General Terms APES
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from summer assignment
Last updated 10:21 PM on 8/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
organic vs inorganic
organic: derived from living organisms (carbon-hydrogen covalent bonds)
inorganic: derived from nonliving components (ionic bonds, rarely contain carbon atoms)
inorganic: derived from nonliving components (ionic bonds, rarely contain carbon atoms)
2
New cards
natural vs synthetic
natural: materials found in nature
synthetic: man made materials
synthetic: man made materials
3
New cards
kinetic vs potential energy
kinetic: energy associated with motion
potential: energy stored due to position
potential: energy stored due to position
4
New cards
radioactive decay
emission of energy in the form of ionizing radiation (can affect atoms of living things)
5
New cards
half life
amount of time it takes 1/2 of the atoms present to decay
6
New cards
consumers/heterotrophs
an organism that cannot produce its own food; must eat other plants/animals to get energy
7
New cards
decomposers
an organism that decomposes organic material (soil bacterium, fungus, invertebrate)
8
New cards
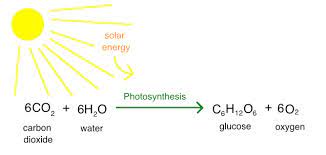
photosynthesis
process of plants using sunlight to synthesize foods from CO2 and H2O
*reactants and products in image*
*reactants and products in image*
9
New cards
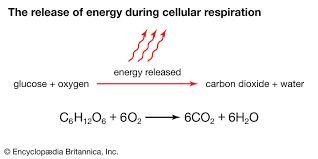
cellular respiration
series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP
*reactants and products in image*
*reactants and products in image*
10
New cards
aerobic vs anaerobic
aerobic: needs oxygen to occur
anaerobic: does NOT need oxygen to occur
anaerobic: does NOT need oxygen to occur
11
New cards
law of conservation of matter
matter is neither created nor destroyed
12
New cards
1st law of thermodynamics
energy in a closed system is neither lost nor gained
13
New cards
2nd law of thermodynamics
entropy constantly increases in a closed system
14
New cards
entropy
a measure of randomness or disorder of a system
15
New cards
organism
an individual animal, plant, or single-celled life form
16
New cards
adaptation
the process of change by which an organism or species becomes better suited to its environment
17
New cards
mutation
the changing of structure of a gene, resulting in a variant form that may be transmitted to subsequent generations
18
New cards
gene
the basic physical and functional unit of heredity; made up of DNA
19
New cards
trait
a specific characteristic of an individual
20
New cards
chromosome
found in the nucleus of most living cells, carry genetic information in the form of genes
21
New cards
gene pool
the stock of different genes in an interbreeding population
22
New cards
natural selection
a mechanism of evolution;
organisms that adapt are more likely to survive and pass on genes that aided their success
organisms that adapt are more likely to survive and pass on genes that aided their success
23
New cards
species
a class of things of the same kind and with the same name
24
New cards
population
a group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding
25
New cards
community
an interacting group of various species in a common location
26
New cards
ecosystem
a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment
27
New cards
producers/autotrophs
an organism that can produce its own food using light, water, CO2
28
New cards
biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a pr
29
New cards
extinction
the dying out or extermination of a species
30
New cards
plate tectonics
major landforms are created as a result of Earth’s subterranean movements (mountains, volcanoes, earthquakes)
31
New cards
weathering
the process of wearing or being worn by long exposure to the atmosphere
32
New cards
climate change
produces more weather extremes
33
New cards
rocks vs minerals
rocks: generally made up of two or more minerals
mineral: a naturally occurring substance with distinctive chemical and physical properties, composition and atomic structure
mineral: a naturally occurring substance with distinctive chemical and physical properties, composition and atomic structure
34
New cards
climate vs weather
climate: the average weather conditions in a place
weather: a specific event that happens over a few hours
weather: a specific event that happens over a few hours
35
New cards
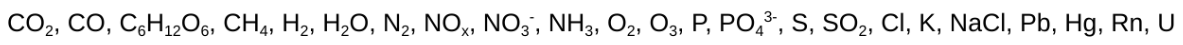
full name of each of these chemical abbreviations
carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, glucose, methane, hydrogen, water, nitrogen, nitrogen oxides?, nitrate, ammonia, oxygen, ozone, phosphorus, phosphate, sulfur, sulfur dioxide, chlorine, potassium, salt, lead, mercury, radon, uranium