Physiology Exam 3 Lecture 9B [The Vascular System and Blood Flow: Cabeza]
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Most of your blood is in _____ circulation
systemic
mostly in the veinous side
Characteristics of systemic circulation
Operating pressure is high
Response to increase CO2 = Dilate
Resistance to flow = variable
Length of vessels = long
Vessel compliance = variable
Characteristics of pulmonary circulation
Operating pressure is low
Response to increase CO2 = Little effect
Resistance to flow = low
Length of vessels = short
Vessel compliance = very high
Both arteries and veins contain a tough outer layer called the
Tunica adventitia (connective tissue that holds everything together)
Arteries have a _____ muscle layer and Veins have a ____ muscle layer
Thick, thin
Muscle layer (Tunica media) is all
Circular smooth muscle
no longitudinal smooth muscle in Blood vessels
Elastic and white fibrous tissue
Gives elasticity to blood vessels allowing them to stretch
Innermost layer of blood vessels
Tunica intima (endothelium)
layer of cells
Anatomy difference between veins and arteries
veins have unidirectional valves (only in the majory veins)
Arteries do not have valves
No exchange of gases, nutrients, or wastes takes place at the
Major vessels.
Major vessels have their arterioles and capillaries to provide them with necessary blood
All exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes takes place at the
Capillaries
The terminal arteriole is the
blood vessel leading up into the capillary
Only one cell thick (only the endothelium)
Blood enters the capillary bed through a structure called the _____ and then this structure spreads out into a bunch of capillaries
metarteriole
There are _____ that regulate if the capillary is open or closed
Sphincters
Blood enters the capillary through the arterial side goes through the capillary and then returns to the veinous side for flow
Yes, yes it does
In a closed capillary
Sphincters constrict
greatly reduced flow into capillaries
mainly goes through metarteriole to throughfare channel and then back into venous side
