Lesson 2: Plate Tectonics, Sea Floor Spreading, and the Theory of Continental Drift
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Continental Drift
The idea that Earth's continents move slowly over the surface.
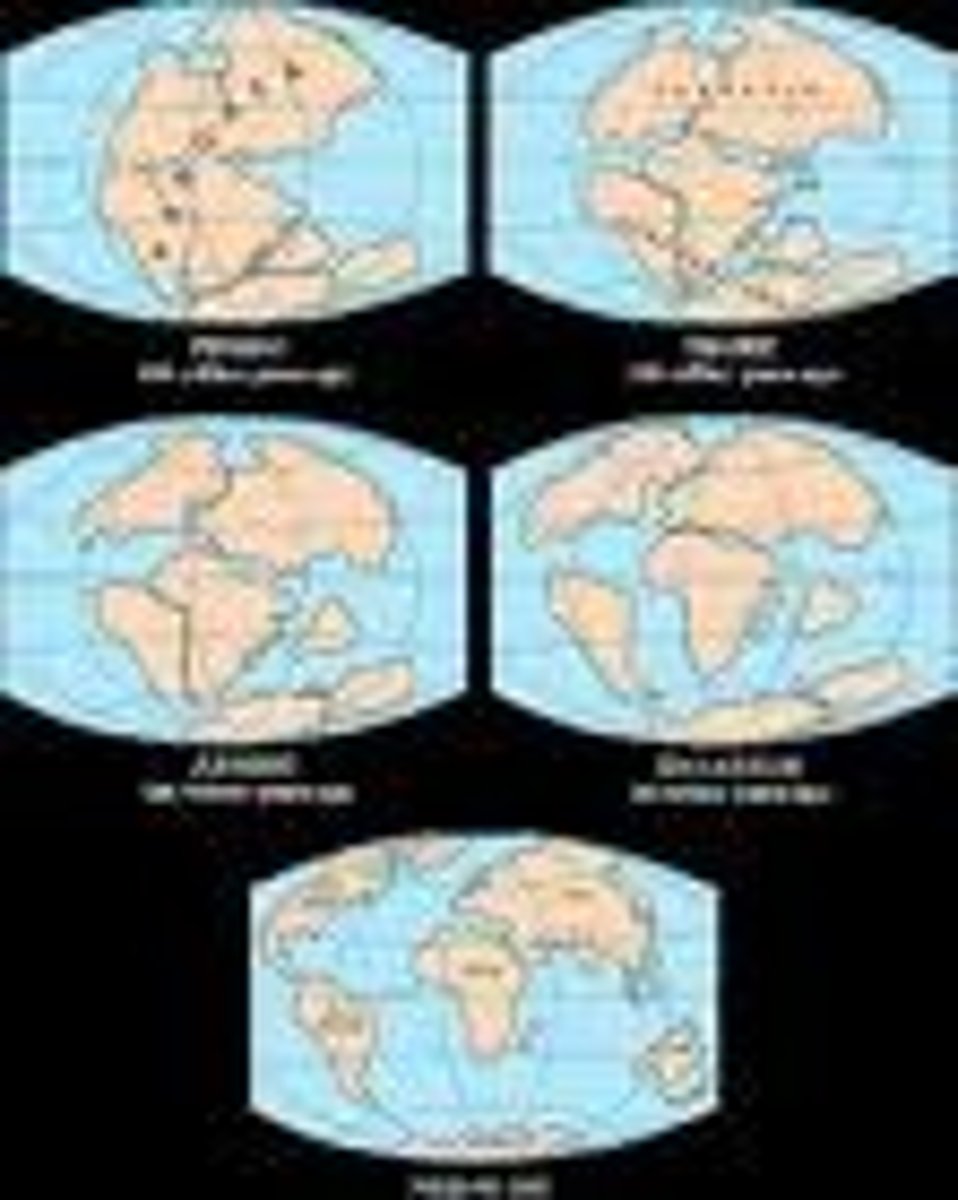
Pangaea
The supercontinent that existed 300 million years ago.
Fossil
Any trace of an ancient organism that has been preserved in rock.

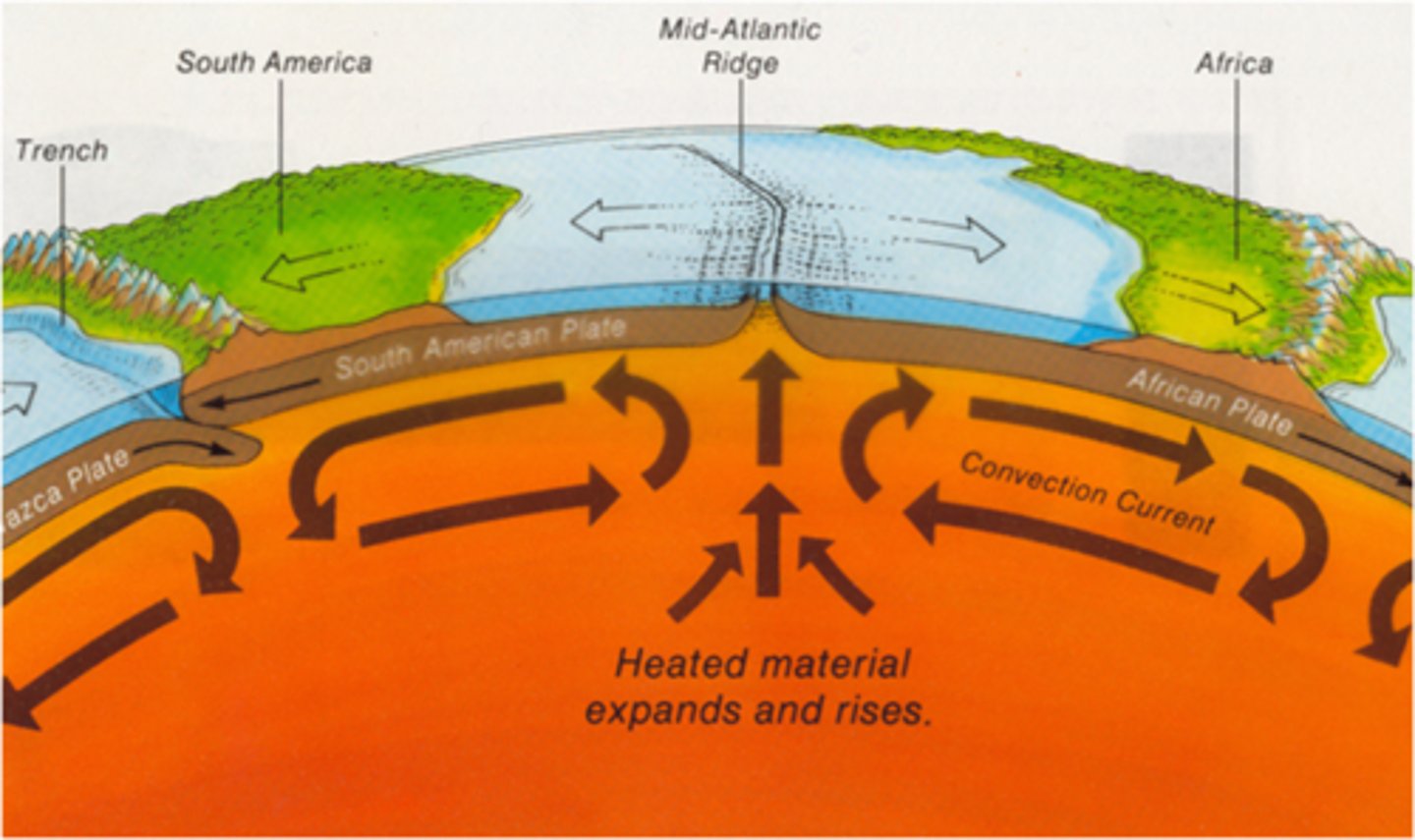
Mid-Ocean Ridge
Mountain ranges that form along the middle of some ocean floors as a result of sea-floor spreading.
