Normal Fetal Brain Anatomy
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Ectoderm
What does the CNS develop from
5 weeks LMP
When does the CNS start developing
Middle
Where does the neural tube start to close
Day 38 LMP
When does the cranial end of the neural tube close
Day 40 LMP
When does the caudal end of the neural tube close
End of 6th week
When does the neural tube differentiate into 3 primary vesicles
Prosenchephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon
What 3 primary vesicles does the neural tube differentiate into
Prosenchephalon
What is 1
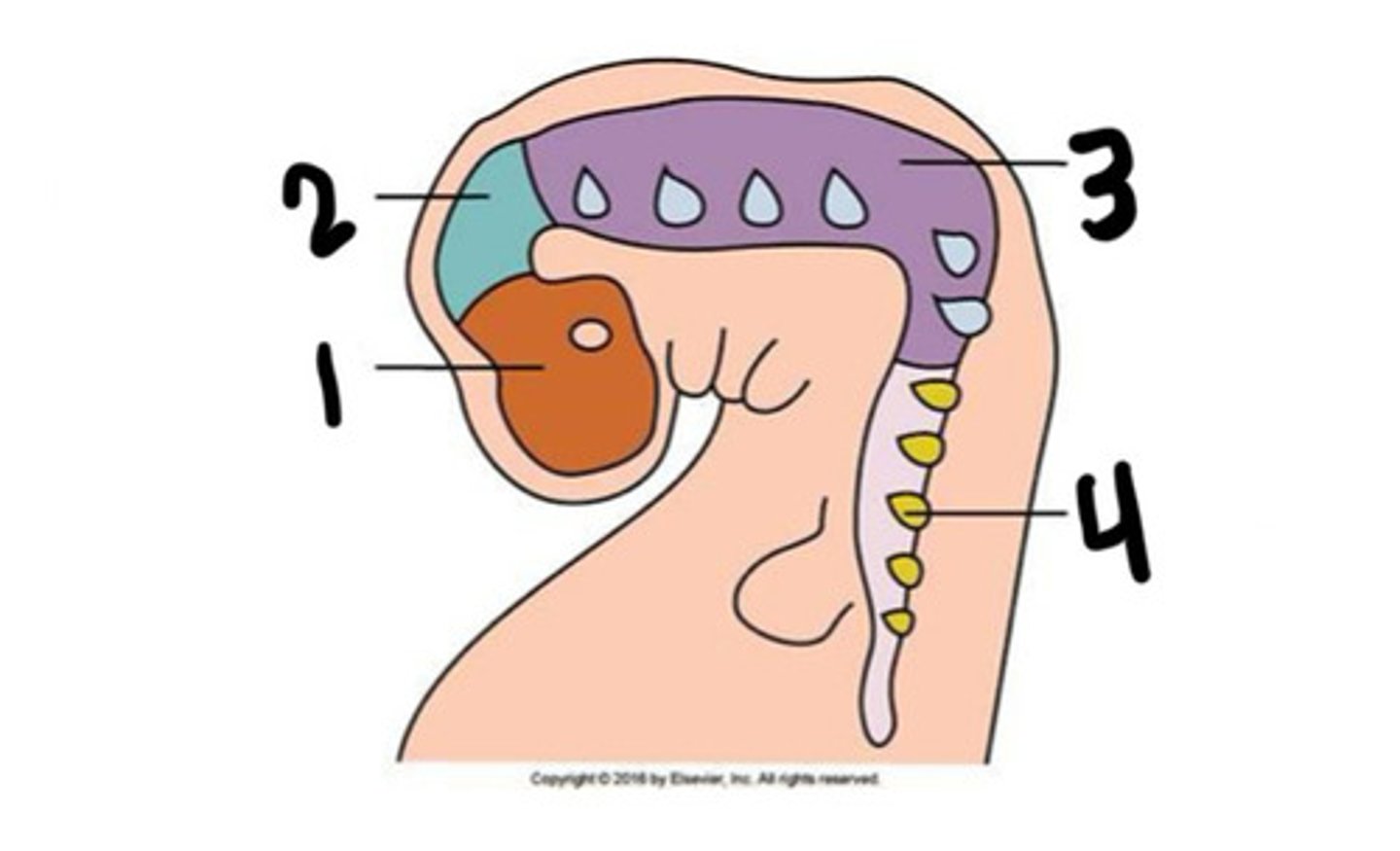
Mesenchephalon
What is 2
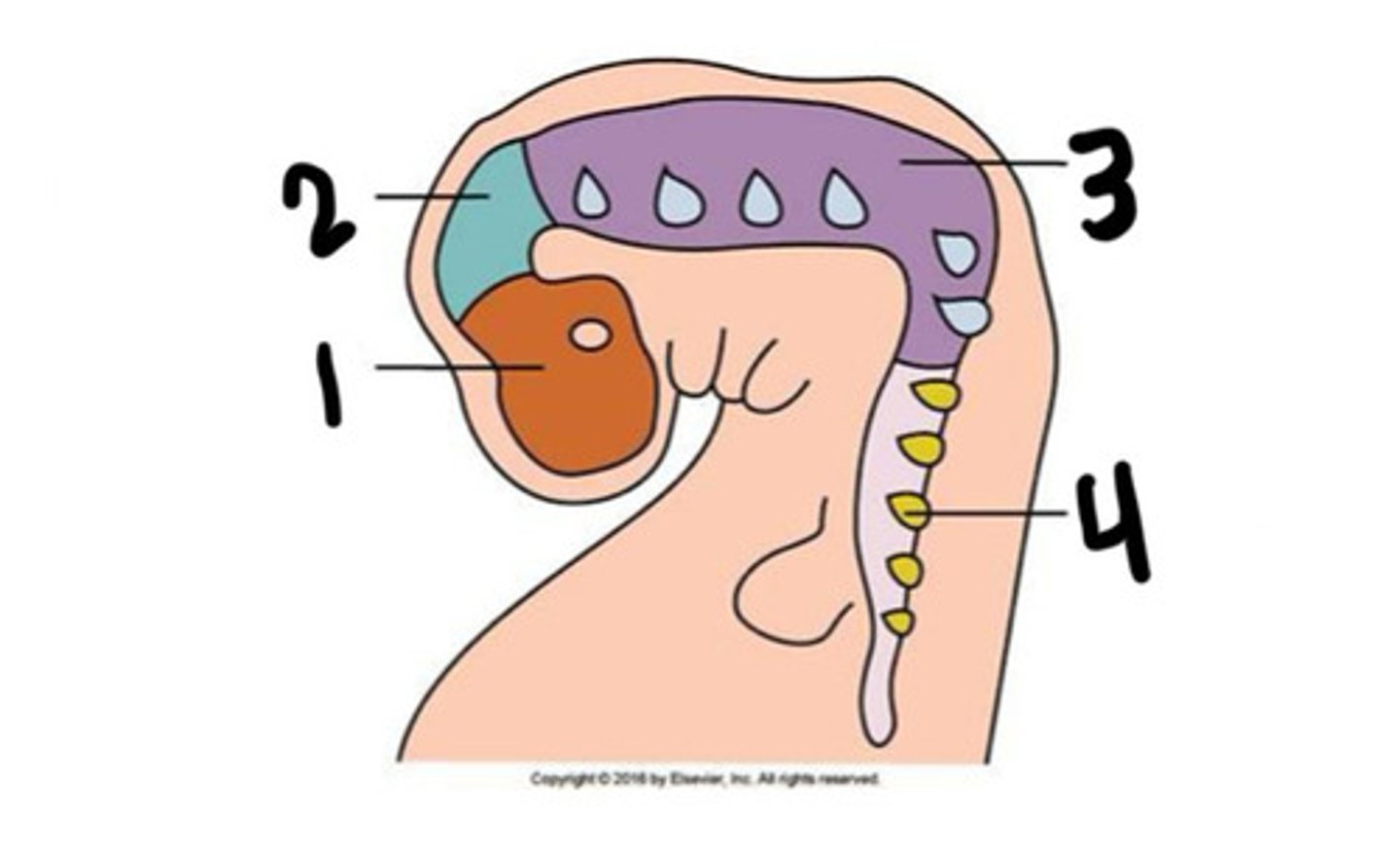
Rhombencephalon
What is 3
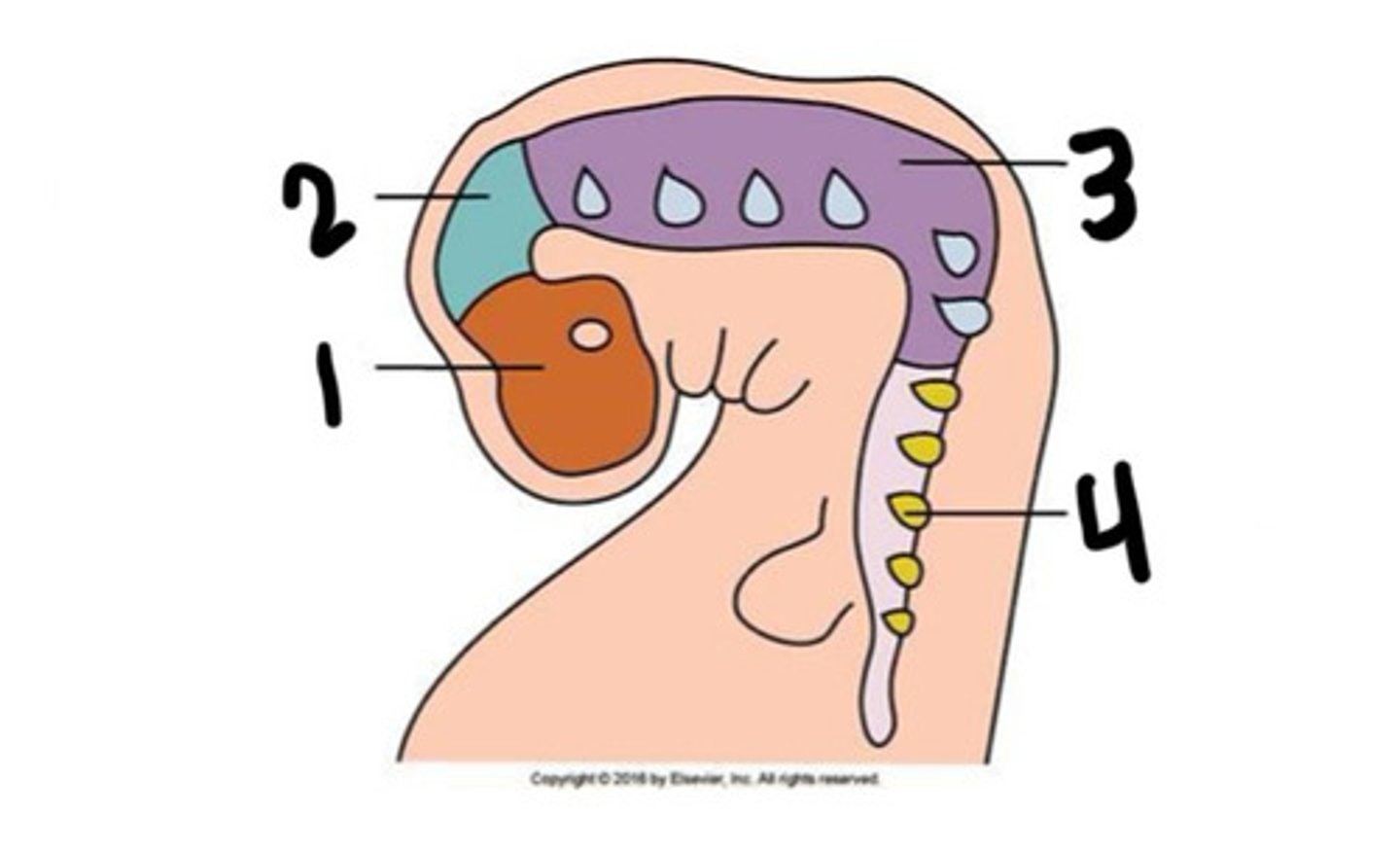
Spinal cord
What is 4
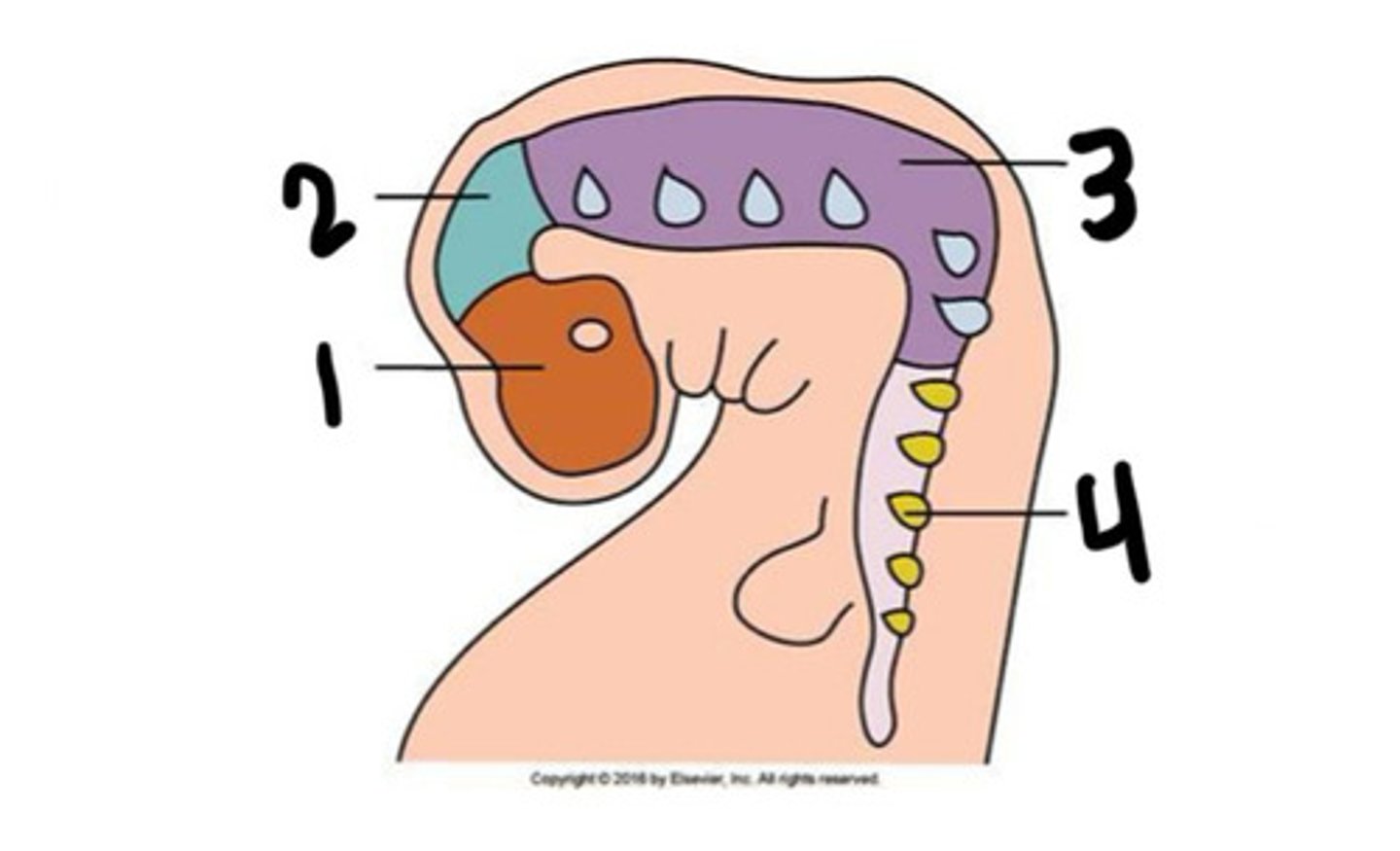
Forebrain
What is Prosenchephalon also known as
Midbrain
What is mesencephalon also known as
Hindbrain
What is rhombencephalon also known as
Rostral end
What end of the neural tube differentiates into the 3 vesicles
Telencephalon and diencephalon
What does the prosencephalon divide into?
