4. Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography, & Magnetic Resonance Imaging
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
True or false: You can literally ultrasound anything. All you have to know is your anatomy.
true
In ultrasonography, high-frequency ________ waves penetrate tissue (or don’t) and bounce back to the transducer. In order to be effective, ________/________ is needed.
sound; water/fluid
How is the electric current generated in ultrasound?
crystals in the transducer convert the sound waves to electric current
How is an image produced with ultrasound?
computer in ultrasound machine converts the electric current to an image
How does fluid appear on ultrasound?
black
How does soft tissue (liver) appear on ultrasound?
gray
How does fibrous tissue (diaphragm) appear on ultrasound?
white
How does solid material appear on ultrasound?
white line with black under it
Sound waves do not go through ________ or ________ things.
air; solid
When using ultrasound, we must think about the ________ content of the tissue.
water
Waves travel in a ________ from the ________.
straight; probe
color indicates that there are no waves back
black
color indicates that all the waves come back
white
color indicates that there are some waves back
grey
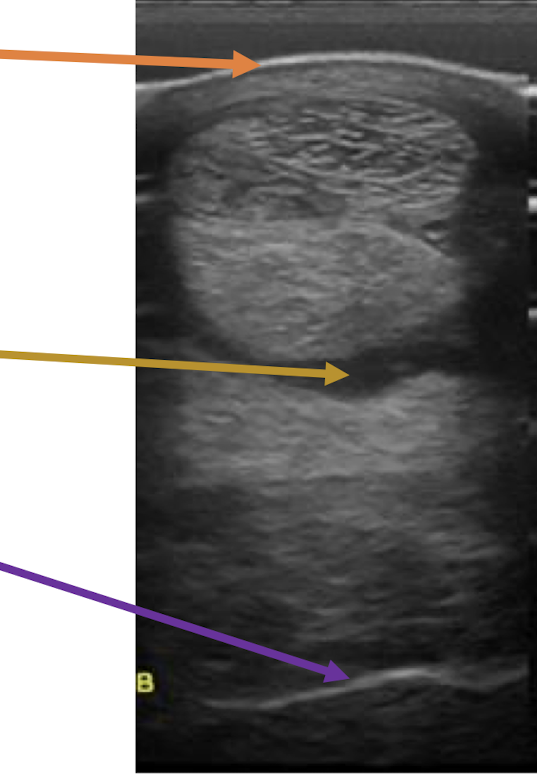
What is the orange arrow showing?
skin
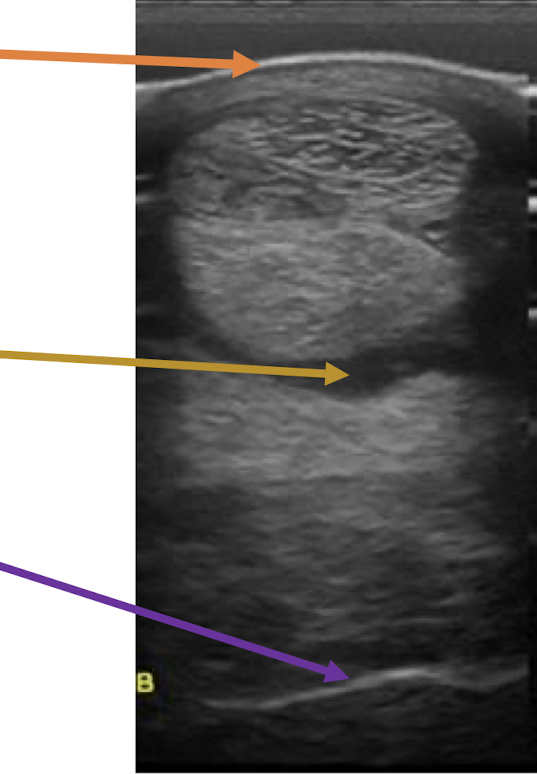
What is the yellow arrow showing?