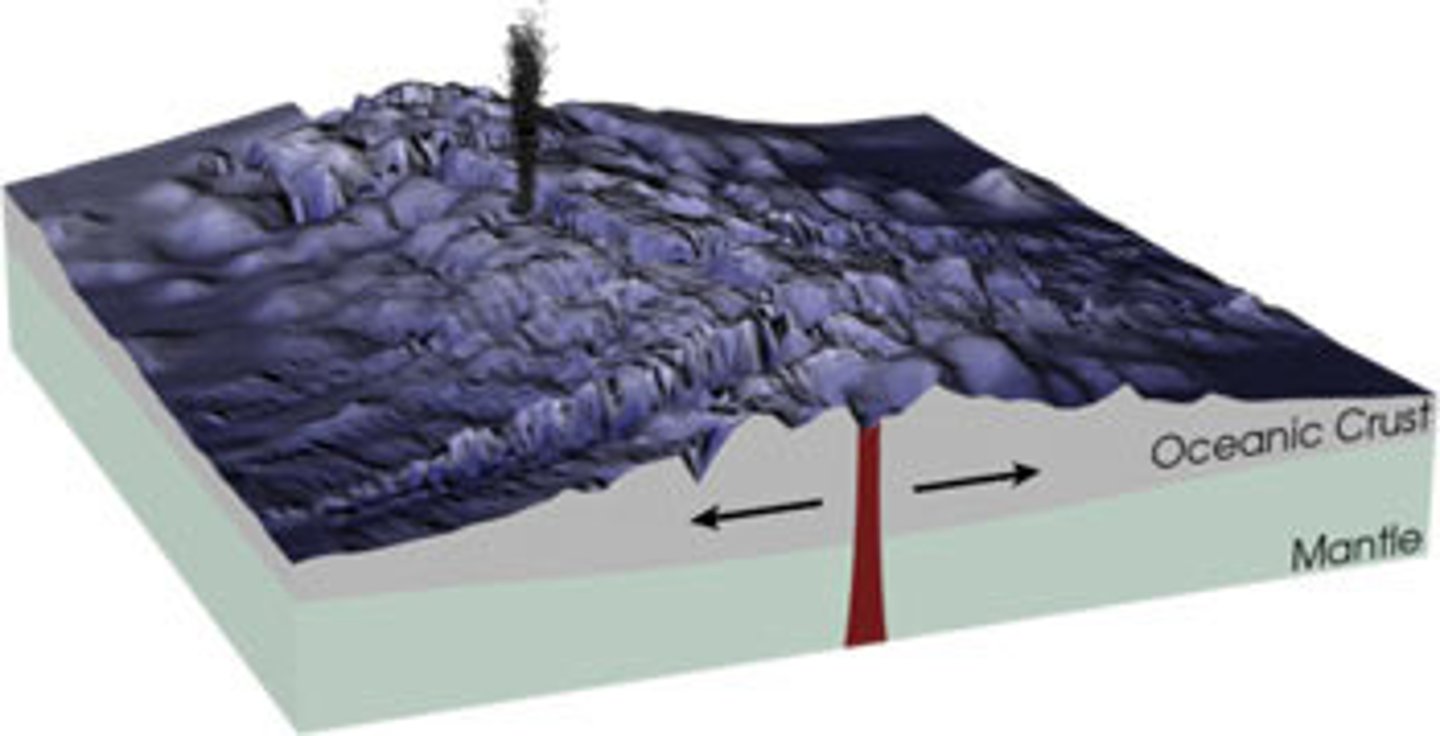
Sea-Floor Spreading
The process of continually adding new material to the ocean floor at mid-ocean ridges.
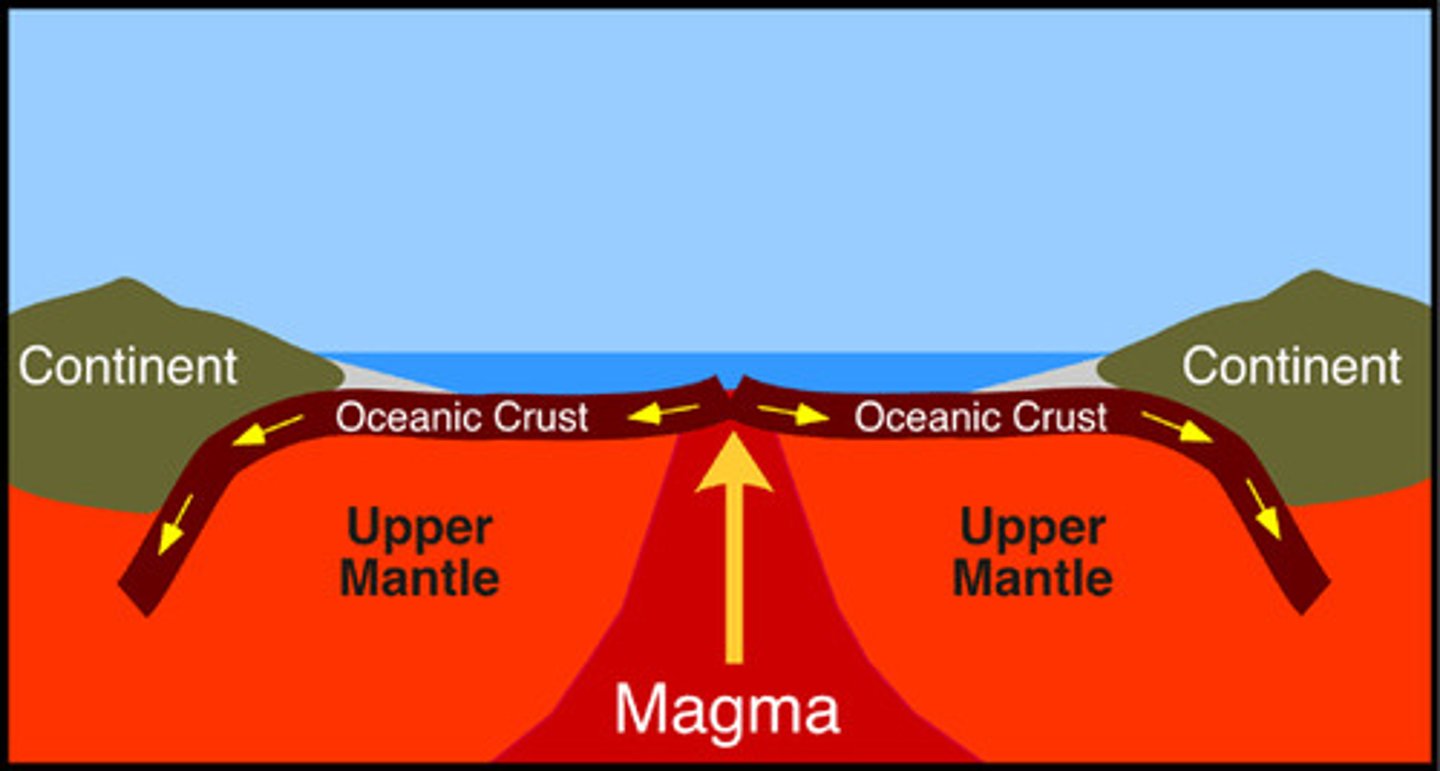
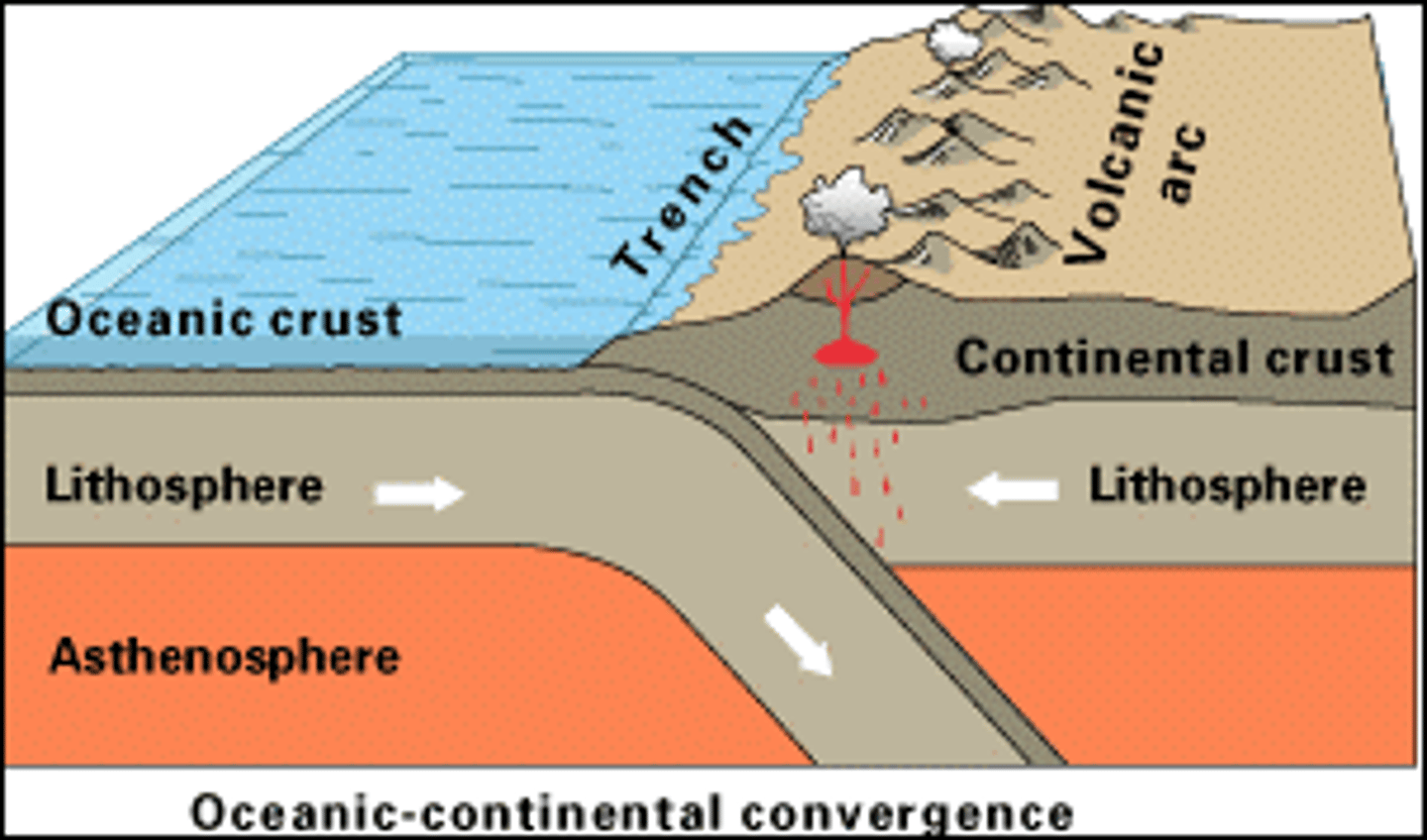
Deep-Ocean Trenches
Deep underwater canyons where ocean crust bends downward and returns to the mantle.
