[PT10118] [1T1S] [2] Managerial Function: Planning
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Process of defining an organization’s direction, setting goals, and outlining strategies to achieve them
Organization Planning
Four major functions of managers (Lamond, 2004)
Plan
Organize
Lead
Control
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MANAGERS
Vision and mission
Strategizing
Goals and objective
Plan
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MANAGERS
Organizational design
Culture
Social networks
Organize
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MANAGERS
Leadership
Decision-making
Communication
Groups/teams
Motivation
Lead
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF MANAGERS
Systems/processes
Strategic human resources
Control
Deciding in advance what is to be done, when, where, how, and by whom it is to be done
Bridges the gap from where we are to where we want to be
Planning
Why is planning important? (6)
Improve future performance
Minimizes risk and uncertainty
Facilitates the coordination of activities
Provides direction for action
Identifies future opportunities and threats
Set out standards for controlling
Four types of organization planning
Strategic planning
Tactical planning
Operational planning
Contingency planning
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
Setting of broad, long-range goals by top managers
A long term, systematic process by which an organization defines its direction, sets priorities, and allocates resources to achieve its mission and vision
Strategic planning
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
The identification of specific, short-range objectives
Responsibility of middle/lower level managers to set and oversee tactical strategies
How the company will implement its strategic plan
Tactical planning
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
The setting of work standards and schedules
What happens in each day to execute the tactical plan
Operational planning
TYPES OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
Backup plans in case primary plans fail
Covers a range of possible scenarios and appropriate responses for these scenarios to prepare in advance
Contingency planning
STRATEGIC PLANNING
This communicates the organization’s reason for being, and how it aims to serve its key stakeholders
It also includes a summation of the firm’s values
Mission
STRATEGIC PLANNING
Describes the organization’s aspiration for the future
Vision
STRATEGIC PLANNING
Guiding principles and beliefs that shape the organization’s culture, behavior and decision-making
Core values
STRATEGIC PLANNING
What are the three criteria needed in a vision statement?
Time horizon
Measurability
Unique appropriation
STRATEGIC PLANNING
What criterion of a vision statement is described below:
Specific date in the future by which the entity will determine if it has achieved the strategy and when the vision will be achieved
Time horizon
STRATEGIC PLANNING
What criterion of a vision statement is described below:
A single or small set of measurable goals that can be objectively assessed for achievement
Can be quantitative or qualitative
Measurability
STRATEGIC PLANNING
What criterion of a vision statement is described below:
A succinct statement of how the entity will effectively deliver his services, meet the needs of its client, and achieve the vision
Unique appropriation
What are examples of operational plans? (6)
Schedules
Policies
Rules and regulations
Specific task assignments
Protocol
Documenting and tardiness
Five process steps of organizational planning
Develop a strategic plan
Translate into tactical plan
Create an operational plan
Execute plans
Monitor progress and adjust
FIVE PROCESS STEPS OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
What step is described below:
Set big picture goals that are aligned with the company’s mission, vision, and values
Know the company profile
Develop a strategic plan
FIVE PROCESS STEPS OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
What step is described below:
Set measurable, time sensitive goals for each team
Translate into a tactical plan
FIVE PROCESS STEPS OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
What step is described below:
Establish a process for the department and employees that outline the work they deliver that includes their roles, tasks, job description, policies and procedures, etc.
Create an operational plan
FIVE PROCESS STEPS OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
What step is described below:
Put that operational plan into action, incorporating tactical and strategic plans
Execute plans
FIVE PROCESS STEPS OF ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING
What step is described below:
Run reports and analyze whether the operational plans are meeting the tactical plans
Modern monitoring, providing results and creating revisions (strategy) in order to achieve the goals of the company
Monitor progress and adjust
These are essentials for organizing tasks, used to guide the planning process
Models of planning tools
Five models of planning tools
Gantt Chart
PERT (Program Evaluation Review Technique)
Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
Logic Model
SWOT Analysis
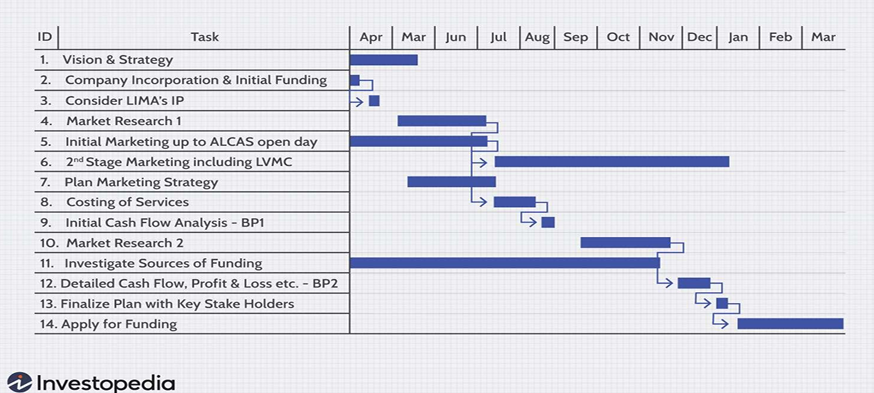
What model of planning tool is shown on the picture?