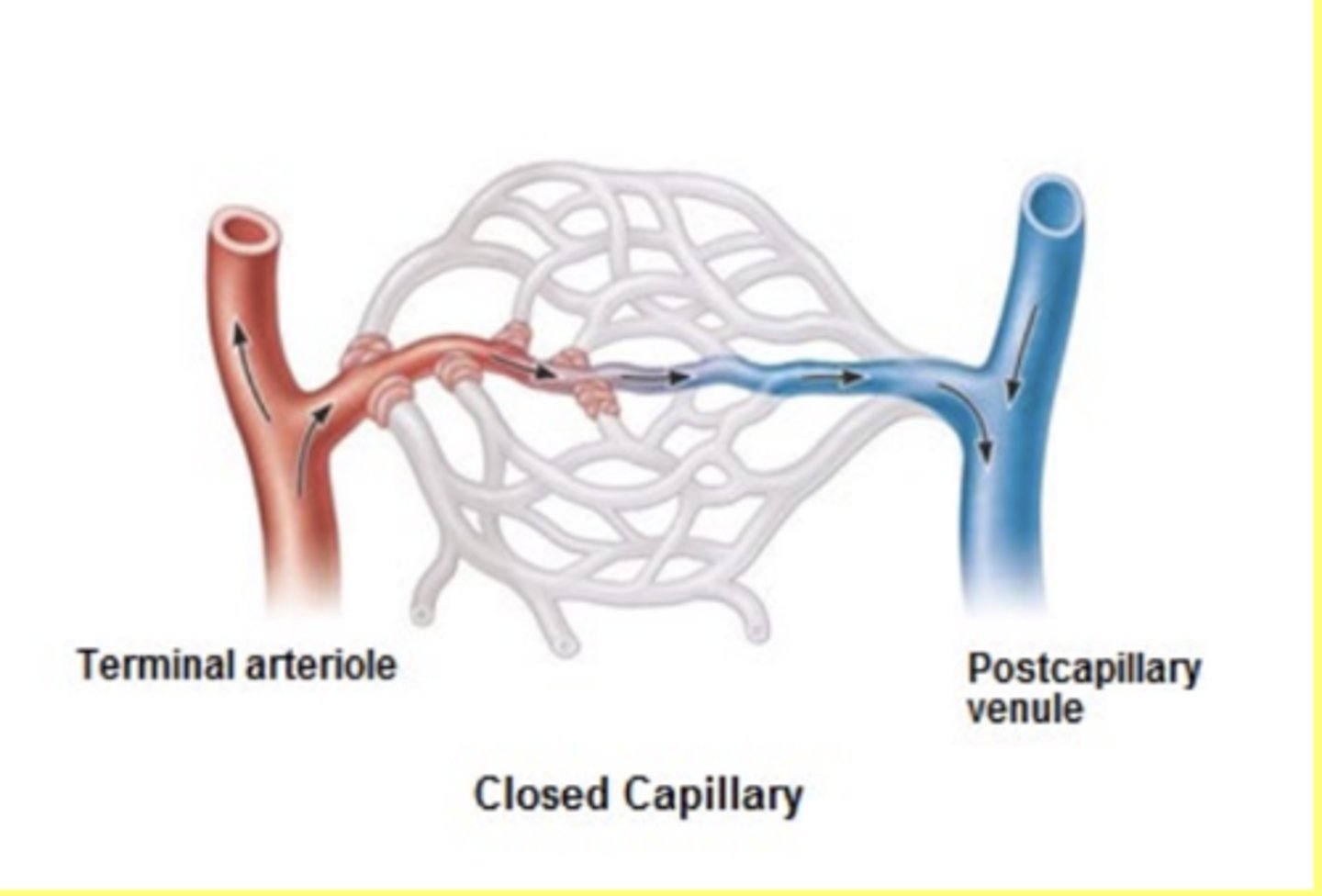
Capillaries do not have ______ muscle
smooth muscles
All capillaries are _____ cell thick, containing only the ____
one, endothelium
Being only one cell thick allows for
exchange of materials easier and faster
Conducting arteries are ______ and help maintain pressure
compliant
Vessel expands when you pump blood into it and then squeezes on the blood due to its
elastic properties
(its not contracting it is elastic)
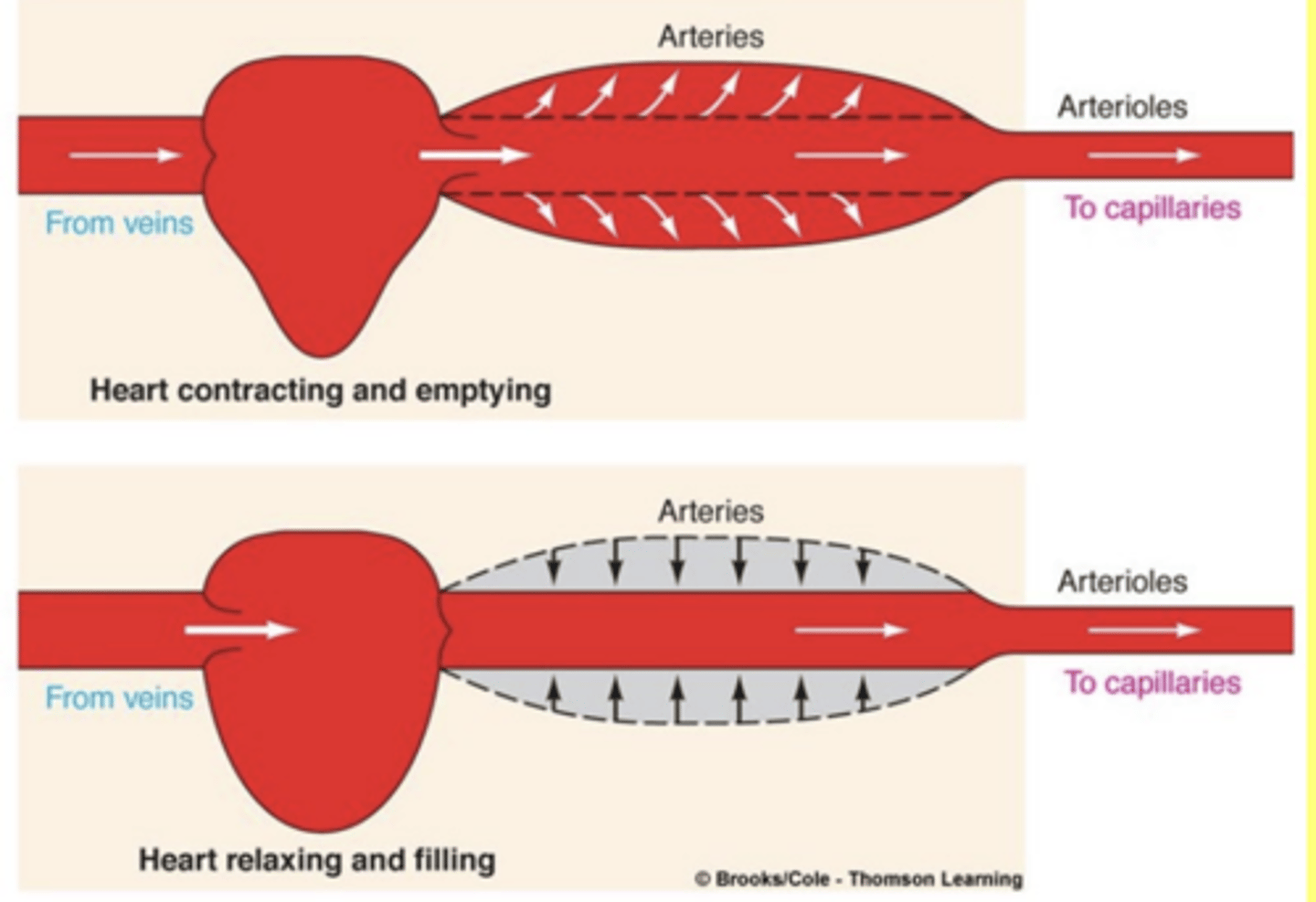
Veins are _____ complaint than the arteries and operate at lower pressure
more
Because of the property of veins being more compliant than arteries is the reason why
blood is more on the venous side than artery side of the body
Veins operate under ___ pressure
low
Veins travel between
major muscle masses
as muscle contracts it squeezes veins
Veins are very compliant, have valves, and along with muscle contraction they help insure
unidirectional flow
SUMMARY: The pulmonary circulation has ___ of the blood, is extremely ____, is short, and operates at lower pressure