Cerebral hemispheres
What does the telencephalon become
Thalmus and hypothalamus
What does the diencephalon become
Learned behaviour and personality
What is the cerebrum in control of
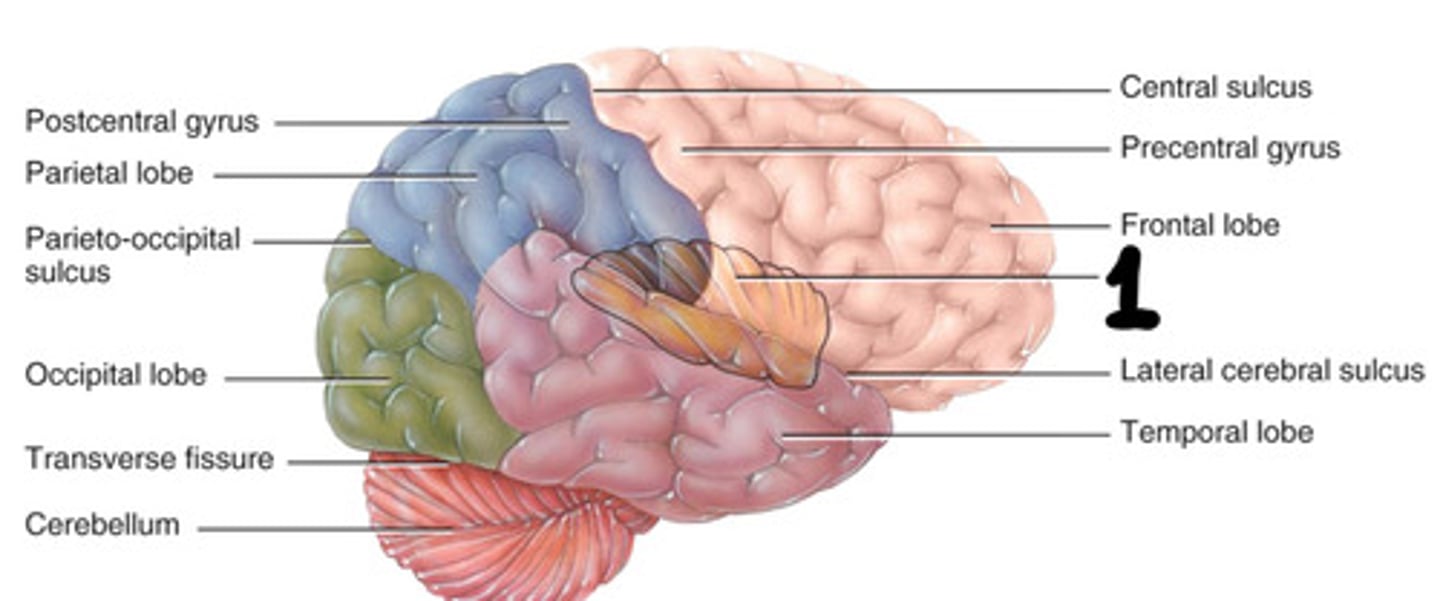
Frontal lobes, parietal lobes, temporal lobes, occipital lobes, insula lobes (2 of each)
What are the 10 lobes in the cerebrum
Personality, voluntary motion
What does the frontal lobes do
Peripheral sensory
What are the parietal lobes in control of
Smell, taste, hearing
What are the temporal lobes in control of
Vision
What are the occipital lobes in control of
Motor and sensory function of organs
What are the insula in control of
Frontal lobe
What is 1
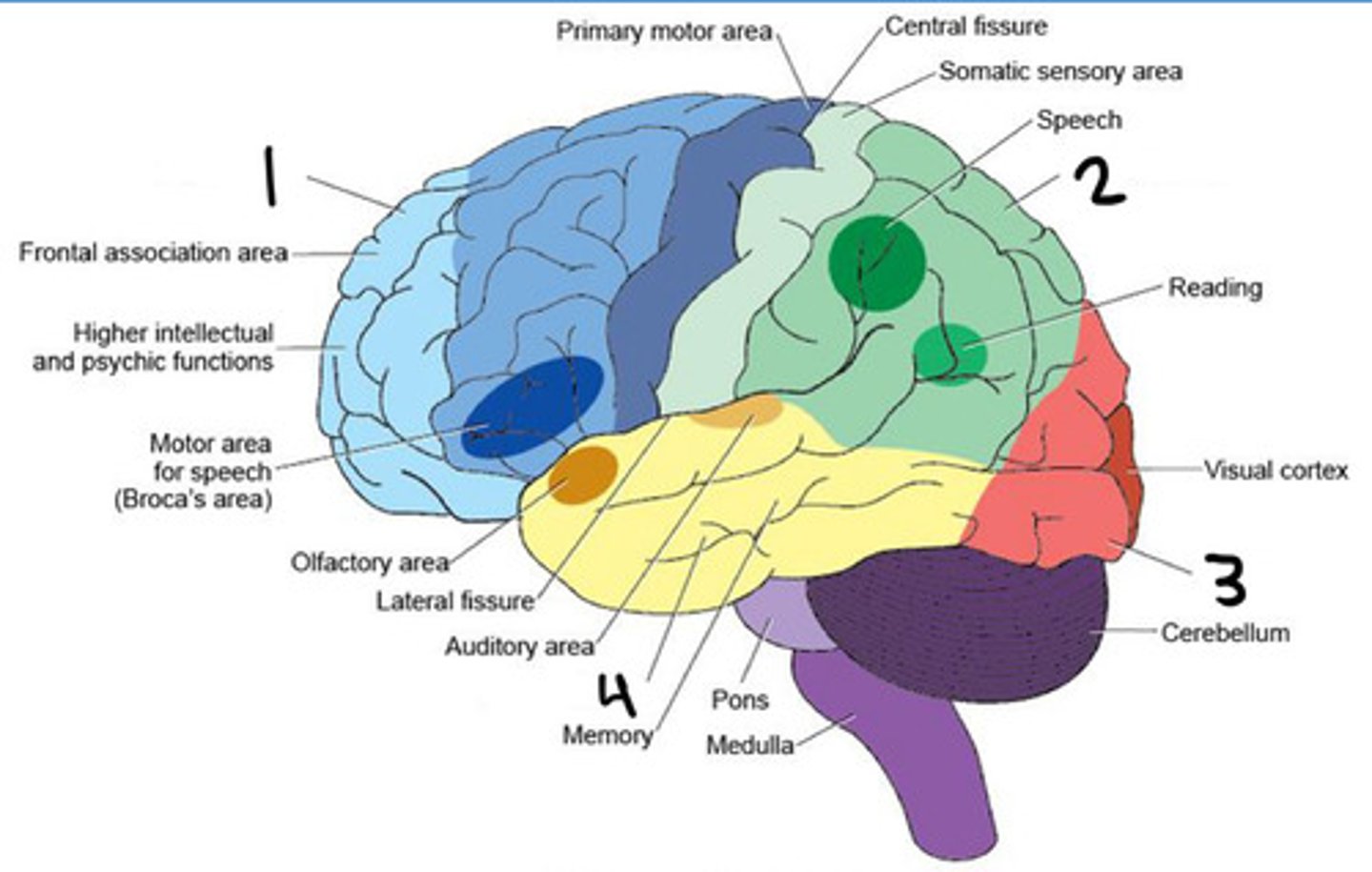
Parietal lobe
What is 2
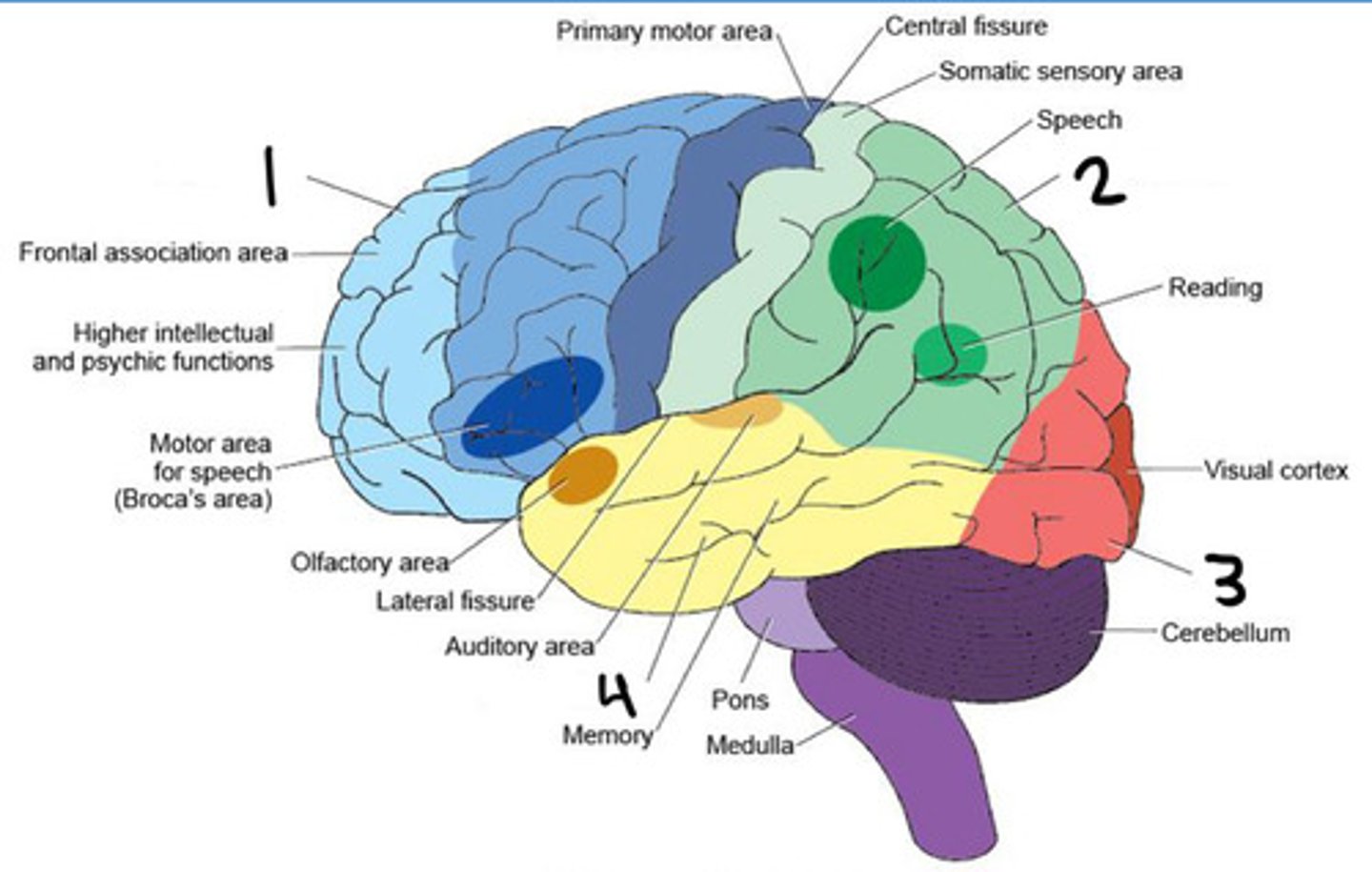