Gantt Chart
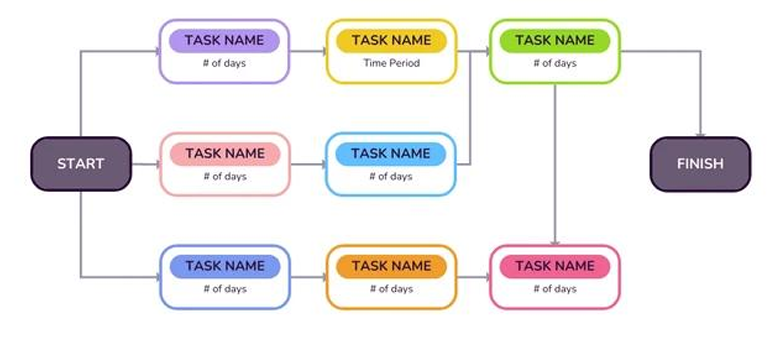
What model of planning tool is shown on the picture?
PERT (Program Evaluation Review Technique)
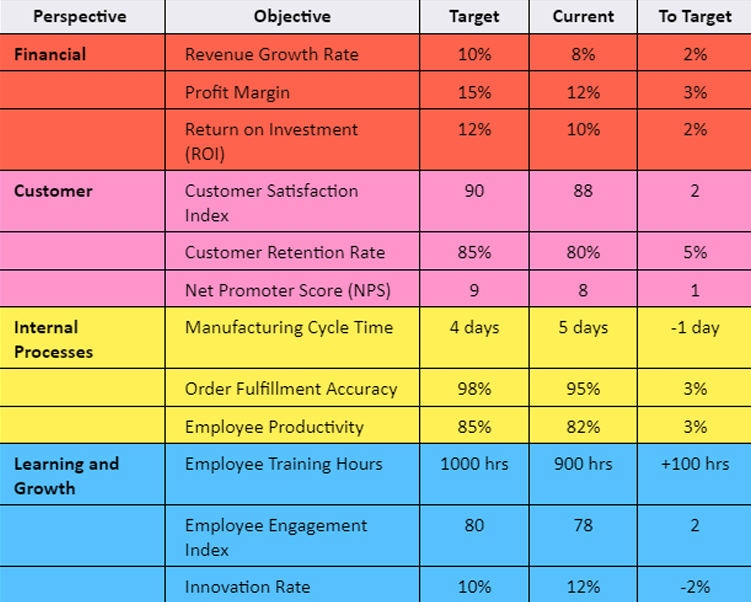
What model of planning tool is shown on the picture?
Balance Score Card
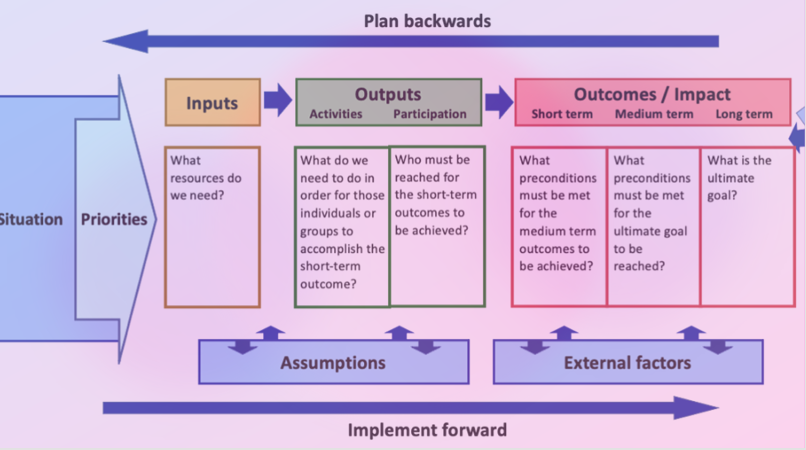
What model of planning tool is shown on the picture?
Logic Model
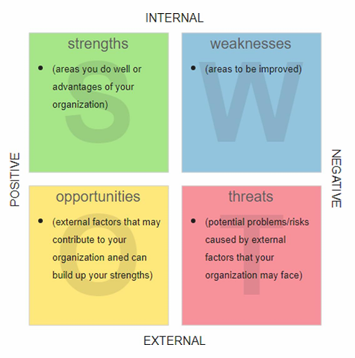
What model of planning tool is shown on the picture?
SWOT Analysis
Designed to be used in the preliminary stages of decision-making
Common tool in performance analysis and in evaluation studies
Focus in the identification of strong and weak points within an organization and the analysis of opportunities for and threats to, further development
SWOT Analysis
SWOT ANALYSIS
What component is described below:
What does your organization do better than your competition?
Strengths
SWOT ANALYSIS
What component is described below:
What does your organization need to improve upon?
Weaknesses
SWOT ANALYSIS
What component is described below:
What market trends could lead to increased sales?
Opportunities
SWOT ANALYSIS
What component is described below:
What are the advantages competitors have over your organization?
Threats
SWOT ANALYSIS
An internal characteristic that contributes substantially to the realization of the organization’s mission
Strength
SWOT ANALYSIS
An internal characteristic that threatens the function of the organization
Weakness
SWOT ANALYSIS
An external fact or development that, if taken advantage of, can substantially contribute to the realization of the organization’s mission
Opportunity
SWOT ANALYSIS
An external fact or development that has or can have a substantial negative effect on an organization’s performance
Threat