fluid
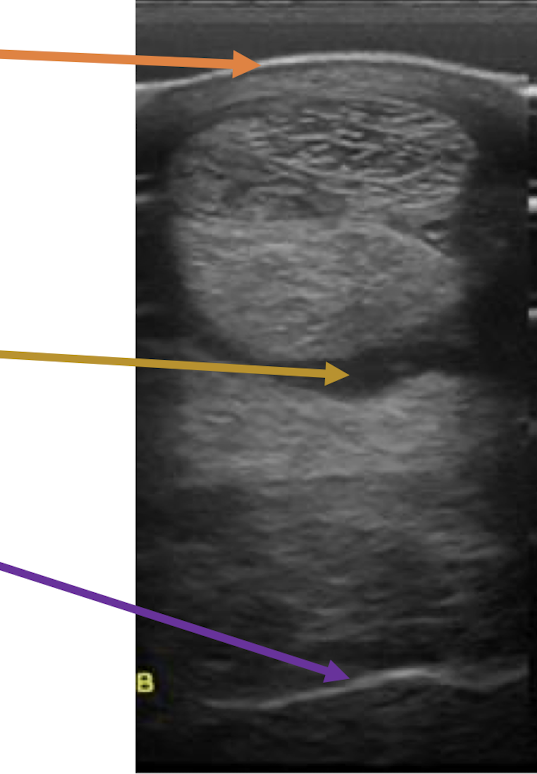
What is the purple arrow showing?
bone
Air is not ________. Therefore, ________ the waves ________ ________.
fluid; all; bounce back
black color on the ultrasound
anechoic
less black but darker than other tissues
hypoechoic
equal grey scale
isoechoic
more white / bright
hyperechoic
cannot see below a structure that reflects back all waves
acoustic shadow
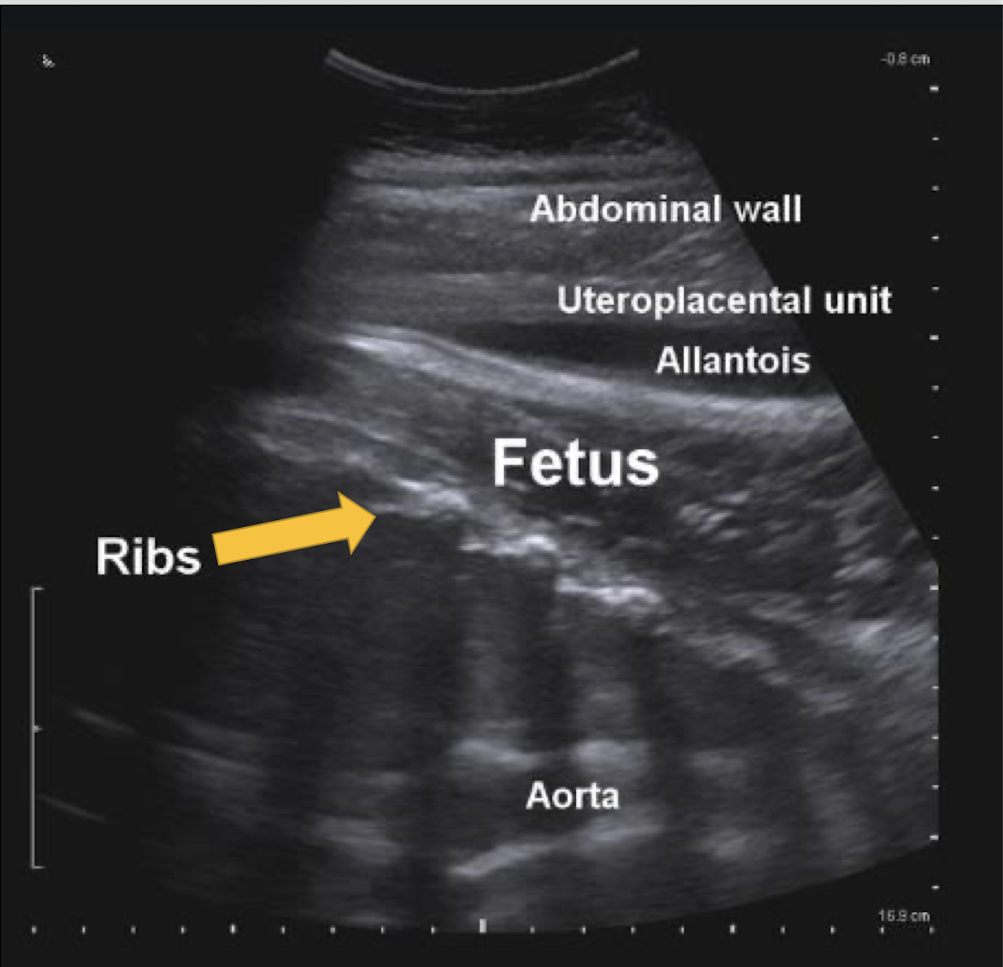
What artifact is this showing?
