Unit 3 VCE Psych AOS 1 - L1-8 no GBA
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Central Nervous System
(CNS) brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous system
Body Nerves that connect to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Connects the central nervous system to the body's organs and limbs.
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions (not consciously controlled), such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary bodily functions (consciously controlled), such as controlling skeletal muscles
Stimulus
Things that initiate nerve impulses (ex. hot room)
Motor Functions
Complex muscle-and-nerve acts that produce movement (walking, writing, typing running etc.)
"Electrochemical"
A nerve impulse is partially electric (change in polarity/charge) and partially chemical (neurotransmitters)
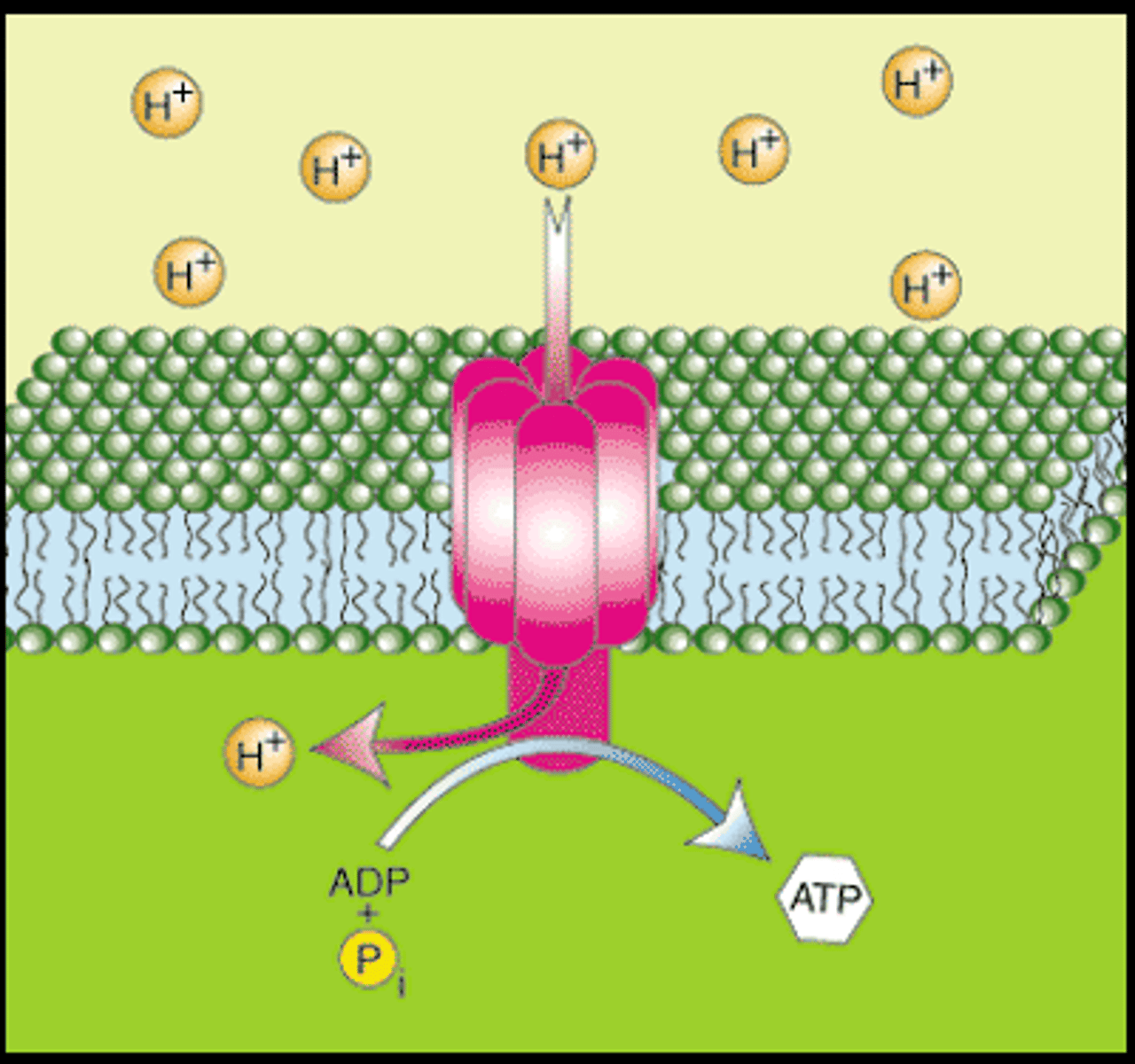
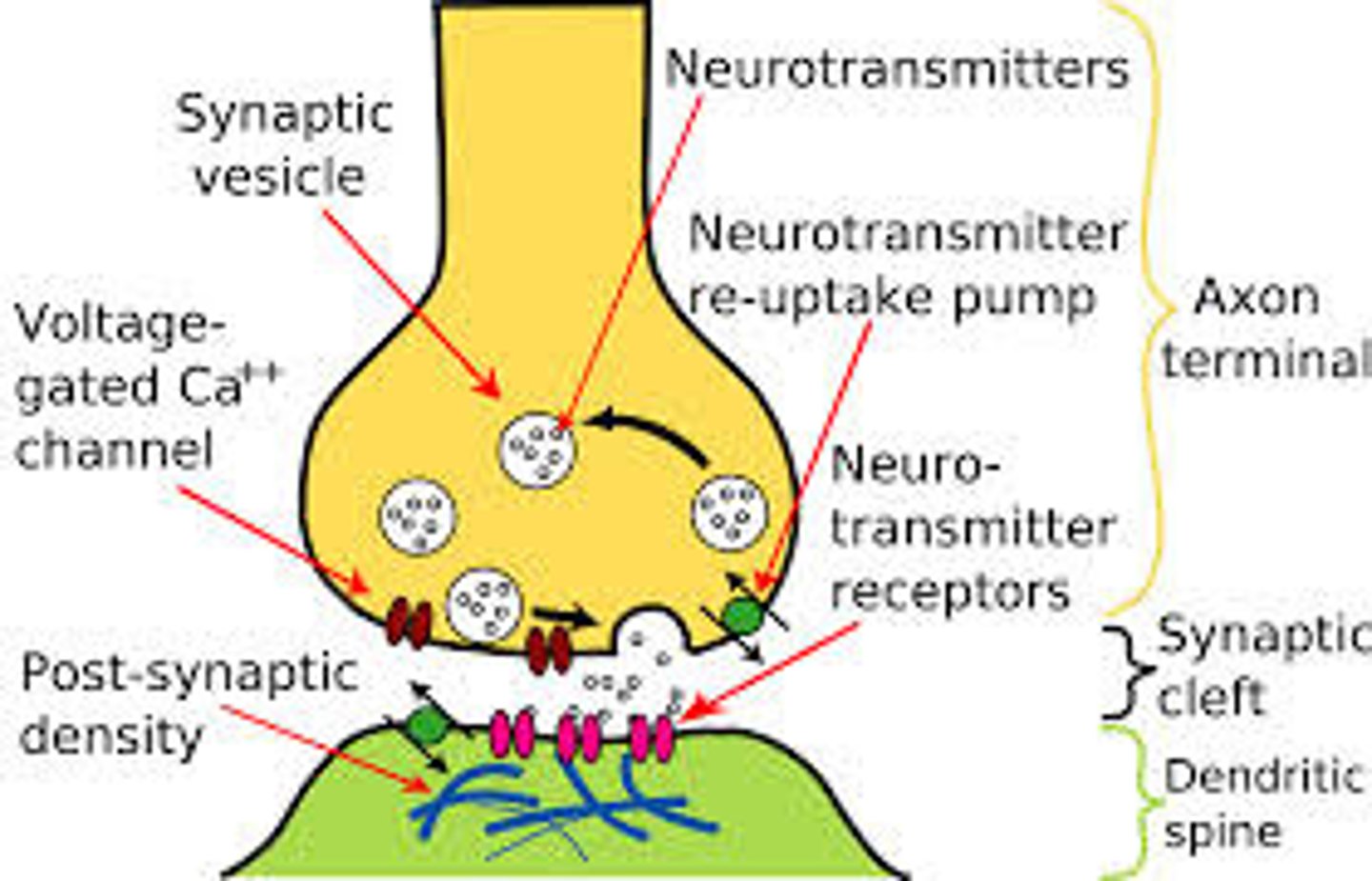
Synapse
Where the nerve impulse is sent (connection of 2 neurons) .
Action Potential changes the charge of the synapse (causes electricity) and Neurotransmitters are sent.