10%, compliant
SUMMARY: The systemic circulation has __ of the blood, is ______ in compliant, is long, and operates at higher pressures
90%, variable
SUMMARY: All blood vessels contain a
smooth muscle layer and a 1 cell thick endothelium
SUMMARY: Exchange of all materials takes place on at
Capillaries
SUMMARY: Artery compliance is important for
blood pressure
SUMMARY: Major veins have ________ to ensure flow towards the heart at low pressure
one way valves
Ohms Law for fluid flow
Q = Blood flow
Blood flow = driving pressure divided by the resistance
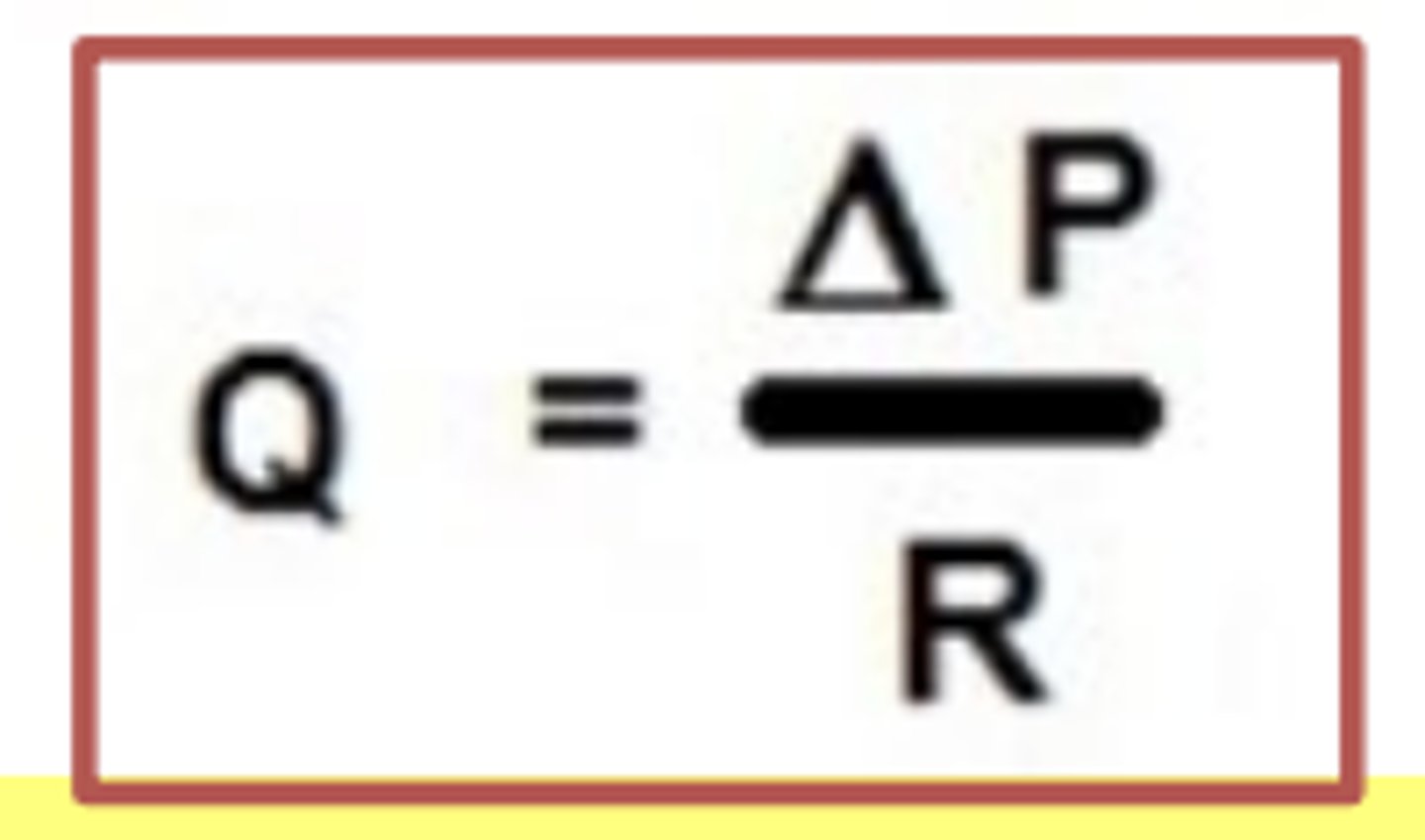
The bigger the driving pressure we get _____ blood flow
more
The higher the resistance
Blood flow goes down
The resistance for the flow of blood depends on the
blood vessel anatomy
Serial resistance
Rt > largest single resistance
total resistance is higher than the highest resistance of any given part. Because its additive
Parallel resistance
Rt < smallest single resistance
Total resistance is always lower than the lowest resistance of any given part