acoustic shadow
brightness deep to anechoic structure
acoustic enhancement
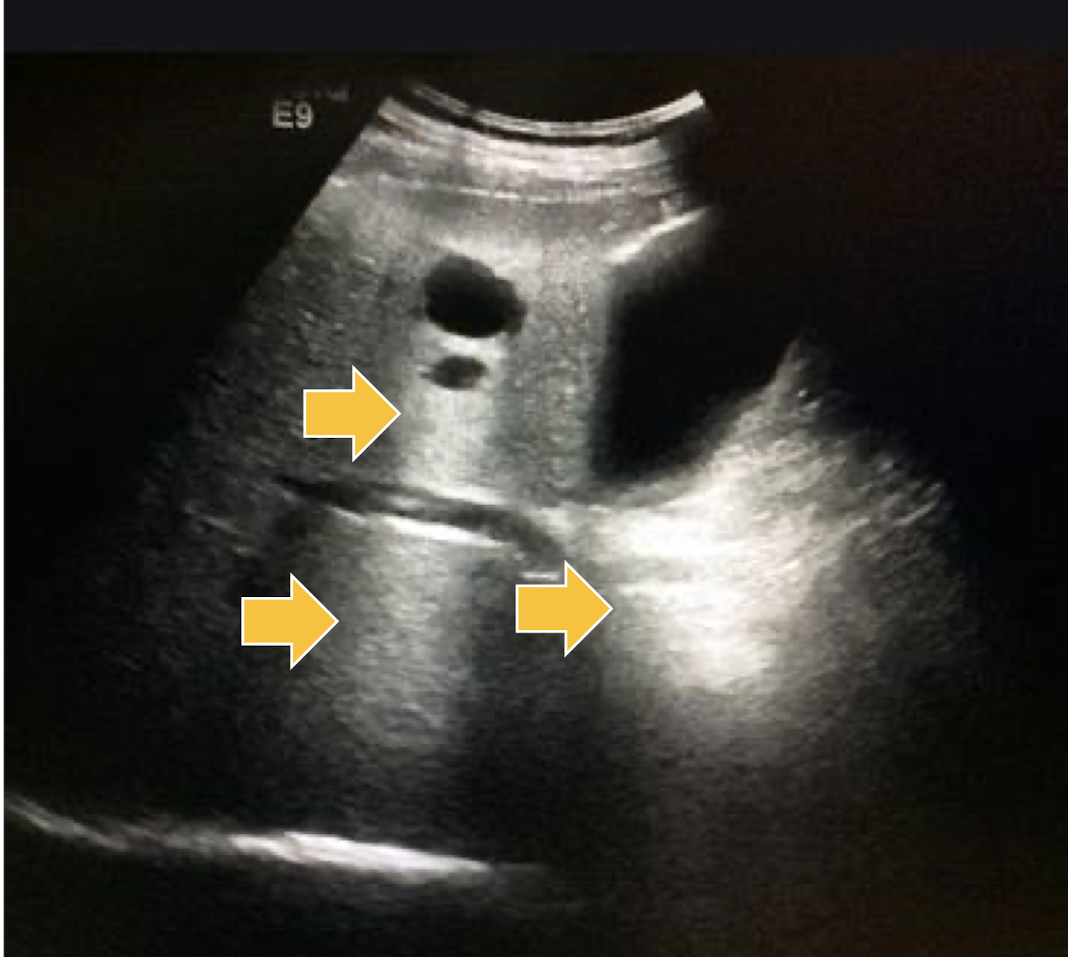
What artifact is this showing?
