Phonation
What to study for the quiz:
- ==Extrinsic/intrinsic muscle functions==
- supra/supersubglottic anatomy
- %%what moves the hyoid and thyroid cartilage%%
- }}anterior and posterior}}
- <<what influences pitch to increase?<<
- <<what influences pitch to decrease?<<
Phonation
- Sound is produced by: the vibration of the vocal folds
- Speech sounds are modified within the: pharyngeal, oral and nasal cavities
- Vocal folds lie within the: laryngeal cavity/larynx
- Larynx is the ___ continuation of the respiratory passage: superior
What is the larynx?
- The larynx contains __ bone: 1 bone
- The larynx has __ cartilages ( __ paired) : The larynx has 9 cartilages and 3 of them are paired
- [[The larynx contains these two types of laryngeal muscles: intrinsic and extrinsic[[
- What is the larynx?: This consists of 1 bone, 9 cartilages, 3 paired cartilages and intrinsic and extrinsic laryngeal muscles
How do we describe a “voice” ?
- Pitch: Fo
- Loudness: Amplitude
- 4 Qualities of Voice: Harsh, breathy, hypernasal, hyponasal
Larynx
The larynx sits opposite approximately these cervical vertebral bodies: third, fourth, fifth and sixth vertebral body
In a child, the larynx sits opposite approximately the __ cervical vertebral body: fourth
The larynx sits opposite approximately the fourth cervical vertebral body in __: children
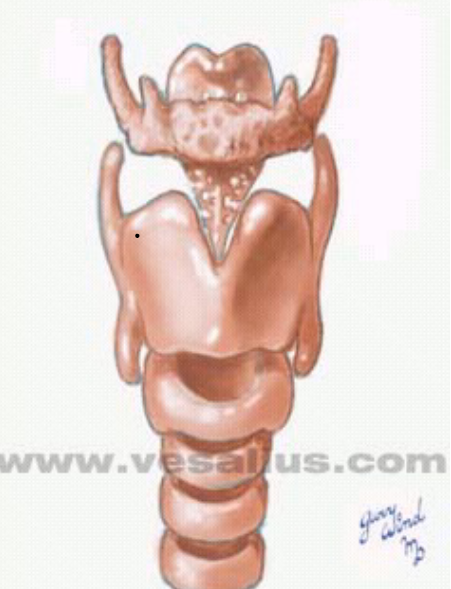
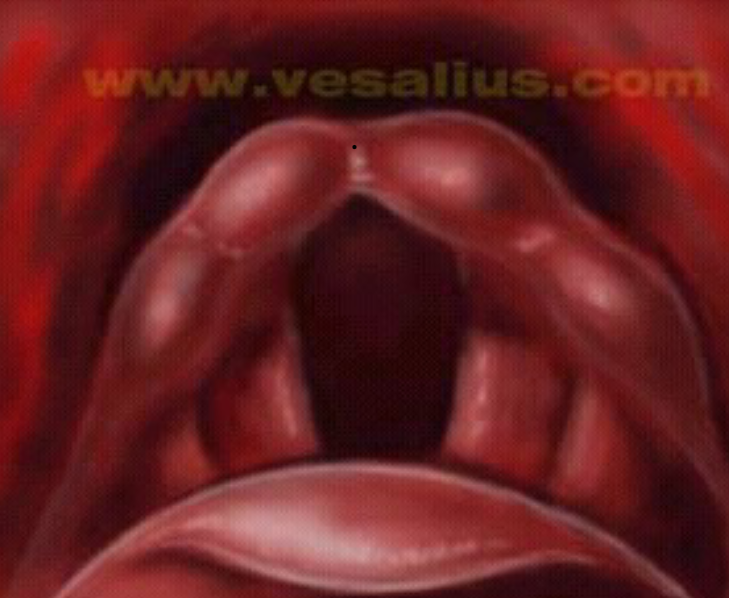
Functions of the Larynx
Three main functions of the larynx: airway protection, phonation and helps on thoracic fixation for specific biological functions
The larynx aids in airway protection by: preventing foreign substances from entering the lungs and expelling the substances trying to enter the lungs (laryngeal reflex activity- cough/spastic closure)
Laryngeal reflex activity: cough/spastic closure
How does the larynx aid in phonation?: It generates sound. (larynx = sound generator)
Larynx = __ generator: sound
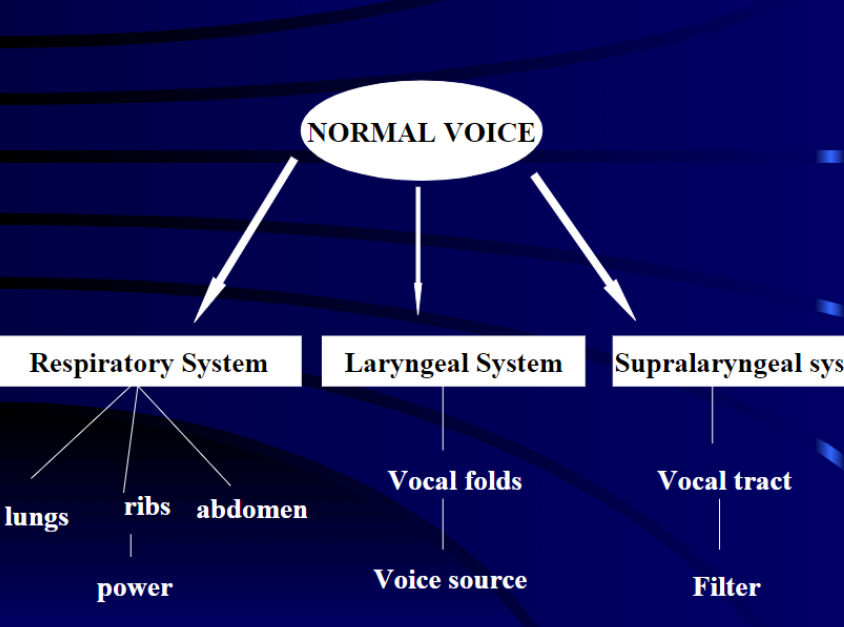
Respiratory system involved in voice production: lungs, ribs, and abdomen provide power
Laryngeal system involved in voice production: vocal folds provide voice source
Supralaryngeal system involved in voice production: vocal tract acts as filter
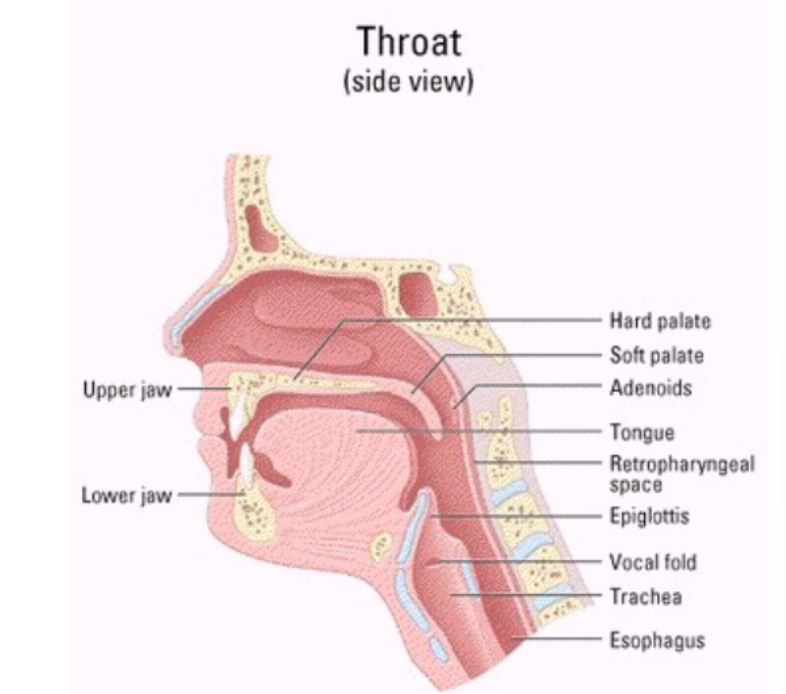
Thoat systems involved in voice production: upper jaw, lower jaw, hard palate, soft palate, adenoids, tongue, retropharyngeal space, epiglottis, vocal fold, trachea, and esophagus
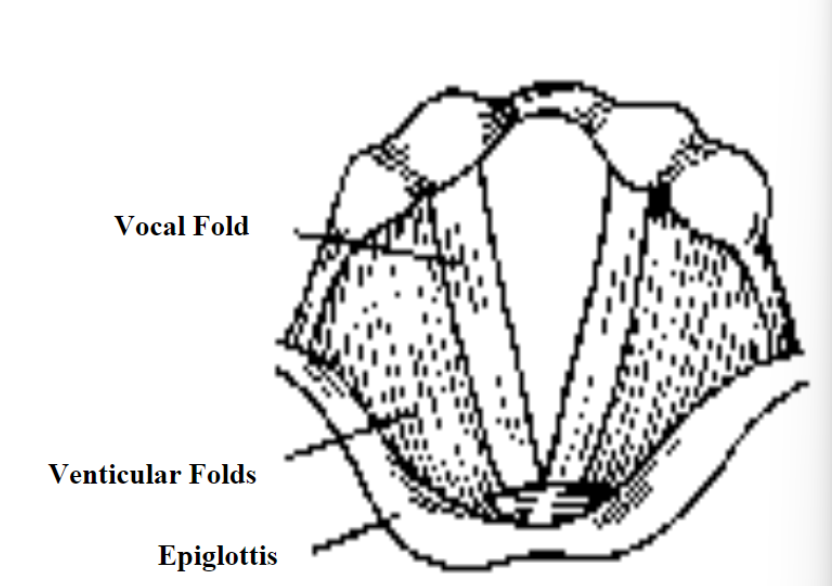
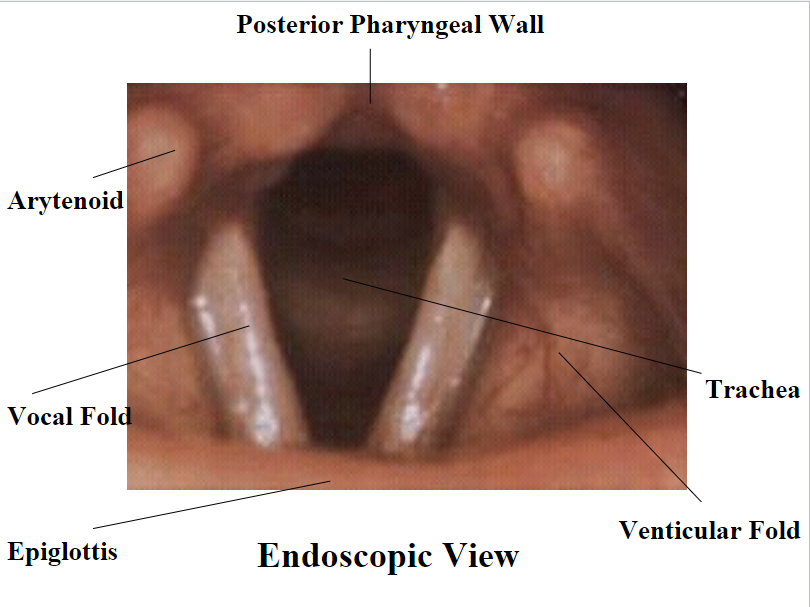
The posterior pharyngeal wall consists of: arytenoid, vocal folds, epiglottis, trachea and venticular fold
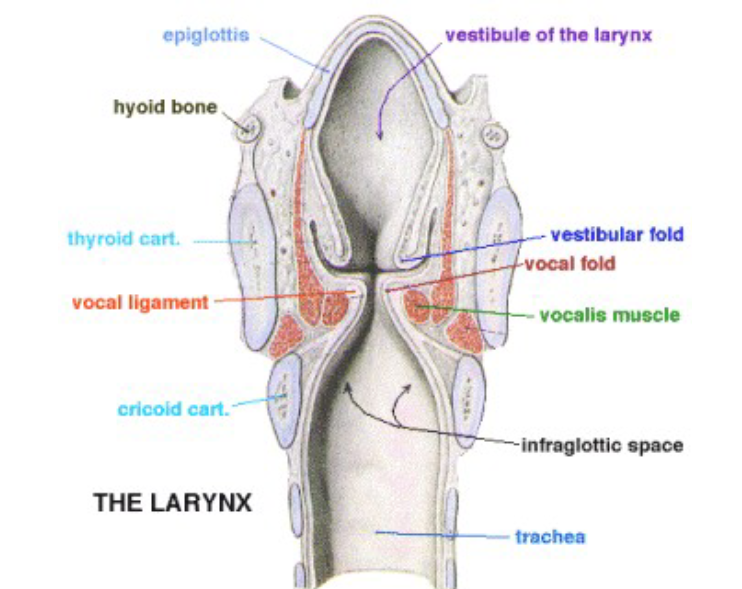
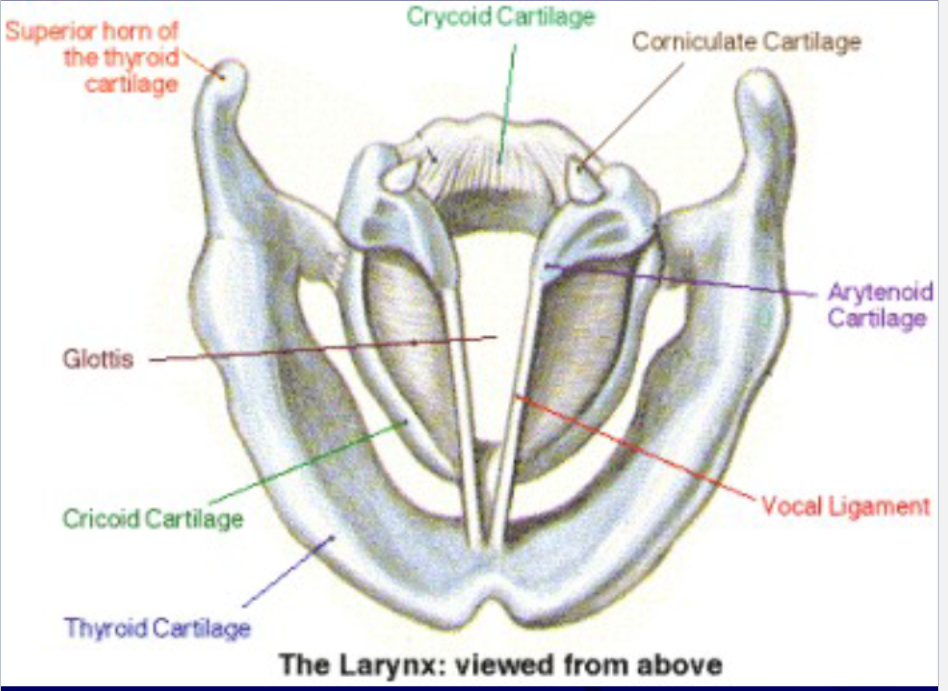
Laryngeal Cavities
What are the three laryngeal cavities?: supraglottal cavity, subglottal cavity, and ventricles
Supraglottal cavity: from the VF to the aryepiglottic folds. It can function as a resonator of the sound produced by the VF
Subglottal cavity: from the VF to the 1st tracheal ring. It’s here that pressure increases until it is sufficient to start VF vibration
Ventricles: lateral space between false and true VF. Resonance
VF: vocal folds you dummy
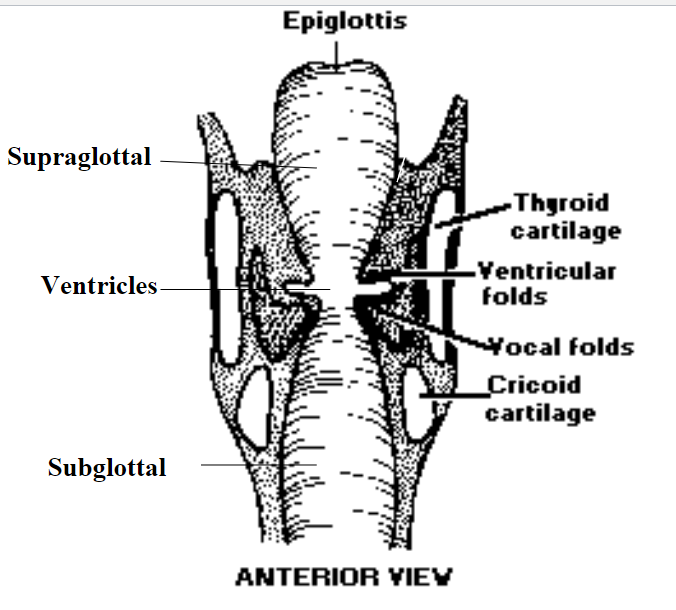
The epiglottis consists of: Supraglottal, ventricles, subglottal, thyroid cartilage, ventricular folds, vocal folds, cricoid cartilage
The 4 Lines of Defense
For the purposes of protecting the airway during a swallow, we have: 4 lines of defense
The 4 lines of defense in protecting the airway during a swallow: epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds, ventricular folds, and vocal folds
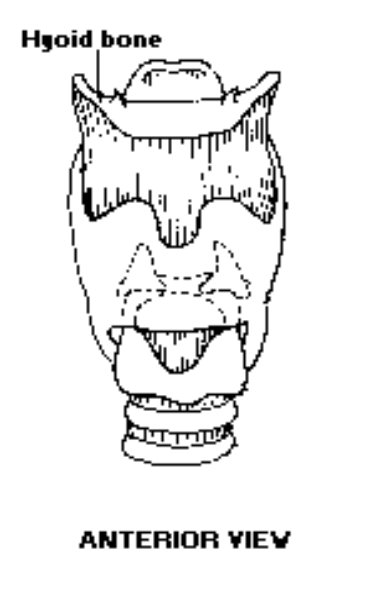
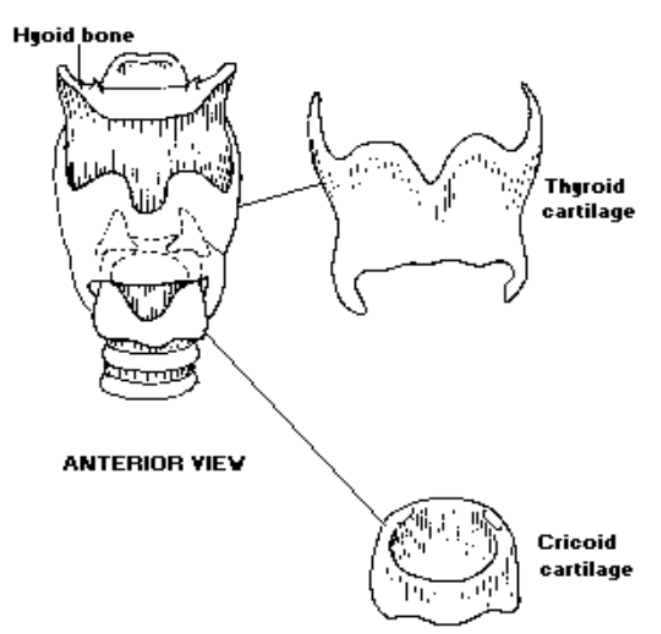
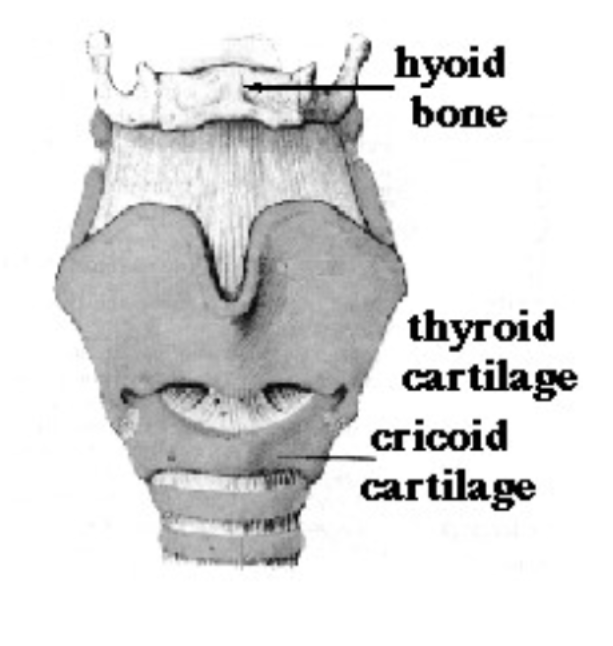
The One Bone: Hyoid Bone
What is the only laryngeal bone? (U-Shaped): The hyoid bone is the only laryngeal bone
This bone is the union between the tongue and the laryngeal structure: The hyoid bone is the union between the tongue and the laryngeal structure
__ bone is the only bone in the body that is not attached to another bone: hyoid
What shape is the hyoid bone?: U-shaped
The hyoid bone is part of the: laryngeal system attachment for superior and inferior extrinsic laryngeal muscles
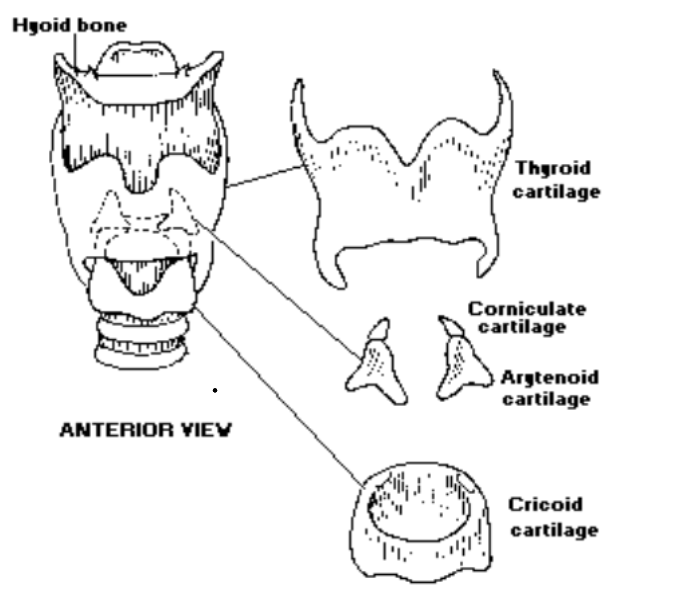
Laryngeal Cartilages
- How many types of laryngeal cartilages are there?: There are six types of laryngeal cartilages
- How many total laryngeal cartilages are there?: There are 9 total laryngeal cartilages and 3 of them are paired
- List out all of the laryngeal cartilages: 1 thyroid, 1 cricoid, 2 arytenoids, 2 corniculated, 2 cunneiforms, 1 epiglottis
- __ / 9 laryngeal cartilages are paired: 3
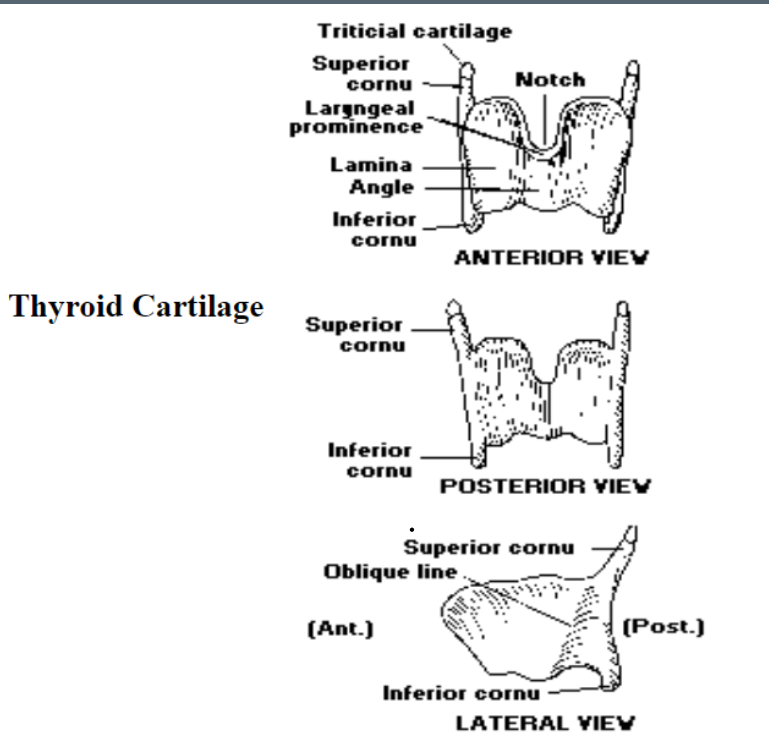
1. Thyroid Cartilage
Is the thyroid cartilage paired or unpaired?: the thyroid cartilage is unpaired
The thyroid cartilage is a __ cartilage: hyaline
The thyroid cartilage superior cornu attaches indirectly to: the major cornu of the hyoid bone
The thyroid cartilage inferior cornu attaches posteriorly to the: cricoid cartilage
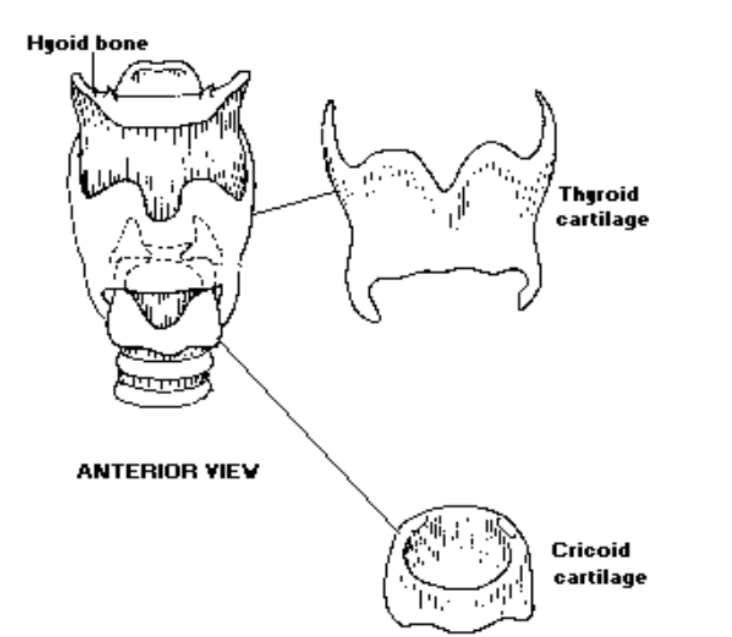
2. Cricoid Cartilage
Is the cricoid cartilage paired or unpaired?: The cricoid cartilage is unpaired
The cricoid cartilage is a ___ cartilage: hyaline
The cricoid cartilage sits on top of the: trachea
The cricoid cartilage is shaped like: a signet ring
The anterior arch of the cricoid cartilage: The anulus is the anterior arch of the cricoid cartilage
The posterior lamina of the cricoid cartilage: THe signet is the posterior lamina of the cricoid cartilage
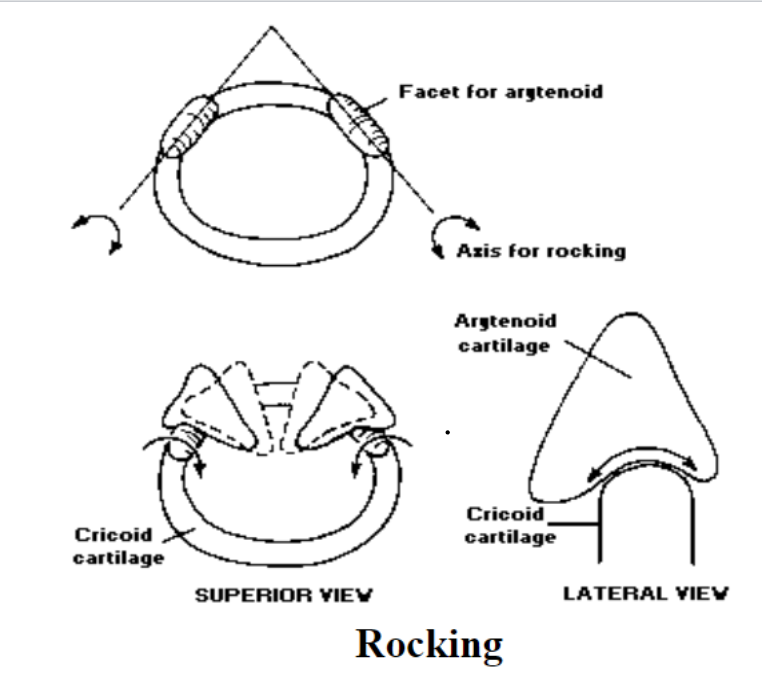
How many articular facets does the cricoid cartilage contain?: The cricoid cartilage contains 4 articular facets
The 4 articular facets of the cricoid cartilage: 2 with thyroid to allow a rocking motion; 2 with arytenoids
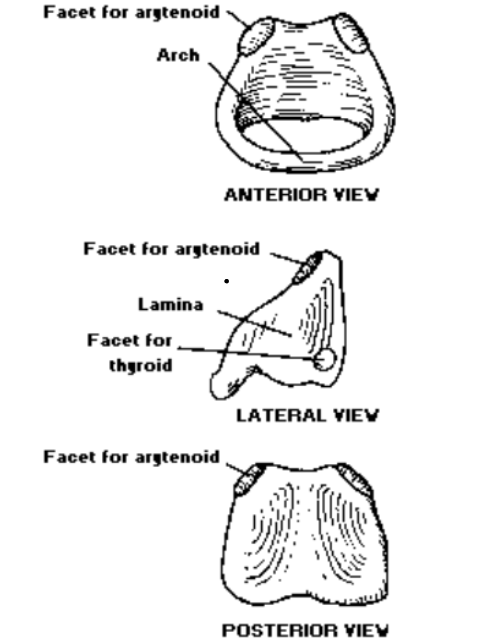
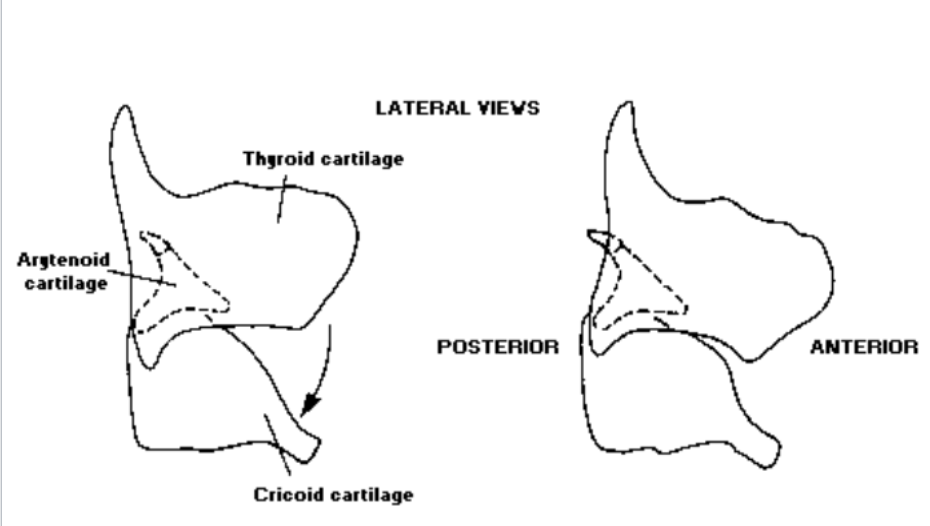
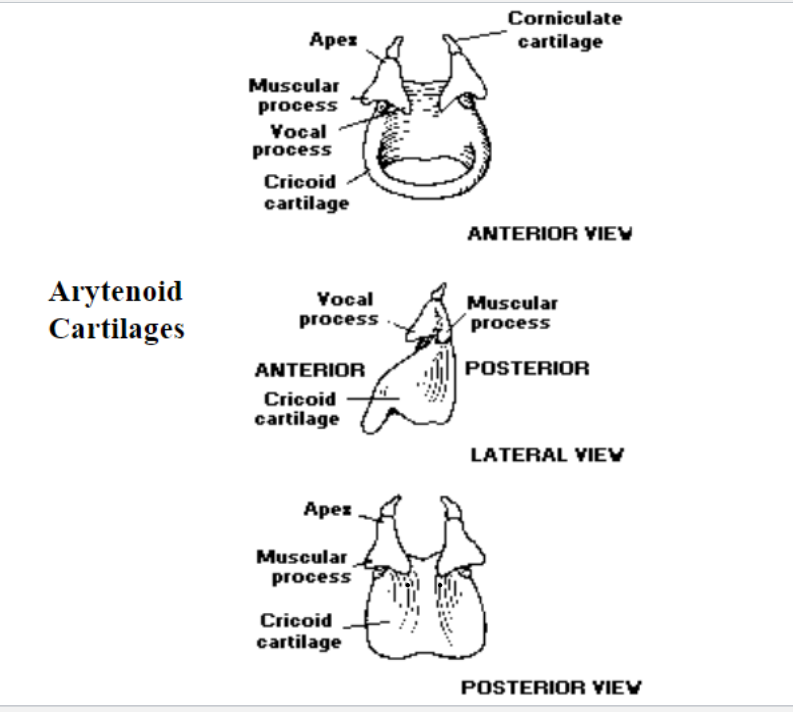
3. Arytenoid Cartilages
Are arytenoid cartilages paired?: Yes, arytenoid cartilages are paired
Arytenoid cartilages consist of these two parts: hyaline + elastic
Arytenoid cartilages position: Arytenoid cartilages sit on top of the superior surface of the signet portion of the cricoid cartilage
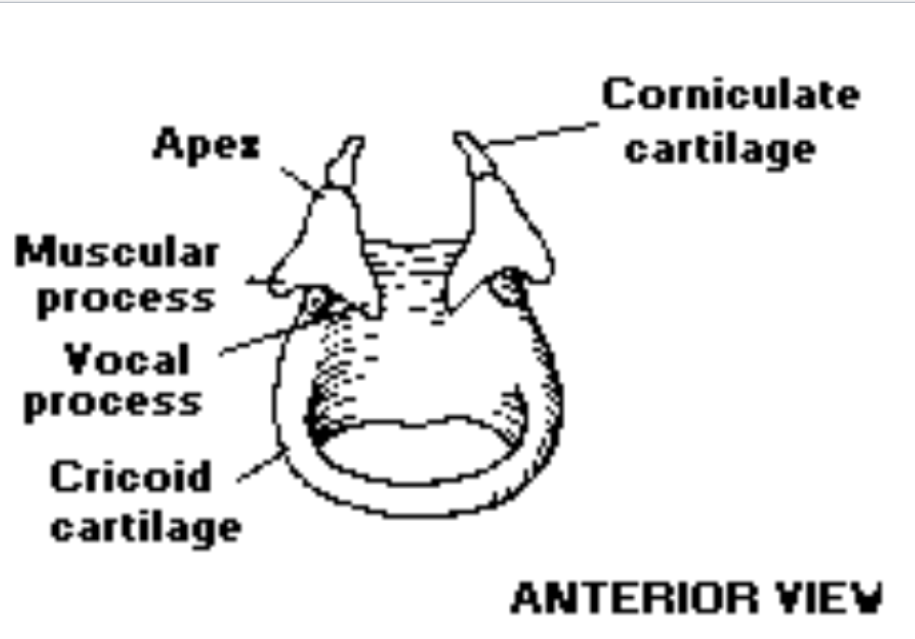
What is the shape of the arytenoid cartilage?: The arytenoid cartilage is pyramid shaped and consists of an apex and base
Arytenoid cartilage lateral projection: Muscular process (insertion of the cricoarytenoid muscle)
Arytenoid anterior projection: vocal process (posterior attach vocal fold)
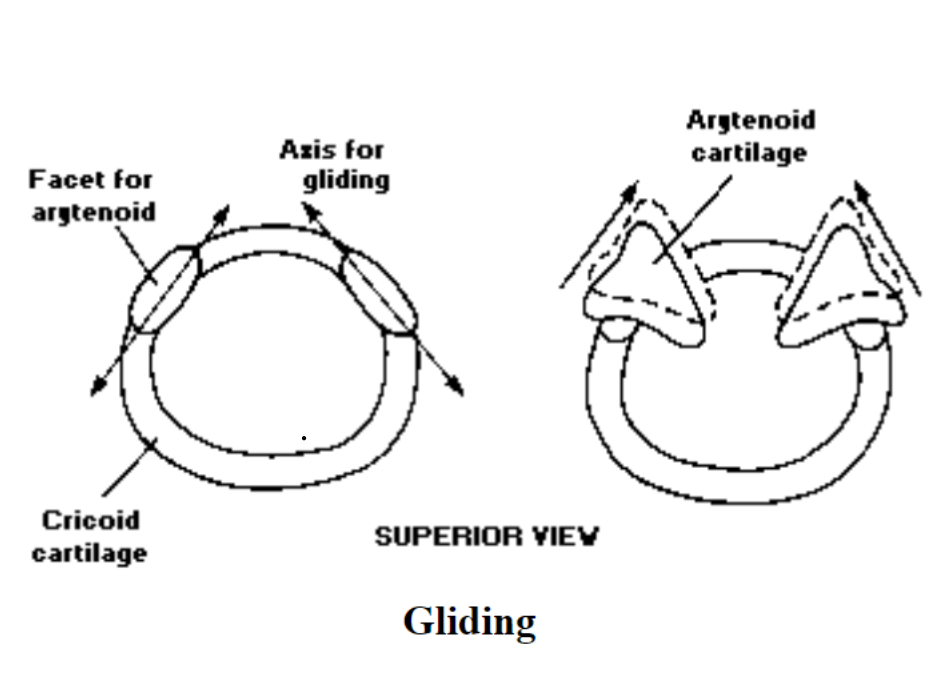
Movements of the Arytenoid Cartilages
What are the different types of movement of arytenoid cartilages?: rocking forward, rocking backward, gliding and NO rotational movement
Arytenoid cartilage rock in these two directions: forward and backwards
Arytenoid Cartilages have NO ___ movement: rotational
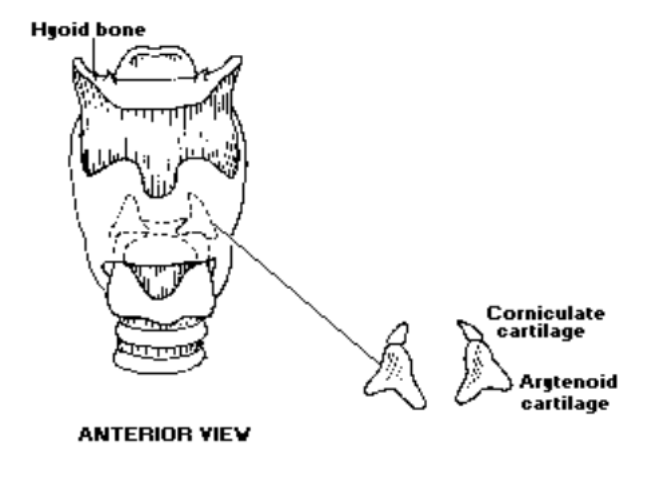
4. Corniculated Cartilages
Are corniculated cartilages paired or unpaired?: Corniculated cartilages are paired
Are corniculated cartilages elastic?: Yes, corniculated cartilages are elastic
Where are corniculated cartilages located?: Corniculated cartilages sit on top of the apex of the arytenoid cartilages
What is the shape of corniculated cartilages?: Corniculated cartilages are pyramid shaped
What is the function of corniculated cartilages?: Corniculated cartilages are part of the arytenoids
5. Cuneiform Cartilages
Cuneiform cartilages are paired with ___ cartilages: small, nod-shaped
Are cuneiform cartilages elastic?: Yes, cuneiform cartilages are elastic cartilages
Where are cuneiform cartilages embedded?: Cuneiform cartilages are embedded in the mucous membranae
What is the biological function of cuneiform cartilages?: The biological purpose of cuneiform cartilages is acting as a supportive framework for a corniculated fold tissue running from corniculate to the epiglottis cartilage = aryepiglottic fold
What is the nonbiological function of cuneiform cartilages: The cuneiform cartilages have no nonbiological role even for phonation