In the circulatory system most of the systems are
Parallel
Because we want low resistance
Circulatory system through the digestive tract going to the liver
Portal system
Branch of capillaries that reform and then reforms a whole bunch of different capillaries in another organ
Thus GI system has higher resistance due to this portal system
The renal system is also
A portal type system
Poiseuille's law
Relates how different factors relate to resistance
n = viscosity
r= radius
L= Length
ΔP = difference in pressure
π = 3.14
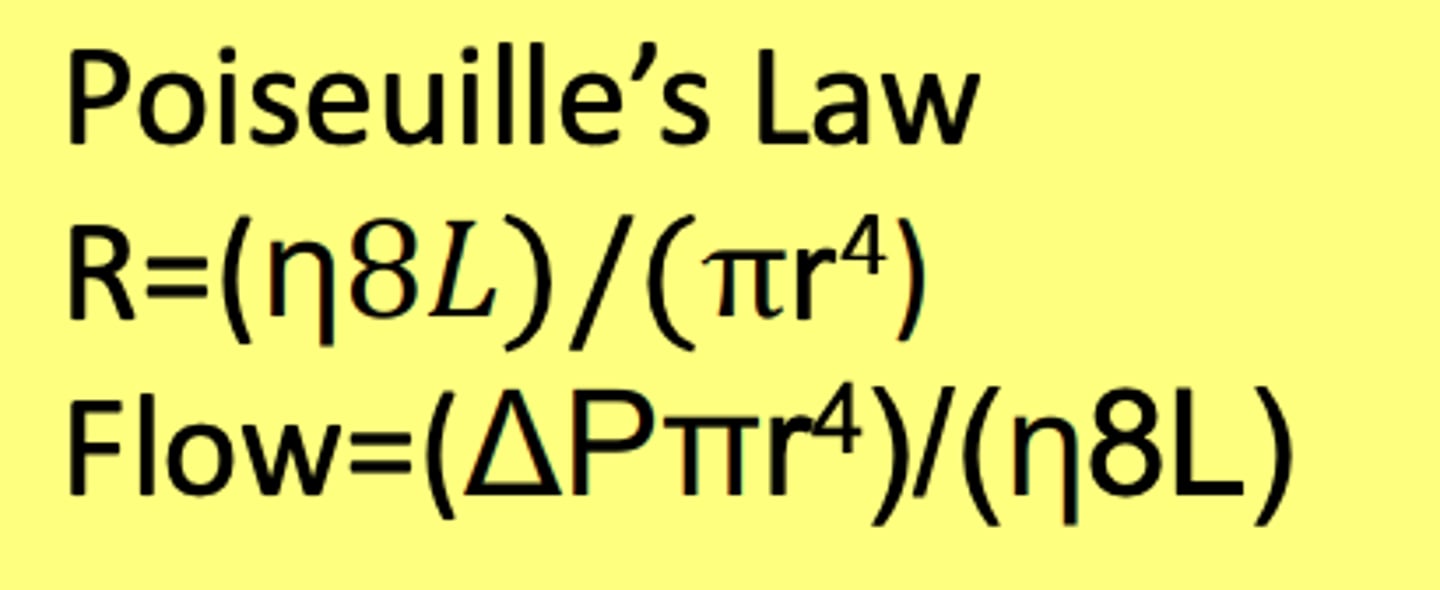
BREAKING DOWN POISEUILLE: Length (L)
The longer the length of a blood vessel the more resistance
BREAKING DOWN POISEUILLE: Viscosity (n)
The more viscous the higher resistance
NOTE:
Viscosity is how thick a liquid is. So it makes since that the thicker it is the more resistance
BREAKING DOWN POISEUILLE: radius (r)
The higher the r value the lower the resistance.
r is to the 4th power in the equation meaning that when you chance it it has a major effect on resistance.
