Chapter 22: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Profiling
22.1: Basic Characteristics of SNPs
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP): It constitutes a single-base-pair change originating from a spontaneous mutation that can be a base substitution, insertion, or deletion at a single site.
If an SNP originating from a spontaneous mutation occurs in the germ line, it can be inherited by offspring and can spread in the human population.
Advantages of using SNP loci as markers for forensic application:
- SNPs are abundant within the human genome; therefore, a sufficient number of SNP loci that are suitable for human identification can be selected.
- In SNP analysis, amplicons are usually 50–100 base pairs in length and are smaller than that in STR analysis.
- SNP loci have lower mutation rates than STRs and are, therefore, useful for specialized human identification such as paternity testing.
- It is possible to achieve high-throughput SNP analysis by utilizing multiplex SNP assays.
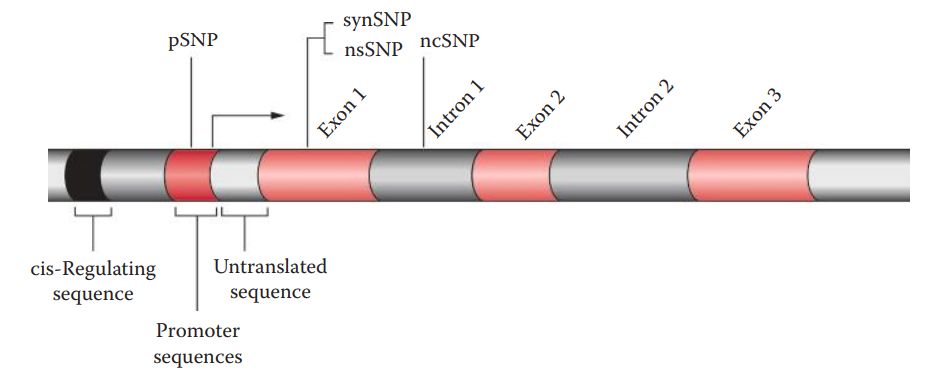
22.2: Forensic Applications of SNP Profiling
HLA-DQA1 Locus
HLA-DQA1 gene: A member of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) family, which contains a large number of genes involved in the immune response in humans.
DQα AmpliType® kit: The first commercial kit, developed in the late 1980s by Cetus Corporation in Emeryville, CA.
Polymarker systems are:
- Capable of analyzing a small amount of DNA sample.
- Capable of analyzing degraded DNA samples which is not possible in VNTR analysis.
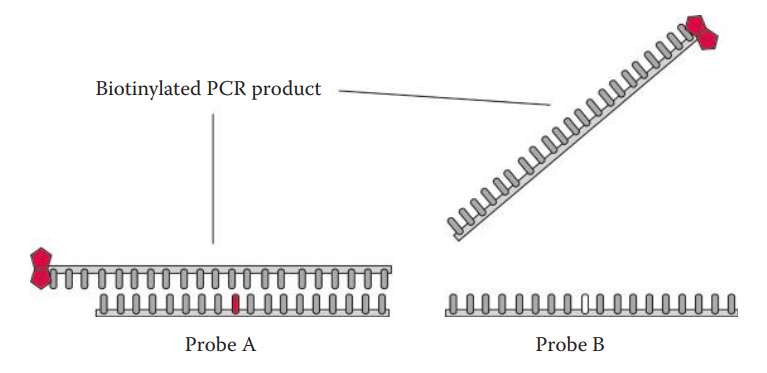
Both DQα AmpliType® and Polymarker kits utilize the allele-specific oligonucleotide (ASO) hybridization technique.
ASO technique analyzes single-nucleotide variations, such as SNPs, at a given locus.
It is based on the principle that ASO probes, usually 14–17 bases in length, hybridize to their complementary DNA sequences to distinguish known polymorphic alleles.