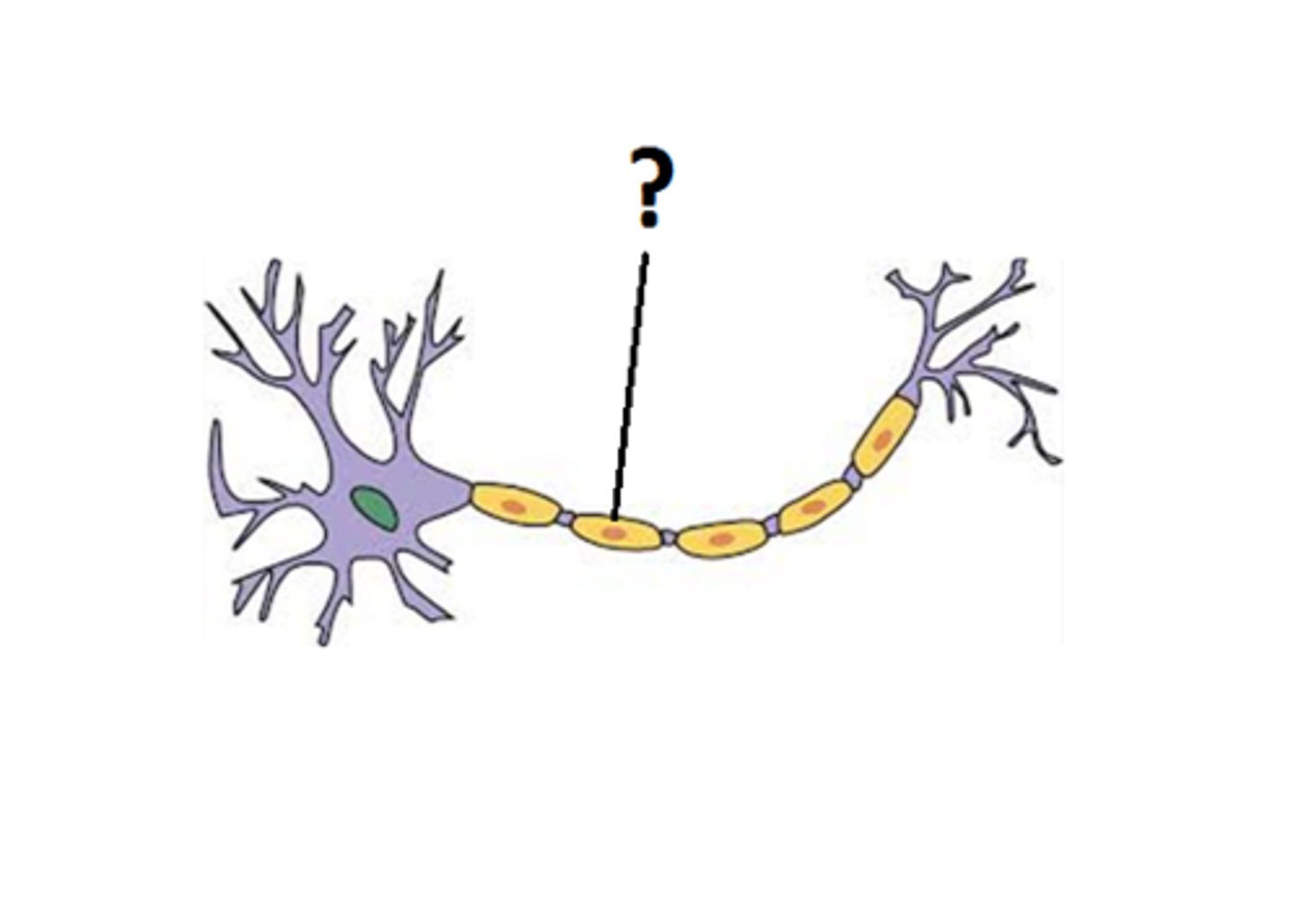
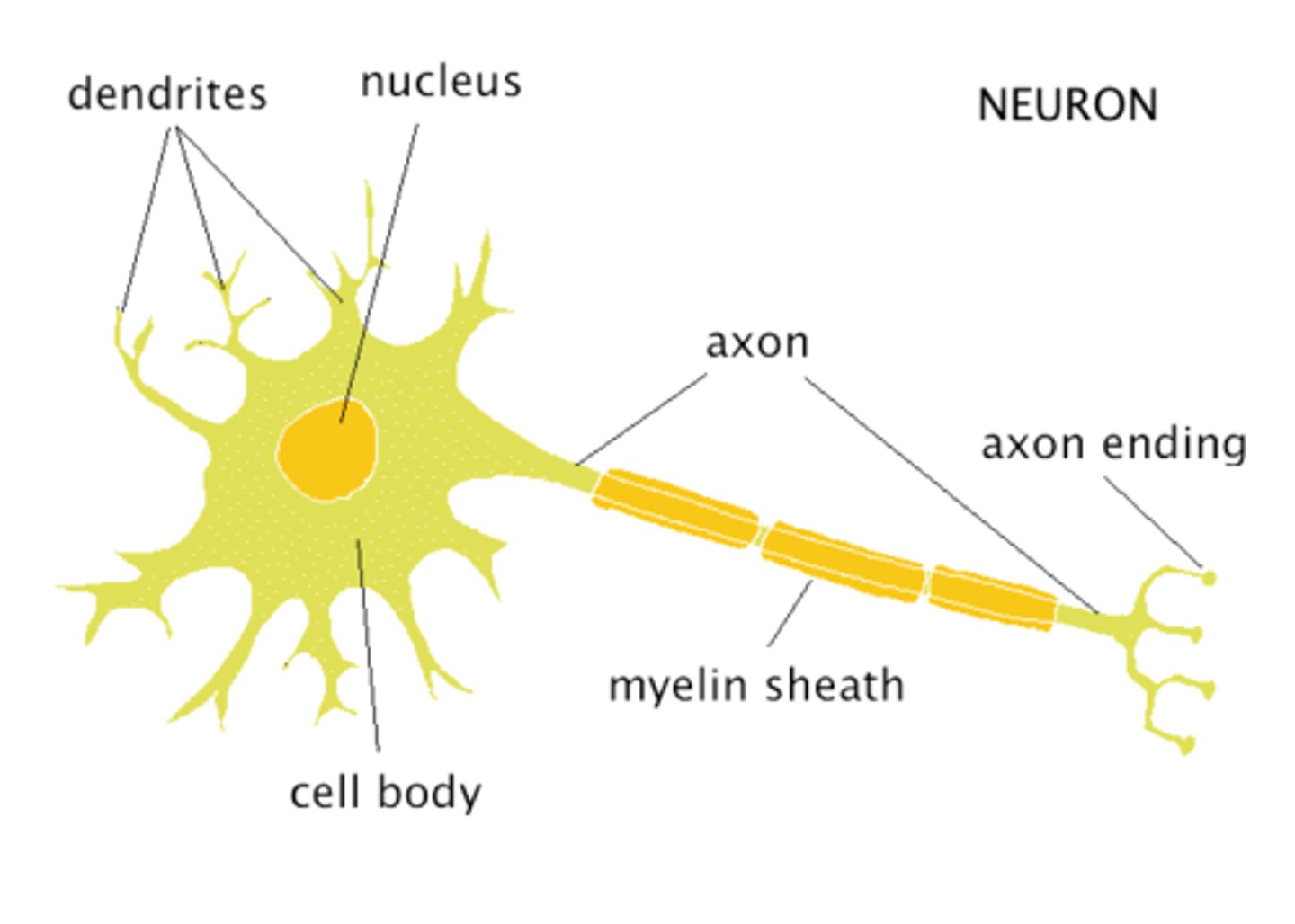
Myelin Sheath
Offers protection to the neuron, Speeds up nerve impulses.