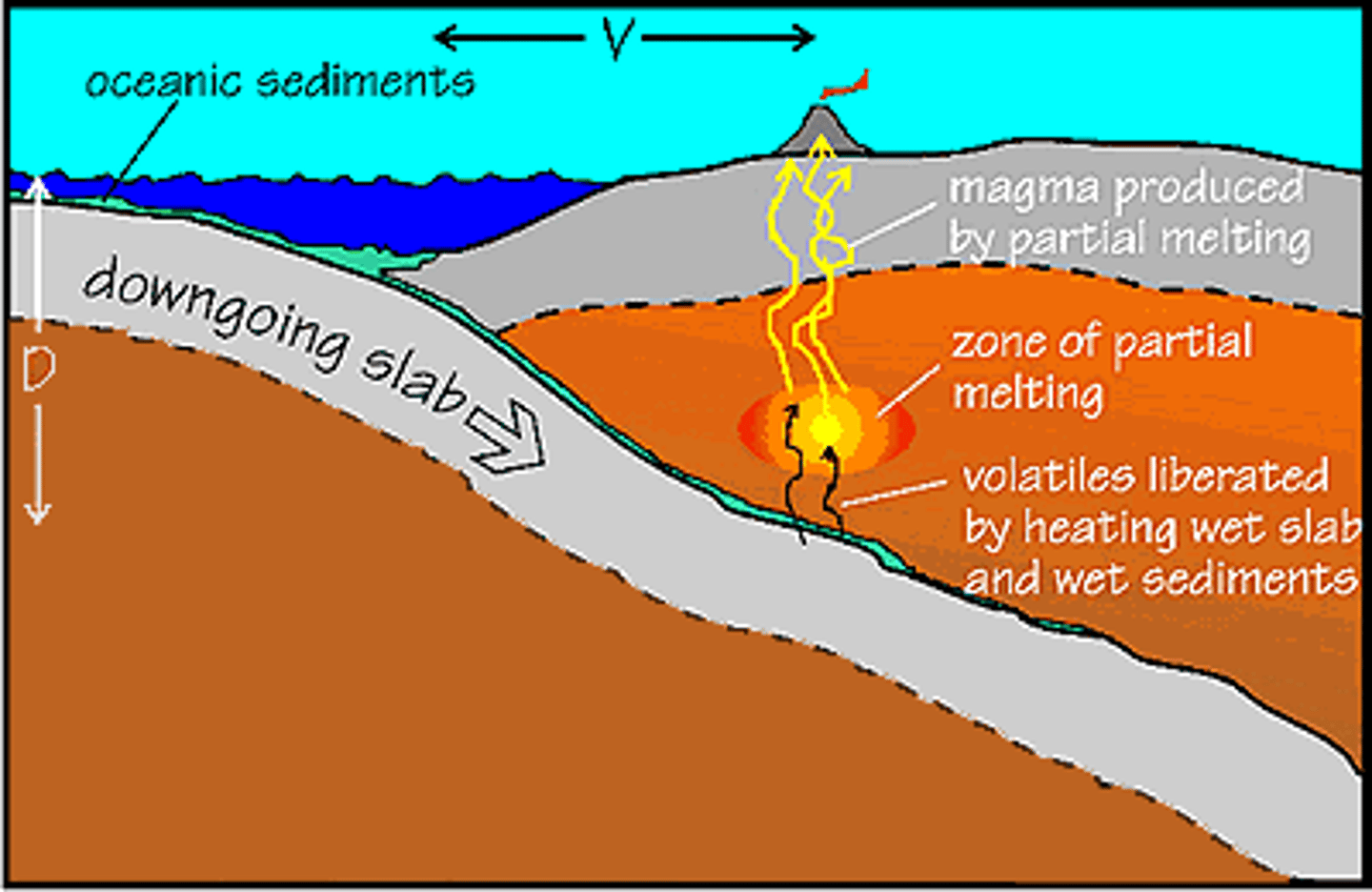
Subduction
The process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle.
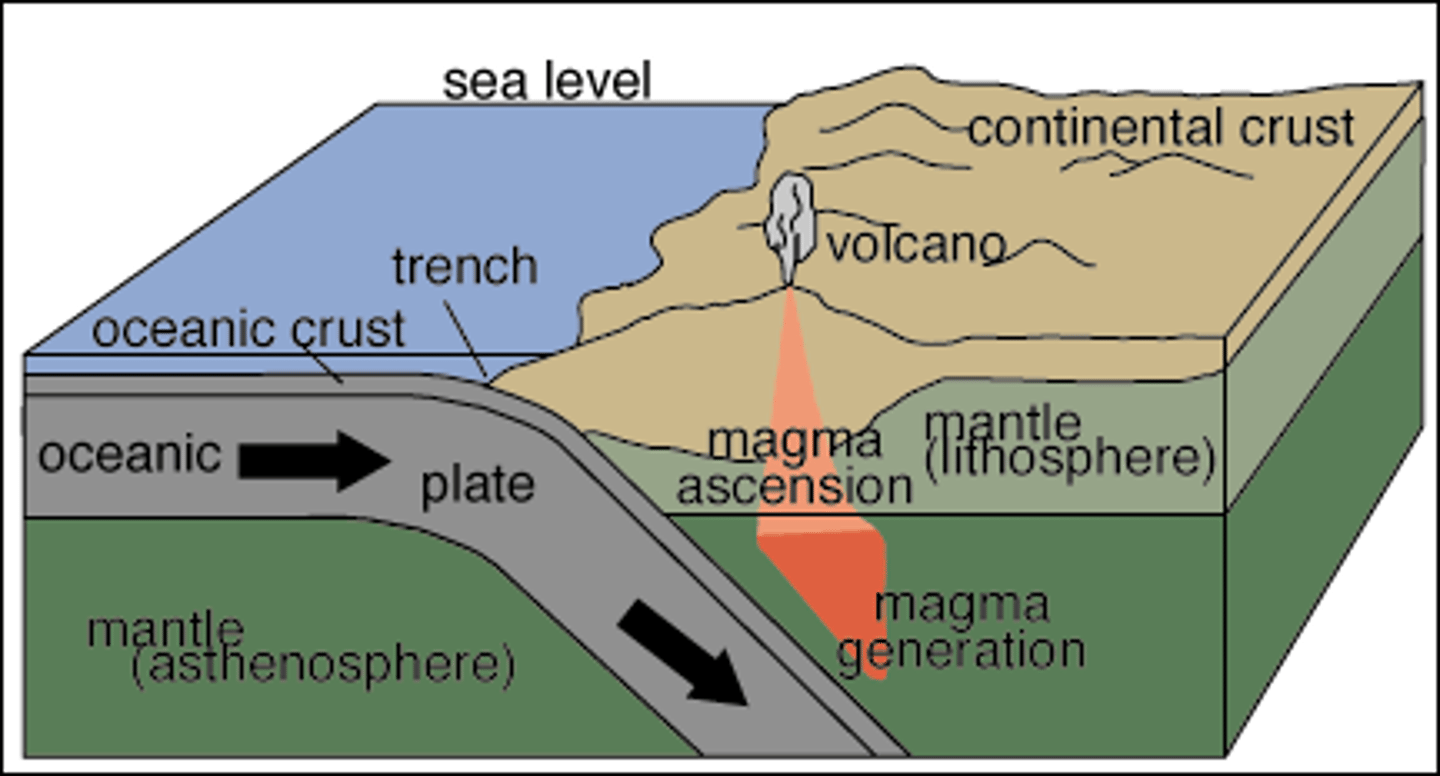
Tectonic Plate
One of several pieces of Earth's lithosphere that float on and move across the aesthenosphere.