Occipital lobe
What is 3
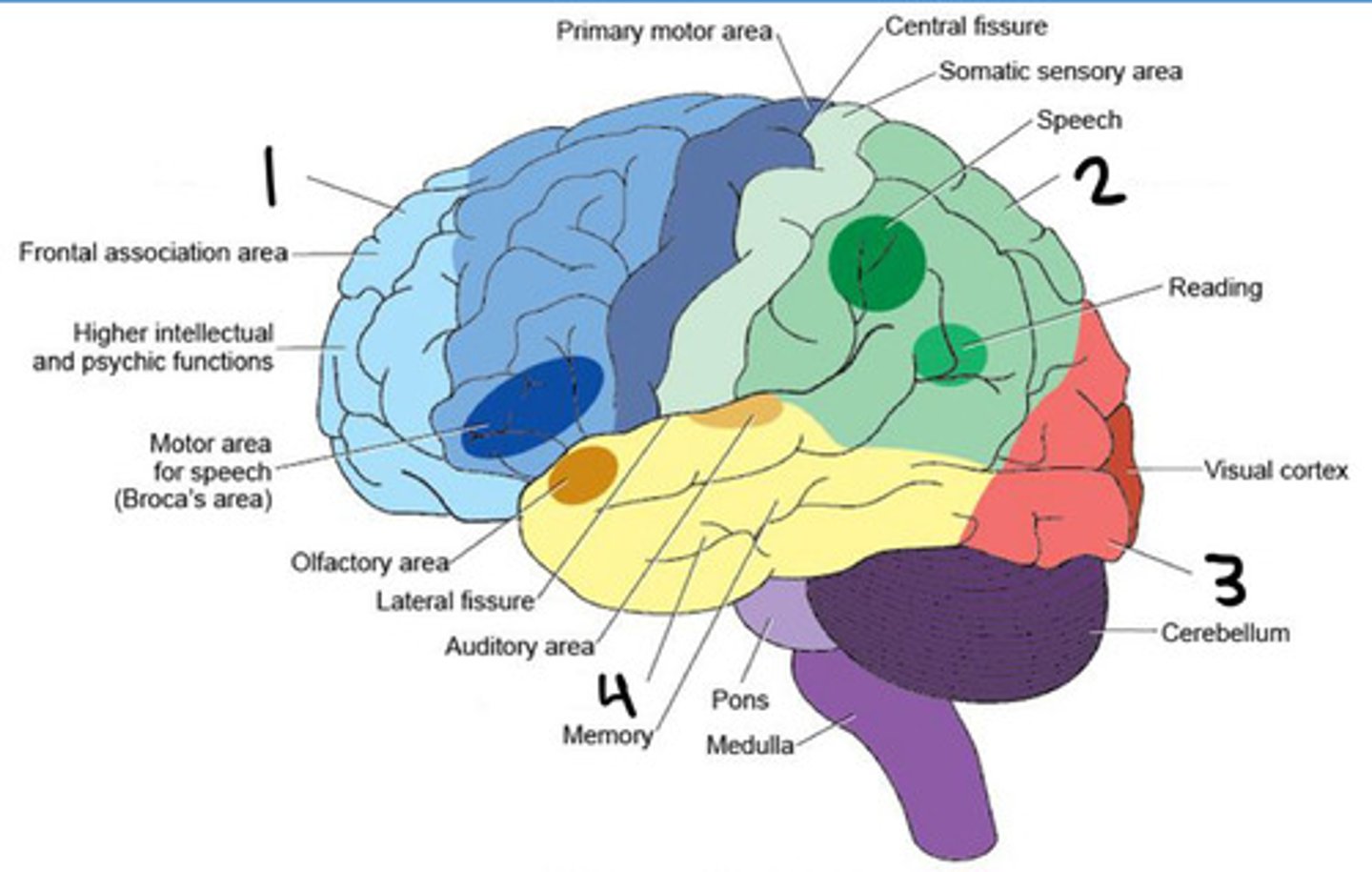
Temporal lobe
What is 4
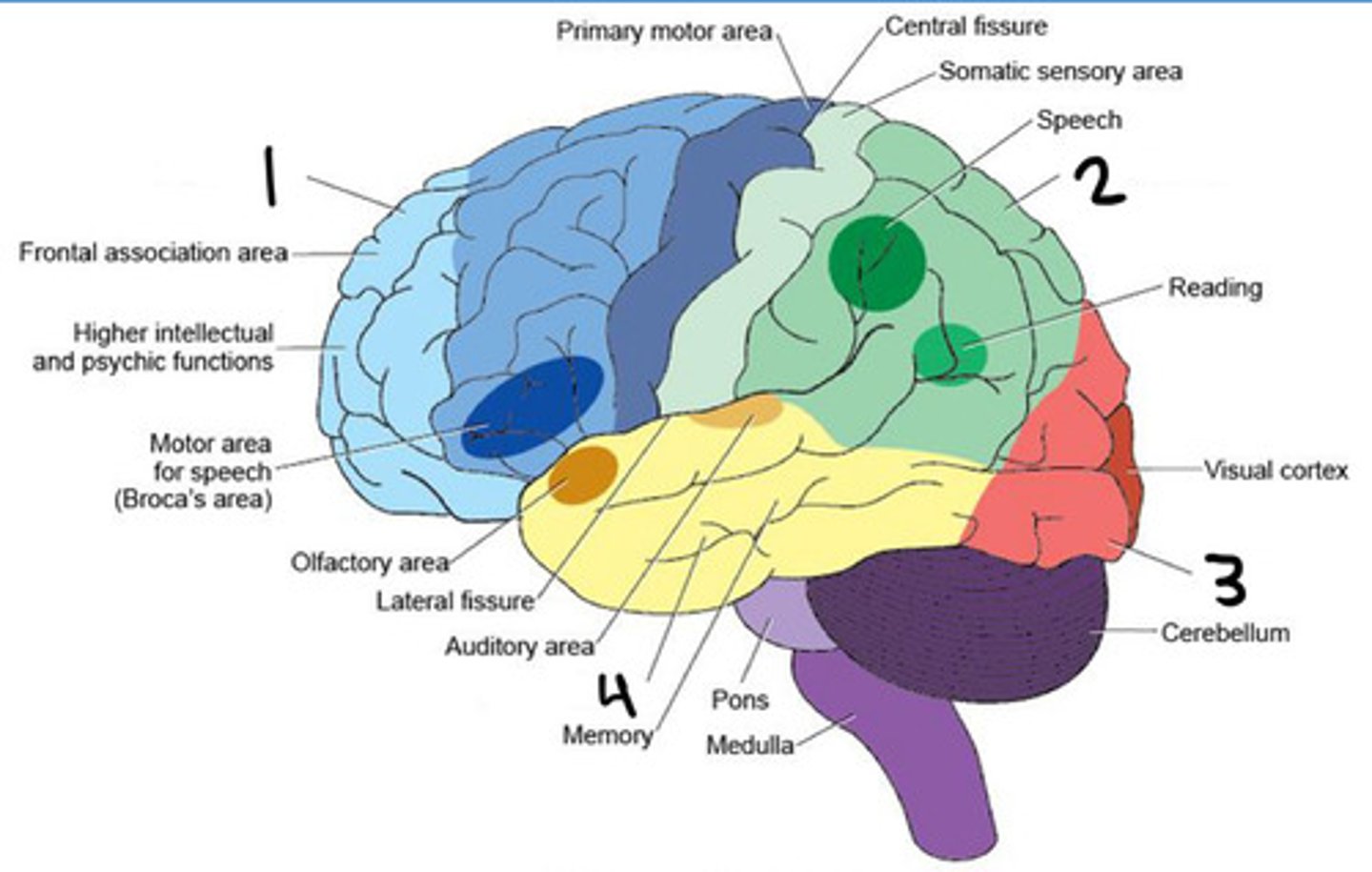
Insula
What is 1
Thalamus
What does the diencephalon become
Grey matter
What matter is the thalamus made up of
Main relay center for sensory impulses
What is the purpose of the thalamus
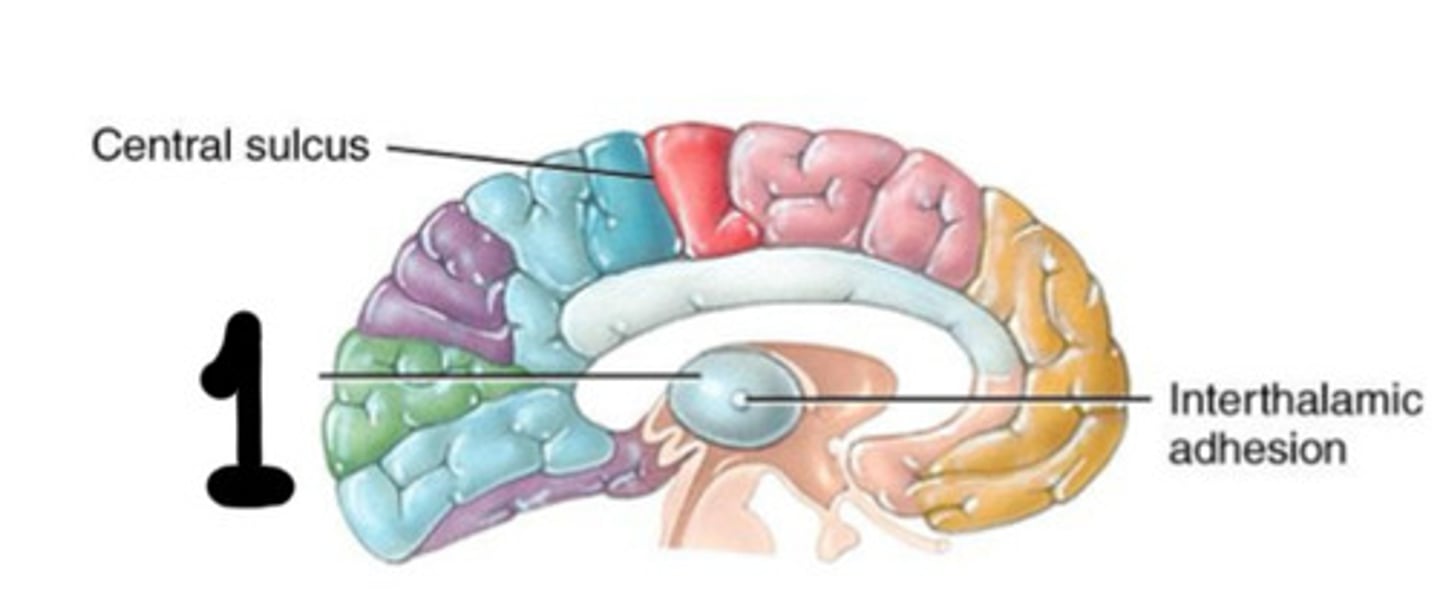
Massa intermedia
What connects the Thalmus to the 3rd ventricle
Posterior
What is the thalamus to the CSP
Thalamus
What is 1
Midbrain
What does the mesencephalon become
Mesencephalon
What is the smallest portion of the brain
Cerebral peduncles
What does the midbrain create
Aqueduct of Sylvius
What is the midbrain anterior to
Superior, middle, inferior
What are the three cerebellar peduncles?