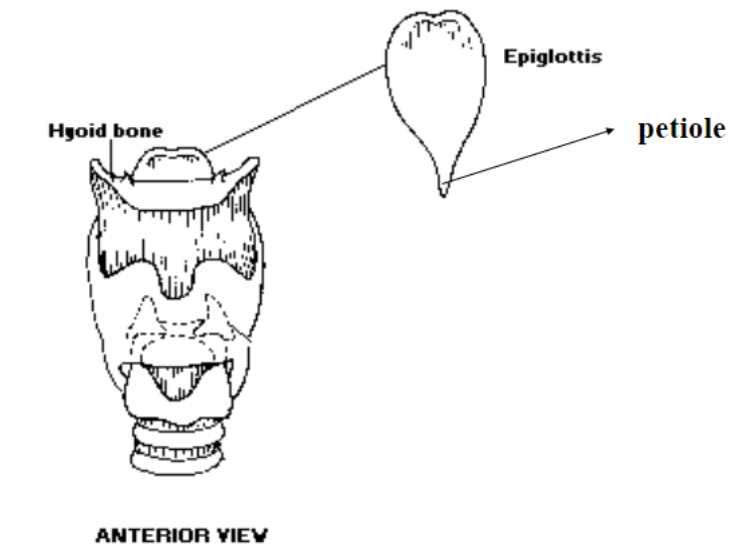
6. Epiglottis
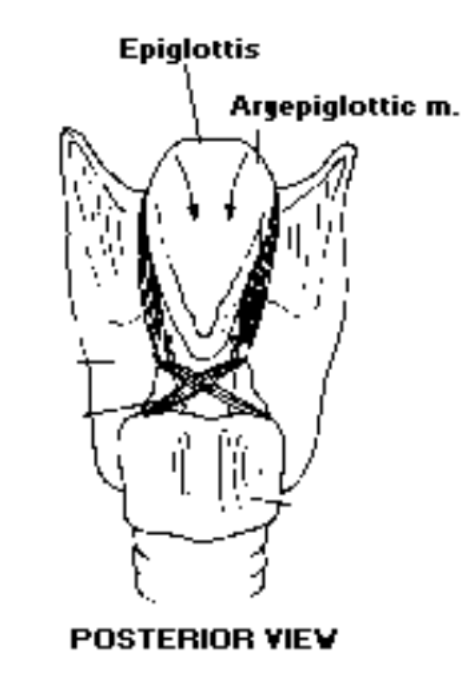
Is the epiglottis an unpaired or paired cartilage?: The epiglottis is an unpaired cartilage (leaf-shaped)
What shape is the epiglottis?: The epiglottis is leaf shaped
Is the epiglottis elastic?: Yes, the epiglottis is elastic
The petiolus of the epiglottis: The petiolus attaches to the inside of the thyroid- epiglottis becomes very thin
What happens when the petiolus attaches to the inside of the thyroid?: The epiglottis becomes very thing
Where does the anterior surface of the epiglottis attach?: The anterior surface of the epiglottis attaches to the hyoid bone by ligaments
What is the biological function of the epiglottis?: The biological function of the epiglottis is to close off the airway directing food toward esophagus during swallowing
What is the nonbiological function of the epiglottis?: The nonbiological function of the epiglottis has to do with tongue position. The tongue position moves the epiglottis but no real function for phonation or articulation
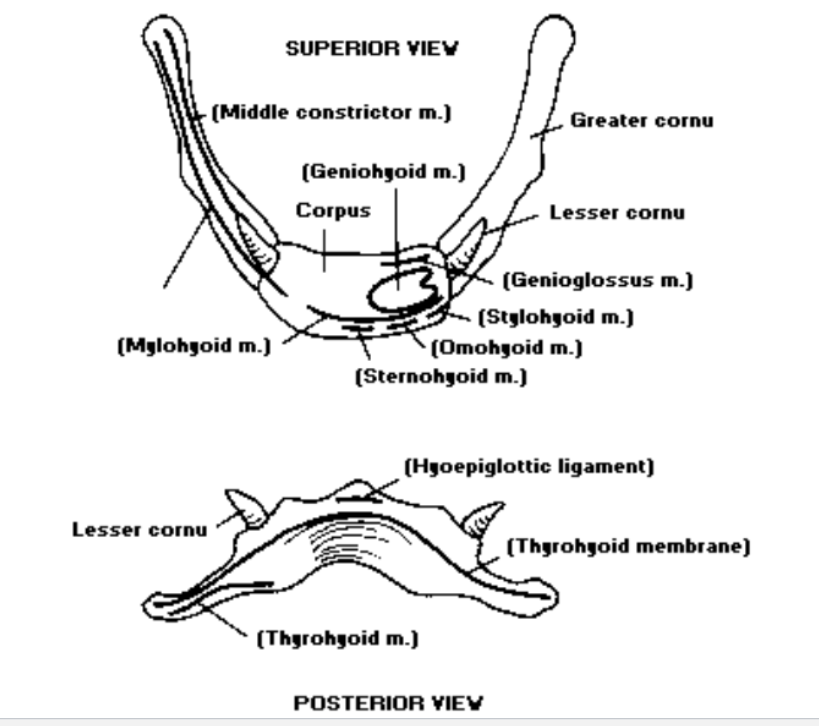
Extrinsic Laryngeal Muscles
- How many extrinsic laryngeal muscles are there?: There are 8 extrinsic laryngeal muscles
- One extrinsic laryngeal muscle attaches to the: laryngeal structure
- The second extrinsic laryngeal muscle attaches to the” outside of the larynx- mandible, mastoid or styloid process and thorax
- 4 extrinsic laryngeal muscles are ___: suprahyoid
- Which 4 extrinsic laryngeal muscles are suprahyoid?: 1) digastric: ant + post belly, 2) geniohyoid, 3) mylohyoid, 4) stylohyoid are the 4 extrinsic laryngeal muscles that are suprahyoid
- There are __ infrahyoid extrinsic laryngeal muscles: 4
- Which four extrinsic laryngeal muscles are infrahyoid?: 1) thyrohyoid, 2) sternohyoid, 3) omohyoid, 4) sternothyroid are the four extrinsic laryngeal muscles that are infrahyoid
Muscles of the Larynx
- Larynx Intrinsic Muscles: control sound production
- Extrinsic Larynx Muscles: provide support and position the larynx
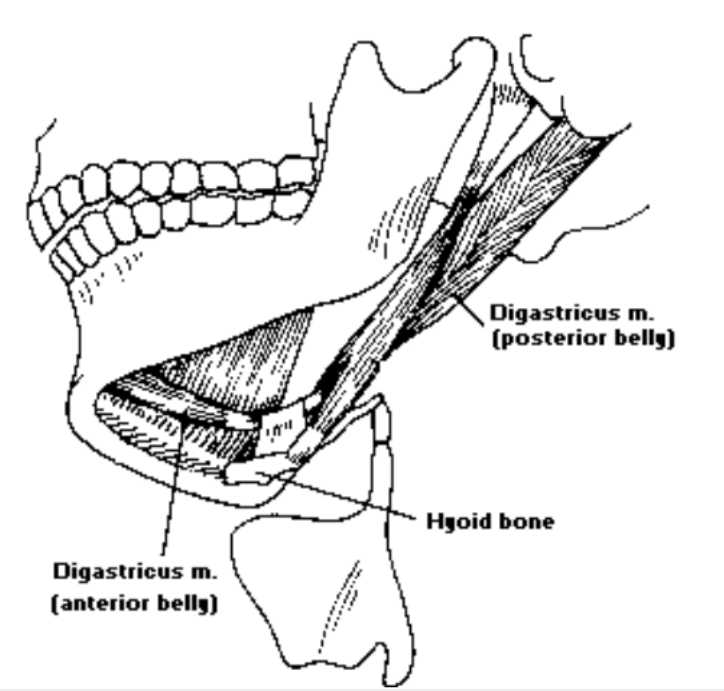
1. Digastric
Digastric is a ___ muscle: Digastric is a suprahyoid muscle
The digastric consists of these 2 muscle sections: The digastric consists of the anterior + posterior belly
The digastric insertion: intermediate tendon connected with the hyoid bone
Digastric anterior belly: pulls the hyoid bone forward and elevates larynx
Digastric posterior belly: pulls the hyoid up and posteriorly and elevates (larynx)
2. Mylohyoid
The mylohyoid is a ___ muscle: The mylohyoid is a suprahyoid muscle
Is the mylohyoid an unpaired or paired muscle?: unpaired
The mylohyoid is a thin muscle forming the: The mylohyoid is a thin muscle forming the floor of the mouth
Mylohyoid origin: The mylohyoid origin is in the inner surface of the mandible
Mylohyoid insertion: The mylohyoid insertion at the area where fibers cross to the midline raphe which extends to the hyoid body
Mylohyoid function: The function of the mylohyoid is to pull the hyoid bone forward and upward (larynx)
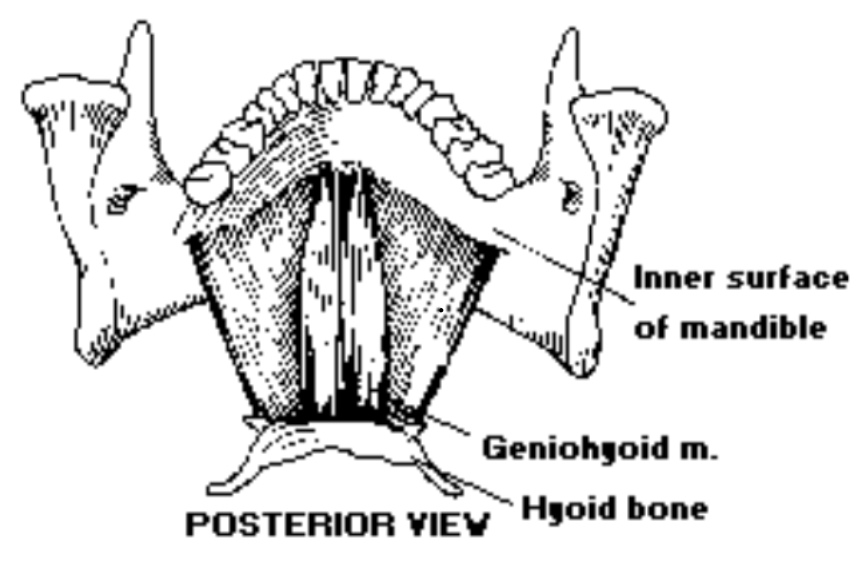
3. Geniohyoid
- The Geniohyoid is a ___ muscle: The Geniohyoid muscle is a suprahyoid muscle
- Is the geniohyoid muscle paired or unpaired?: The geniohyoid is a paired cylindrical muscle that lies on the surface of the mylohyoid
- What shape is the geniohyoid?: The geniohyoid is a cylindrical muscle
- Where is the geniohyoid located?: The geniohyoid lies on the surface of the mylohyoid
- Where is the geniohyoid origin?: The geniohyoid origin is at the mandibular symphasis of the mandible
- Where is the geniohyoid insertion?: The geniohyoid insertion is at the anterior surface of the hyoid body
- What is the geniohyoid function?: The geniohyoid pulls the hyoid bone forward and upward (larynx)
4. Stylohyoid
The stylohyoid is this type of muscle: The stylohyoid is a suprehyoid muscle
Is the stylohyoid a paired or unpaired muscle?: The stylohyoid is a paired muscle
Where is the stylohyoid located: The stylohyoid is a long slender muscle located on the surface of the posterior belly of the digastric
Where is the origin of the stylohyoid?: The origin of the stylohyoid is located at the styloid process of the temporal bone
Where is the stylohyoid insertion?: It is on the body of the hyoid
What is the stylohyoid function?: The stylohyoid pulls the hyoid bone posteriorly and upward (larynx)
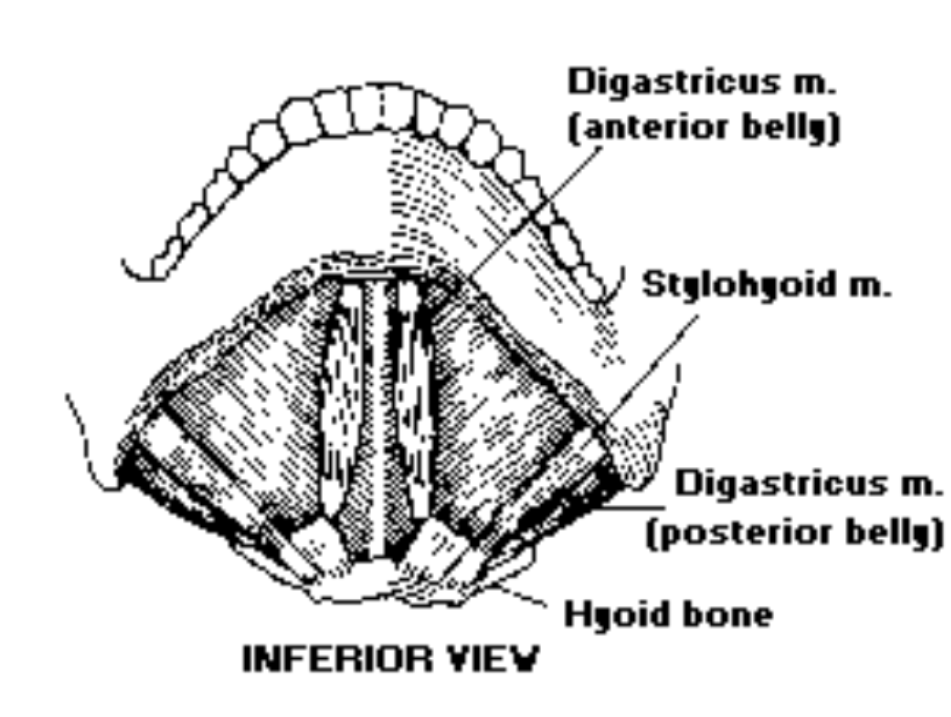
Suprahyoid Muscles
- Suprahyoid muscles form a sling supporting the ___: Suprahyoid muscles form a sling supporting the hyoid and secondarily, the larynx
- Suprahyoid muscles anterior portion: 1) Digastric anterior 2) Geniohyoid 3) Mylohyoid
- Suprahyoid muscles posterior portion: 1) digastric posterior 2) stylohyoid
- Suprahyoid muscles anterior portion function: pulls the hyoid up + forward (larynx), front vowels /i, u/, consonants w/ high front tongue position (/sh/, /s/)
- Suprahyoid muscles posterior portion function: pulls the hyoid up + backward (larynx)
Clinical Implications of Suprahyoid Muscles
- Why are the syprahyoid muscles active during swallowing?: The suprahyoid muscles are active during swallowing to raise the larynx. It helps to prevent aspiration into the airway
- When suprahyoid muscles are not functioning appropriately, this happens: When suprahyoid muscles are not functioning properly, it results in swallowing difficulty
5. Omohyoid
The omohyoid is this type of muscle: The omohyoid is an infrahyoid paired muscle
Omohyoid structure: The omohyoid is a long narrow 2-part muscle on anterior and lateral surface of the neck- inferior + superior bellies
The origin of the omohyoid: The origin of the omohyoid is located in the inferior belly in the surface of the scapula. It is also located in the superior belly in the immediate tendon connected with the hyoid
Omohyoid insertion occurs at: Omohyoid insertion occurs in the inferior belly at the intermediate tendon. It also occurs in the superior belly in the great horn of the hyoid
The function of the omohyoid is to: The function of both the omohyoid is to pull down the thyroid
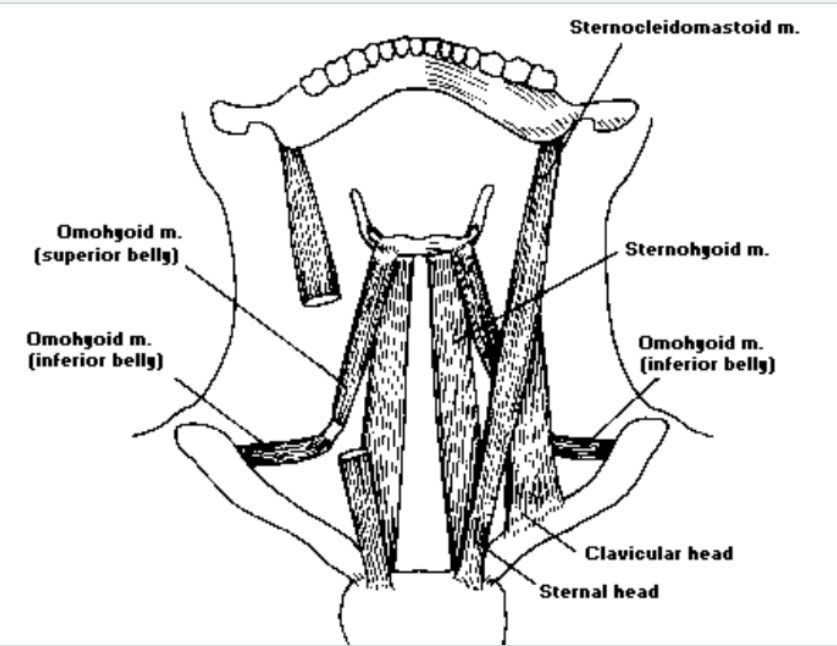
6. Thyrohyoid
The thyrohyoid is this type of muscle: The thyrohyoid is an infrahyoid paired muscle
Where is the thyrohyoid located?: The thyroihyoid is a thin muscle lying deep to the omohyoid
Where is the origin of the thyrohyoid?: The origin of the thyrohyoid is the oblique line of the thyroid lamina
Where is the thyrohyoid insertion?: The thyrohyoid insertion is at the greater horn (cornu) of the hyoid bone
What is the thyrohyoid function?: The function of the thyrohyoid is to decrease distance between the thyroid and hyoid
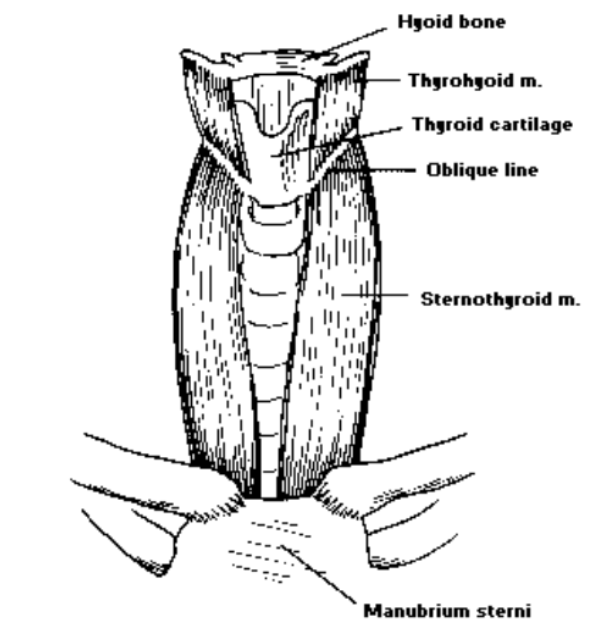
7. Sternohyoid
- What kind of muscle is the sternohyoid?: The sternohyoid is an infrahyoid paired muscle
- Where is the sternohyoid located?: The sternohyoid is a thin muscle lying on the anterior side of the neck
- Where is the origin of the sternohyoid?: The origin of the sternohyoid is at the manubrium and end of the clavicle
- The insertion of the sternohyoid is at: The insertion of the sternohyoid is at the hyoid body
- What is the function of the sternohyoid?: The function of the sternohyoid is to pull down the hyoid bone
8. Sternothyroid
What type of muscle is the sternothyroid?: The sternothyroid is an infrahyoid paired muscle
Where is the sternothyroid located?: The sternothyroid is a long thin muscle on the anterior side of the neck
What is the sternothyroid origin?: The sternothyroid origin is located at the manubrium and costal cartilage of the first rib
Where is the sternothyroid insertion?: The sternothyroid insertion is the oblique line of the thyroid
What is the sternothyroid function?: The sternothyroid pulls down the thyroid
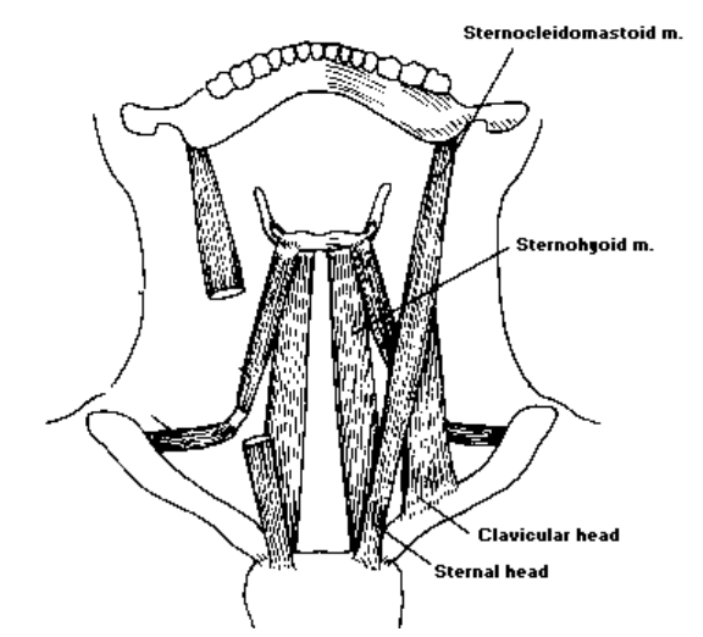
Intrinsic Laryngeal Muscles
- How many intrinsic laryngeal muscles are there?: There are 5 intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- Where do the intrinsic laryngeal muscles attach?: In the intrinsic laryngeal muscles, both attachments (origin and insertion) attach to laryngeal structures such as laryngeal cartilages
