached to?
Ciliary processes and is suspended between cornea and lens
What is the main function of the iris?
Regulates amount of light entering the eye by changing size of the pupil
What is a diagram showing the movement of the iris?
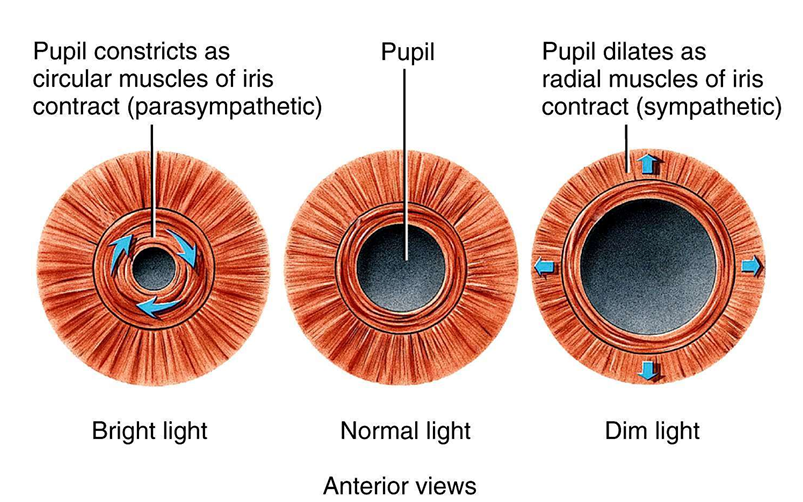
Where does the retina cover?
Posterior segment of the eye
What are the properties of the retina?
Highly vascularised - appears red under examination
Where is the edge of the retina joined to?
Choroid is pigmented with melanin, absorbing any scattered light that enters the eye
How many layers of neurons are the retina made of?
3 neuron types
What are the types of neurons in the retina?
Photoreceptor, bipolar, ganglion
What are the 2 types of photoreceptor neurons?
Cones and rods
What are the cones responsible for in the retina?
Colour vision, essential for bright light function, found at fovea centralis
What are the rods responsible for in the retina?
Found around edge of retina, essential for dark function
What are the ganglion neurons responsible for?
Pass signals from the retina to the optic nerve fibres
Where does the optic nerve leave?
Back of eye at optic disc
Where do the central retinal artery and central retinal vein enter and leave?
Optic nerve via optic disc
What are the 2 cavities in the eye?
Anterior and posterior
What does the anterior cavity of the eye consist of?
Anterior and posterior chambers and contains aqueous humour - front of the eye
What does the posterior cavity of the eye contain?
Vitreous humour - back of the eye
Where is the anterior cavity of the eye located?
Cornea and the iris
Where is the posterior cavity of the eye located?
Iris and the lens
What are both eye cavities filled with?
Aqueous humour secreted by the ciliary body
How often is aqueous humour replaced and what is its role?
Every 90 minutes and maintains intraocular pressure between 16-25mmHg
What is the primary function of the vitreous humour?
Holds the retina flush against the choroid
What is vitreous humour made up of?
Water with collagen fibres and hyaluronic acid, some phagocytic cells
What do phagocytic cells in the vitreous humour do?
Removes debris e.g., dead retinal cells
Is vitreous humour renewed?
No - it is stagnant
What are floaters?
Harmless pieces of debris casting a shadow onto the cornea - happens when the patient looking at a single bright colour for a period of time