acoustic enhancement
sound waves reflecting multiple times between 2 strong reflectors
reverberation artifact
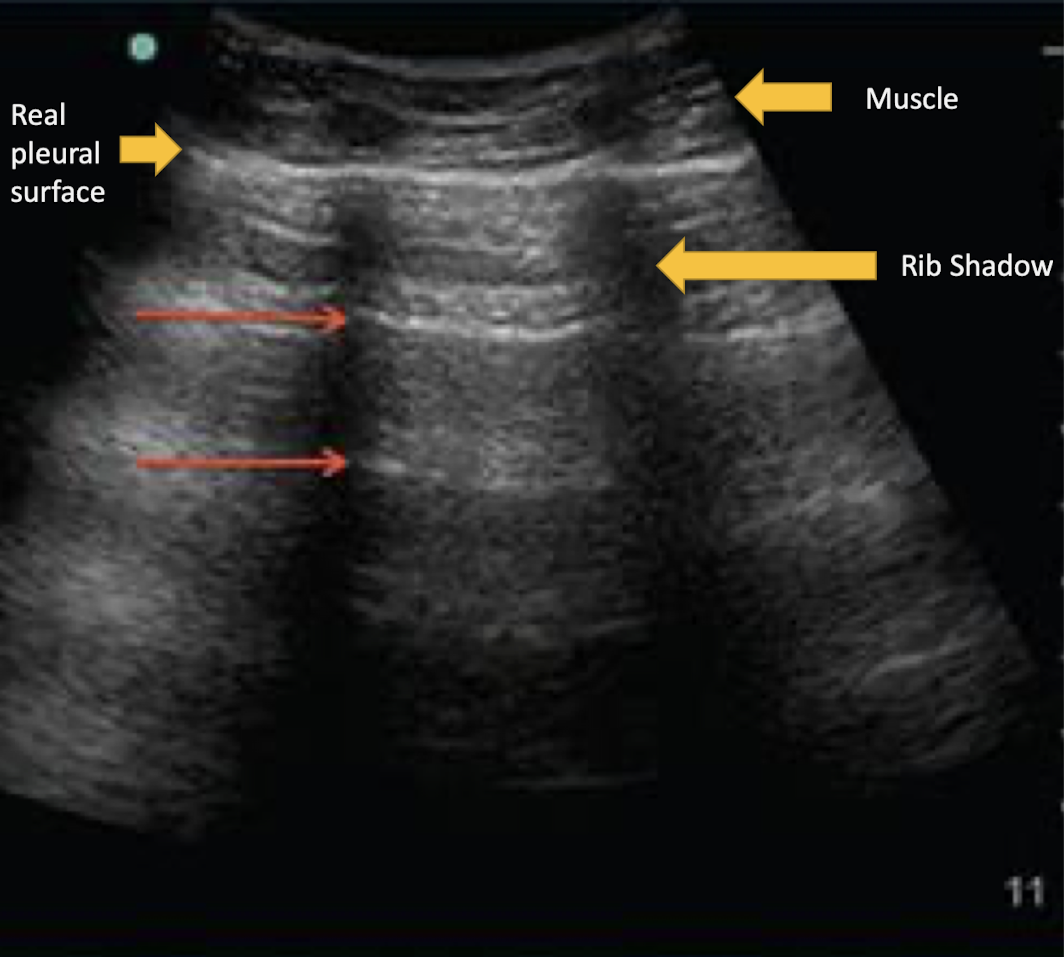
What artifact is this showing?
reverberation artifact
Where is reverberation artifact most common?
