11.3 Reflection and refraction
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
When does reflection occur?
Reflection occurs when a wave changes direction at a boundary between two different media, remaning in the original medium.
Draw reflection off a mirrored surface.
The light waves remain in the original medium (the air). We represent the path taken by the light wave as a ray. The ray shows the direction of energy transfer and so the path taken by the wave.
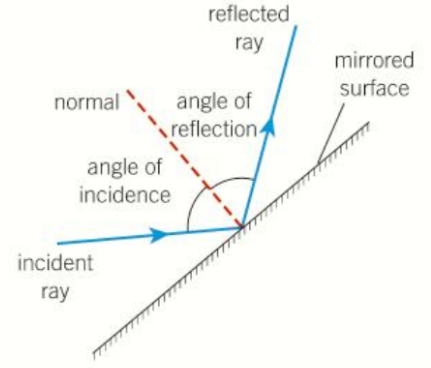
What is the law of reflection?
Whenever waves are reflected, it states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
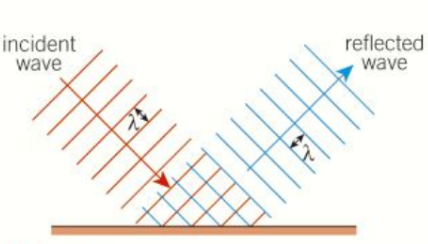
What happens when waves are reflected?
When waves are reflected their wavelength and frequency do not change. This can be shown by these wavefronts.
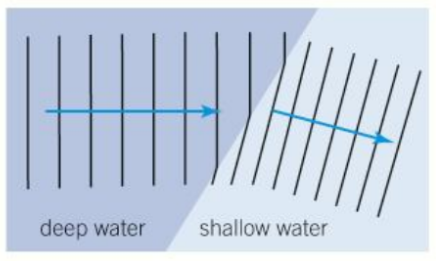
When does refraction occur?
Refraction occurs when a wave changes direction as it changes speed when is passes from one medium to another. Whenever a wave refracts there is always some reflection
What happens when waves are refracted?
Unlike reflection, refraction does have an affect on the wavelength of the wave, but not its frequency. If the wave slows down its wavelength decreases and the frequency remains unchanged.
What happens to the speed of water waves when there is changes to movement in water?
When a wave enters shallower water, it slows down and the wavelength gets shorter.