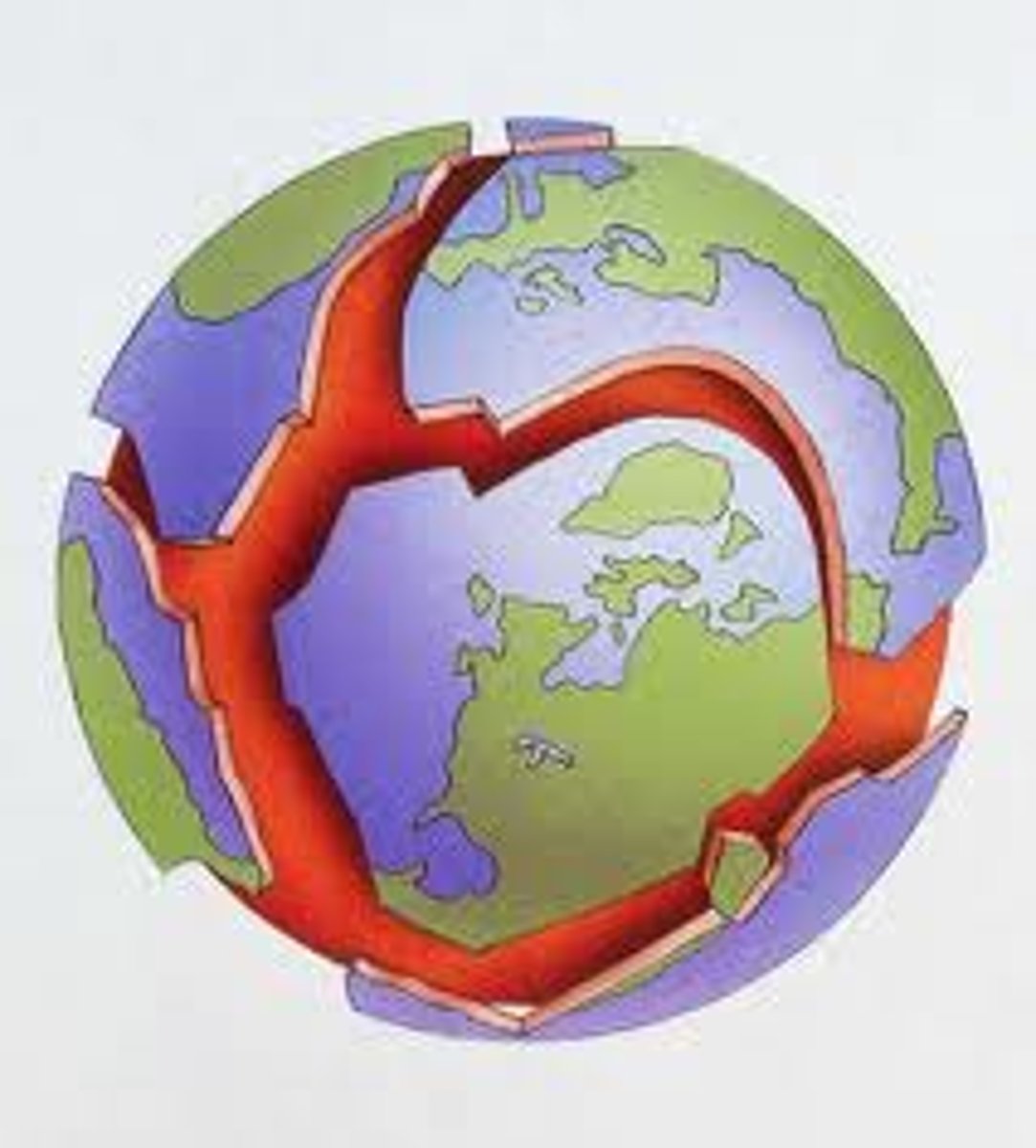

Divergent Boundary
A place where two tectonic plates move away from one another.
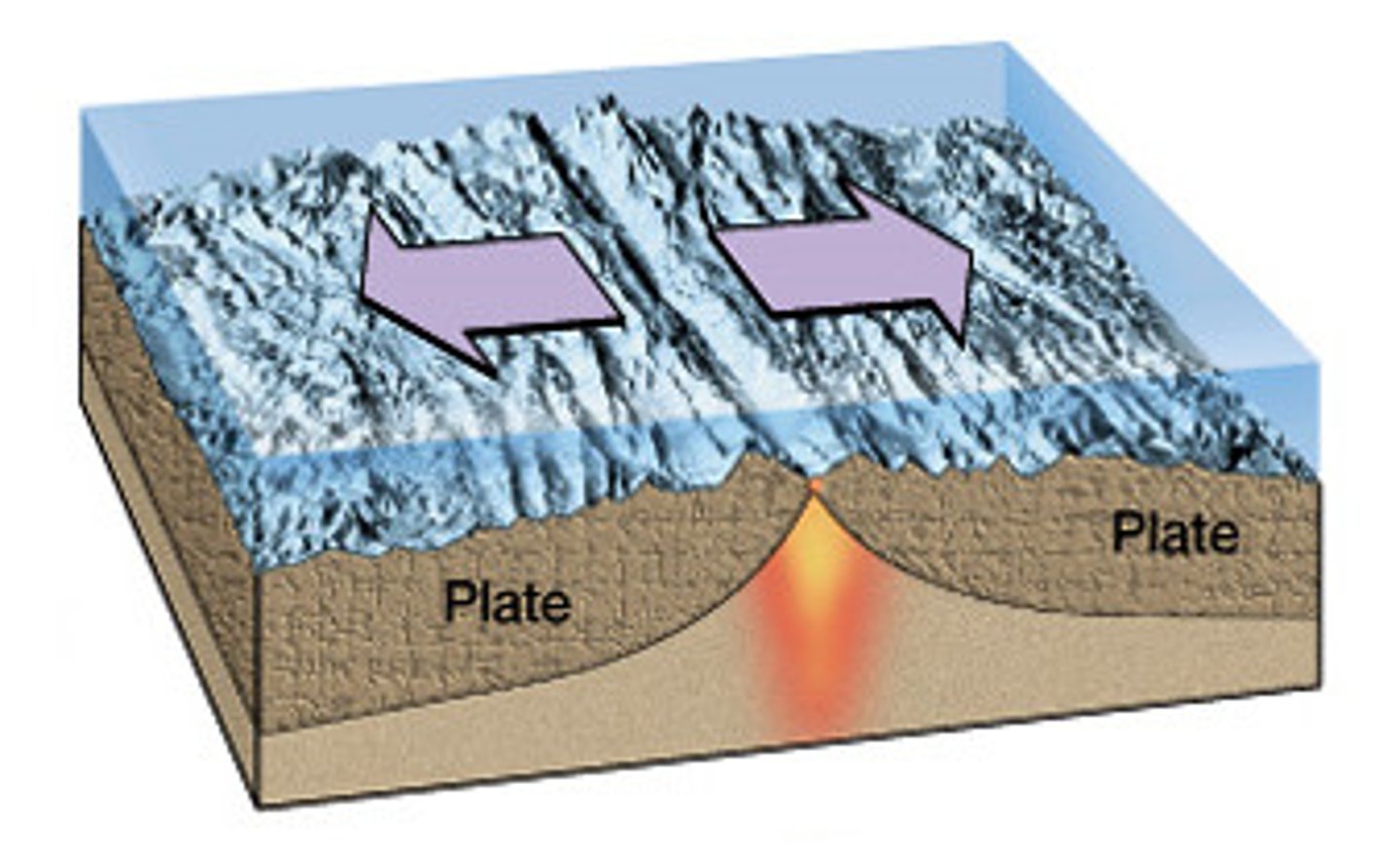
Convergent Boundary
A place where two tectonic plates come together.