NOTE:
If something is ever in the denominator it has an inverse relationship. Thus decrease r = increase Resistance
Poiseuille's law is important
because it is by regulating the diameter of the arterioles that we can have a large effect on blood flow through a given capillary. The state of the precapillary sphincters plays the major role in regulating blood flow through a capillary bed
The pulsatile blood pressure is maintained by the
major arteries because of their compliance and muscular layers
From the terminal arterioles all the way back to the heart pressure is
steadily falling with only about 20 mm/Hg of pressure driving blood back to the heart
The largest fall in blood pressure occurs at the
arterioles. Because these have the highest resistance. These are the major resistance vessels that help to maintain the general or systemic blood pressure
The most resistant vessels are the
Arterioles
Pulse pressure is
the difference in pressure experienced by the major arteries between systole and diastole:
Pp = Psys - Pdias
120 mmHg - 70mmHg = 50 mmHg
The mean arterial pressure
MAP = Pdias + 1/3 (Pp)
70 mmHg + 17 mmHg = 87 mmHg
As you get older your Blood vessels get
Harder
As vessels get stiffer they
are less compliant
Systolic pressure goes up
Disystolic pressure goes down
MAP =
CO * TPR (total peripheral resistance)
LaPlace's Law
Tension = Pressure x radius
Therefore, the larger a blood vessel is the more tension will be experienced on the wall of the vessel for the same pressure
Aneurisms occur in ______
larger vessels, never at capillary beds
Although capillaries are very small their combined
cross section is very large
Because of the large cross section of capillaries
blood flow through a capillary bed is slower than in the arteriole or venule associated with it
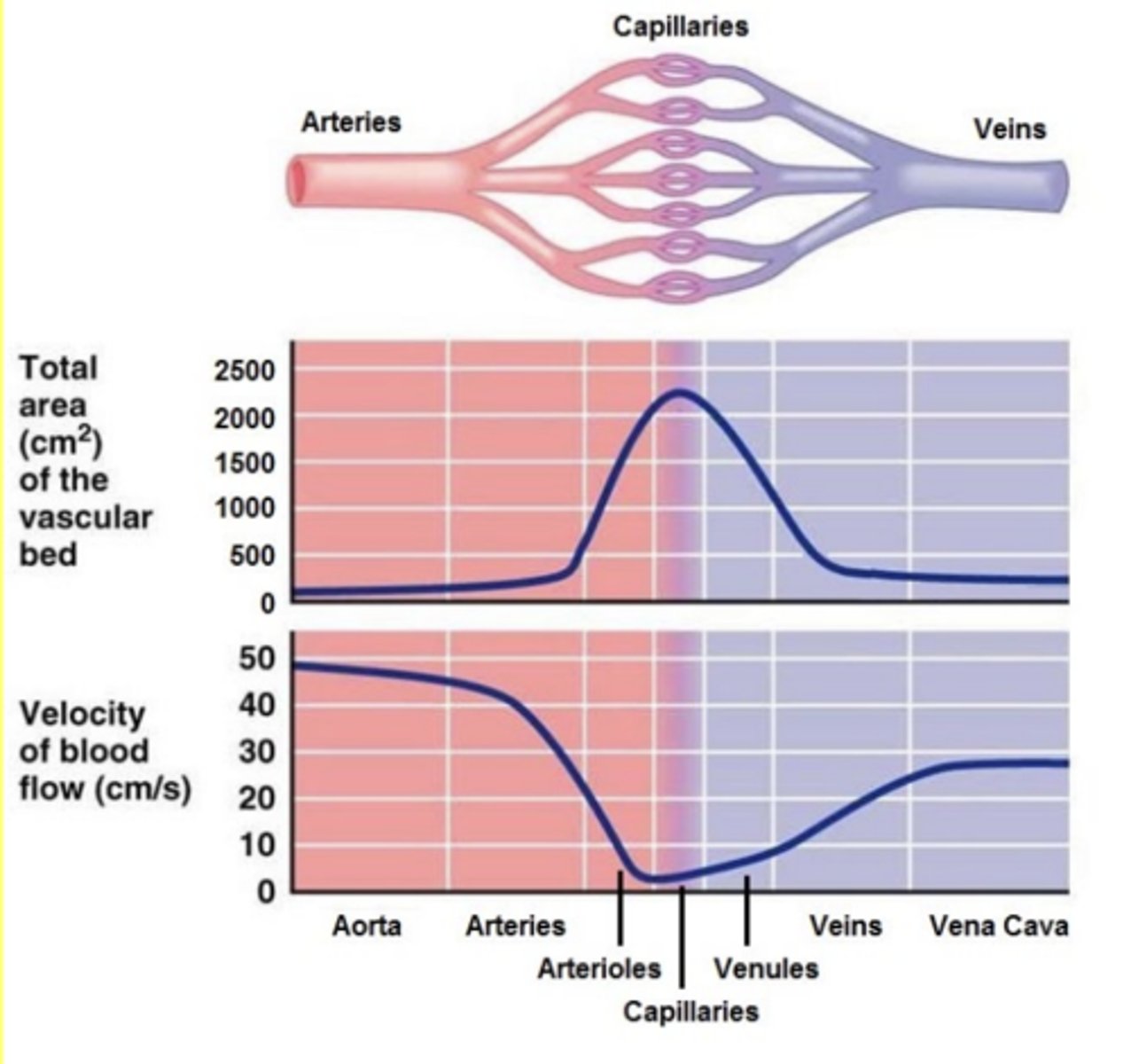
Blood is slowest through
capillaries
Why is blood slowest through capillaries
To allow for exchange
SUMMARY: Flow of blood follows Ohm's law such that flow is proportional to
pressure differences along the blood vessel and inversely proportional to the resistance of the blood vessel
SUMMARY: Overal resistance in one vessel is just the sum
of the resistance of the parts of the blood vessel
SUMMARY: Overall resistance to a vessel that splits into 2 vessels is the product of resistance of each vessel divided by the sum of the resistance. Thus