Thalamus
What does the cerbral aqueducts look similar to
If cerebellum is in the image then is is the cerbral penduncles
How can you tell if you are seeing the thalamus or the cerebral peduncles
Cerebral peduncles
What are the arrows pointing to
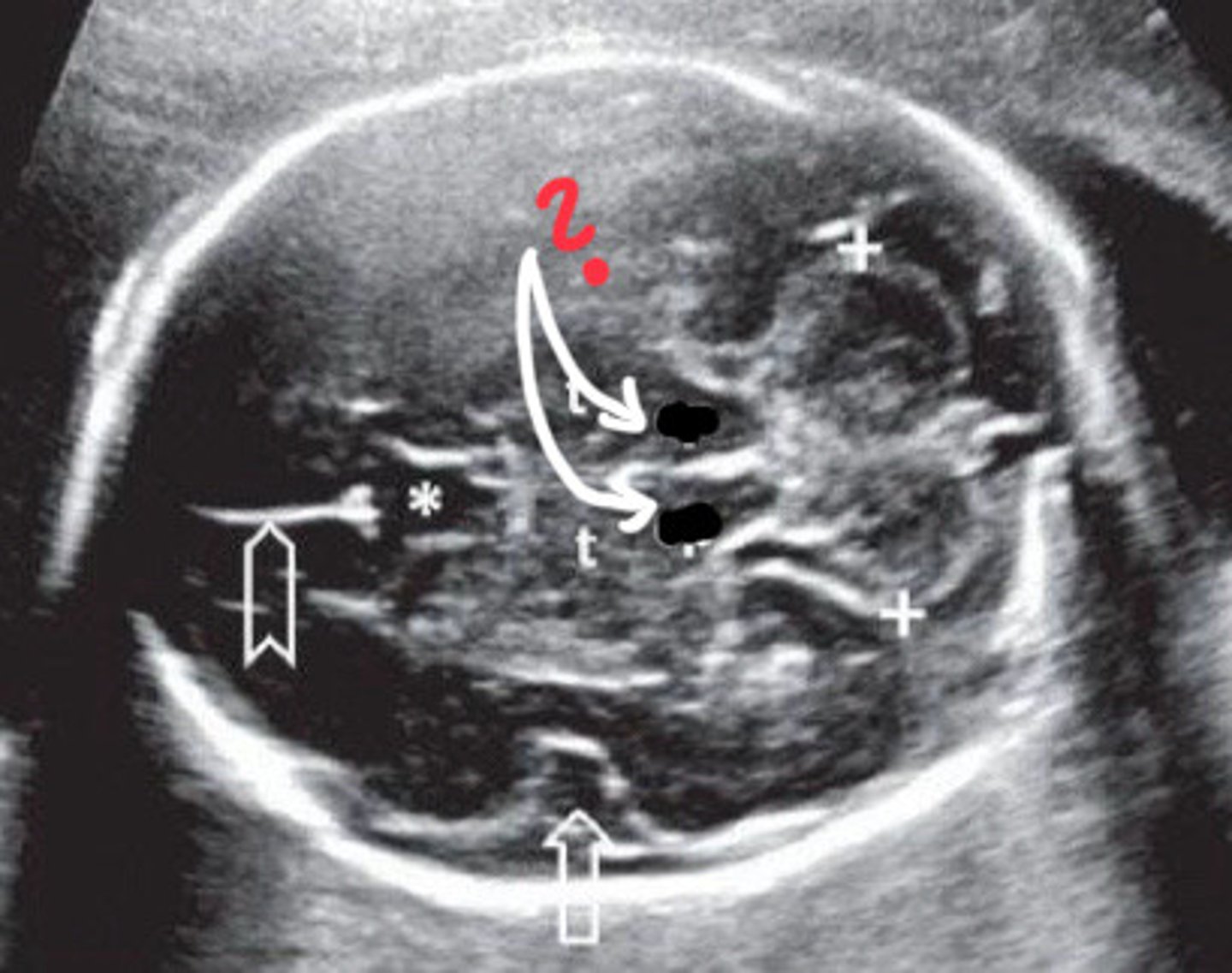
Thalamus
What is 1
Cerebellar penducles
What is 2
Hindbrain
What is the reombencephalon
Mesencephalon and myelencephalon
What does the rhombencephalon divide into
Cerebellum and pons
what is the metencephalon become?
Midbrain and medulla oblongata
What is the pons located between
Cerebrum to cerebellum
What does the pons connect
Bridge
What does pons mean (which explains what it does)
Medulla oblongata
What is the myelencephalon become
Pons to the spinal cord
What does the medulla oblongata extend from
HR, respiratory rhythm, BP