- Lateral cricoarytenoids are these types of muscles: intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- Interarytenoid muscles are these types of muscles: intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- The two types of interarytenoid muscles are: transverse and oblique
- Posterior cricoarytenoids are these types of muscles: intrinsic laryngeal muscles
- The cricothyroid is this type of muscle: The cricothyroid is an intrinsic laryngeal muscle
- The thyroarytenoids are these types of muscles: The thyroarytenoids are intrinsic laryngeal muscles
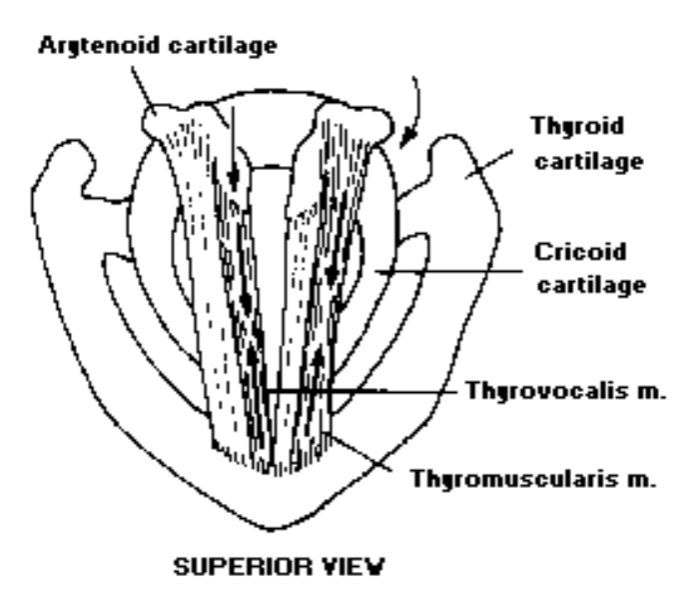
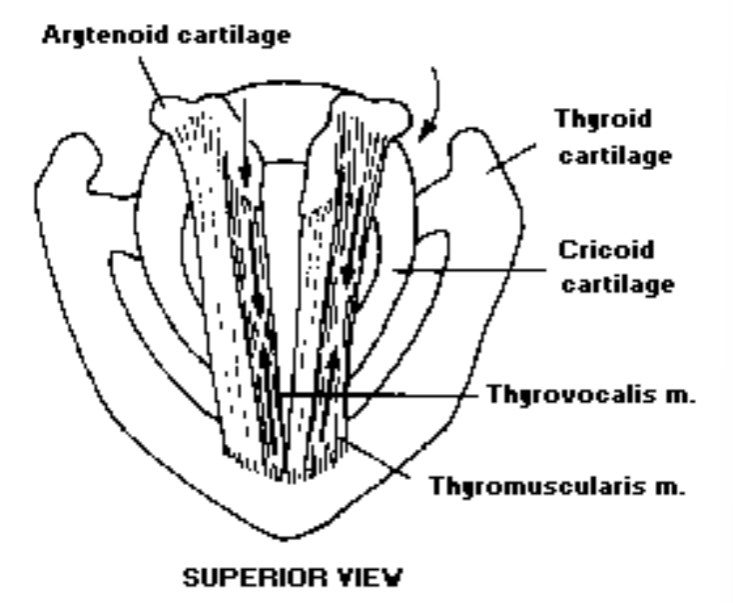
- What are the two types of thyroarytenoid muscles?: The thyrovocalis and thyromuscularis are the two types of thyroarytenoid muscles
- What are the functions of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles?: 1. shape of the glottis 2. vibration of the vocal folds
- List the intrinsic laryngeal muscles: The intrinsic laryngeal muscles are the interarytenoid muscles (transverse and oblique), lateral cricoarytenoid, posterior cricoarytenoid, cricothyroid, and thyroarytenoid (thyrovocalis and thyromuscularis)
1. Interarytenoids
What are interarytenoids?: Interarytenoids are unpaired muscle with fibers oriented in 2 directions
List the different types of interarytenoids: The two types of interarytenoids are the transverse arytenoid and the oblique arytenoid
What type of muscle is the transverse arytenoid?: The transverse arytenoid is an interarytenoid
What type of muscle is the oblique arytenoid?: The oblique arytenoid is an interarytenoid
Where is the origin of the transverse arytenoid?: The origin of the transverse arytenoid is at the lateral margin of one arytenoid and courses to the lateral margin of the other arytenoid
Where is the insertion of the transverse arytenoid?: The insertion of the transverse arytenoid is at the arytenoid of the opposite side
What is the function of the transverse arytenoid?: The function of the interarytenoid is abducting arytenoids, i.e. closing the glottis
Where is the oblique arytenoid located?: The oblique arytenoid is superficial to the transverse arytenoid
Where is the origin for the oblique arytenoid?: The origin of the oblique arytenoid is at the base of one arytenoid and courses to the apex of the other arytenoid
Where is the insertion for the oblique arytenoid?: The insertion for the oblique arytenoid is at the arytenoid of the opposite side
What is the function of the oblique arytenoid?: The oblique arytenoid adducts arytenoids, i.e., closing the glottis
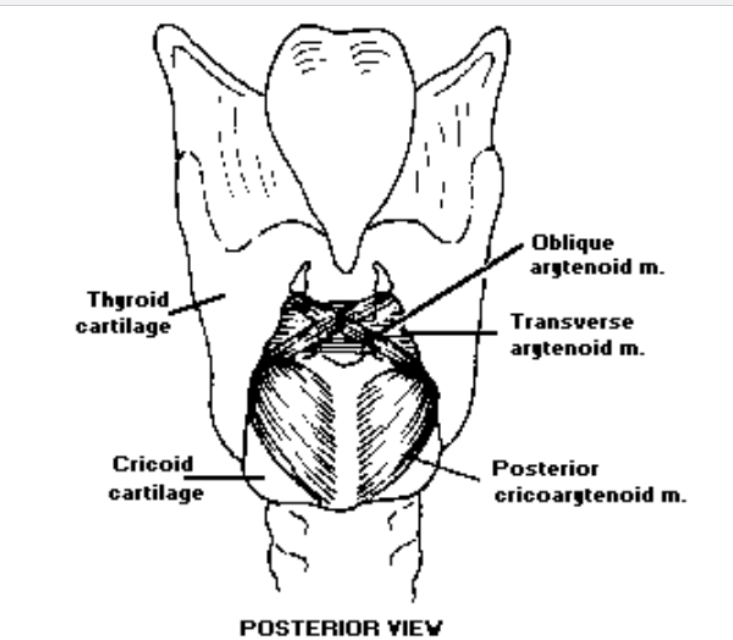
2. Lateral Cricoarytenoid
What is the lateral cricoarytenoid?: The lateral cricoarytenoid is a fan-shaped muscle lying along the upper surface of the cricoid cartilage
Where is the origin of the lateral cricoarytenoid?: The lateral cricoarytenoid origin is in the upper border or the cricoid
Where is the insertion for the lateral cricoarytenoid?: The insertion for the lateral cricoarytenoid is on the anterior surface of the muscular process of the arytenoid
What is the function of the lateral cricoarytenoid?: The lateral cricoarytenoid adducts the vocal processes of the arytenoids, i.e. closing the membranous glottis
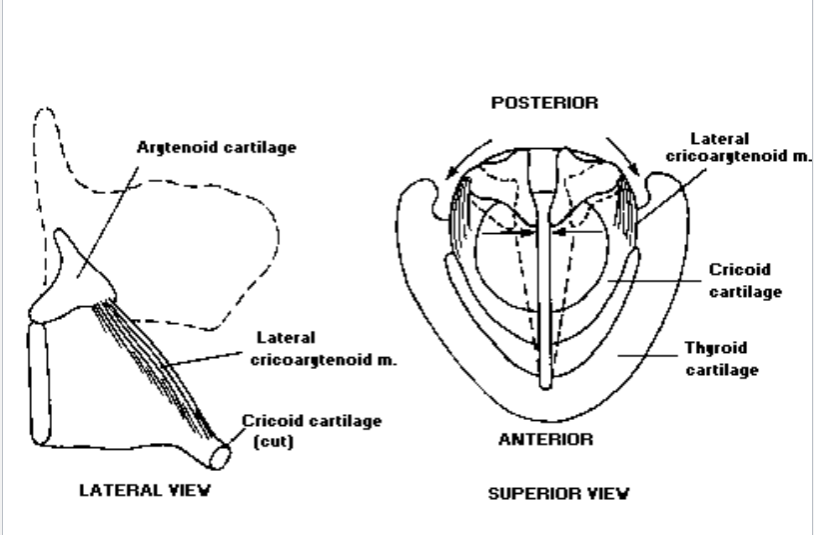
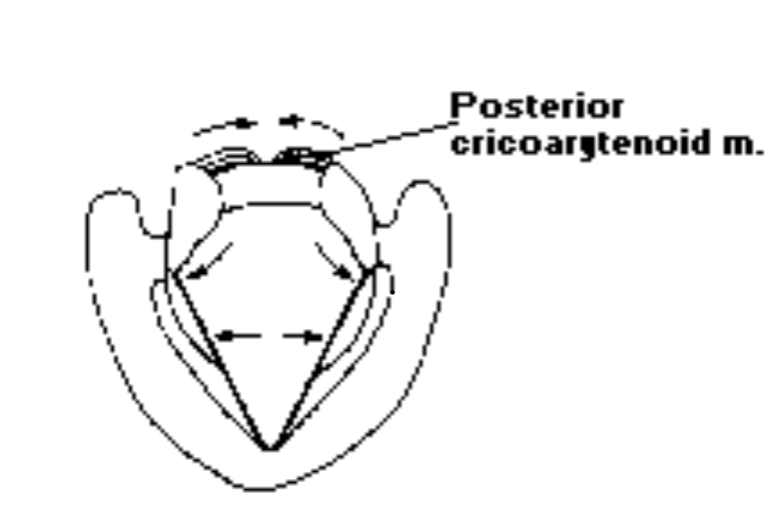
3. Posterior Cricoarytenoid
What is the posterior cricoarytenoid?: The posterior cricoarytenoid is a fan-shaped muscle located on the posterior surface of the cricoid
The origin of the posterior cricoarytenoid is: The origin of the posterior cricoarytenoid is on the posterior lamina of the cricoid
The insertion of the posterior cricoarytenoid is: The insertion of the posterior cricoarytenoid is on the posterior surface of the muscular process of the arytenoid
What is the function of the posterisor cricoarytenoid?: The posterior cricoarytenoid abducts the arytenoids, i.e., opening the glottis
4. Cricothyroid
What is the cricothyroid?: The cricothyroid is a fan-shaped muscle located between cricoid and thyroid; consisting of fibers oriented in 2 directions: pars oblique and pars recta
Where is the cricothyroid located?: The cricothyroid is located between the cricoid and thyroid and its fibers are oriented in 2 directions: pars oblique and pars recta
Where is the origin of the cricothyroid?: The origin of the cricothyroid is the arch of cricoid
Where is the insertion for the cricothyroid?: The cricothyroid’s insertion is at the inferior margin of the thyroid
What is the cricothyroid’s shape?: The cricothyroid is fan shaped
What is the function of the cricothyroid?: The function of the cricothyroid is to decrease the distance between the thyroid and cricoid, i.e. increase the distance between the thyroid and arytenoid, (increase the length of the vocal folds, decrease mass and increase tension). Therefore increasing the vocal pitch
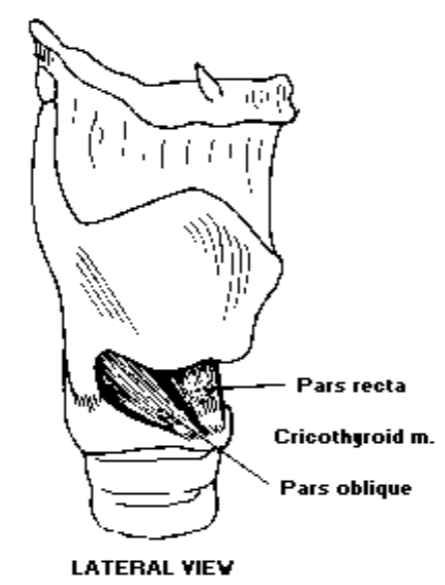
5. Thyroarytenoid
Thyroarytenoid: The thyroarytenoid is a bundle of fibers making up the true vocal folds
The thyroarytenoid can be divided into: 2 muscle groups- 1) thyrovocalis muscle (medially and more active) and 2) Thyromuscularis muscle (laterally and less active)
What is the function of the thyroarytenoid?: The function of the thyroarytenoid is to decrease the distance between thyroid and arytenoid, (decrease the length of the vocal folds, increase mass and decrease tension). Therefore, decreasing the vocal pitch
Motions
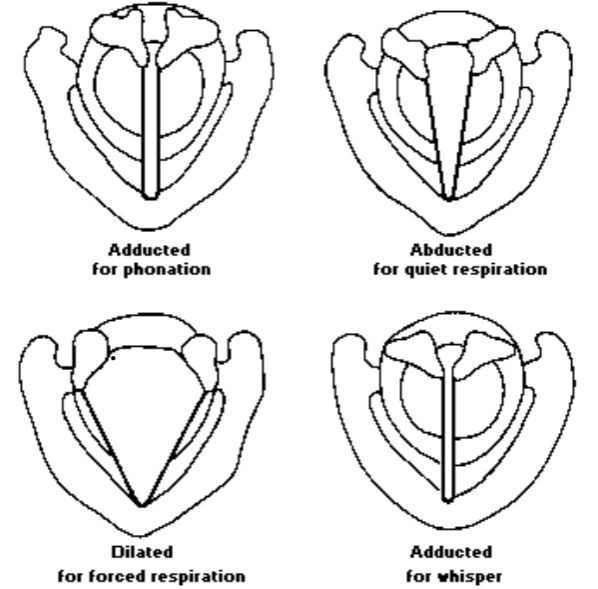
1.Adduction is performed by these muscles: Intraarytenoids (transverse + oblique), lateral cricoarytenoid (LCA), cricothyroid, thyroarytenoid
\
- Abduction is performed by this muscle: posterior cricoarytenoid (PCA)
Do Intraarytenoids (transverse + oblique) adduct or abduct?: Intraarytenoids adduct
Do lateral cricoarytenoids (LCA) adduct or abduct?: Lateral cricoarytenoids adduct
Does the cricothyroid adduct or abduct?: The cricothyroid adducts
Does the thyroarytenoid adduct or abduct?: The thyroarytenoid adducts
Abduction: come apart
Adduction: come together
Raising pitch is performed by this muscle: cricothyroid
Lowering pitch is performed by this muscle: thyroarytenoid
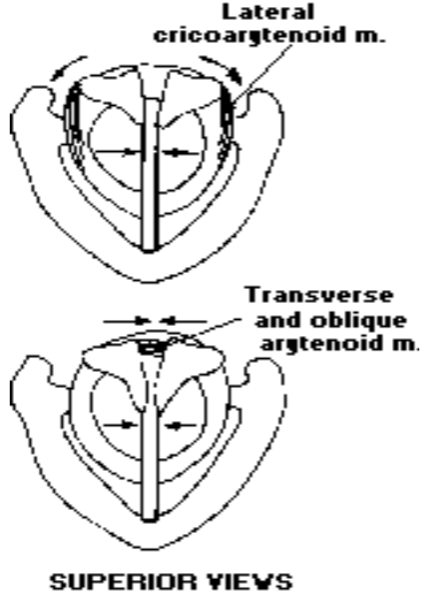
1. Adduction of arytenoids
Intraartytenoids (transverse + oblique) adduct: approximate the arytenoids and brings the arytenoids together, causing them to slide toward the midline >>> squeezing the vocal process
Lateral cricoarytenoid (LCA) adduct: medial compression
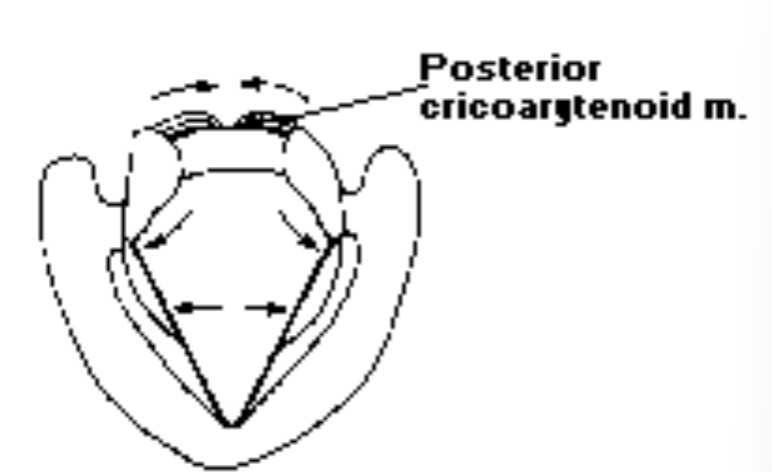
2. Abduction of the Arytenoids
Posterior Cricoarytenoid (PCA) abduction: Pulls the muscular process of the arytenoids posteriorly, rocking the arytenoids back to their axis (active during physical exercise to permit greater air in and out)
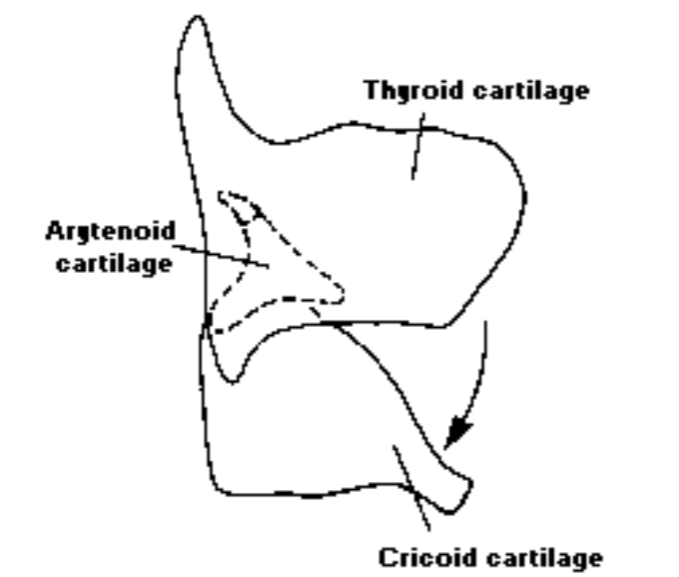
3. Increasing Pitch
- Cricothyroid increases pitch: decreases the distance between the cricoid and the thyroid cartilages, thus elongating the vocal process and places it under increased tension. This increased tension leads to increased pitch. Think of a rubber band
Main Ligaments/Membranes
\
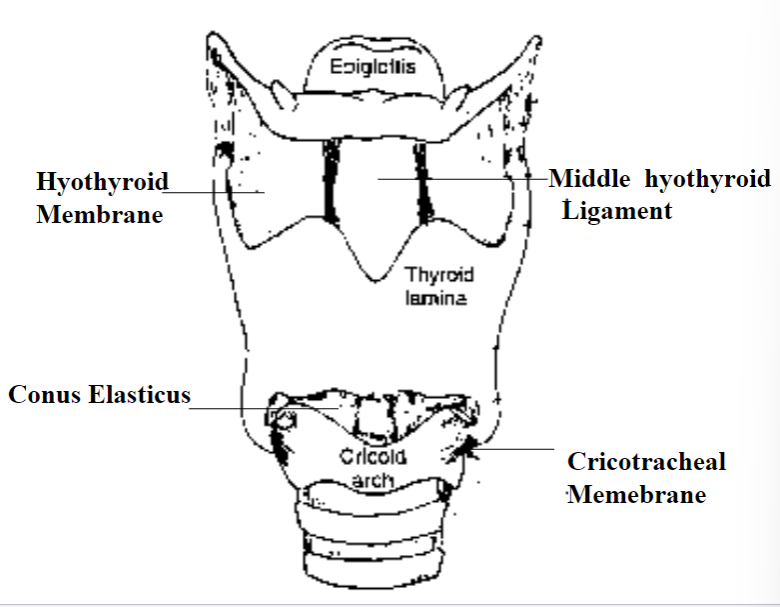
- Hyothyroid membrane: An extrinsic laryngeal connection between hyoid and throid
\
- Middle Hyothyroid Ligament: The thicker portion of the hypothyroid membrane and is also an extrinsic laryngeal ligament
\
- Cricotracheal membrane: an extrinsic laryngeal connection between cricoid and 1st tracheal ring. Easy access to the vocal fold
\
- Posterior Cricoarytenoid Ligament: The largest intrinsic ligament restricting and dictating movements of the arytenoids
\
- Conus elasticus: Membrane covering cricoid arch, thyroid and the vocal fold
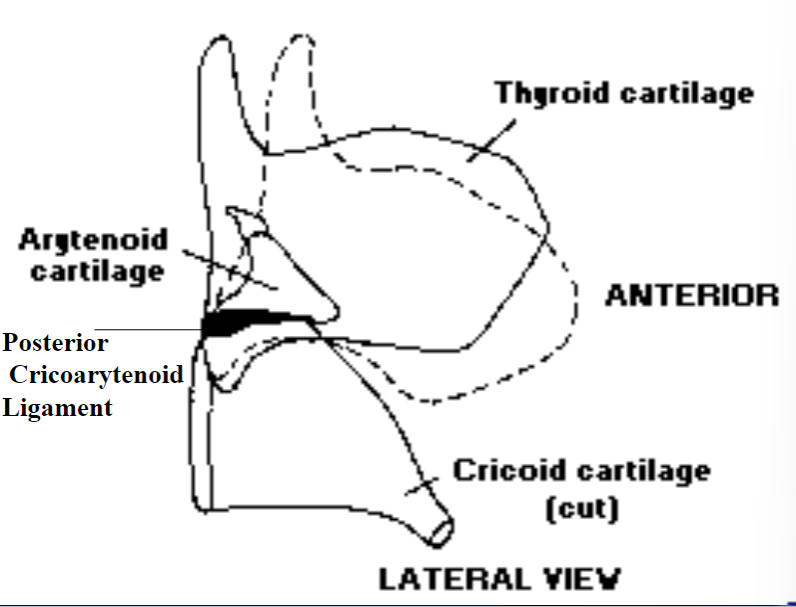
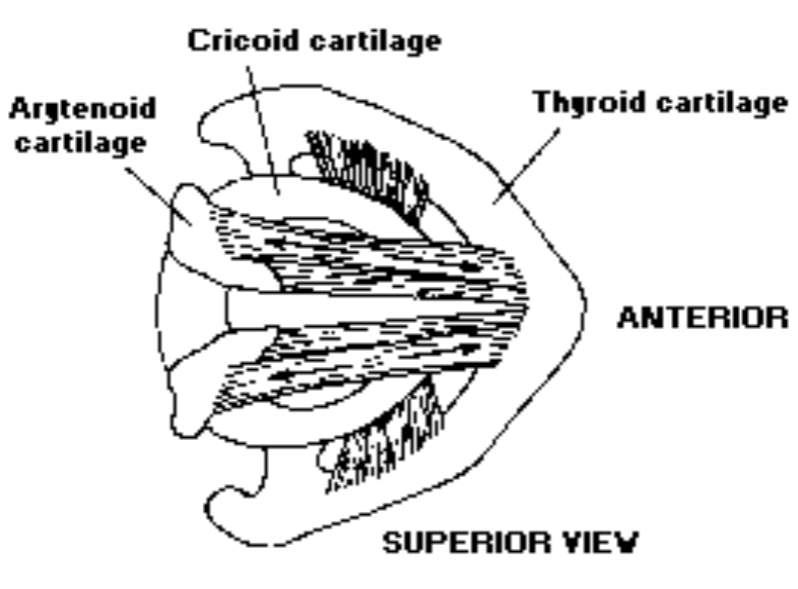
4. Decreasing Pitch
Thyroarytenoid decreasing pitch: Tilts the thyroid backward to relax the vocal process and at the same time pulls the muscular process forward to assist in medial compression