the resistance of such vessels is always less than the component resistance
SUMMARY: The resistance of a vessel is proportional to 1 over the radius raised to the 4th power. Because of this
small changes to the radius of a blood vessel leads to large changes in resistances and the flow of blood
SUMMARY: The pressure experienced by the walls of a blood vessel are proportional to the radius. Therefore
larger vessels have more tension on their walls and it is only larger vessels that experience the formation of aneurism
SUMMARY: Blood flow through the capillaries is the slowest because
of their large cross sectional area
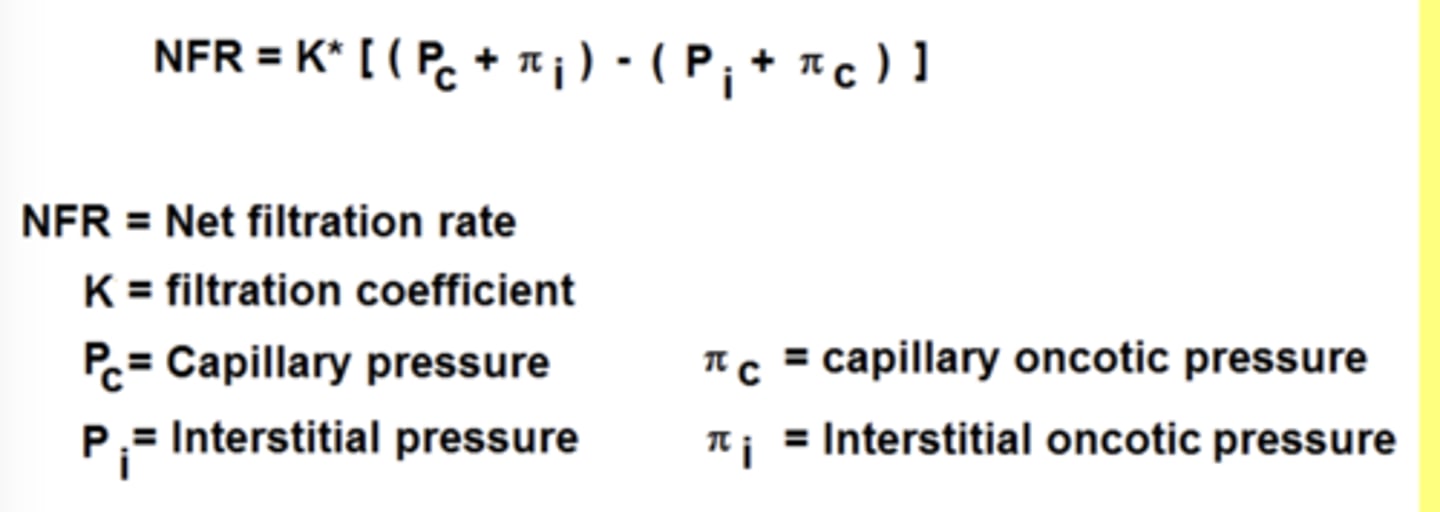
The net filtration pressure for fluid inside and outside a capillary is
NFP = Pressure (out) - Pressure (in)
Hydrostatic pressure is
Always pushing out (pushing pressure)
The pressure that the heart is generating
Oncotic pressure
Pulling force
A form of osmotic pressure (oncotic pressure is osmotic pressure due to proteins)
You can think of hydrostatic pressures as the pressure water itself exerts when
squeezed
Oncotic pressures are
the attraction of water by dissolved proteins
Hydrostatic pressure always ___ water away, while oncotic pressure always ___ water toward them
Push, Pull
Starling-Landis Equilibrium is
Because the capillary hydrostatic pressure is changing as the blood moves through a capillary we need to calculate the NFR at both the
arteriole side of the capillary and at the venule side of the capillary
Measuring both sides of the capillary bed gives us an idea about how the arteriole and venule sides behave and whether there is
an overall net pressure driving fluid in or out of the capillary
At most capillaries there is a net pressure of
1-2 mmHg driving fluid out into the interstitial space
NFR =
K (Hout + Oncotic out) - ( Hin + Oncotic in)
K is a factor determined by how leaky the capillary is
Since there is normally a net pressure driving fluid out of the capillaries we must do something with this fluid or it will
build up in the tissues and there will be a decrease in blood volume occurring at most capillaries being perfused with blood
SUMMARY: Net filtration is determined by pressures driving