What does the medulla oblongata regulate
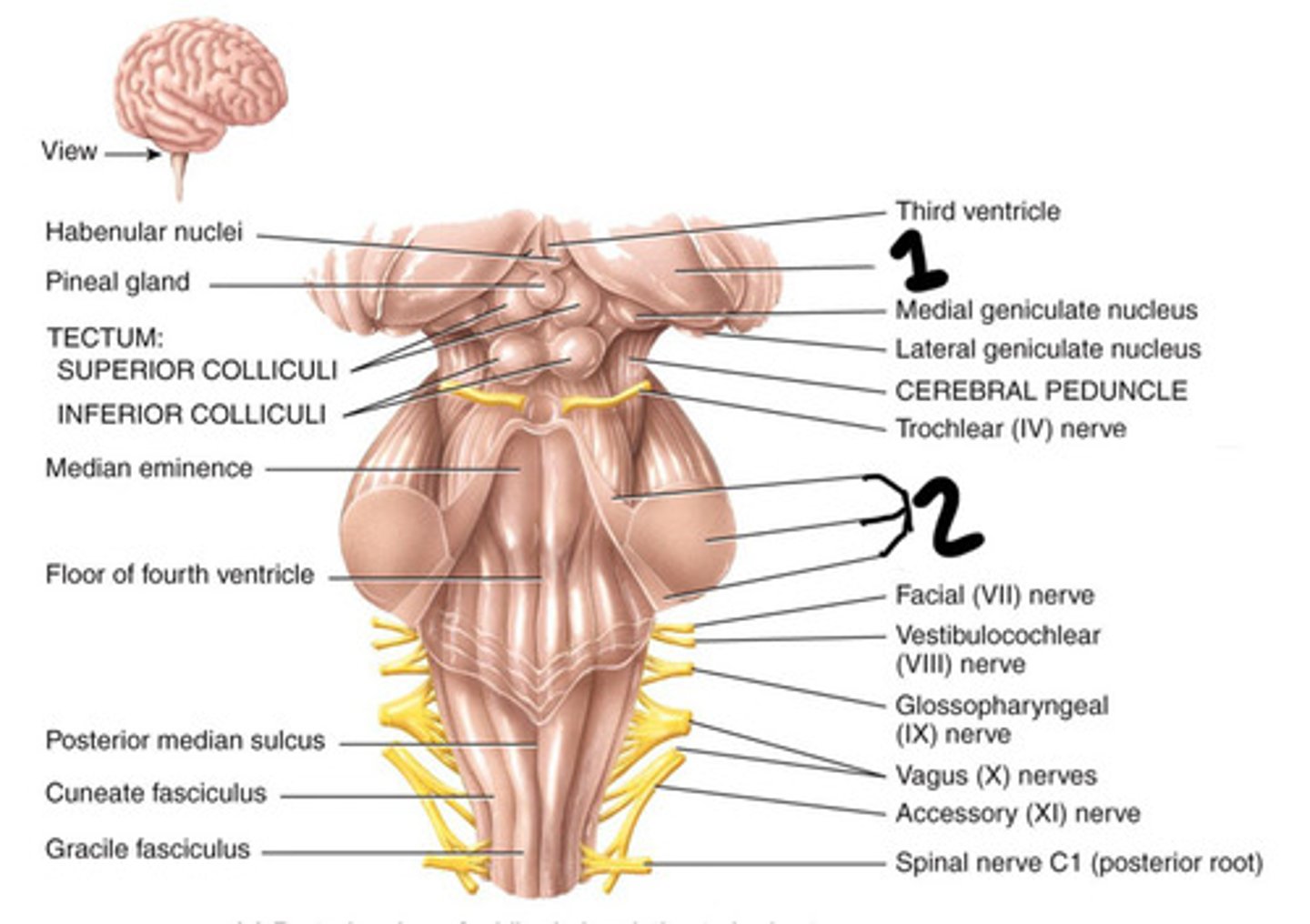
Pons
What is 1
Medulla oblongata
What is 2
Rhombencephalon
What is the 1st neural structure we seen on ultrasound in the 1st trimester
Cerebellum
What is the rhombencephalon
Posterior
What is the cerebellum to the pon and medulla oblongata
Cerebellar vermis and Falx cerebelli
What is the cerebellum separated by
Coordination of movement
What does the cerebellum do?
Hyperechoic
How does the cerebellar vermis appear on ultrasound
Vermis
What is 1
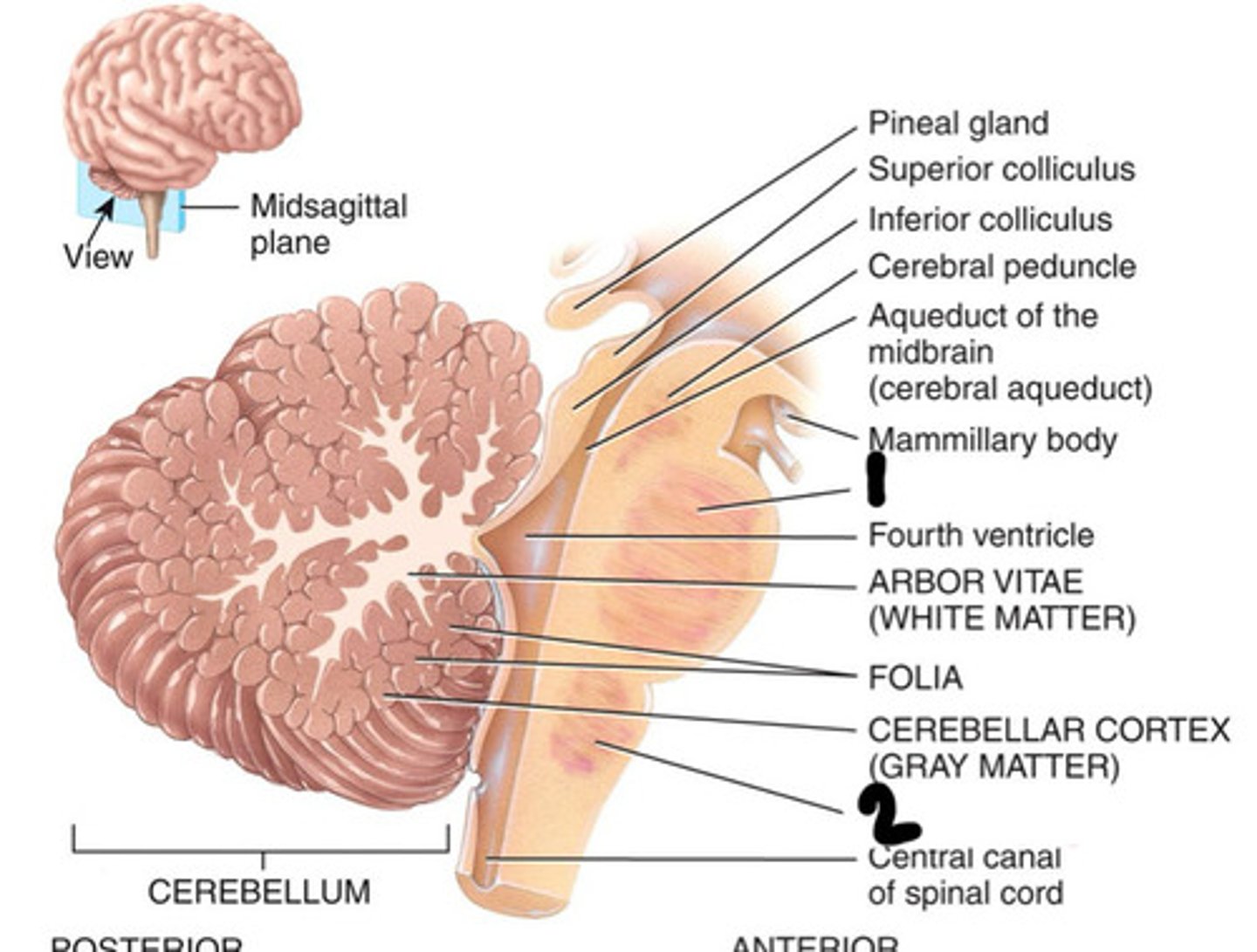
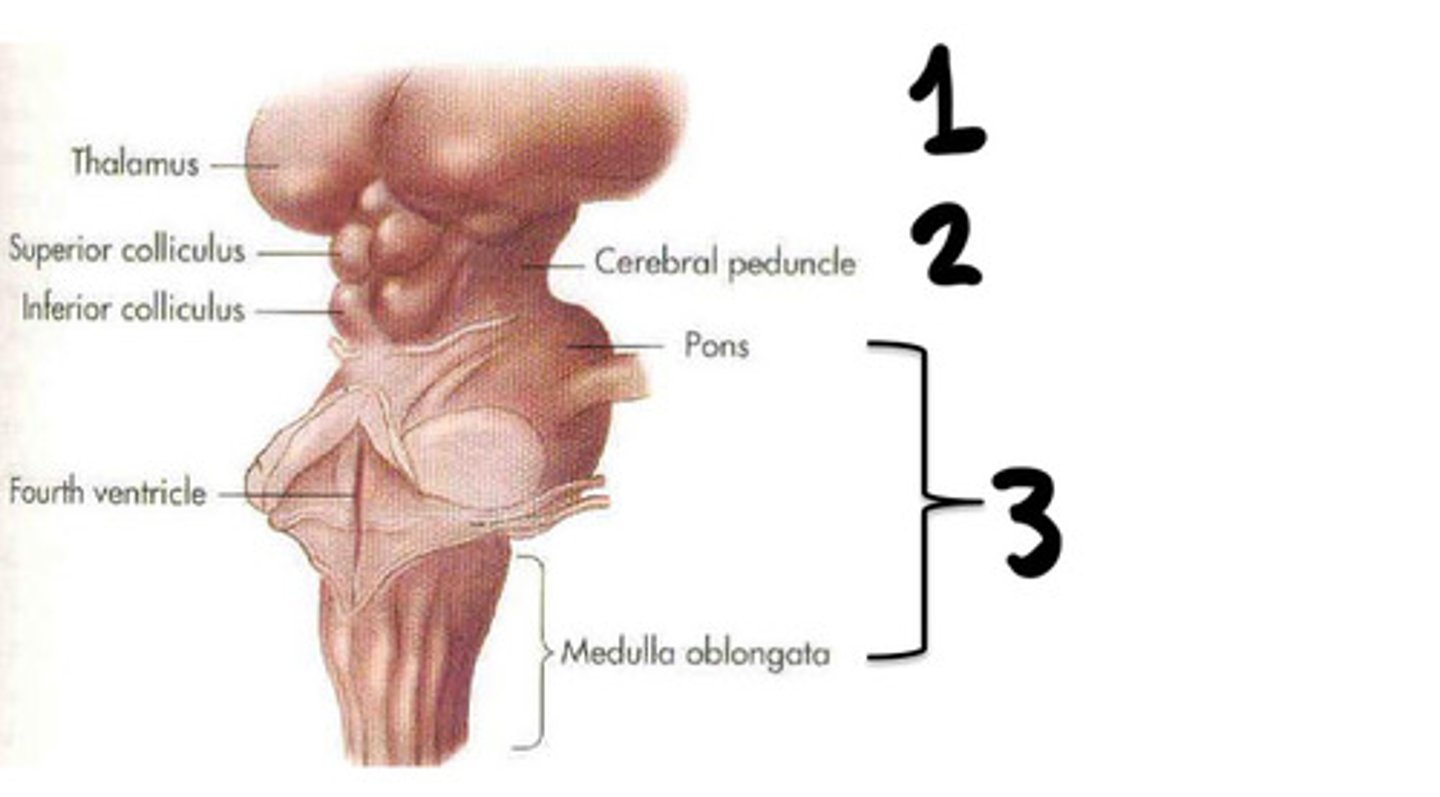
Prosencephalon
What is 1
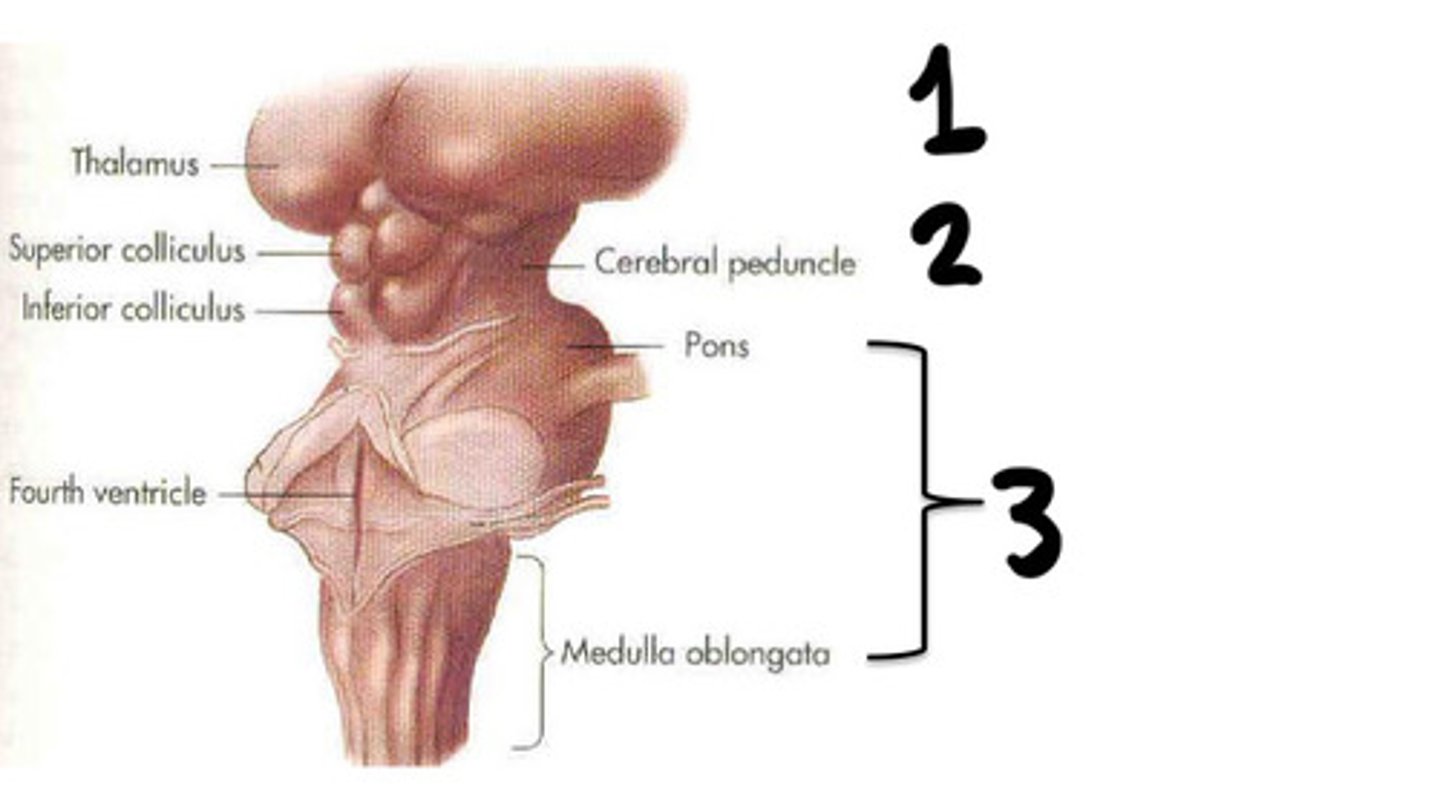
Mesenchaphalon
What is 2
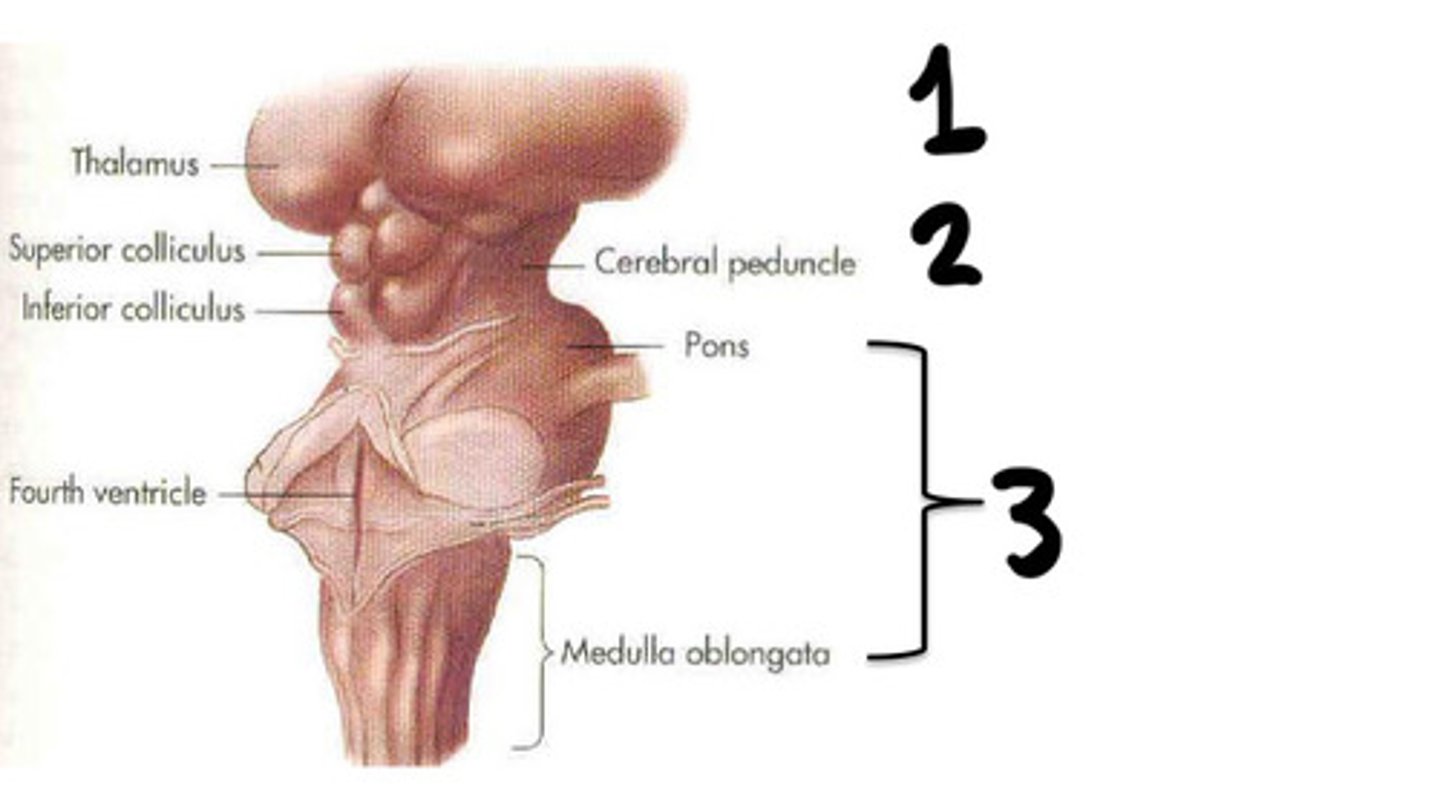
Rhombencephalon
What is 3
CSF and choroid plexus