lung
duplication of image of the opposite side of a strong reflector
mirror image artifact
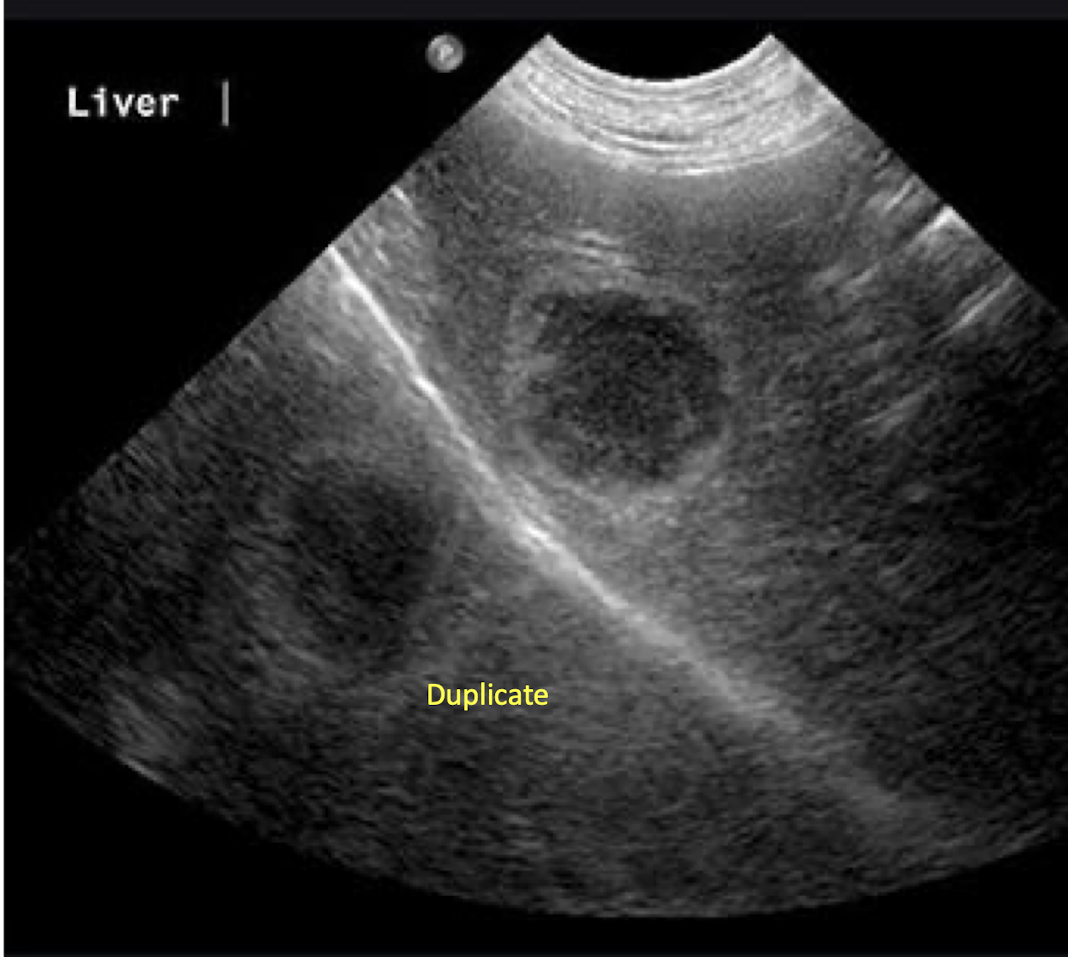
What artifact is this showing?
mirror image artifact
Where is a mirror image artifact the most common to be found? What medium would be the strong reflector here?