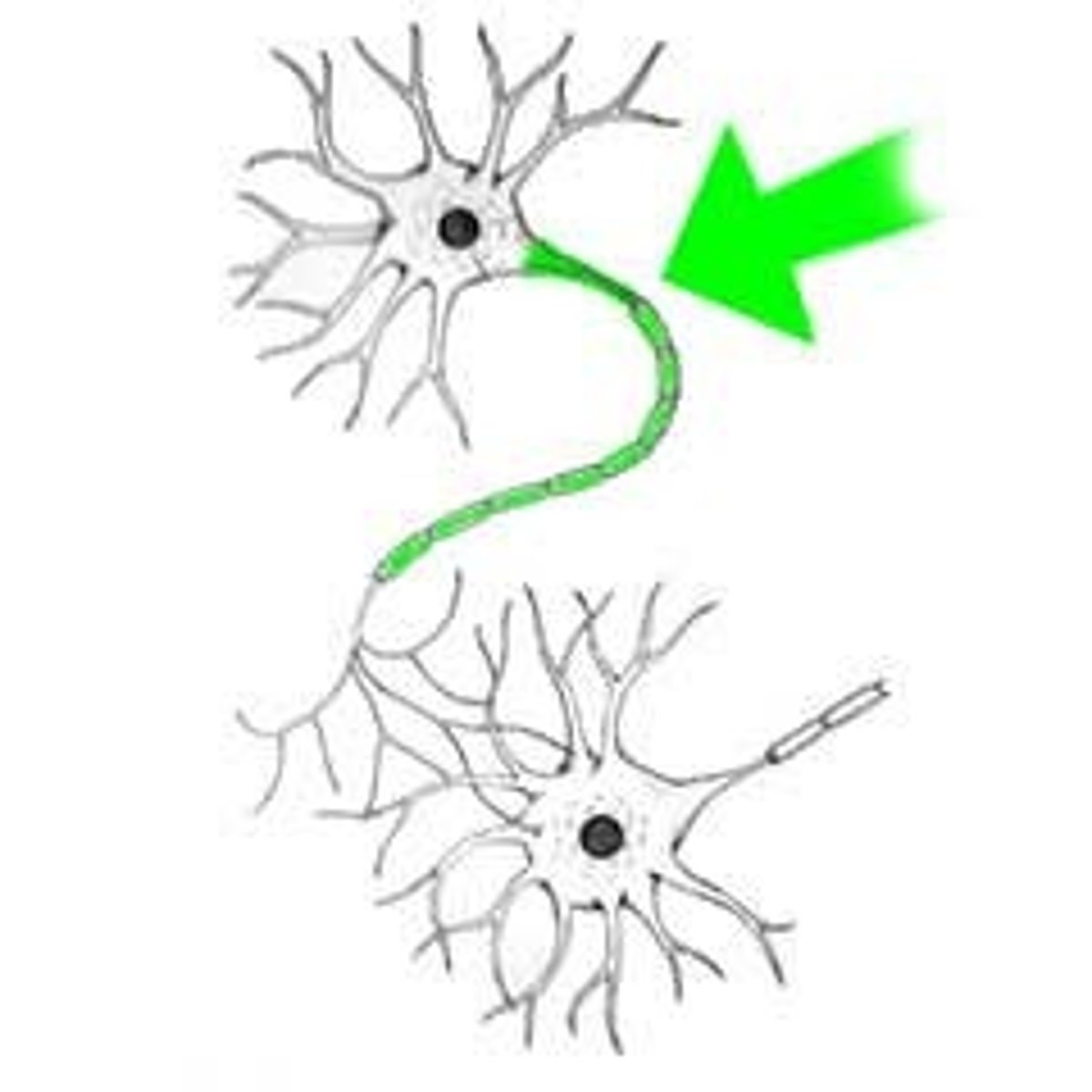
Axon
The long threadlike part of a nerve cell that carry the nerve impulse
Dendrites
Branch like extensions on a neuron that GET signals and connect to the synapse
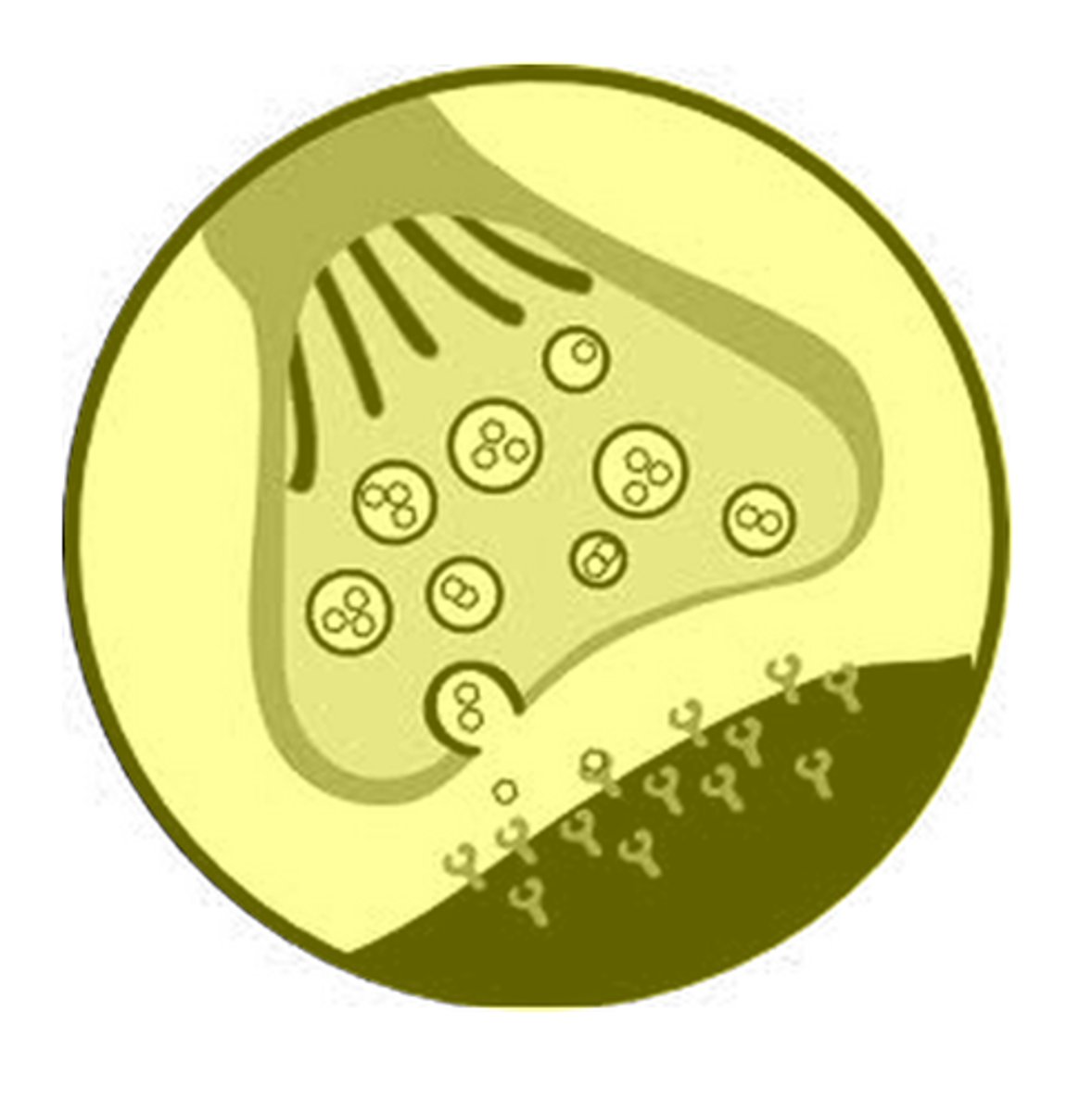
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another 'target' neuron
Sensory Neuron
Nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, smell, sound etc.)
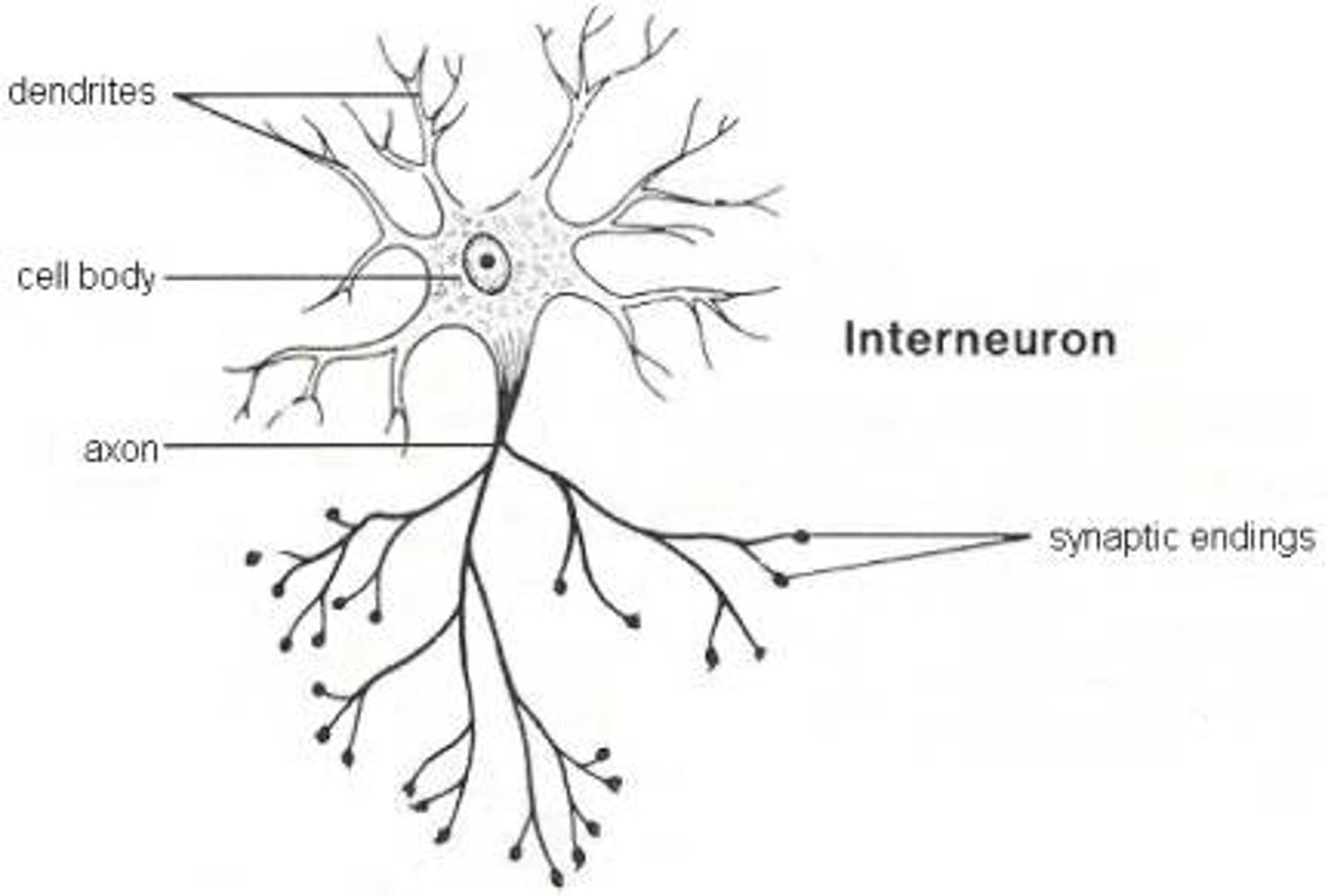
Interneuron
Nerve cells that connect motor neurons and sensory neurons. Only found in the CNS.
Motor Neuron
Nerve cells responsible for making an action or movement happen.
Efferent Tracts
A nerve pathway that goes downwards from the brain toward the PNS carrying motor information
Afferent Tracts
A nerve pathway that goes upward from the spinal cord toward the brain carrying sensory information
Excitatory Neurtransmitters
Stimulates a post synaptic neuron to fire. Activates the brain.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Stops a post synaptic neuron from firing. Calms the brain and helps create balance.