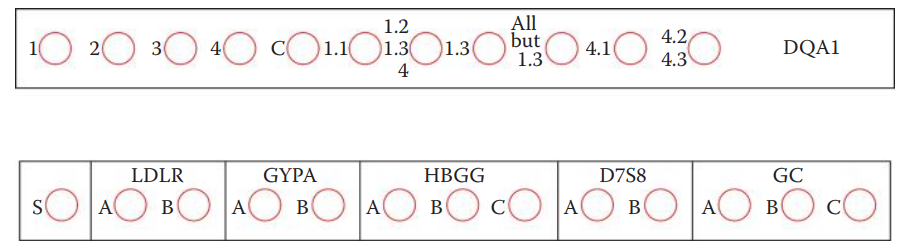
Current and Potential Applications of SNP Analysis
Forensic Applications of SNP Profiling
| Testing | Candidate SNP Loci | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | Autosomal SNPs | Human identification and Human Identification via degraded DNA. |
| mtDNA SNPs | Human identification | |
| Y chromosome SNPs | Paternity testing | |
| Biogeographical origin | Ancestry informative markers (AIMs) | Physical characteristics |
| Biogeographical origin | Ancestry informative markers (AIMs) | Physical characteristics |
| P (gene has role in pigmentation) | Eye color identification (investigative lea | |
| Pathology | KCNH2 (cardiac potassium channel gene) | Determining cause of sudden death from cardiac arrhythmia long QT syndrome |
| SCN5A (encodes cardiac sodium channel gene) | Determining cause of sudden death from cardiac arrhythmia long QT syndrome | |
| Toxicology | CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP2E1 (drug metabolizing enzyme genes) | Investigation of drug overdose (including death) |
22.3: SNP Techniques
- In allele-specific hybridization, allele discrimination is based on an optimal condition allowing only the perfectly matched probe–target hybridization to form.
- Primer extension methods: These are based on the ability of DNA polymerase to incorporate specific deoxynucleotides (dNTPs) complementary to the sequence of the template DNA.
- Allele-specific oligonucleotide ligation: It is based on the condition that only the allelic probe perfectly matched to the target is ligated.
- In the invasive cleavage method, allelic discrimination is based on DNA sequence-specific cleavage by endonucleases.
Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies
- In de novo genome sequencing, uncharacterized genomes or characterized genomes with substantial structural variations are sequenced.
- In resequencing applications, characterized genomes are sequenced. Sequence reads are assembled against an existing reference sequence to identify sequence polymorphisms.
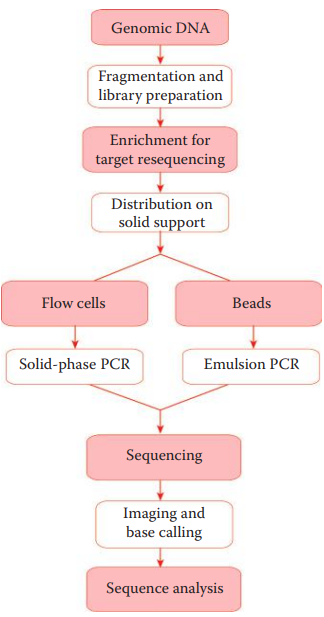
- Target resequencing is a useful method of resequencing that can be utilized for forensic applications. The genomic regions of interest from a DNA sample are selectively isolated through a method known as enrichment.
DNA Samples, Sequencing Library, and Template Preparation
- Human autosomal genome sequencing usually requires converting a DNA sample into a sequencing library.
- Two types of sequencing libraries are usually used:
- Mate-pair library: It is often used in de novo sequencing applications.
- Fragment Library: It is often used for resequencing and forensic applications.
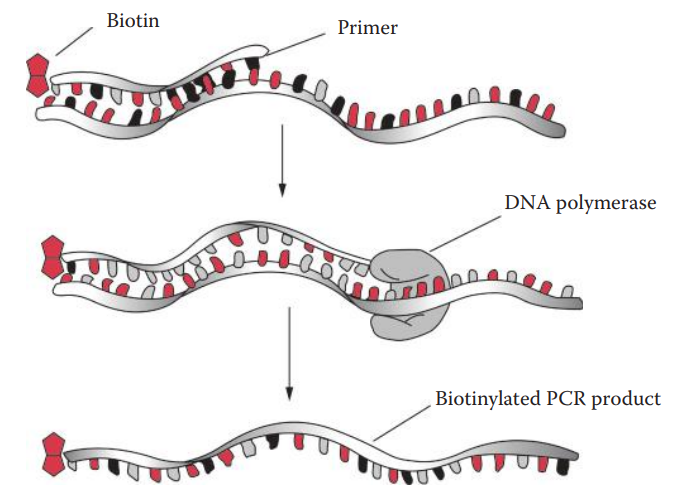
- DNA templates are amplified using either emulsion or solid-phase PCR.
- In the emulsion PCR, single-stranded DNA templates are bound to beads.
- In solid-phase PCR, both forward and reverse primers are attached to a slide.
NGS Chemistry
Pyrosequencing Technology: During this method, each nucleotide substrate is introduced one at a time. Only the correct nucleotide corresponding to the template is incorporated, and pyrophosphate is released.
Cyclic reversible termination: In this method, chain terminators are used to extending a primer sequence complementary to the template DNA.
NGS Coverage
In NGS, sequencing reads are usually not distributed evenly over the genomic regions of interest.
The average number of times that each nucleotide in the genomic regions of interest is sequenced is known as the coverage or the sequencing depth.