thorax/abdomen interface; diaphragm
artifact that occurs when imaging a 3D structure with anechoic fluid
slice thickness artifact
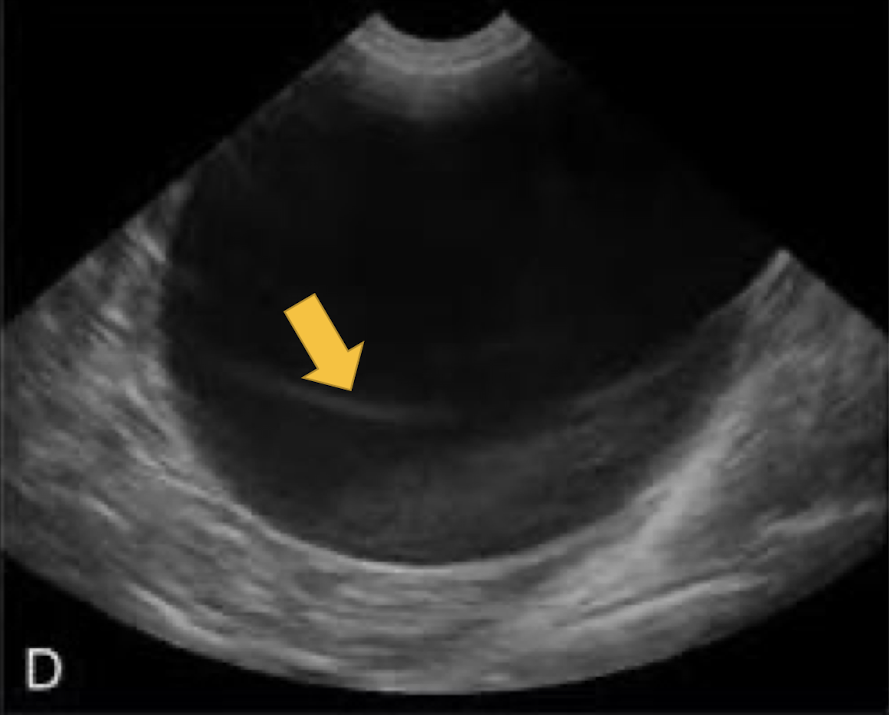
What artifact is this showing?
slice thickness artifact
Where would a slide thickness artifact be most commonly found?
bladder and gall bladder (artificial sludge)
when sound waves bend as they hit a curved surface tangentially
edge-shadowing artifact
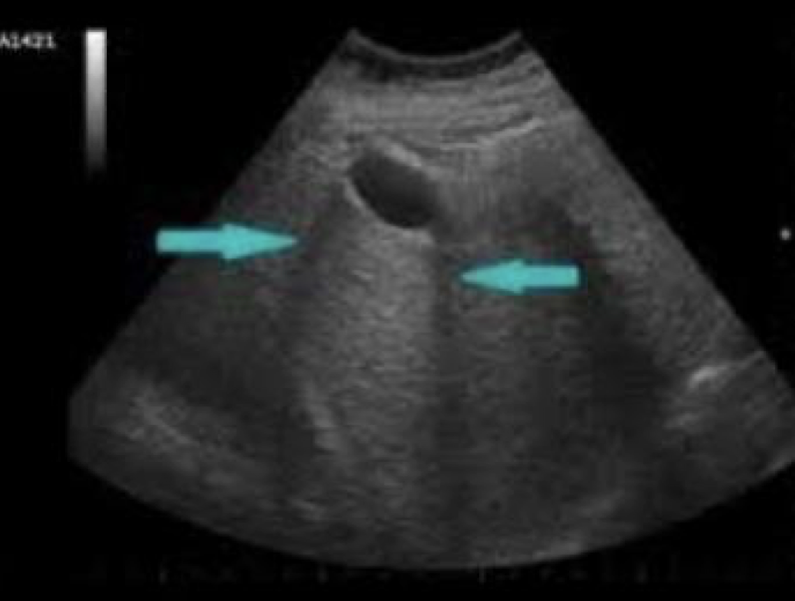
What artifact is this showing?
edge-shadowing artifact
What are the types of ultrasound probes (transducers)?
linear and curvilinear (sector)
Which type of ultrasound probe is most commonly used for equine tendons and gives a large footprint?
linear
Which type of ultrasound probe is most commonly used for small and large animal thorax and abdomen, and has a small footprint?
curvilinear
True or false: Quality of the transducer dictates the quality of the machine and image, and is the most valuable part of the machine.
true
Increased frequency (mHz) means ________ resolution, but ________ depth.
greater; less
Decreased frequency (mHz) means ________ resolution, but ________ depth.
less; greater
What are some indications for ultrasonography?