Dopamine
Excitatory neuromodulator, feel good
Regulates attention, cognition, movement, pleasure, and hormonal processes
(Low amounts: Parkinson's)
Adrenaline
a hormone that may affect memory consolidation of emotionally arousing experiences; also called epinephrine
Glutamate
a neuromodulator that plays crucial roles in the growth and strengthening of synaptic connections during learning and memory formation
Eustress
Positive psychological response to a percieved stressor.
Distress
Negative psychological response to a percieved stressor.
GAS
General Adaption Syndrome, three stage model explaining physiological response to stress that occurs regardless of stressor.
Alarm Reaction stage
First stage of the GAS, during which the body mobilizes its resources to cope with a stressor.
Resistance stage
The second stage of the GAS, when there are intense physiological efforts to either resist or adapt to the stressor.
Cortisol
Stress hormone involved in chronic stress, initially aids body in the stress response, release increases when stressor remains present for an extended period of time.
Adrenaline
Neurohormone that helps the body respond to stress initially in the flight-fight-freeze response
Shock (stage)
Part of Alarm Reaction stage - Body responds as though injured. Resistance to stress is lower than normal.
Counter-Shock (stage)
Part of Alarm Reaction stage - Fight flight freeze response is activated by sympathetic nervous system. Resistance to stress starts to increase above normal
Resistance stage - hormone activity
Cortisol + adrenaline still fighting stressor, body is aroused with more energy to deal with situation, if keeps going can get sick
Exhaustion stage
Third stage of GAS, when Resistance stage lasts too long or stressor is removed, body's coping resources become depleted = serious illness
Dependent variable
Shows any effects of the independent variable.