What do all ventricles contain
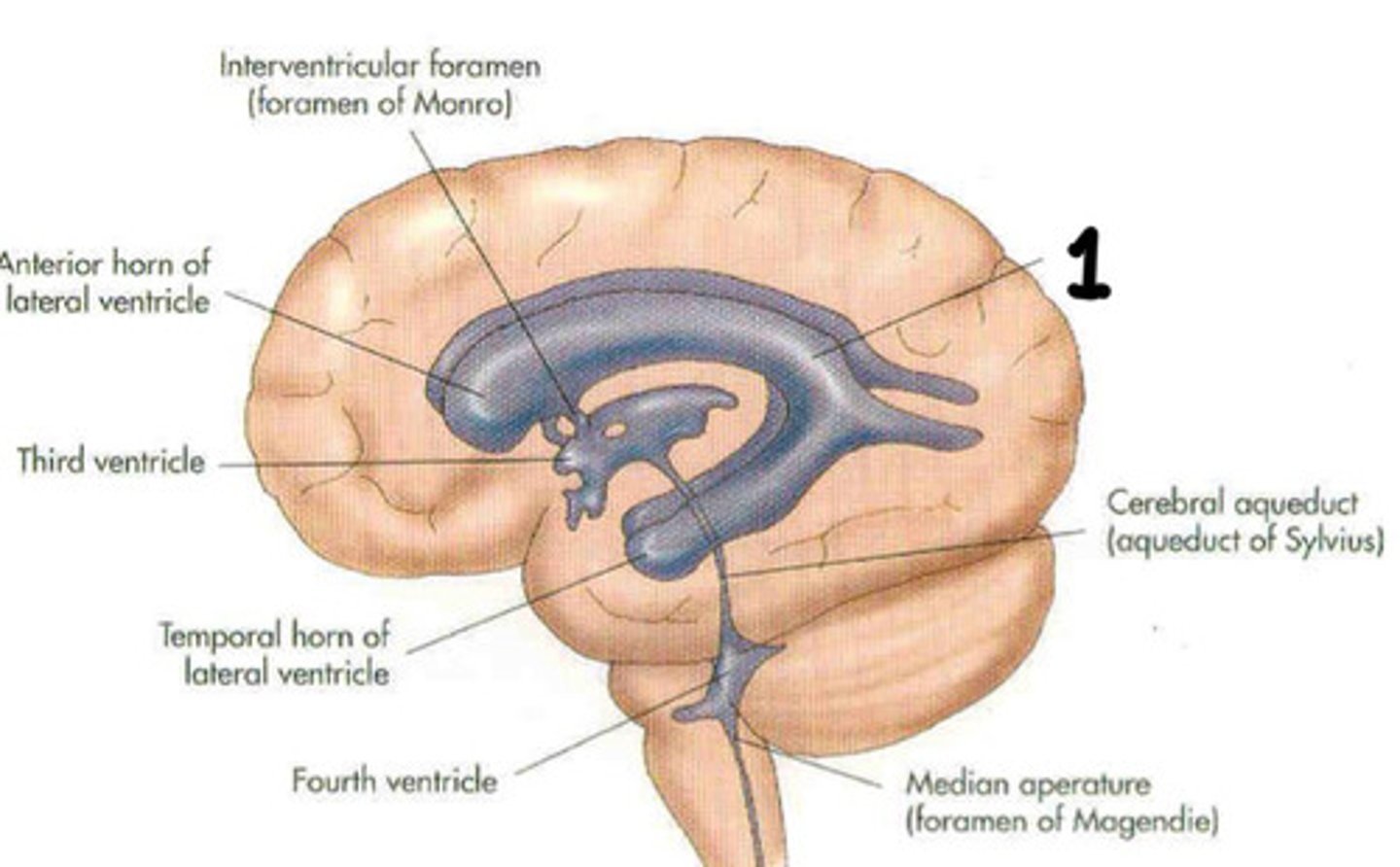
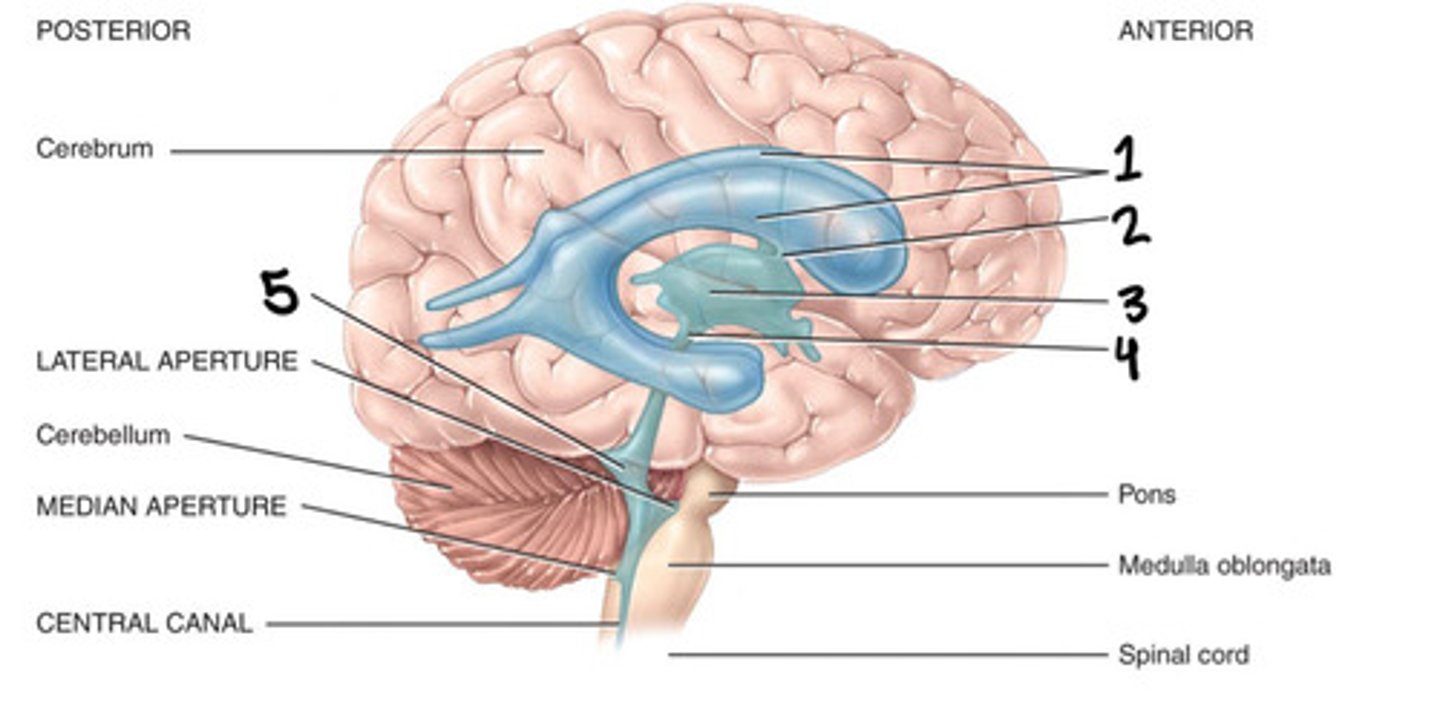
Foramen of monro
What is 1
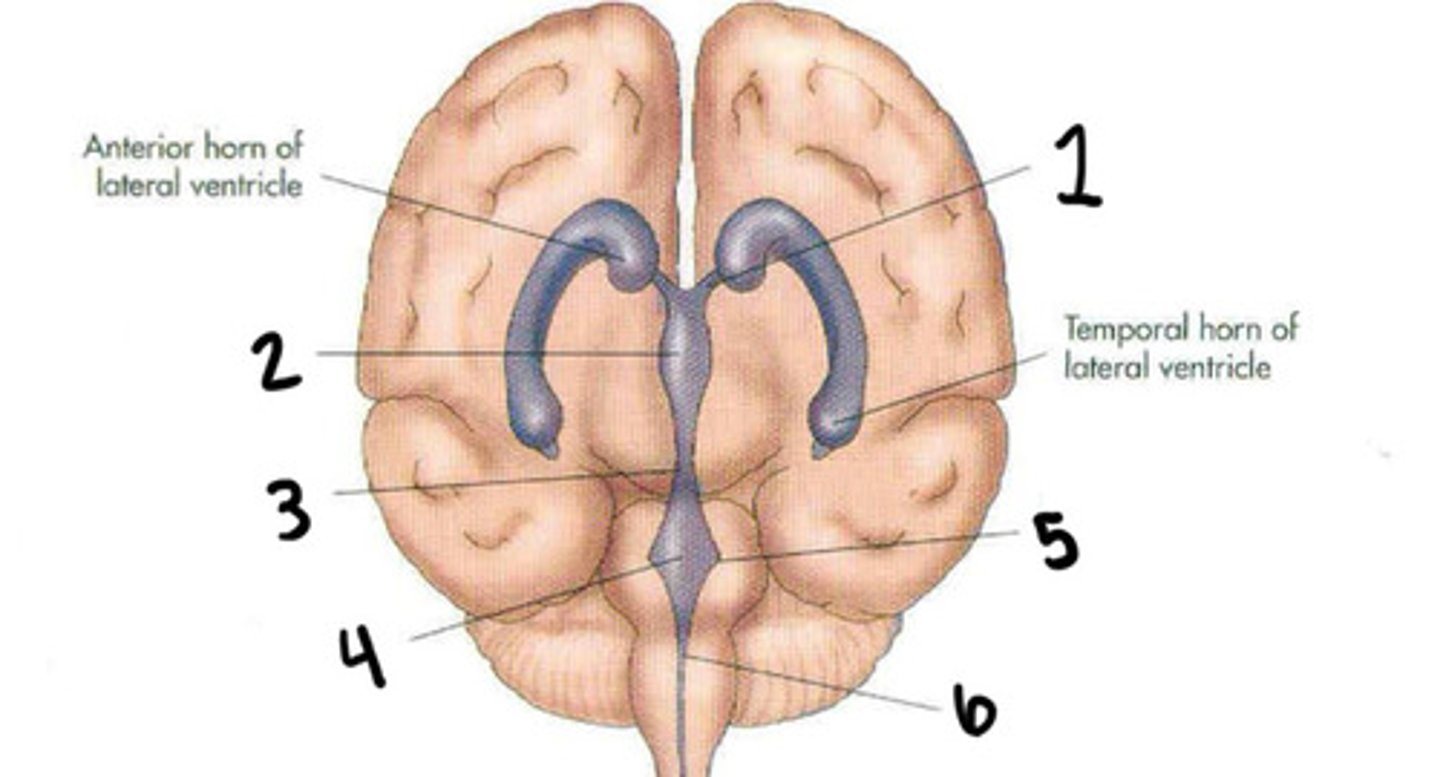
Third ventricle
What is 2
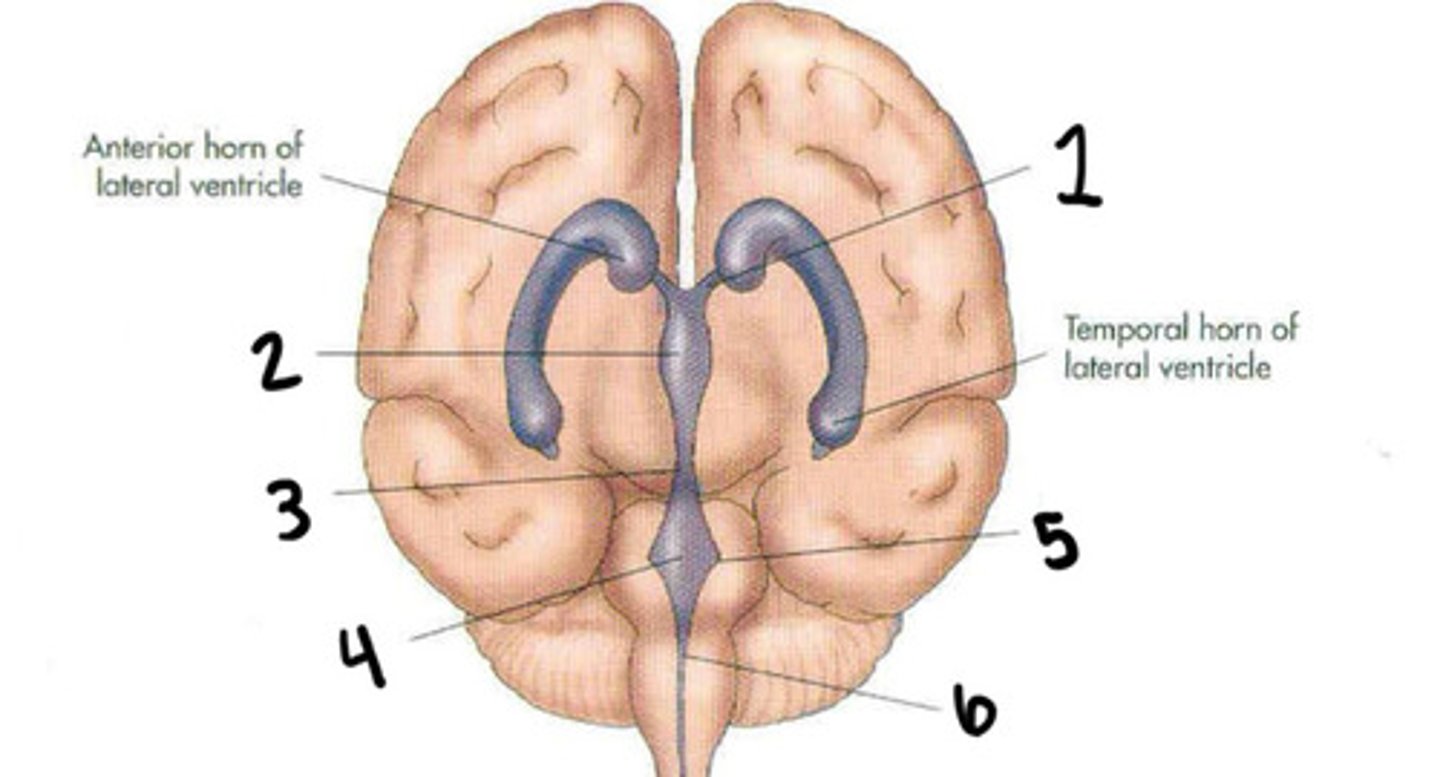
Cerebral aqueduct
What is 3
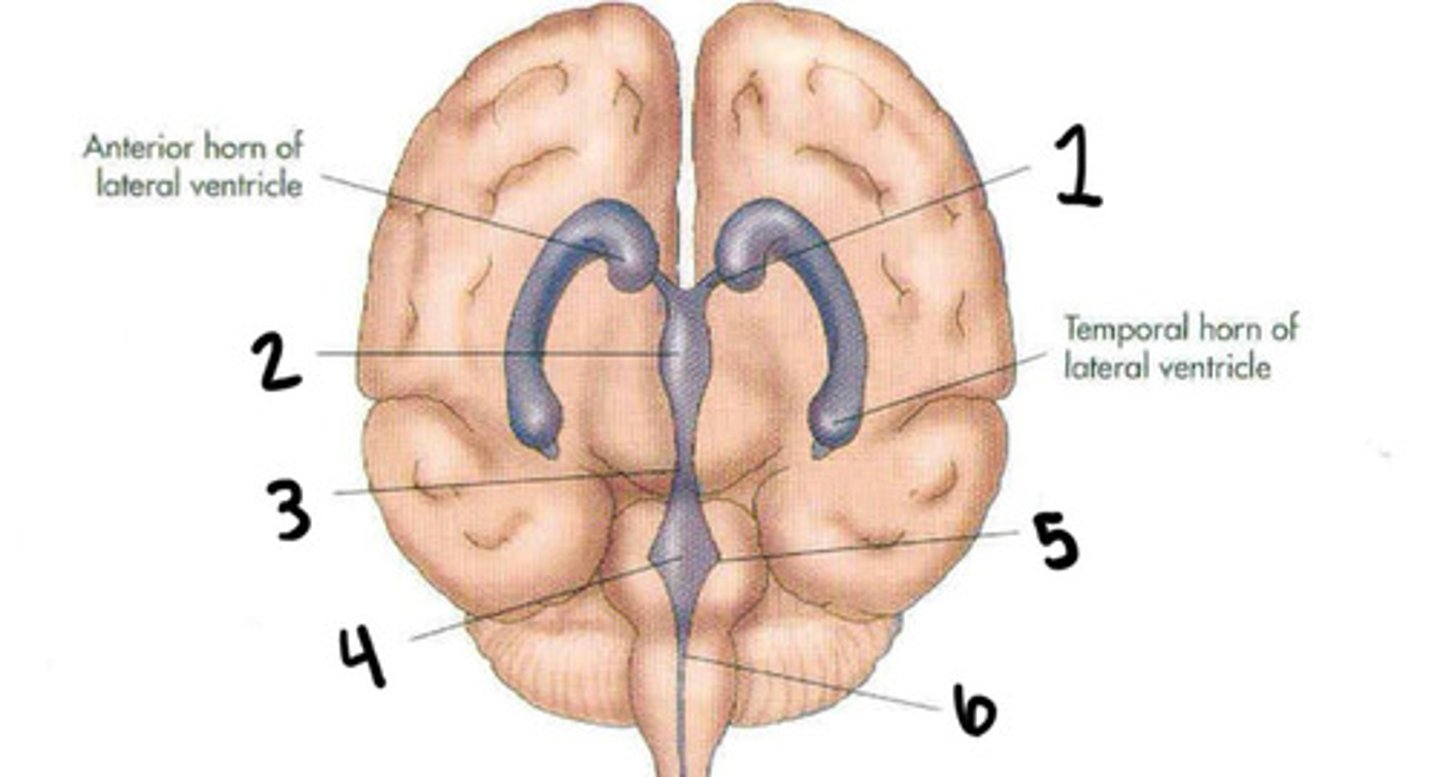
Fourth ventricle
What is 4
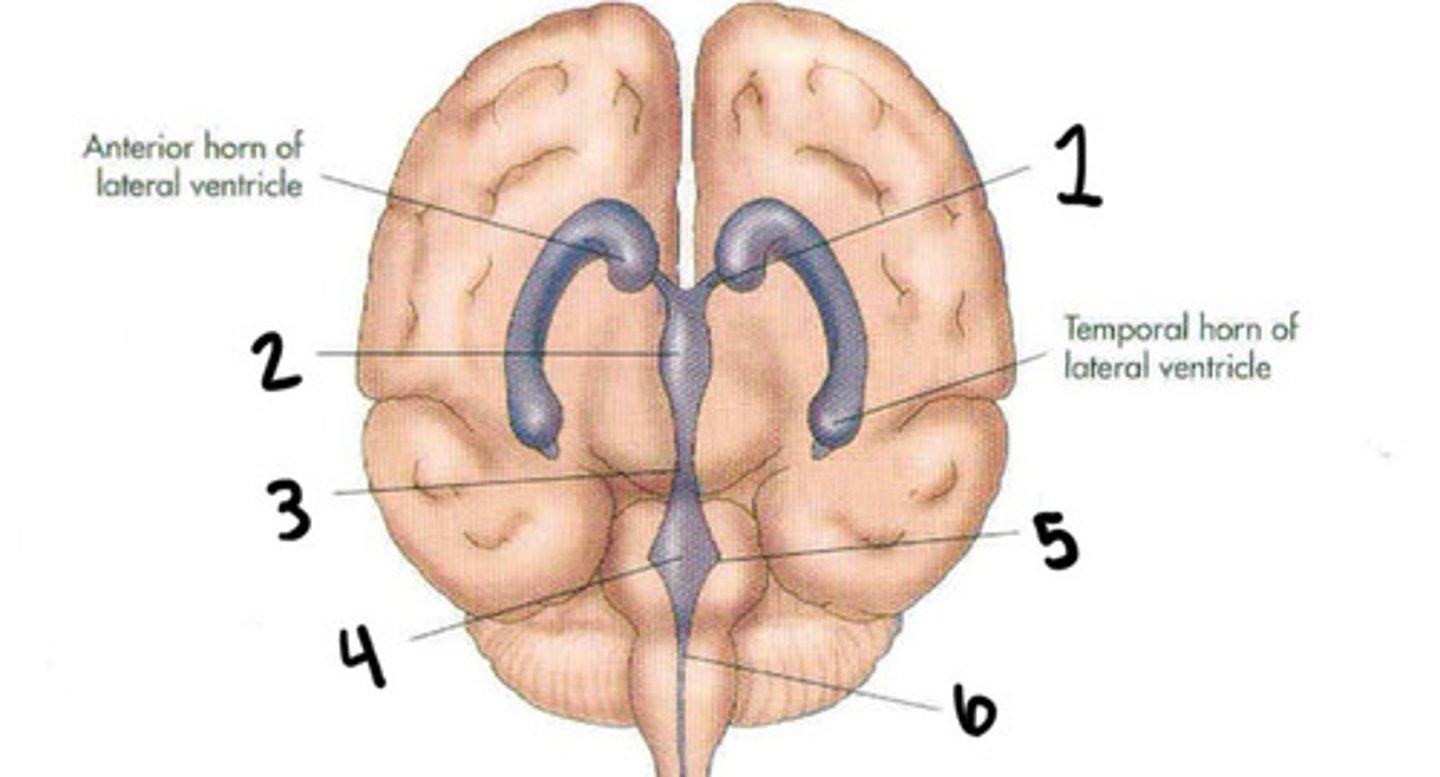
Foramen of luschka
What is 5
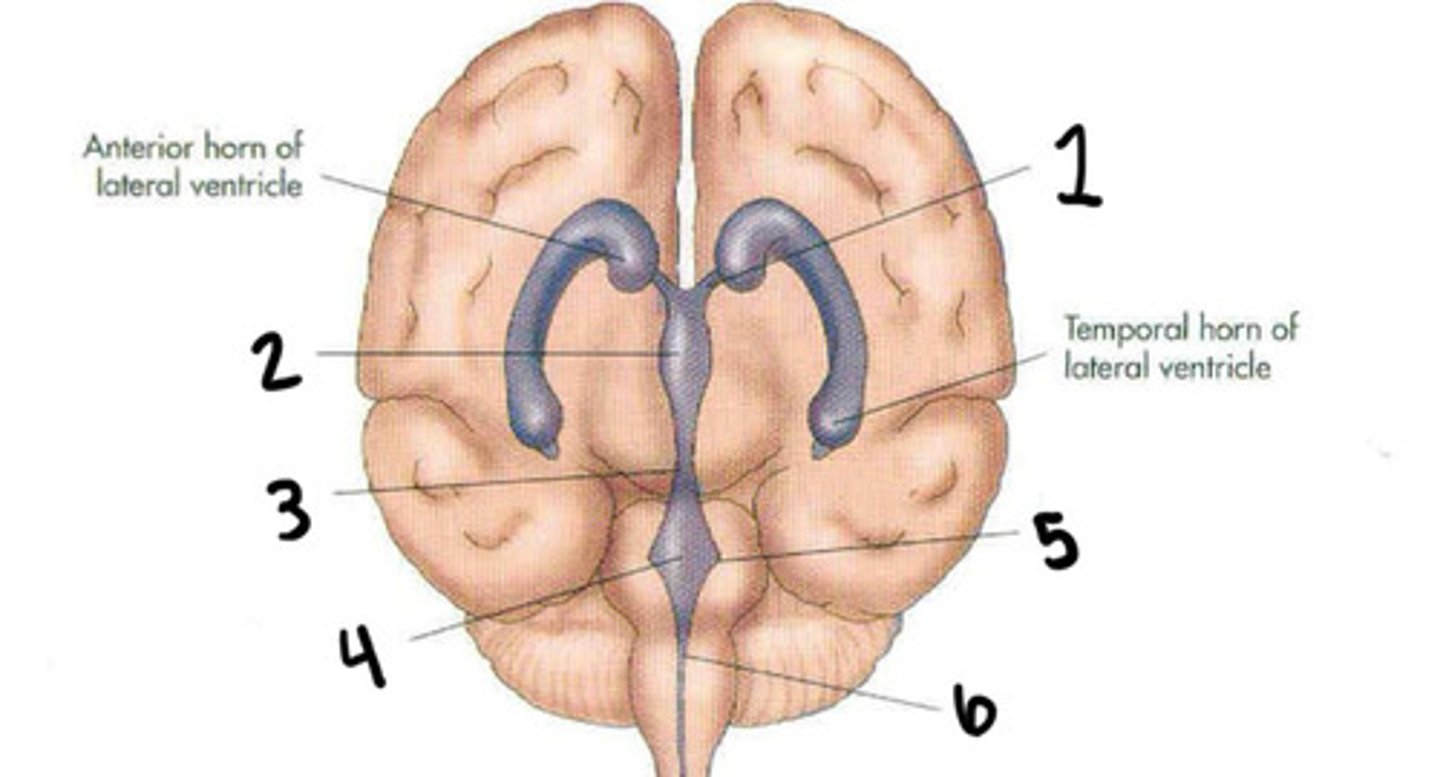
Foramen of magendie
What is 6
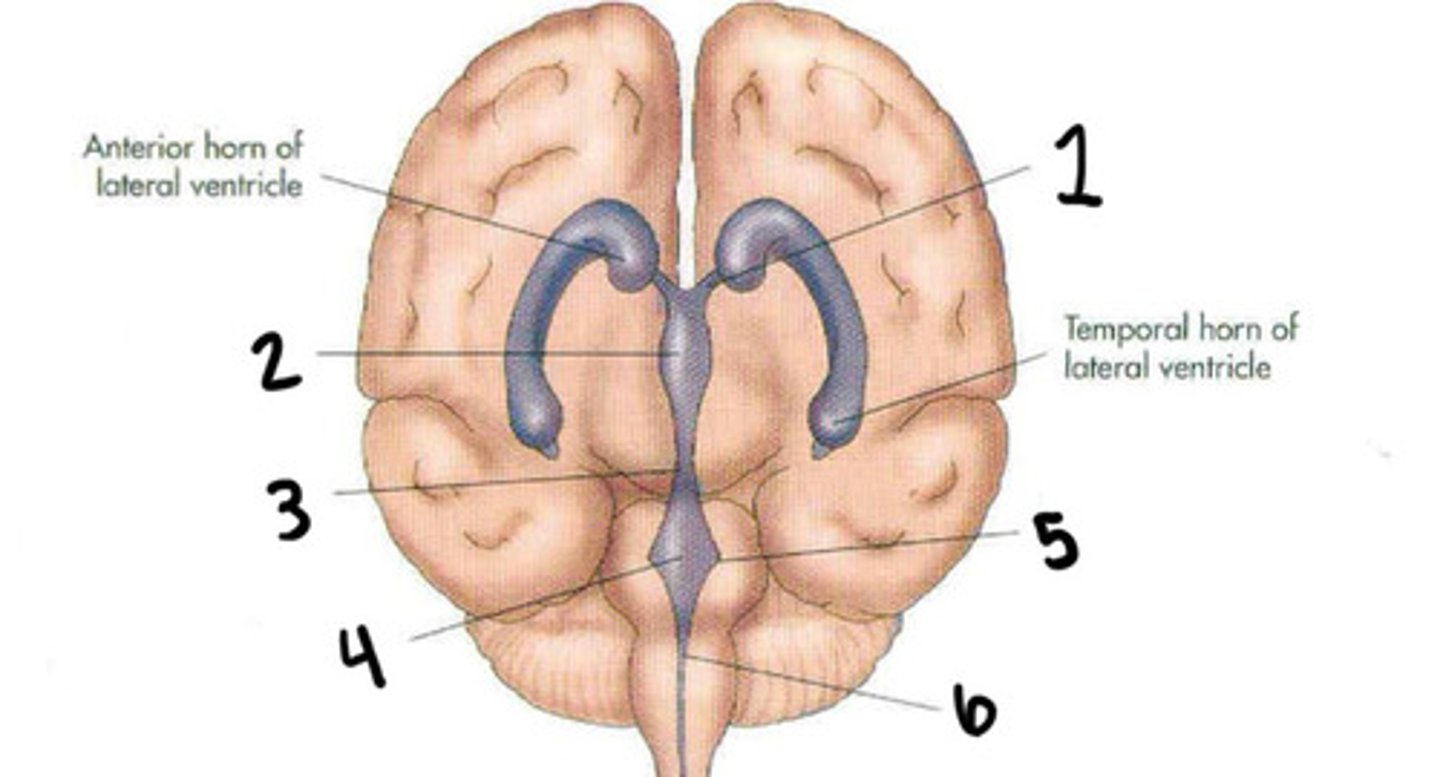
Lateral ventricles
What is 1
Interventricular foramen
What is 2
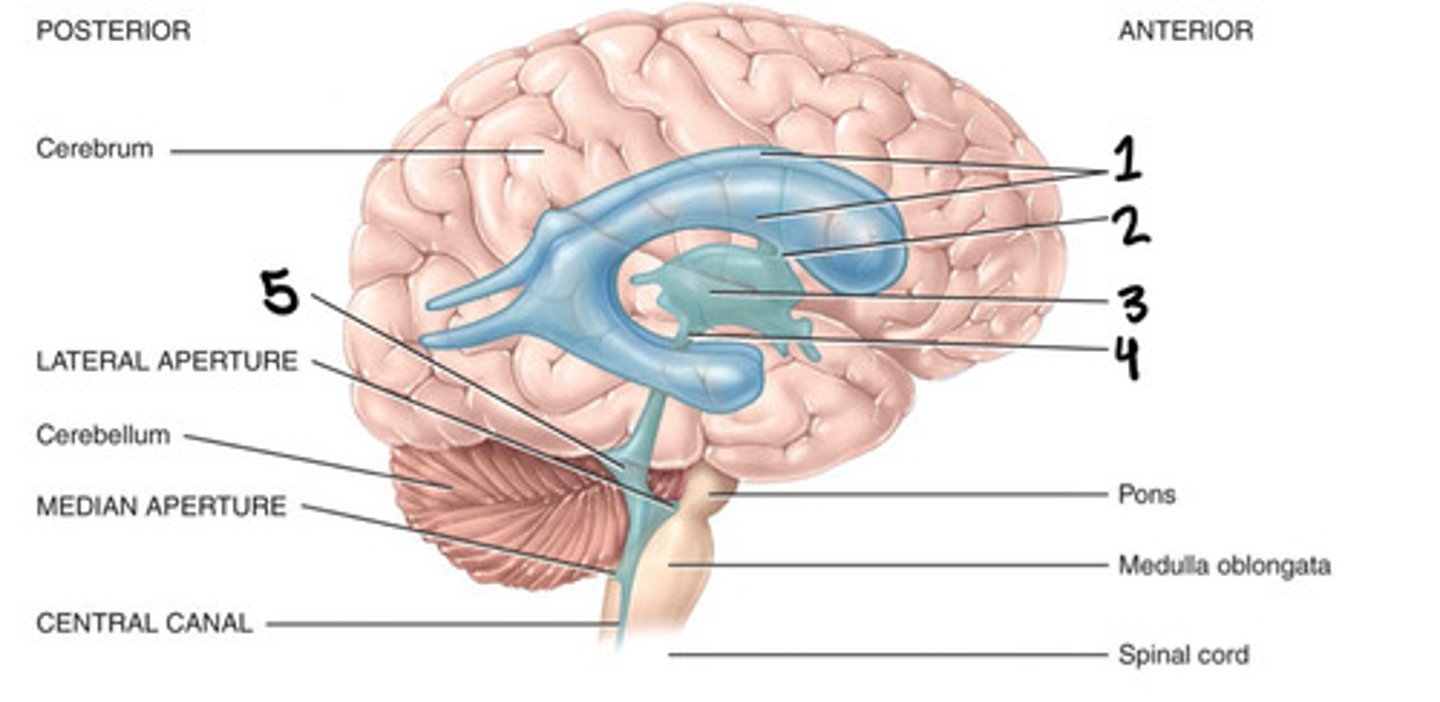
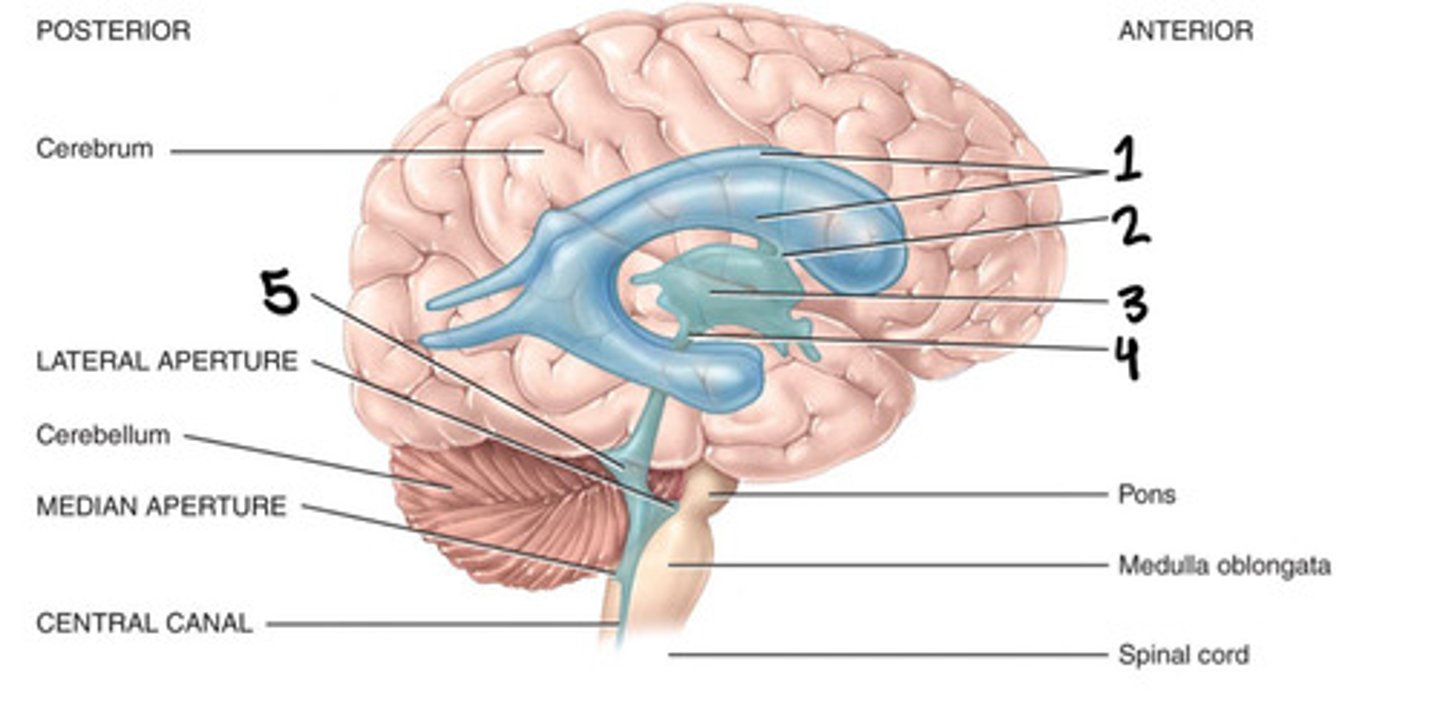
Lateral ventricles, foramen of monro, 3rd ventricle, aqueduct of sylvius, 4th ventricle, foramen of magendie, spinal cord