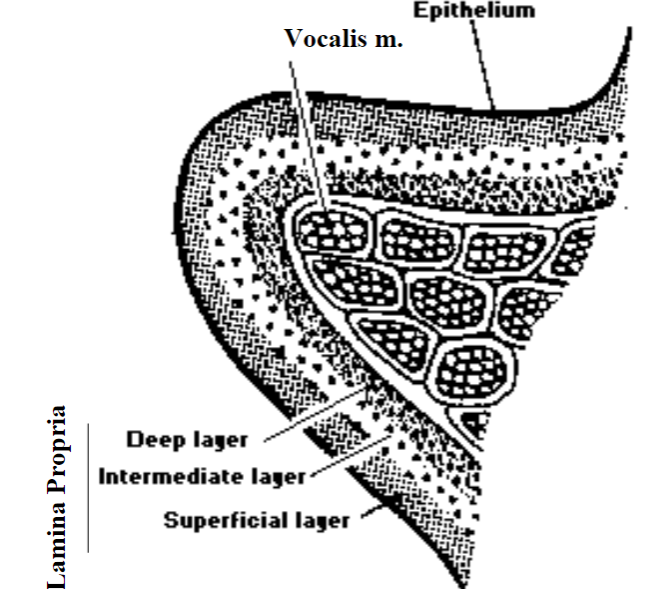
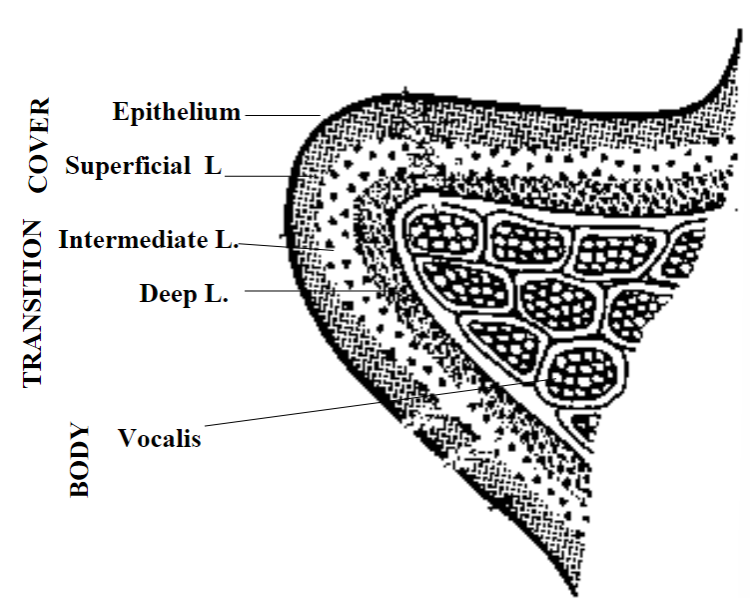
Anatomy of the Vocal Folds
Hirano (1974, 1281) proposed: A 5 layer model for the anatomy of the vocal folds. Consists of the epithelium, lamina propria, intermediate layer, deep layer and vocalis muscle
Epithelium: Outer layer of the vocal folds. Stiff mosaic tissue for protection
Lamina propria: middle layer of vocal folds. Superficial layer (Reinke’s space). Consists of loose fibers with fluid spaces= “cobweb”
Intermediate layer: Elastic fibers with recoil features = soft rubber band.
Deep layer: thick collagenous fibers, less elastic = “cotton thread”
Vocalis muscle: Thyrovocalis. Vibrates the vocal fold for sound production. length + tension, stiff rubber bands
Hirano’s theory: The combination of mechanical properties of the 5 layers determines the mode of vocal fold vibration.
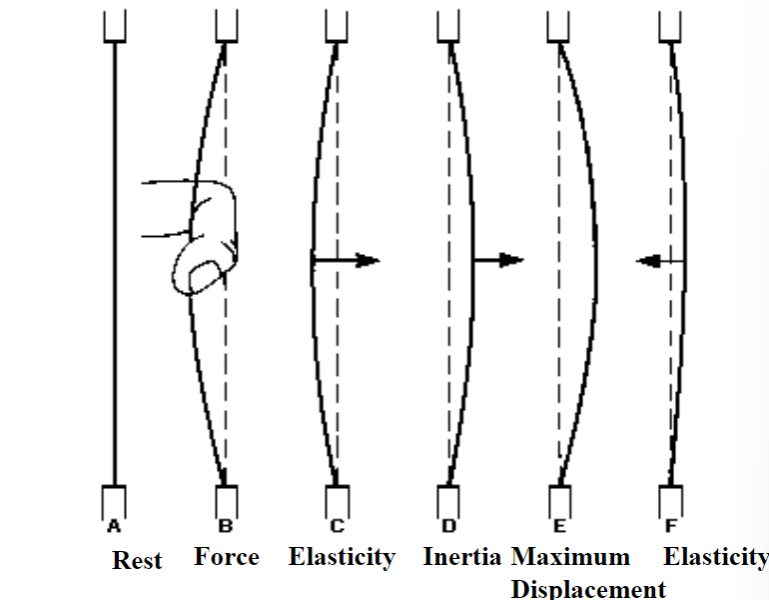
Mechanical Properties
\
- Tension (stiffness): major determinant of Fol increase tension (decrease elasticity) increase vibrations
\
- Mass: thickness. distribution of the vocal fold mass is related to length + tension. increase mass and decrease vibration
\
- Length: source. male vocal folds are longer and vibrate less; increasing length and decreasing vibration
Hydration and Mechanical Abuses
- Increasing our intake of water helps the: vocal fold tissue
Vocal Fold Theories
- Theories to explain production of vocal fold vibration: neurochronaxic, myoelastic-aerodynamic
- Neurochronaxic theory: States that vocal fold vibration is almost totally dependent on the rate of neural impulses received by the laryngeal muscles. Even though nerves can fire (send impulses) quite fast, the rapid pattern of vibration observed during production of high frequencies can not be explained by the rate of nerve impulse
- Myoelastic-aerodynamic theory: widely accepted and takes into account laws of physics which regulates movement/control of air molecules (aerodynamic) and muscle activity (myoelastic)
Aerodynamic
- Laws of physics are used to explain: generation/control of air flow and pressure
Myoelastic
- Myoelastic: states that the laryngeal physical properties (positioning of structures, tension, length, distribution of mass) are controlled by the intrinsic laryngeal muscles (muscle contraction)
Assumptions of Myoelastic Aerodynamic Theory of Vocal Fold Vibration
- The three assumptions of myoelastic aerodynamic theory of vocal fold vibration are: 1) vocal folds are appropriately positioned (postured) in a closed or semiclosed position 2) pressure is built up below the folds 3) folds repeatedly open and close automatically
Implications of Myoelastic Aerodynamic Theory of Vocal Fold Vibration
- Vocal folds do not open and close during phonation because there is: a separate muscle contraction for each opening/closing movement
- Vocal folds open and close automatically, as long as: the folds are in a position of closure or near closure, and there is sufficient buildup of pressure below them
Forces that cause the vocal folds to open
- Forces that cause the vocal folds to open: buildup of air pressure on one side of the vocal folds (below)
Forces that cause the vocal folds to close
- Forces that cause the vocal folds to close: drop in pressure along the glottal margin of folds (explained by Bernoulli effect: high speed of airflow that occurs at the construction causes the walls of the vocal folds to be sucked together due to a drop in air pressure at the margin of the folds)
- Force of elastic recoil of the folds: consider the abducted position of the folds its rest position, once the air pressure building below the folds is enough to blow them apart, the folds are “pushed away” from the rest position - opposing elastic recoil forces will tend to restore the folds to the original position/shape
Important Factors Governing Vocal Fold Vibration
- vocal fold position: degree of adduction
- Glottal adductors: lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, transverse interarytenoid muscle, oblique interarytenoid muscle
- vocal fold myoelasticity: length + tension
- Glottal tensors/relaxors: cricothyroid muscle and thyroarytenoid muscle
- ___ of pressure drop along the folds: amount/size
Methods for Viewing the Vocal Folds (VF)
Laryngoscopy: exam of the interior of larynx
Three main problems with laryngoscopy: The larynx is located deep in the neck, the larynx is dark and vocal folds vibrate more than 100 cycles for second
Where is the larynx located?: The larynx is located deep in the neck
Vocal fold vibration frequency: 100 cycles per sec
Indirect laryngoscopy: Manuel Garcia (1885) France. Dental mirror pushed to the soft palate. Only Larynx structures could be seen.
Direct Laryngoscopy is performed under: anesthesia
Photography of Lx: Paul Moore (1937), MIT, UF High-speed motion pictures and 4000 frames/sec
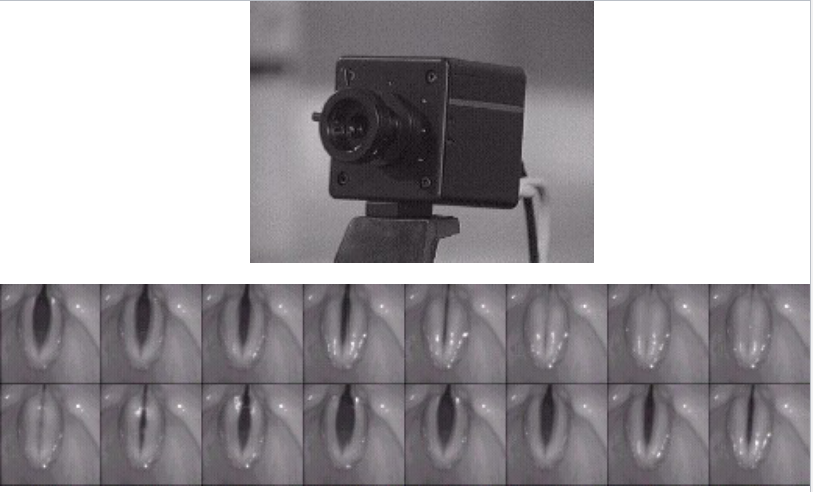
Two types of endoscopy: Rigid and flexible
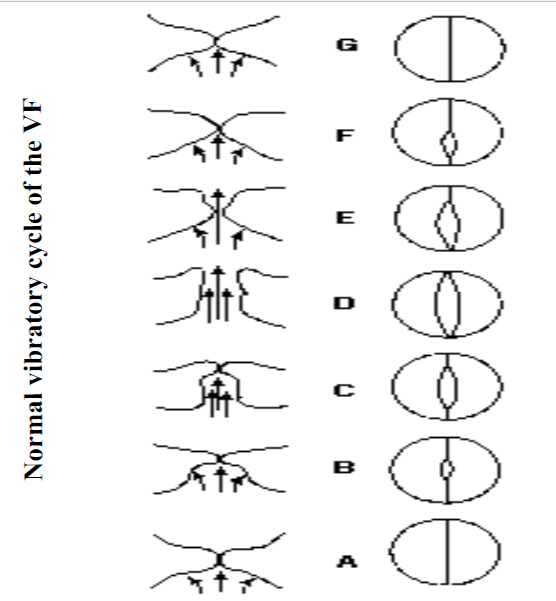
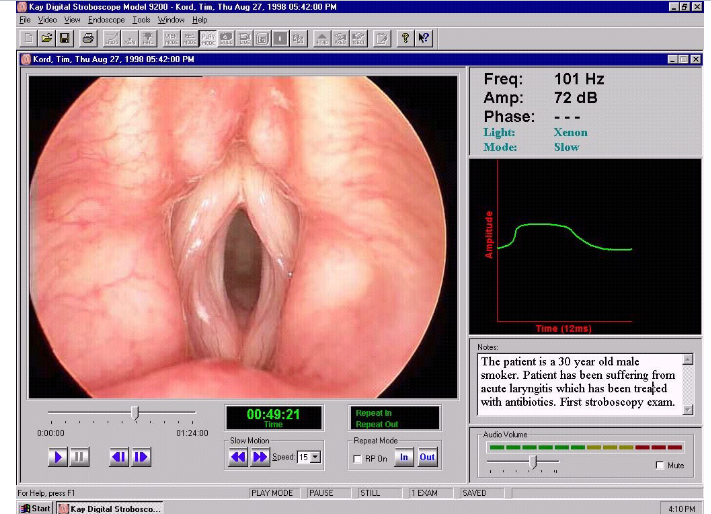
Videostroboscopy: Allows the human eye to see the vibratory motion of the VF in slow motion and directly observes the appratent motion of the larynx
http://www.rrze.unierlangen.de/docs/FAU/fakultaet/med/kli/kphno/phon/ppglotte.htm
http://www.kayelemetrics.com/digitalstrobesample_screens.htm
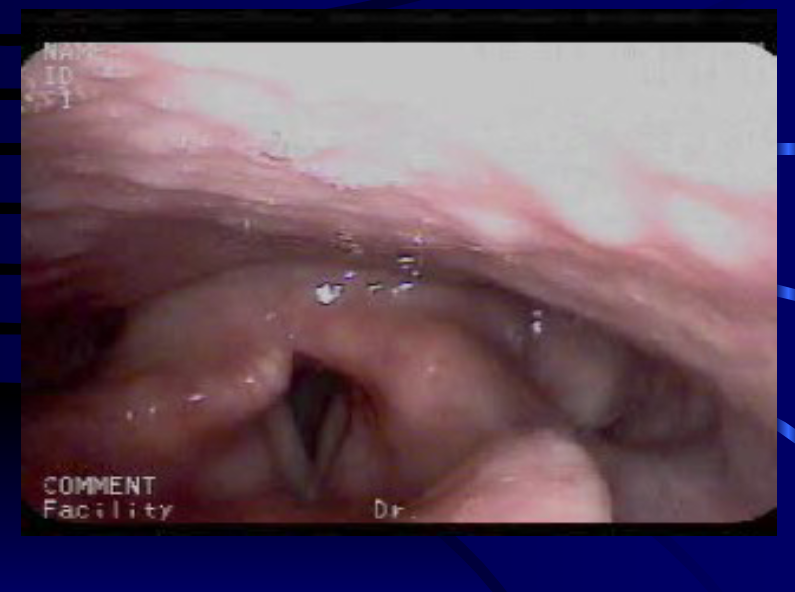
Videostroboscopy
- What three things does a videostroboscopy provide information about?: The nature of vocal fold vibration, presence or absence of pathology, and it documents small changes in the vibratory structure or pattern of vibration
Mechanism of Vocal Frequency Change
- Vocal frequency changes by the amount of: Vocal frequency changes by the amount of tension, mass, and length (muscles…)
- Vocal frequency open/close quotients or phases: Frequency (Hz) >>> Pitch
- 3 modes of vibration >>> 3 ranges of pitch registers: The 3 modes of vibration >>> 3ranges of pitch registers are modal, falsetto, and vocal fry
- Vocal frequency can be changed by changing the: vocal frequency can be changed by changing the airflow and increasing the subglottal pressure
Mechanism of Vocal Intensity Change
- Vocal intensity can be changed by the amount of: vocal intensity can be changed by the amount of glottal resistance (increase medial compression; muscles… increase size of burst of air, increase impact collision of air molecules, increase displacement of acoustic vibration)
- Intensity (SPL) >>> ____: Intensity (SPL) >>> Loudness
- Vocal intensity can be influenced by the size and shape of: vocal intensity can be influenced by the size and shape of the vocal tract (laryngeal, pharyngeal, oral, and nasal)
- Vocal intensity can be changed by these factors: vocal intensity can be changed with air pressure + air flow (speed)
- Vocal intensity change can be caused by an increased: vocal intensity change can be caused by an increased time of closure (LCA)
Clinical Implications (Idk how accurate my answers are. Take it with a grain of salt.)
- How will an impaired respiratory system affect pitch and loudness?: An impaired respiratory system will dampen pitch and loudness because it strains the vocal folds.
- How will additional “weight” on the vocal folds affect pitch and loudness?: Additional weight on the vocal folds affects pitch and loudness because pitch and loudness is contingent upon the pressure from the lungs. Additional weight on the vocal folds will make it harder for the air pressure to go through.
Mechanism of Vocal Quality Variation
- The mechanism of the vocal quality variation is impacted by the quality of the: The mechanism of the vocal quality variation is impacted by the quality of the phonatory system (tissues)
- What does smoking fo to your vocal folds?: Smoking irritates the vocal cords and dries the vocal cord mucosa. It also results in inflammation on the vocal cords. This in turn can cause coughing, sputum, and vocal cord feelings of irritation.
- Sputum: A mixture of saliva and mucus coughed up from the respiratory tract, typically s a result of infection or other disease and often examined microscopically to aid medical diagnosis.
- The coordination of ___ influences the mechanism of vocal quality variation: muscles (tremor)
- What is a disease in which the voice sounds tremorous or shaky?: Spasmodic dysphonia is a disease in which the voice sounds tremorous or shaky because it affects the vocal cords. Parkinson’s disease is also characterized by tremor and muscle weakness/slowness. Patients with Parkinsons notice that their voice becomes weak and tremulous
- The shape and configuration of the ___ can affect the mechanism of vocal quality variation: The shape and configuration of the vocal tract (cleft palate) can affect the mechanism of vocal quality variation
- How does the voice sound when there is a hole in the palate?: If there are holes (fistulas) in the palate, some consonant sounds such as s, z, and sh are harder to pronounce. In terms of vocal quality, holes in the palate could lead to nasal sounding speech. If the soft palate is not able to properly close off the mouth from the nose while speaking, air escaped through the noes.
- The size of ___ can affect the mechanism of vocal quality variation: The size of resonators (oral, nasal, pharyngeal) can affect the mechanism of vocal quality variation
- The three types of resonators are: oral, nasal, and pharyngeal
- What is the edge of the vibrating tissue called?: The edge of the vibrating tissue is the periodicity
(slide 140)