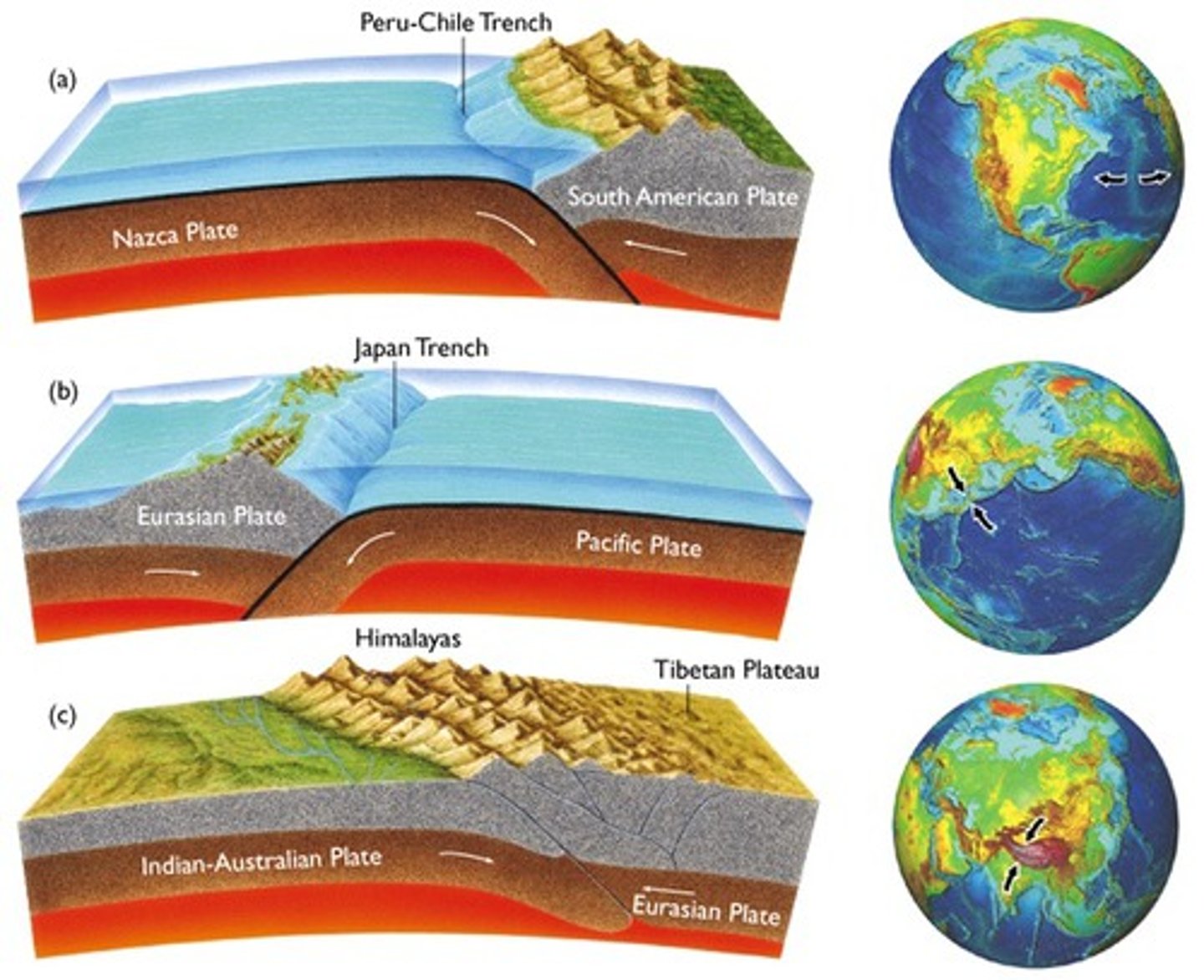
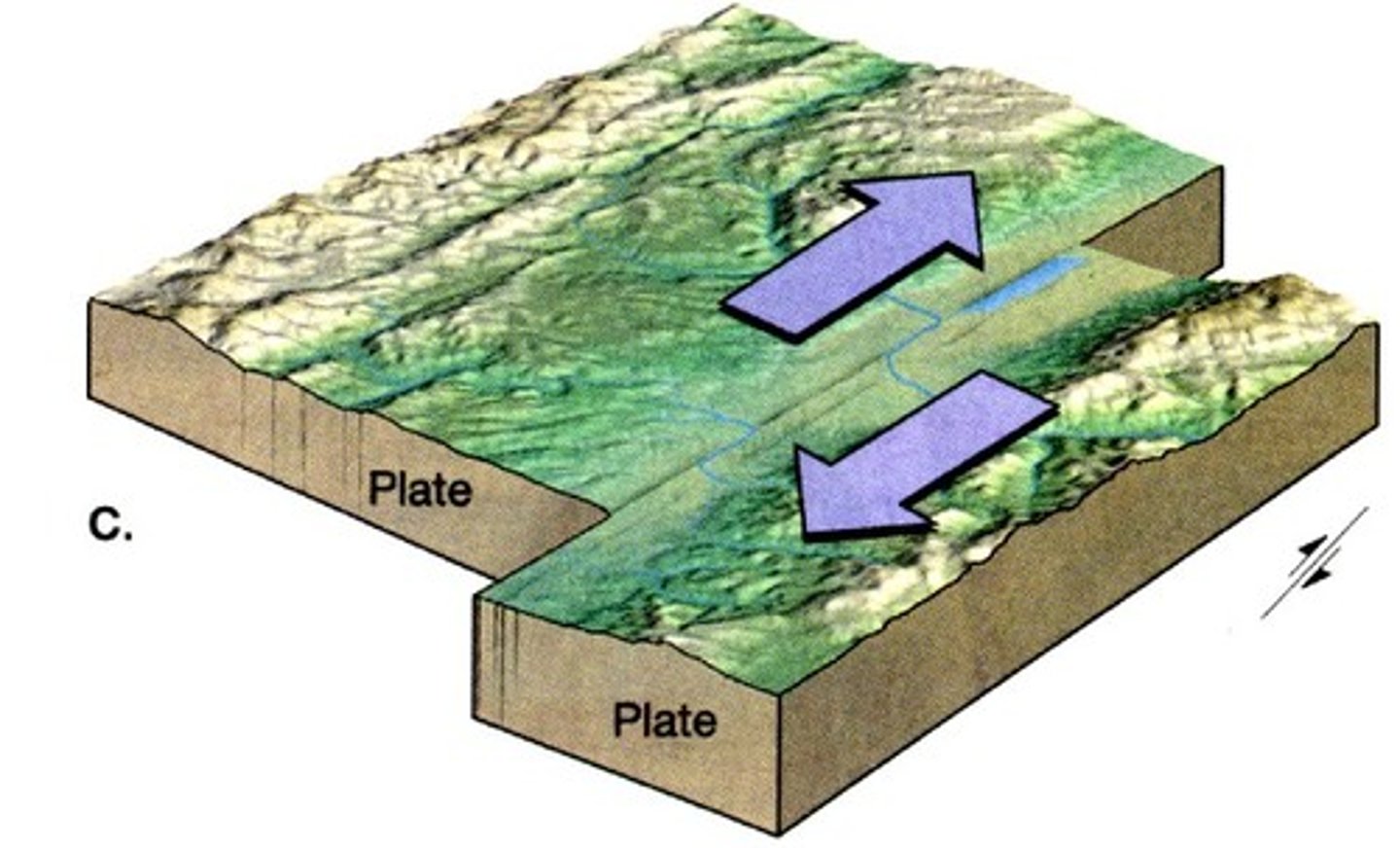
Transform Boundary
A place where two tectonic plates slide past one another.