List the flow through the ventricles in order from start to end
Third ventricle
What is 3
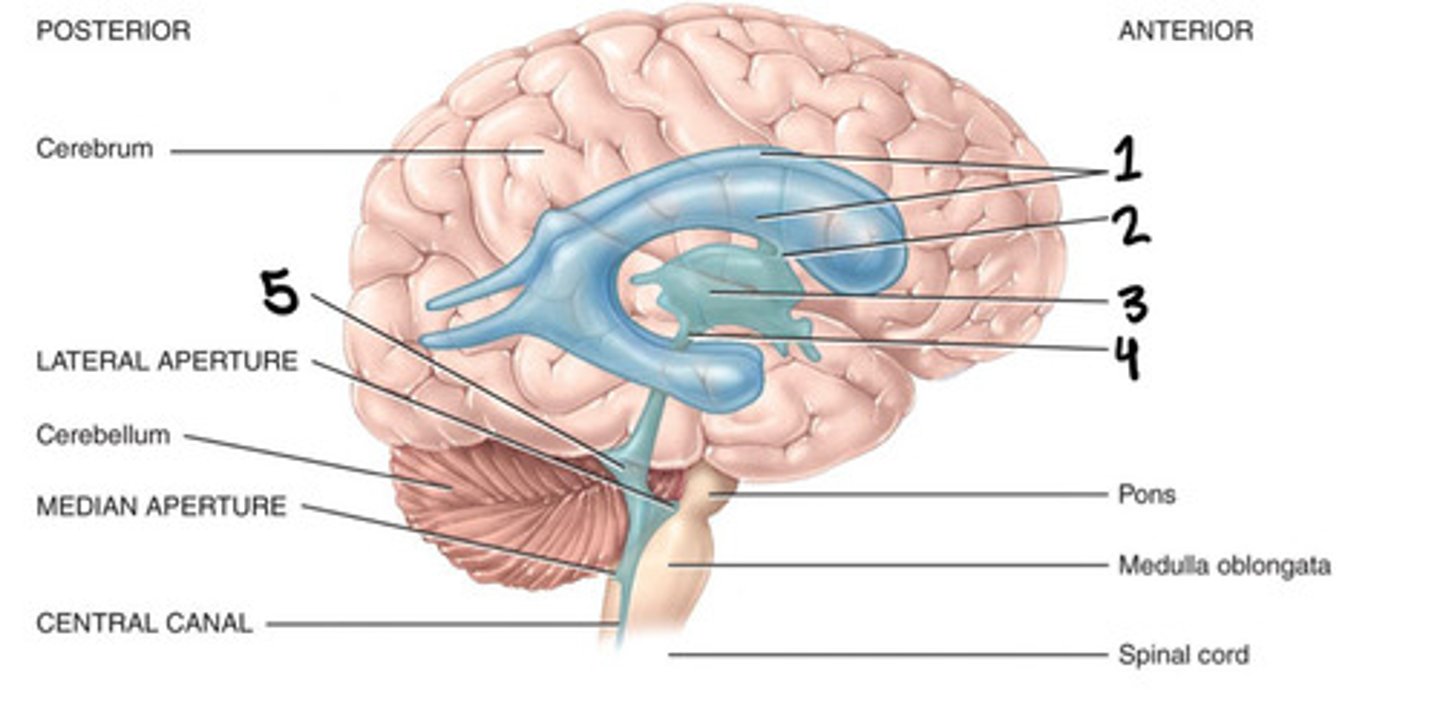
Cerebral aqueduct
What is 4
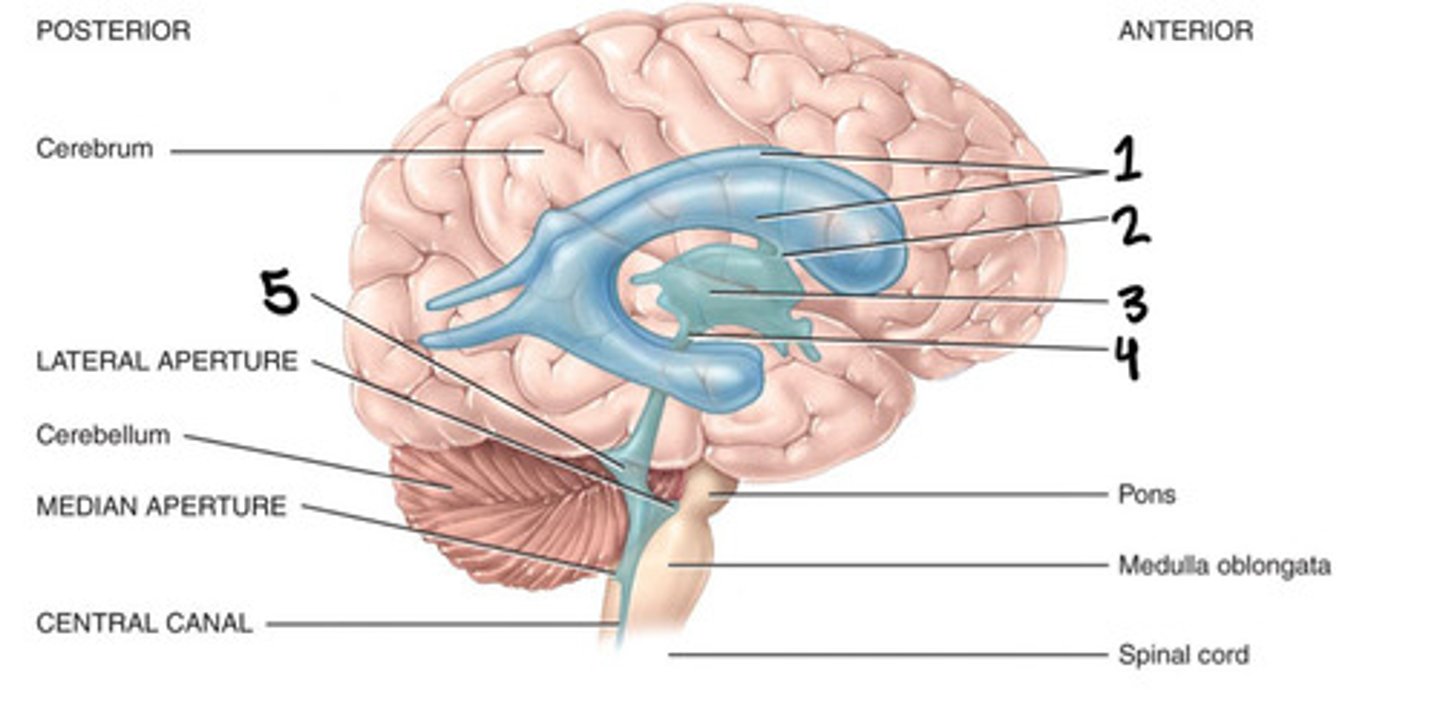
Trigone
What is 1
Fourth ventricle
What is 5
Magendie and luschka
What 2 foramen are found in the 4 ventricle
Medial aspect
Where on the 4th ventricle is foremen of magendie found
Cerbral aqueduct
What is the aqueduct of sylvius also known as
Interventricular foramen
What is the foramen of Munro also know as
Lateral aspect
Where on the 4th ventricle is foramen of luschka found
Spinal cord
What does the foramen of magendie connect to
Communicates with the meninges of the brain
What does the two foramen of luschka do
Median aperature
What is the foramen of magendi also known as
Lateral aperture
What is the foramen of luschka also known as
Anterior, posterior, and inferior or frontal, occipital, and temporal
What are the three horns of the lateral ventricles
No
Is there any choroid plexuses located anterior to the foramen of Monroe in the frontal horn
Anterior horn
What is the frontal horn also known as
Posterior
What is the occipital horn also known as
Inferior
What is the temporal horn also known as
Trigone or atria
What is the junction of the body, occipital, and to temporal horns of the lateral ventricles called
Thin
Is the 3rd ventricle thin or thick
True
T/F: because the 3rd ventricle is thin you can't really see it on ultrasound
Between thalami and inferior to corpus callosum
Where is the 3rd ventricle located
Foramen of monro or interventricular foramen
What foramen doing the 3rd ventricle communicate with the lateral ventricles