The Pediatric Voice: Special Considerations
The most important consideration in pediatric population is: In the pediatric population, the most important consideration is the preservation of the airway
The ____ is almost the most important system of the entire infant: The larynx/airway is almost the most important system of the entire infant

Anatomical Differences
Voice pathologists should be aware of the differences between: The differences between the adult and pediatric laryngeal anatomy and physiology is something voice pathologists should be aware of.
The differences between adult laryngeal anatomy and pediatric laryngeal anatomy are more significant than: The differences between adult laryngeal anatomy and pediatric laryngeal anatomy are more significant than mere size of the structures

Position of the Larynx
The position of the larynx in an adult: In an adult, the larynx sit opposite approximately the fifth or sixth vertebral body
The position of the larynx in a child: In a child, the larynx sits opposite approximately the fourth cervical vertebral body
The position of the larynx in an infant: IN an infant, the larynx can rise as high as first or second cervical body during swallowing
Think [5-6]-[4]-[1-2] adult-child-infant larynx
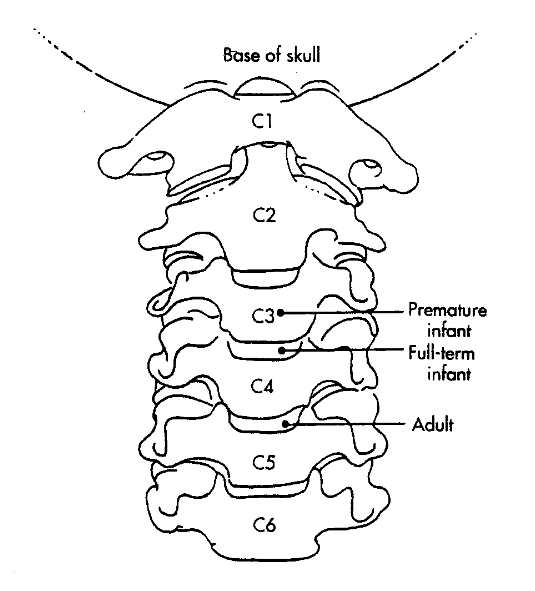