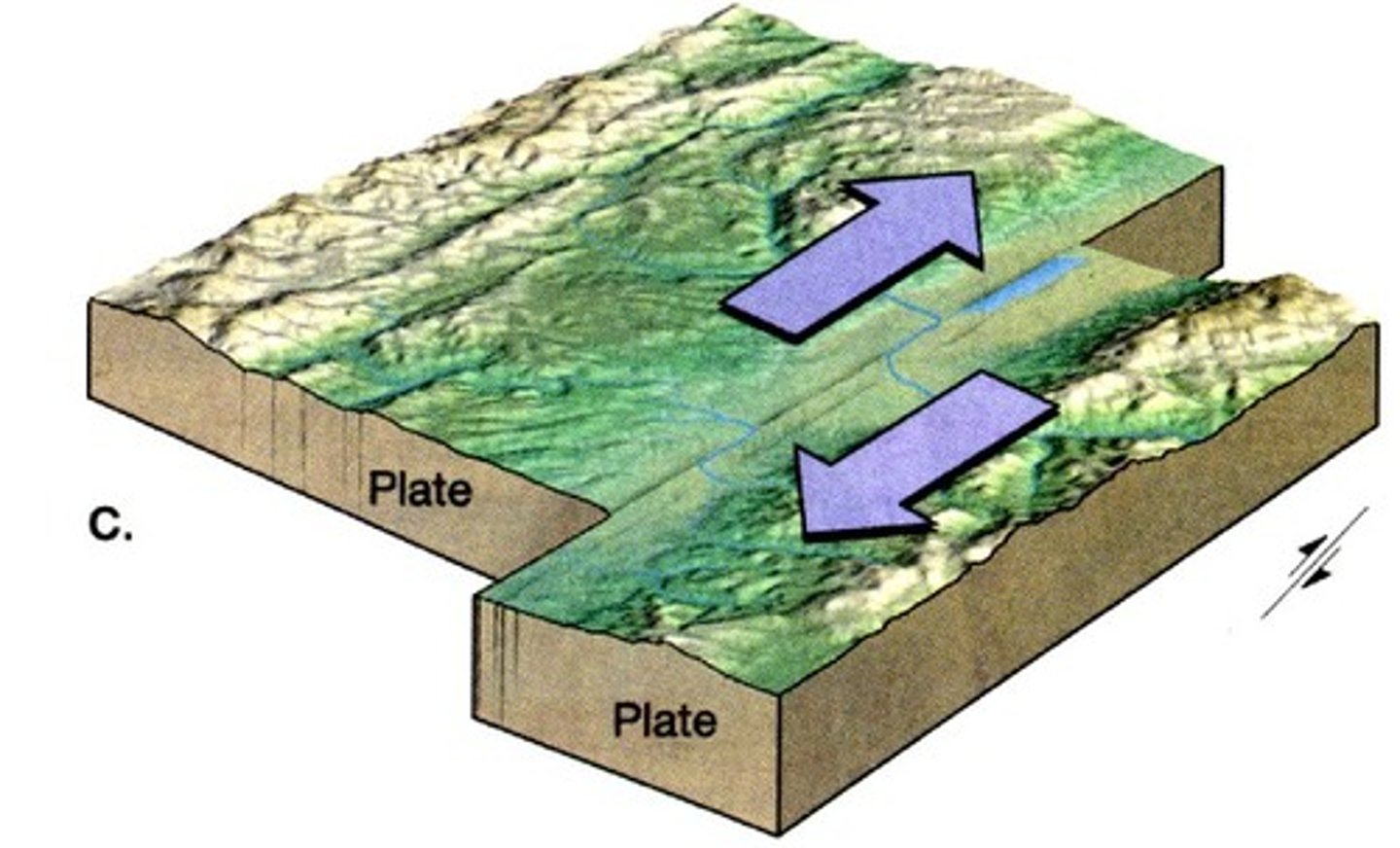
Plate Tectonics
This theory states that Earth's plates are in slow, constant motion, driven by convection current in the mantle.
Fault
Break in the Earth's crust where rocks have slipped past one another.
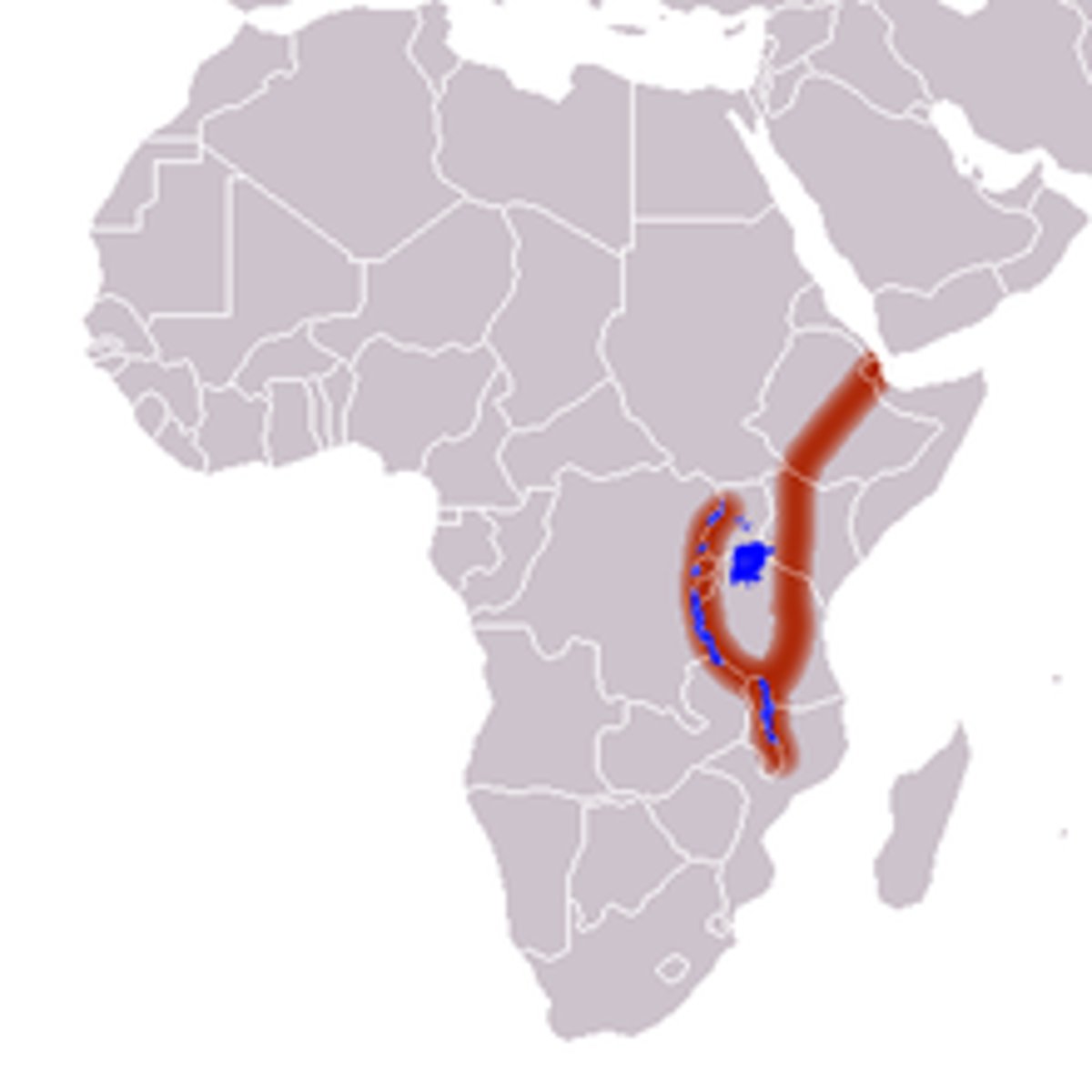
Rift Valley
The landform appears where crust diverges on land.