Hypothesis
A tentative and testable prediction of the relationship between two or more events or characteristics.
Operational hypothesis
A research hypothesis that states how the variables being studied will be observed, manipulated and measured.
Extraneous variable
Any variable other than the IV that can cause a change in the DV and therefore affect the results of the experiment in an unwanted way.
Confounding variable
A variable other than the IV that has had an unwanted affect on the DV, making it impossible to determine which of the variables has produced the change in the DV.
Individual participant differences
The differences in personal characteristics and experiences of the individual participants in an experiment.
Placebo
The inactive 'fake' substance or treatment which substitutes for the real substance or treatment in an experiment.
Placebo effect
Occurs when there is a change in the responses of participants due to their belief that they are receiving some kind of experimental treatment and they respond in accordance with that belief, rather than to the effect of the IV.
Experimenter effect
Occurs when there is a change in a participant's response due to the researcher's expectations, biases or actions, rather than to the effect of the IV.
Order effect
Occurs when performance, as measured by the DV, is influenced by the specific order in which the conditions, treatments or tasks are presented rather than the IV.
Participants
The people used in an experiment or any other kind of research study.
Sampling
The process of selecting participants for a research study.
Convenience sampling
Random sampling
Stratified sampling
Random-stratified sampling
Convenience sampling
Involves selecting participants who are readily available without any attempt to make the sample representative of a population.
Random sampling
A sampling procedure that ensures every member of the population of research interest has an equal change of being selected as a participant for a study (and that the selection of one participant does not influence the selection or non-selection of another)
Stratified sampling
Dividing the population to be sampled into distinct subgroups, or strata, then selecting a separate sample from each stratum in the same proportions as they occur in the target population.
Random-stratified sampling
Involves identifying all of the people within each stratum of research interest, then randomly selecting samples of proportionate size from within each stratum.
Experimental group
The group exposed to the experimental condition in which the IV under investigation is present.
Control group
The group exposed to the control condition in which the independent variable is absent.
Random allocation
When participants selected for the experiment are as likely to be in one group as the other.
Counterbalancing
Systematically changing the order of treatments or tasks for participants in a 'balanced' way to counter the unwanted effects on performance of any one order.
Single-blind procedure
The participants are not aware of the condition of the experiment to which they have been allocated and therefore the experimental treatment.
Double-blind procedure
The participants and the researcher directly involved with the participants are unaware if the conditions to which the participants have been allocated.
Standardised instructions
The instructions given to all participants for each condition are predetermined and identical in terms of what they state and how they are administered.
Standardised procedures
The techniques used for making observations and measuring responses to ensure they are identical for all individual participants.
Within groups design
Each participant is involved in both the experimental and control conditions of an experiment so the effects of individual participant differences balance out exactly.
Between groups design
Each participant is randomly allocated to one of two entirely separate conditions or groups.
Qualitative data
Information about the qualities or characteristics of what is being studied. They are descriptions, words, meanings, pictures, texts and so on.
Quantitative data
Information about quantities or amounts of what is being studied. Usually expressed in the form of units of measurement or numbers.
Case studies
An intensive, in-depth investigation of some behaviour or event of interest in an individual, small group or situation.
Observational study
Involves collecting data by carefully watching and recording behaviour as it occurs.
Naturalistic observation
When the researcher views a naturally occurring behaviour of interest in an inconspicuous or unnoticeable manner so that their presence does not influence the behaviour being observed.
Self-reports
The participant's written or spoken responses to questions, statements or instructions presented by the researcher.
Mean
The arithmetical average of all the individual scores in a set of scores.
Median
The middle score of a set of scores.
Mode
The most frequently occurring score in a set of scores.
Conclusion
A decision or judgement about what the results obtained from an investigation mean.
Generalisation
A decision or judgement about how widely the findings of a study can be applied, particularly to other members of the population from which the sample was drawn.
Ethics
Standards that guide individuals to identify good, desirable or acceptable conduct.
Ethical Considerations in research
To ensure that no psychological or physical harm is caused to research participants.
Confidentiality
Voluntary participation
Withdrawal rights
Informed consent
Debriefing