Laryngeal Structures
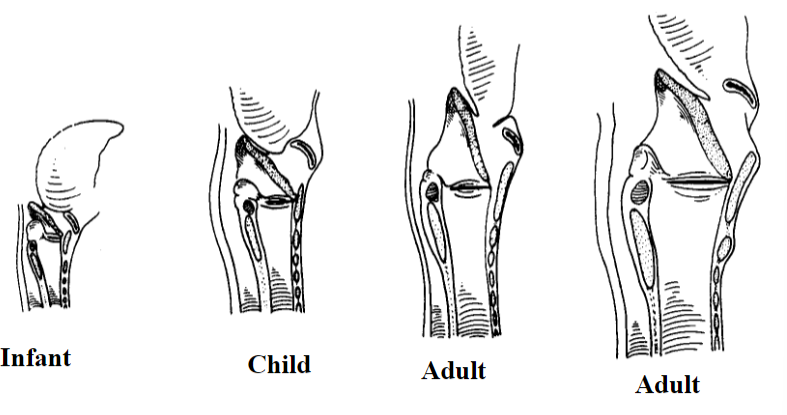
In the pediatric larynx, the thyroid notch is: The thyroid notch is not as prominent in the pediatric larynx as it is in the adult larynx. It is obscured by the overlapping hyoid bone.
The thyroid cartilage of the pediatric larynx is: In the pediatric larynx, the thyroid cartilage is not as prominent as it is in the adult. However, it is more rounded with no midline vertical ridge.

In addition to the thyroid cartilage of the pediatric larynx, what else is also not prominent?: The cricoid cartilage of the pediatric larynx is also not prominent
This can be felt as a depression between the thyroid and the cricoid in the adult larynx; however, in the pediatric larynx it is just a little slit: In the adult larynx, the cricothyroid membrane can be felt as a depression between the thyroid and the cricoid; however, in the pediatric larynx it is just a little slit
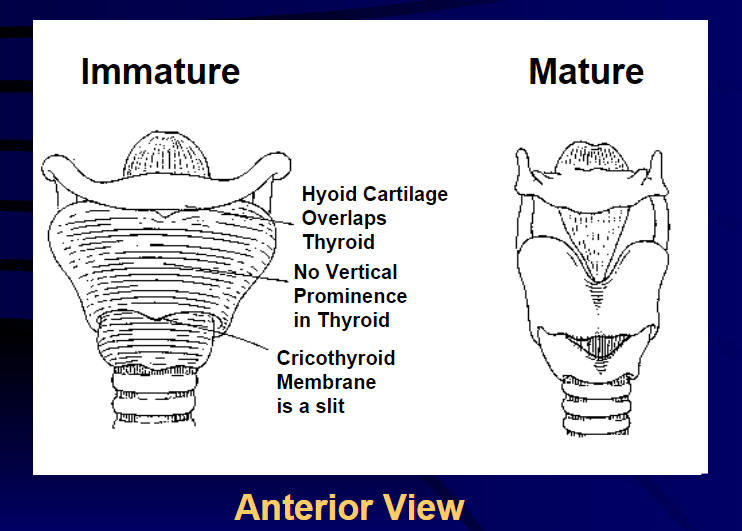
What are the three main differences between an immature and mature larynx?: An immature larynx’s hyoid cartilage overlaps the thyroid, there is no vertical prominence in the thyroid and the cricothyroid membrane is a slit

What is the diameter of the pediatric trachea?: The pediatric trachea is 4-5mm in diameter
What are the aryepiglottic folds and cartilages large compared to?: The aryepiglottic folds and the arytenoid cartilages are large relative to other laryngeal structures.
How many infant epiglottis are omega shaped?: It is estimated that 50% of infant epiglottis are omega shaped.