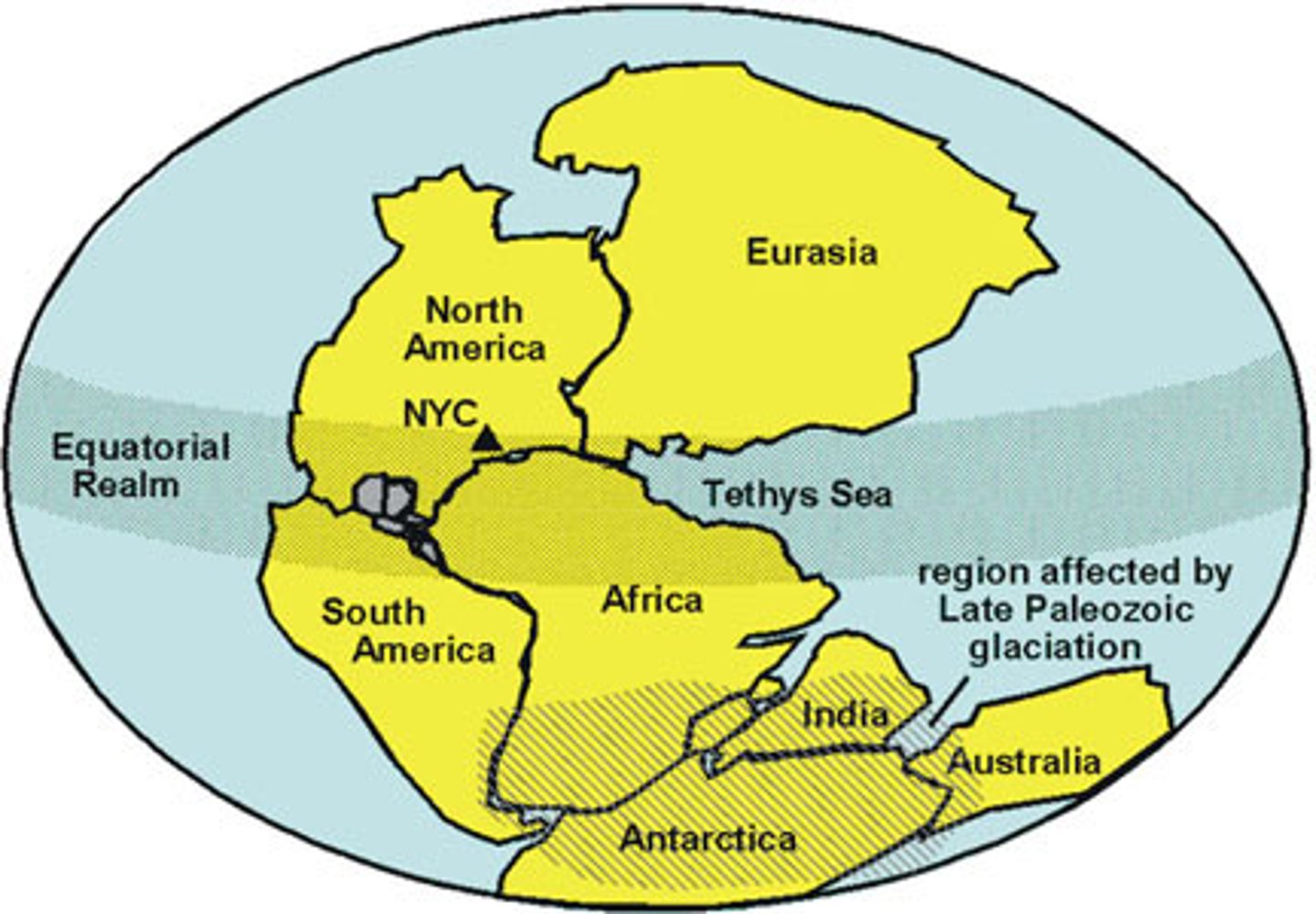
What did Wegener think happens during continental drift ?
Continents slowly move over time
New crust forms at...
Mid-ocean ridges
Oceanic crust is subducted and destroyed (returned to the mantle) at ...
deep-ocean trenches
How do mountains form?
Continental plates collide
At what boundary type do two plates pull apart?
Divergent
What tectonic plate do we (Florida) live on?
North American Plate
Bonus question: What is Ms. Ryan's favorite plate (name)?
Juan de fuca
Strato-Volcanoes, those which produce sudden and violent eruptions, are MOST likely to be found along what type of plate boundary? (Divergent, Convergent, Transform)
Convergent
How did the Himalayan Mountains form?
The Indian and Eurasian continental plates colliding
How are earthquakes measured?
By seismometers which make seismographs.
What evidence did Alfred Wegener use to propose his hypothesis of Continental Drift?
The landmasses today look like they could fit together like the pieces of a Jigsaw Puzzle, Similar fossils on opposing continents, and evidence of tropical plants in places that could never support that kind of life unless they had moved!
Evidence of seafloor spreading includes:
The pattern of sediment layers, radiometric dating of seafloor (younger rock found closer to the ridge, older rock further away) and the magnetic patterns found on the seafloor
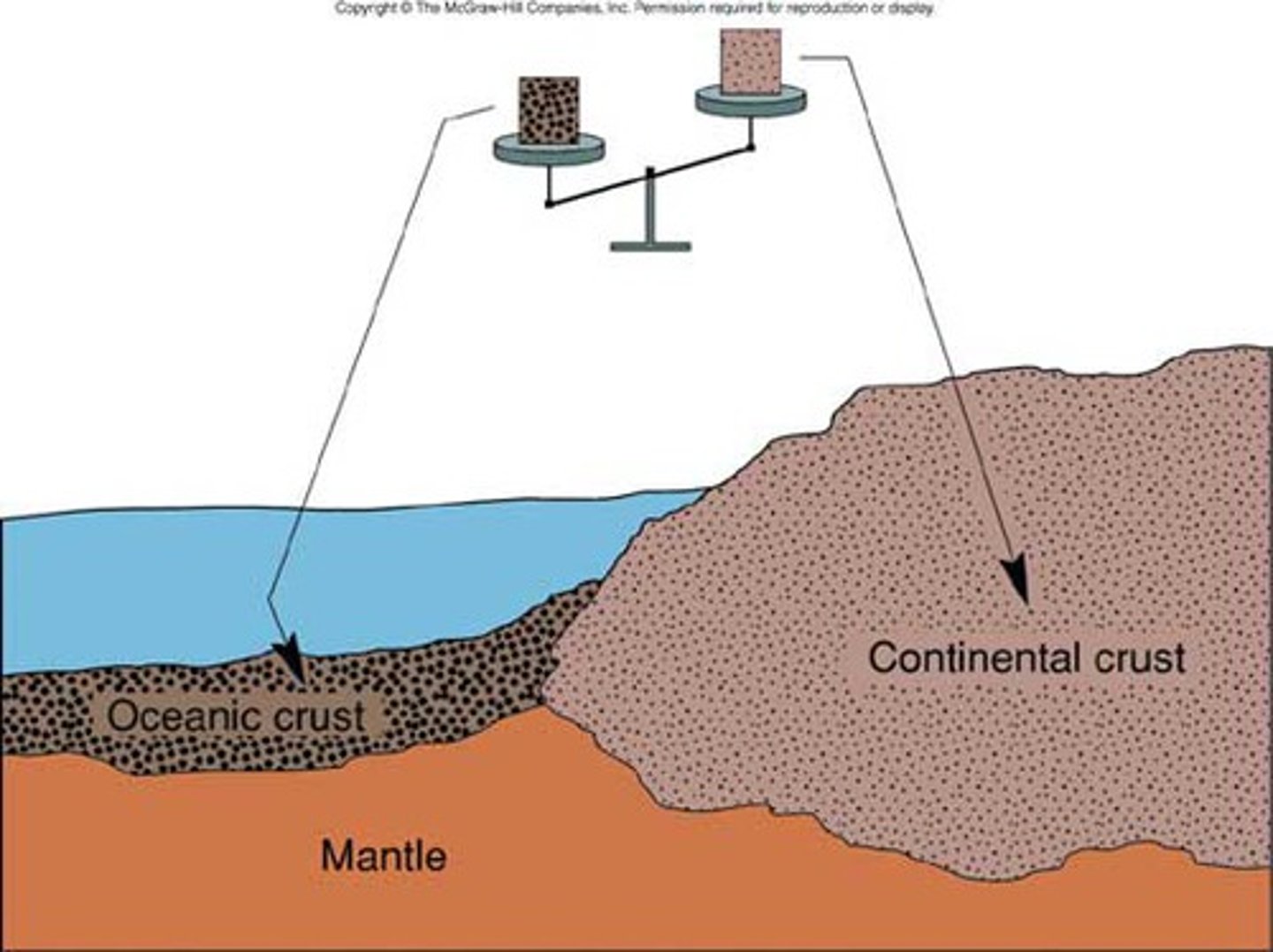
continental crust
The portion of the earth's crust that primarily contains granite, is less dense than oceanic crust, and is 20-50 km thick
oceanic crust