I
I
image soft tissue (anything with water content)
image surface of bone and lung for irregularity
When using ultrasound, how many planes need to be imaged? What are they?
2; transverse and longitudinal
What does the transverse plane tell us?
size of the lesion
What does the longitudinal plane tell us?
how much of the tissue (length) is involved with the lesion
True or false: Ultrasonography can be used for real-time imaging and has Doppler mode.
true
Using real-time imaging with ultrasonography, what can be assesse?
M
D
movement
direction of blood flow
x-ray tube in a circle that rotates at a pre-determined speed
computed tomography (CT)
What allows for the differentiation of structures in CT? What is this similar to?
the intensity of x-ray; radiographs
In computer tomography, a ________ reconstructs the data acquired from the detectors to make a “slice” image.
computer
True or false: In CT, software programs can reconstruct slices into a 3D image.
true
In tomography, ________ slices allow ________ location. In radiographs, you must take ________ views to figure this out.
2D; 3D; many
In CT, what structures cannot be seen?
soft tissue
In order to take a CT, how does the animal have to be?
anesthetized or very heavily sedated
CT imaging in a horse is generally limited to what?
C
D
H
carpus/tarsus
digit
head
What are indications for CT?
D
I
I
I
detailed evaluation of bone
image the head
image the spine
image the abdomen
In CT, what does any imaging of soft tissues require?
injection of contrast solution to enhance the contrast of soft tissues
All tissues have a lot of what proton? Why?
hydrogen protons; they are made of water (H2O)
In
True or false: Protons in different tissues relax differently and there is superior contrast in tissues.
true
When using MRI, what is extremely important to remember?
R
U
remove horseshoes
use non-magnetic anesthesia equipment
Both MRI and CT allow for what?
tomography and 3D reconstruction
has better contrast resolution and is superior for imaging soft tissues
MRI
is superior for imaging bone because it doesn’t have as much water and is superior for fracture planning
CT
True or false: You can evaluate cartilage with MRI, but not CT, unless contrast is used.
true
In MRI, use different types of ________ and measure different types of ________ to allow for greater ________ and focus on different types of structures (bone vs. soft tissue).
pulses; relaxation; contrast
What are the indications for MRI in equine?
imaging soft tissue and bone lesions in areas where ultrasound is not possible (the foot)
True or false: In equines, there are similar limitations with MRI in structures that may be imaged as CT, since the horses have to fit in the magnet.
true
What are MRI indications in small animals?
N
M
T
P
neuroimaging
musculoskeletal
tumor staging
possible abdomen and cardiac
inject a drug (called a radiopharmaceutical) that is bound to a rapidly decaying radioactive atom and the drug has a propensity for certain tissue
nuclear scintigraphy
What is the most common radiopharmaceutical used in nuclear scintigraphy?
technetium-99m (99mTc)
drug that has a propensity for hydroxyapatite in bone
methylene diphosphonate
By what and where is hydroxyapatite formed? What is the signal of radioactive atomy?
osteoblasts in areas of active bone formation; proportional to bone resorption
In nuclear scintigraphy, ________ camera detects decay of radioactive atoms, which can take a few minutes.
gamma
True or false: With nuclear scintigraphy, it is comparative, meaning you need to image both sides.
true
What are indications for nuclear scintigraphy in equine?
F
L
M
U
S
M
fail to localize lameness with blocks
localize lameness but no lesions on radiographs or ultrasound
multiple limb lameness
upper limb or axial musculoskeletal issue
suspect fracture not imaged on radiographs
mild, intermittent lameness that precludes blocking
What are indications for nuclear scintigraphy in small animals?
R
T
M
renal function
thyroid
musculoskeletal