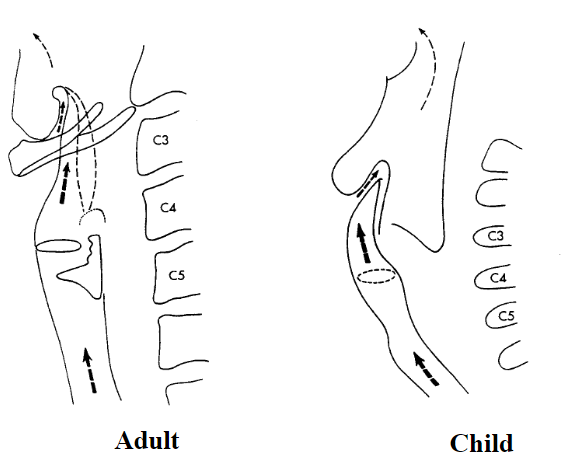
What shape does the airway in an adult take and where does it start?: In an adult, starting from the base of the tongue, the airway takes a rather straight vertical shape.
What shape does the larynx take in a child?: In a child, the larynx takes a curved shape.
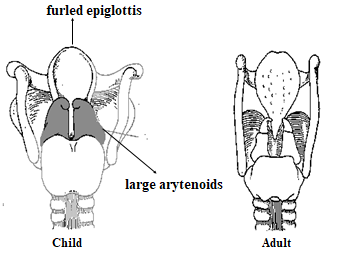
What distinguishes a child’s larynx from an adult’s larynx?: A child’s larynx contains a furled epiglottis and large arytenoids making it different from an adult’s larynx
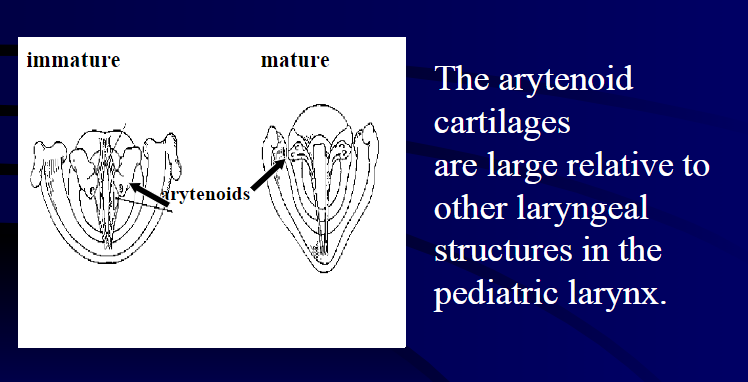
The arytenoid cartilages are large relative to other laryngeal structures in the: pediatric larynx
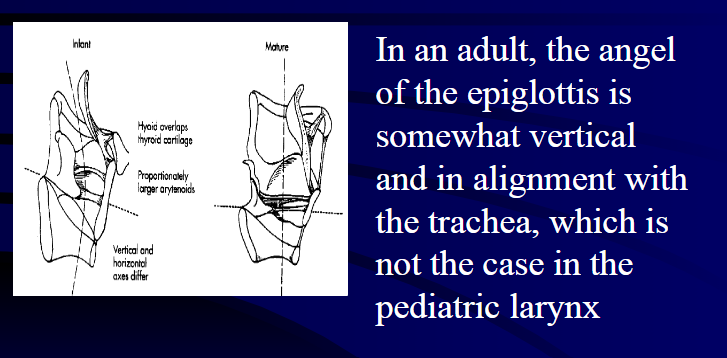
In an adult, the angel of the epiglottis is: In an adult, the angel of the epiglottis is somewhat vertical and in alignment with the trachea, which is not the case in the pediatric larynx.

Vocal Folds
Length of the Entire Vocal Fold
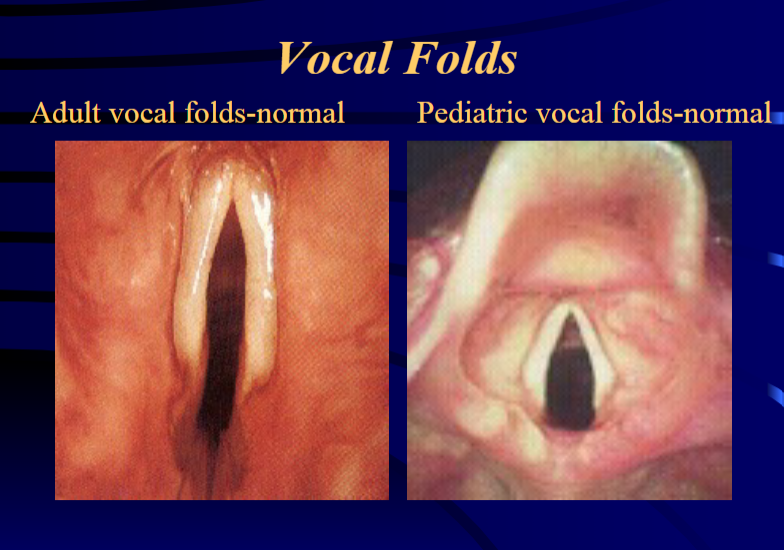
What is the length of the entire vocal fold in newborns?: THe length of the entire vocal fold in newborns is about 2.5-3.0 mm, with gender difference up to the age of 10
What is the length of the entire vocal fold length in adult males?: In adult males, vocal fold length is about 17-21 mm.
What is the length of the entire vocal fold length in female adults?: In female adults, the vocal fold length is about 11-15mm.
Why may normal respiratory pressure be enough to deform the laryngeal structure (e.g Laryngomalacia and Tracheomalacia)?: Because of the pliable tissue lining the pediatric larynx, normal respiratory pressure may be enough to deform laryngeal structure (e.g. Laryngomalacia and Tracheomalacia)
What aspect of the pediatric airway should be considered while conducting laryngoscopy, stroboscope and intubation?: the curved shape of the pediatric airway should be considered while conducting laryngoscopy, stroboscope and intubation

What should be taken into consideration while considering a cricothyroctomy or a cricothyroid puncture?: The narrowness of the cricothyroid membrane depression in the pediatric larynx should be taken into consideration while considering a cricothyroctomy or a cricothyroid puncture. It is also important if a botox injection is considered.

How are pathologies of the larynx treated?
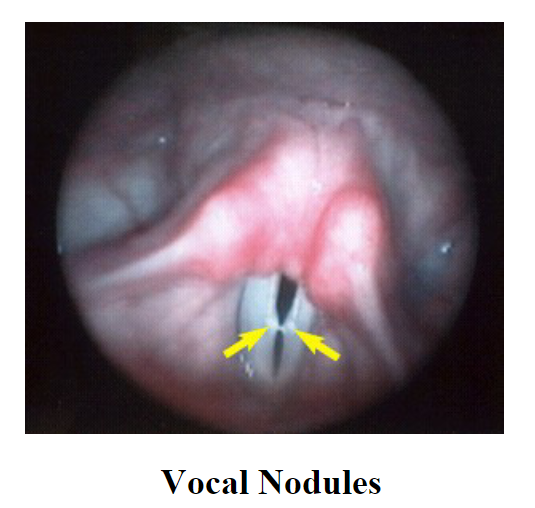
How is surgery (otolaryngologist) used to treat the larynx?: Surgery is used to remove mass lesions (i.e. polyps, cysts). There are also injections to increase vocal fold mass (gel foam, fat), thyroplasty and arytenoid surgeries.
How is pharmacology (otolaryngologist) used to treat the larynx?: Pharmocology can be used to treat the larynx and two examples of these are steroids (used to treat edema) and BOTOX (used to treat spasmodic dysphonia)

What are six ways that the pathology of the larynx can be treated with voice therapy?: The pathology of the larynx can be treated with voice therapy from a speech language pathologist. Some techniques that can be used involves vocal hygiene counseling, eliminating vocally abusive patterns, building strength of the laryngeal muscles, increasing the resonance of the voice, laryngeal massage, and exploring the emotional/social aspects of the problem.

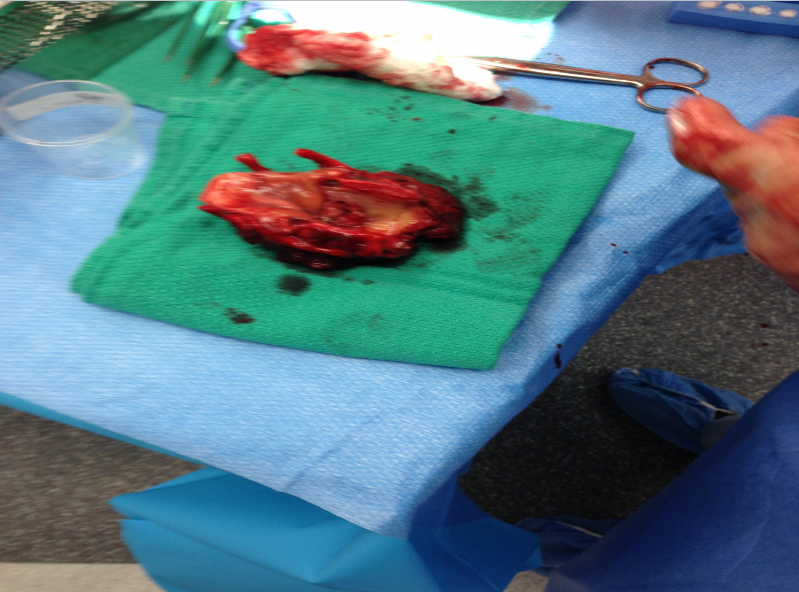
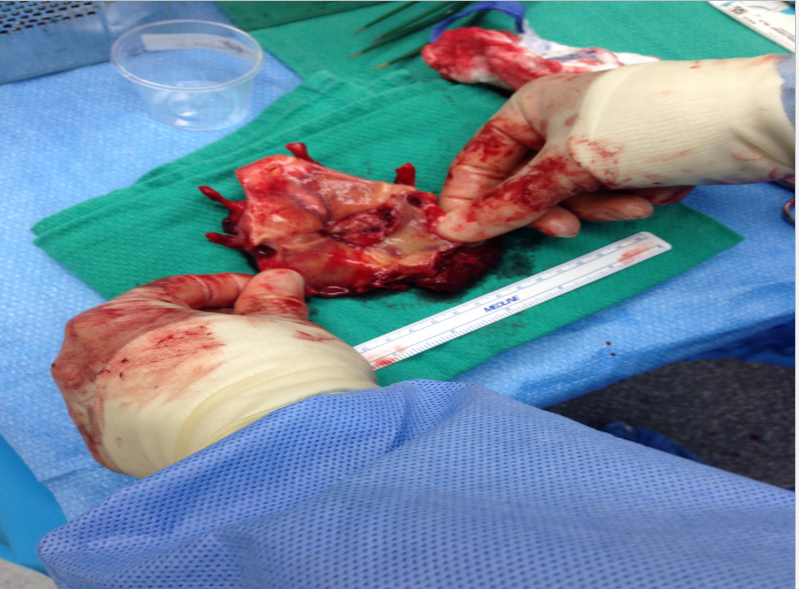
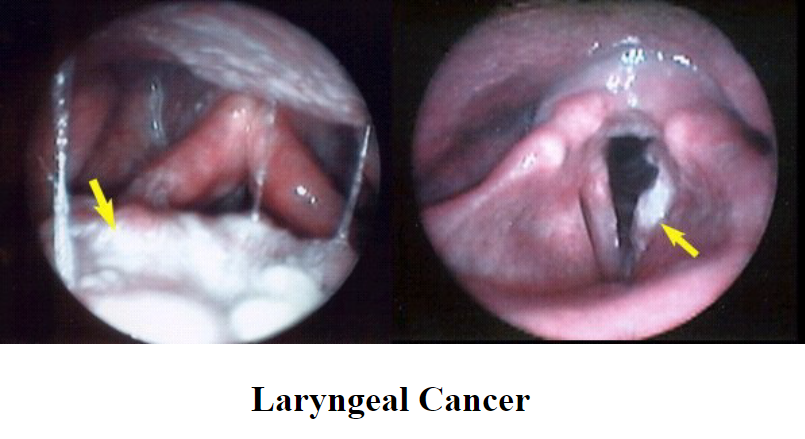
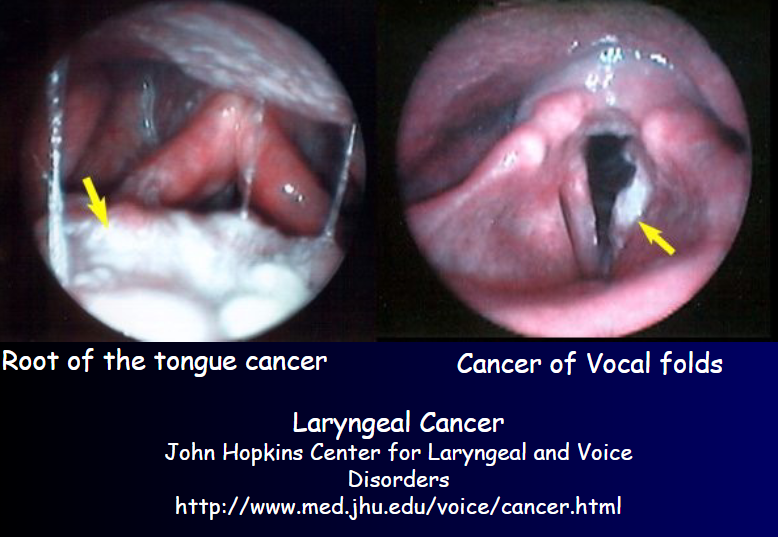
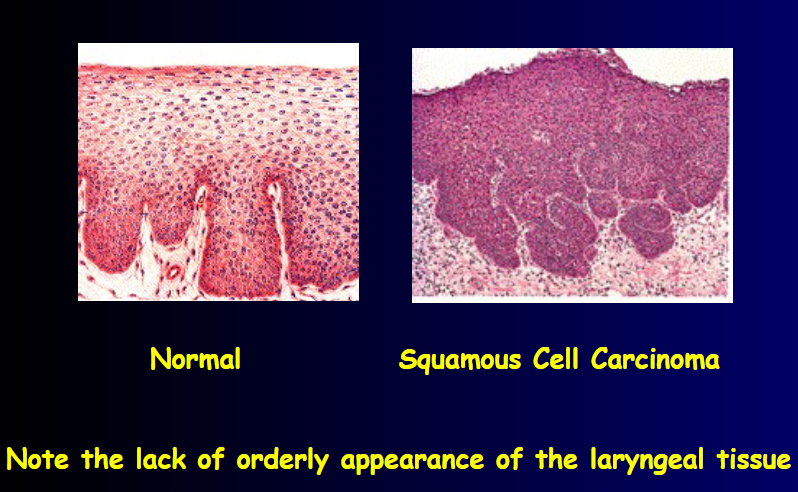
Carcinoma: lump in the neck, tenderness in neck, hoarseness, dysphagia, dyspnea, biopsy required for DX
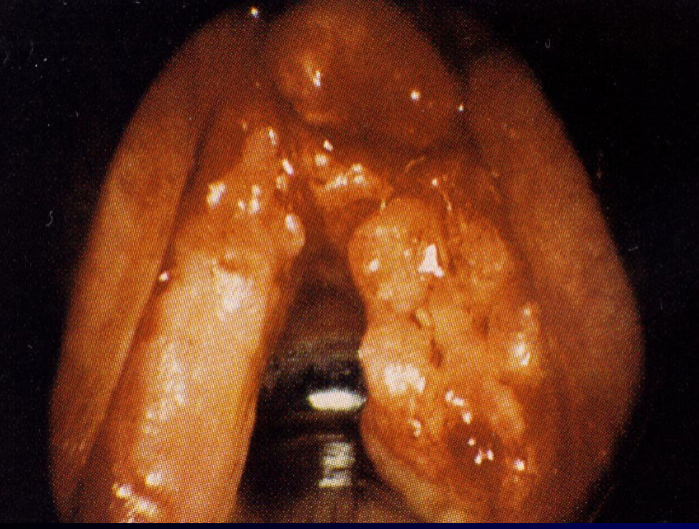