fluid out of a capillary minus pressures driving fluid into the capillary
SUMMARY: The rate of Net filtration is determined by
the leakiness of the capillary (K)
SUMMARY: Hydrostatic pressures
push fluid away
SUMMARY: Oncotic pressures
Pull fluid towards them
SUMMARY: At most capillaries there is a net pressure of
1-2 mm/Hg driving fluid out
Lymphatic vessels are found
throughout the tissue
Lymphatic vessels function by
having button-like junctions that act as pores
Valves that allow lymph flow to go in one direction
Usually run next to veins so that muscles can help pump the fluid back to the heart
The lymphatic vessels connect to
nodes which are part of the immune system
The lymphatic vessels drain their fluid
into the subclavian trunks of the venous system so that the fluid can return to the heart and the circulation
SUMMARY: Lymphatic vessels have blind ends with ______ valves that allow fluid into the vessels
button
SUMMARY: Lymphatic vessels have valves and run along
side veins to help move fluid towards the heart
SUMMARY: The fluid of the lymphatic system re-enters the circulation at
the subclavian veins
KEY TERM: Pulmonary circulation
blood circulation from the right heart to the lungs
KEY TERM: Systemic circulation
blood circulation from the left heart to every part of the body except the lungs
KEY TERM: Arterioles
major resistance vessels of the circulatory system which account for the overall blood pressure
KEY TERM: Endothelium
the one cell thick inner lining of all blood vessels which also form the capillaries
KEY TERM: Precapillary sphincters
the annular smooth muscle cells that surround the precapillary arterioles and regulate blood flow into the capillary
KEY TERM: Vascular shunt
The vessel through a capillary bed that allows some blood to flow through the bed even when the capillary bed is closed
KEY TERM: Compliance
the ability a blood vessel to stretch and take on a larger volume of blood at a given change in pressure
KEY TERM: Muscle pumps
a structural feature of veins and lymphatic vessels that travel between major muscle groups such as that when the muscle contract they squeeze the vessels and move fluid towards the heart due to the presence of of valves on the vessel
KEY TERM: Ohm's law
The relation between pressure, resistance, and flow.
Flow = Pressure difference/vascular resistance