thinner, more dense, younger crust making ocean floor, mostly made of basalt
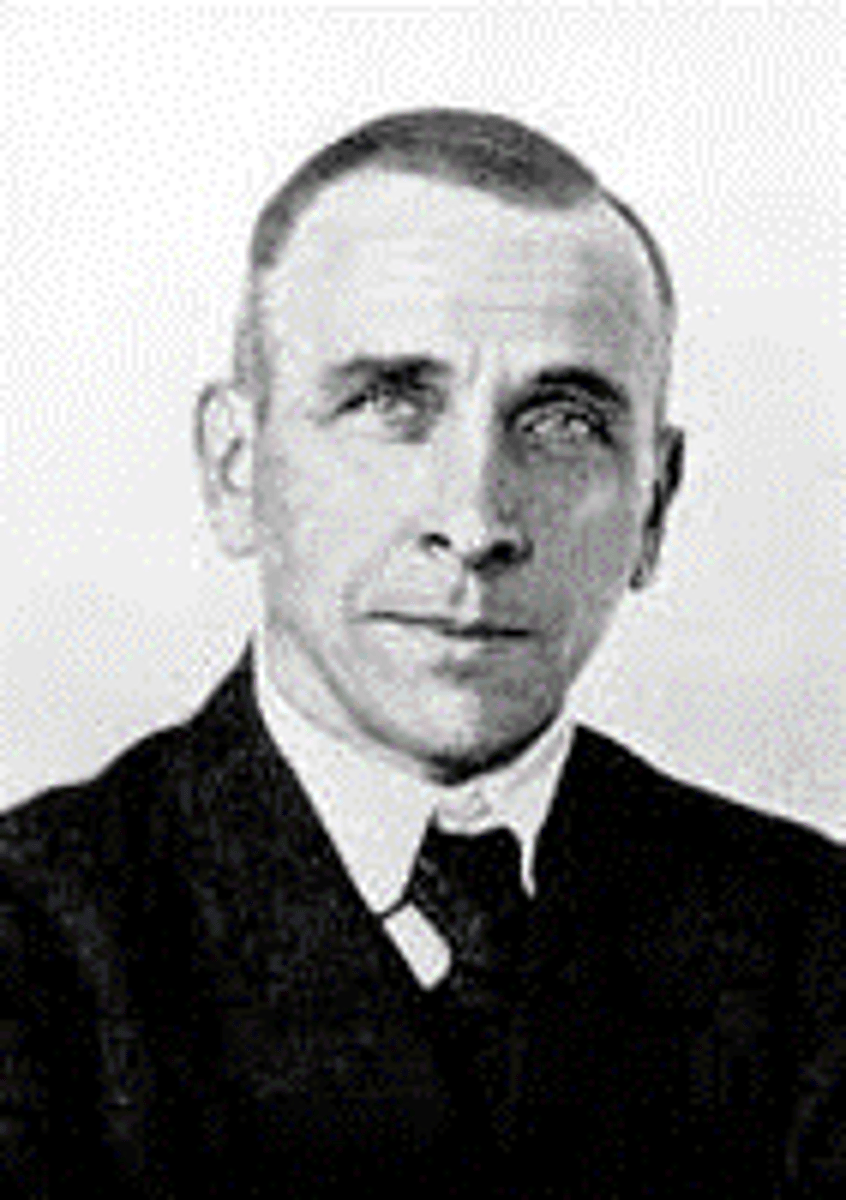
Alfred Wegner (1880-1930)
German Meteorologist who proposed the theory of continental drift in 1912. He could not determine what the driving force behind continental movements was. Despite several lines of evidence the scientific community at the time overwhelmingly rejected his idea that the continents could move. He died in Greenland on a scientific expedition to study weather.

Harry Hess
American geologist who is considered one of the founding fathers of the theory of Plate Tectonics. He discovered seafloor spreading (published in 1962) based on mapping of the ocean floor using SONAR data that he collected during World War II.
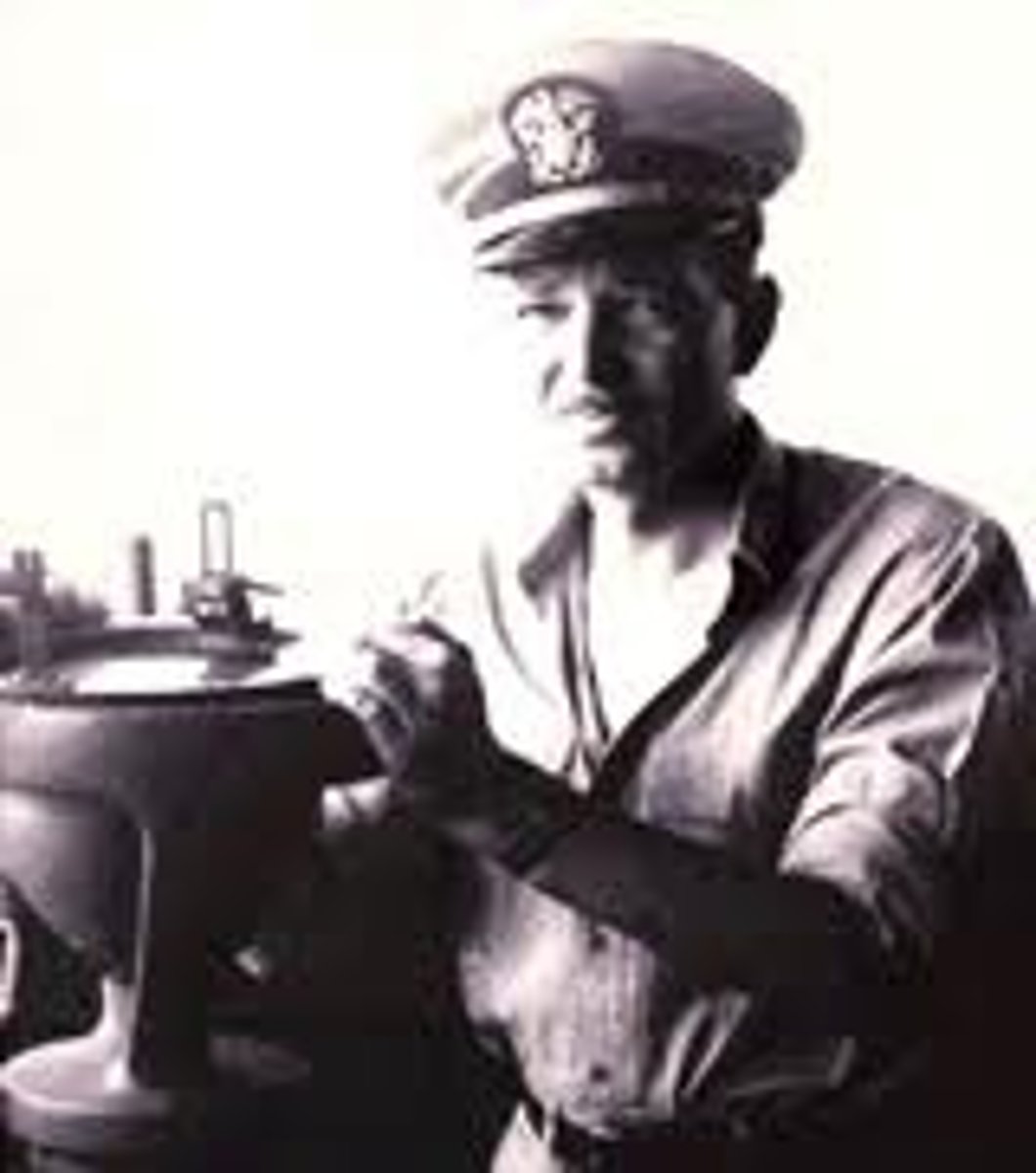

Many of the technologies used to discover evidence that led to plate tectonics theory were a by product of what events in US History?
Military activity during war times. WW2 - Sea floor Spreading was discovered from SONAR and magnetometers identified the matching mineral banding patterns on either side of the mid-atlantic ridge. During the Cold War seismometers deployed by the US military identified plate boundaries based on earthquake patterns.

Seafloor Spreading (step-by-step process)
Lava pushes through the boundary between two tectonic plates. The lava cools and hardens into new igneous rock. Rocks are pushed further away from the ridge by the newly formed rock. Over millions of years, rock is continually being pushing away form the ridge resulting in the movement of continents.