Carcinoma incidence: 2-5% of all malignancies
Carcinoma induces persistent: hoarseness
Causes of carcinoma: smoking, environmental irritation, chemicals, metabolic disturbances, unknown
50-70% of laryngeal cancers are associated with: smoking
Carcinoma has a synergistic effect with: alcohol
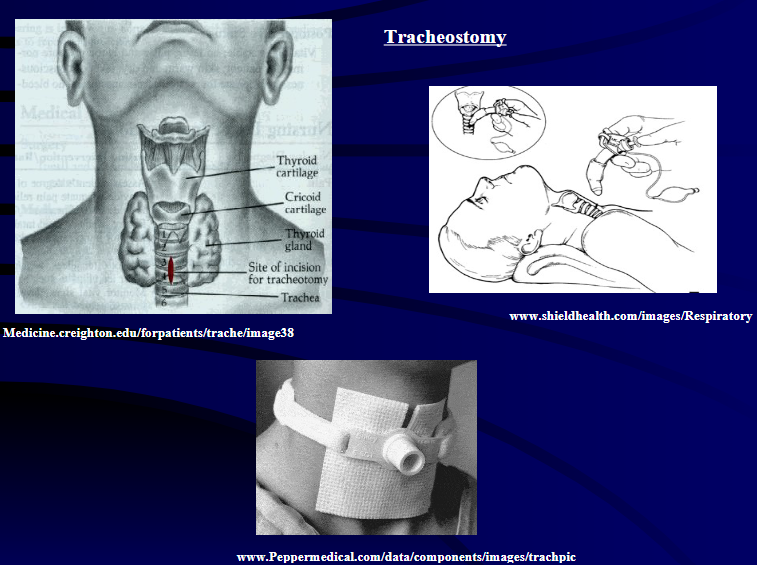
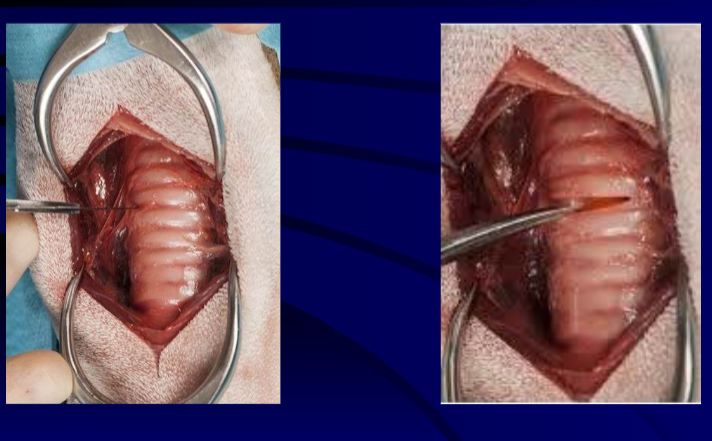
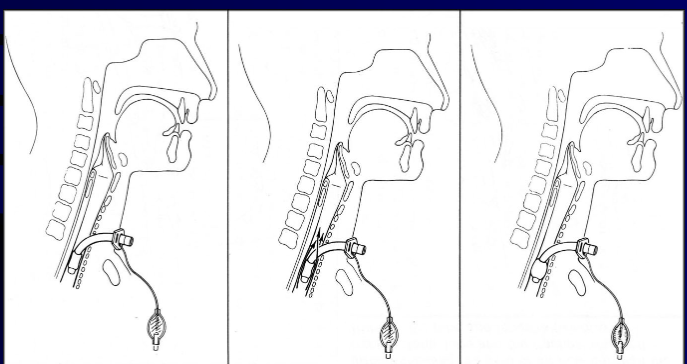
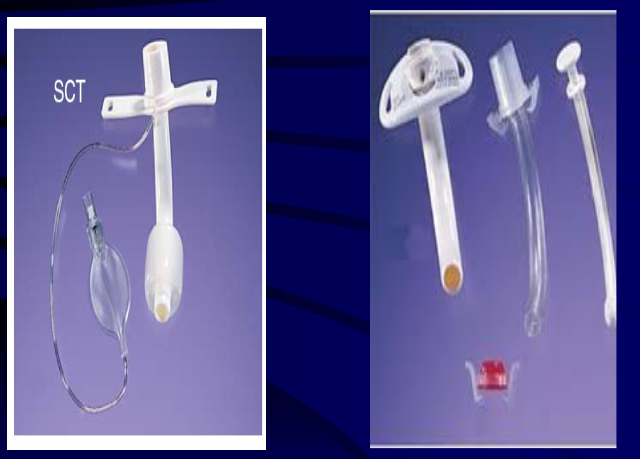
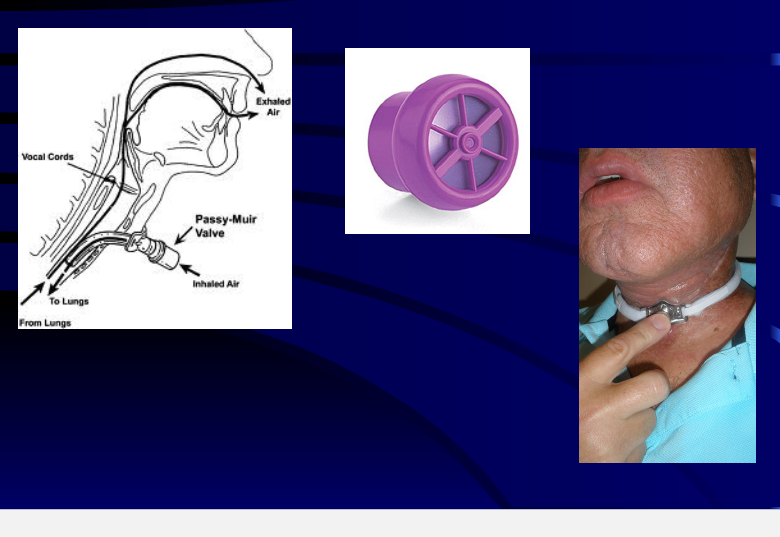
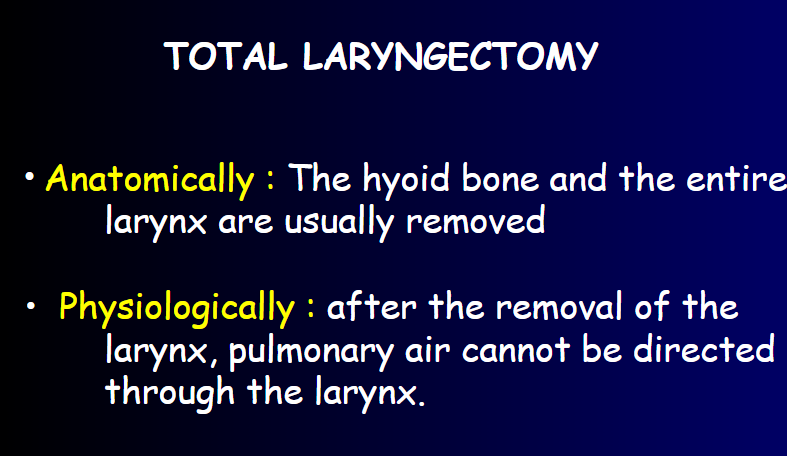
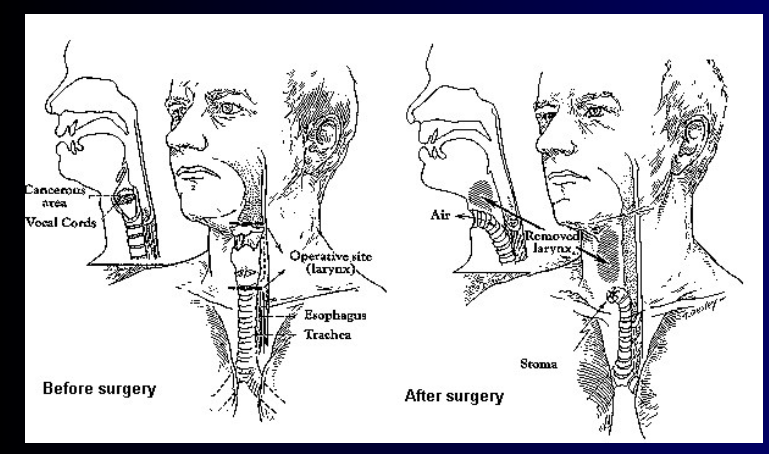
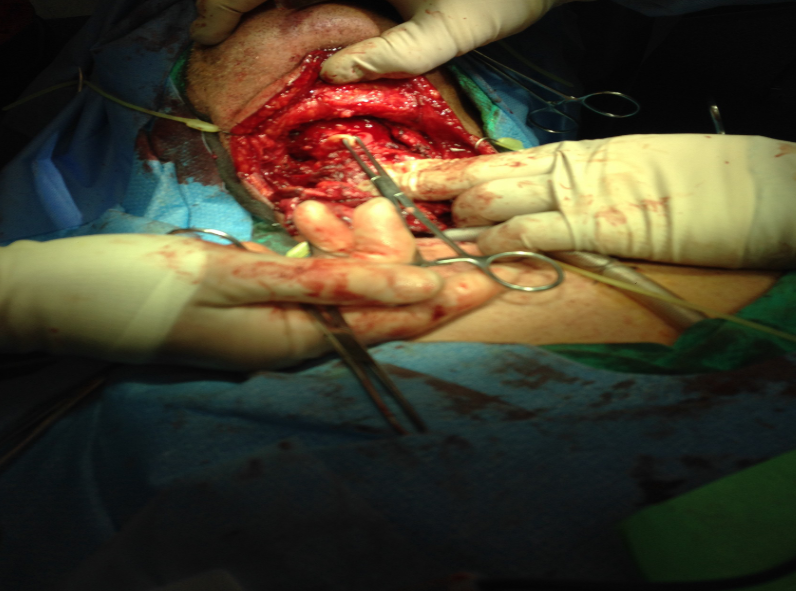
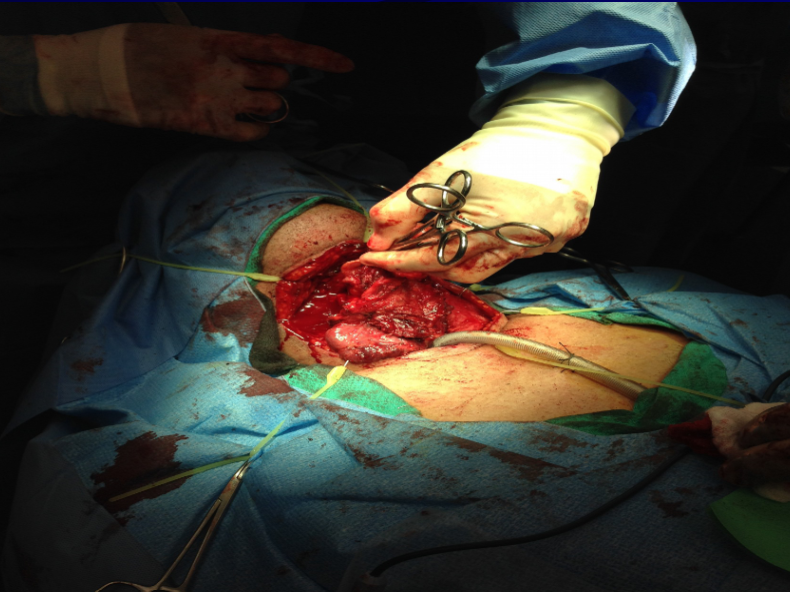
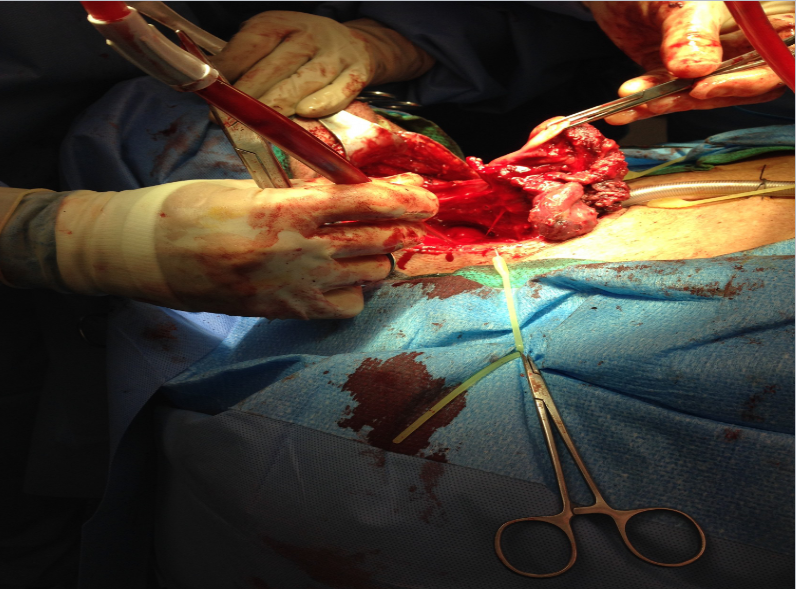
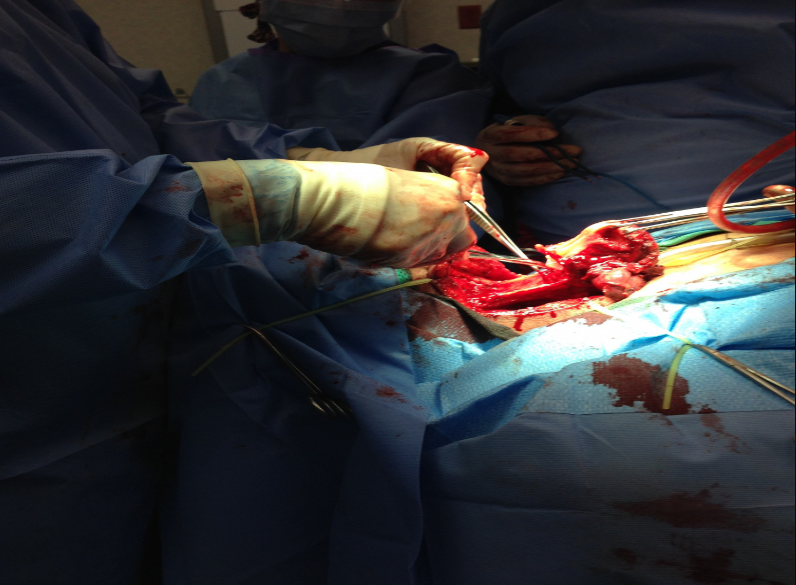
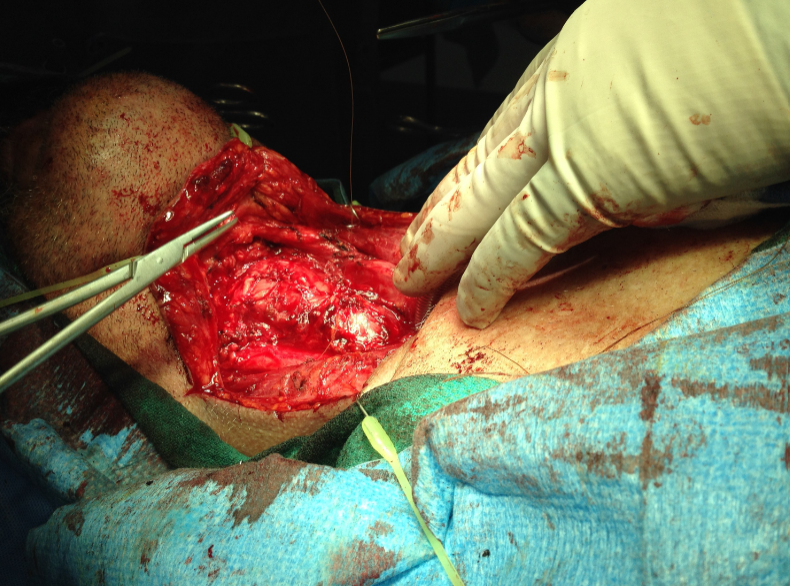
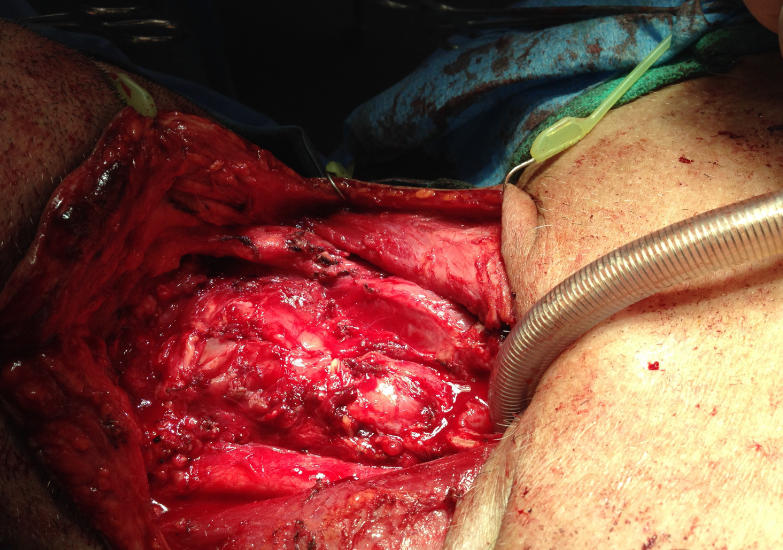
Total laryngectomy anatomically: The hyoid bone and the entire larynx are usually removed
Total laryngectomy physiologically: after the removal of the larynx, pulmonary air cannot be directed through the larynx

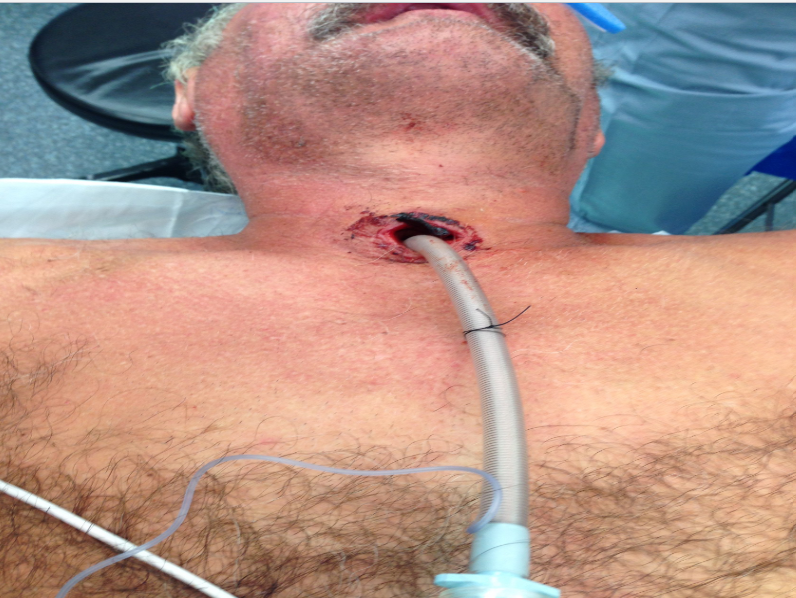
The upper portion of the teaches (windpipe) is brought out to the: front of the neck to create a permanent opening called a stoma
When a laryngectomy patient inhales, air passes directly through: the stoma into the trachea and then into the lungs
The connection between the mouth and the esophagus is: usually not affected, so food and liquid can be swallowed just as they were before the operation