Lecture 1 - Introduction to the brain part 1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is behavioural science ?
The field of science that relates BEHAVIOURS to BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
What are the three tasks all living things face ?
Secure energy and essential nutrients
Avoid harm and danger
Reproduction
What is evolution through natural selection ?
Having new VARIATIONS occur and if the environment favours those variations, they’ll continue to reproduce. (keeping the good, throwing out the bad)
All animals have similar WHAT but have evolved differently to meet their WHAT needs
All animals have similar SKELETONS, MUSCLES and BODY PARTS but have evolved differently to meet their ENVIRONMENTS needs
Evolutionary approach to behaviour
WHAT
WHAT
Evolutionary approach to behaviour
Species-specific behaviours
Continuity / conservation of behaviour
What is species-specific behaviour
The natural ACTIONS and RESPONSES shared by nearly all members of a given SPECIES - won’t continue into other species (eg. having a spinal cord, opposable thumbs)
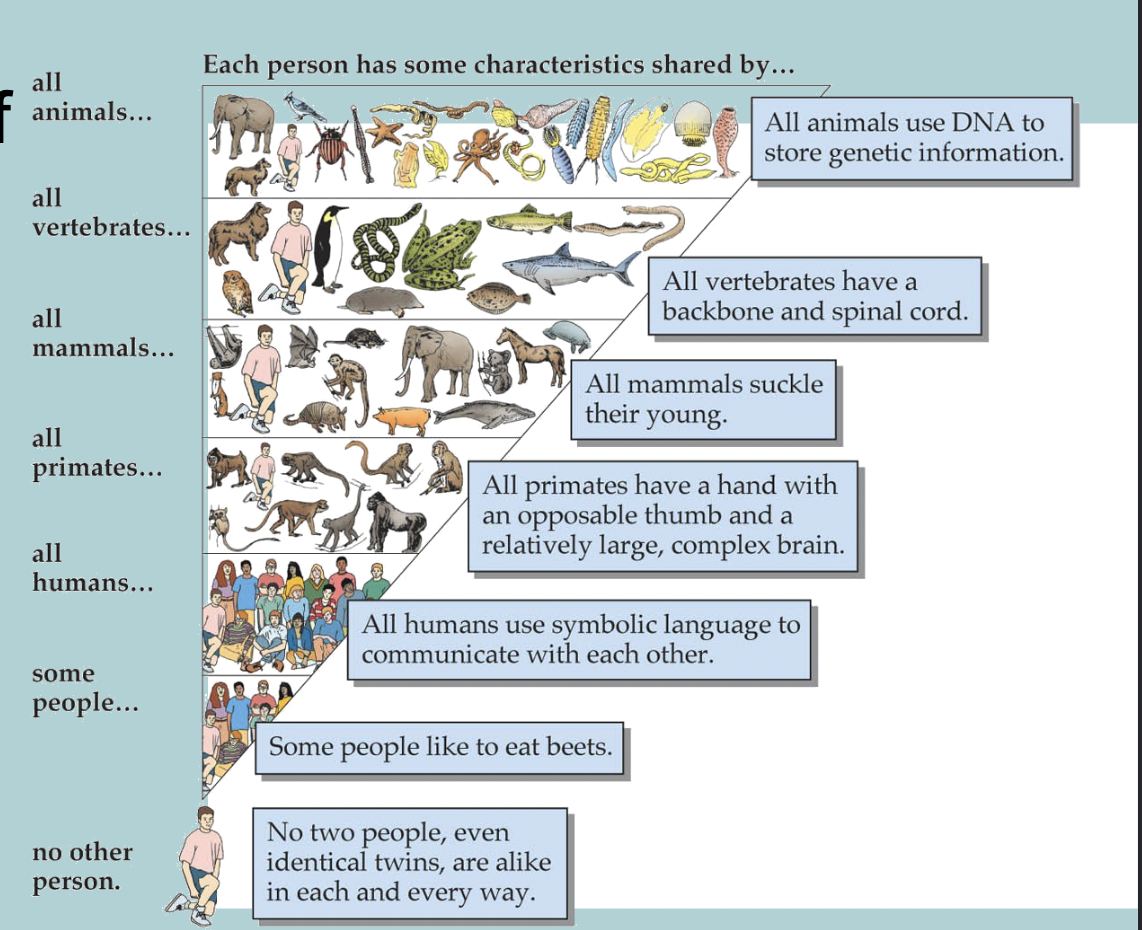
What is the continuity / conservation of behaviour
As the groups become more specific (animals, vertebrate etc) it’s the continuity of a behaviour that will be maintained (eg. eating, hunting)
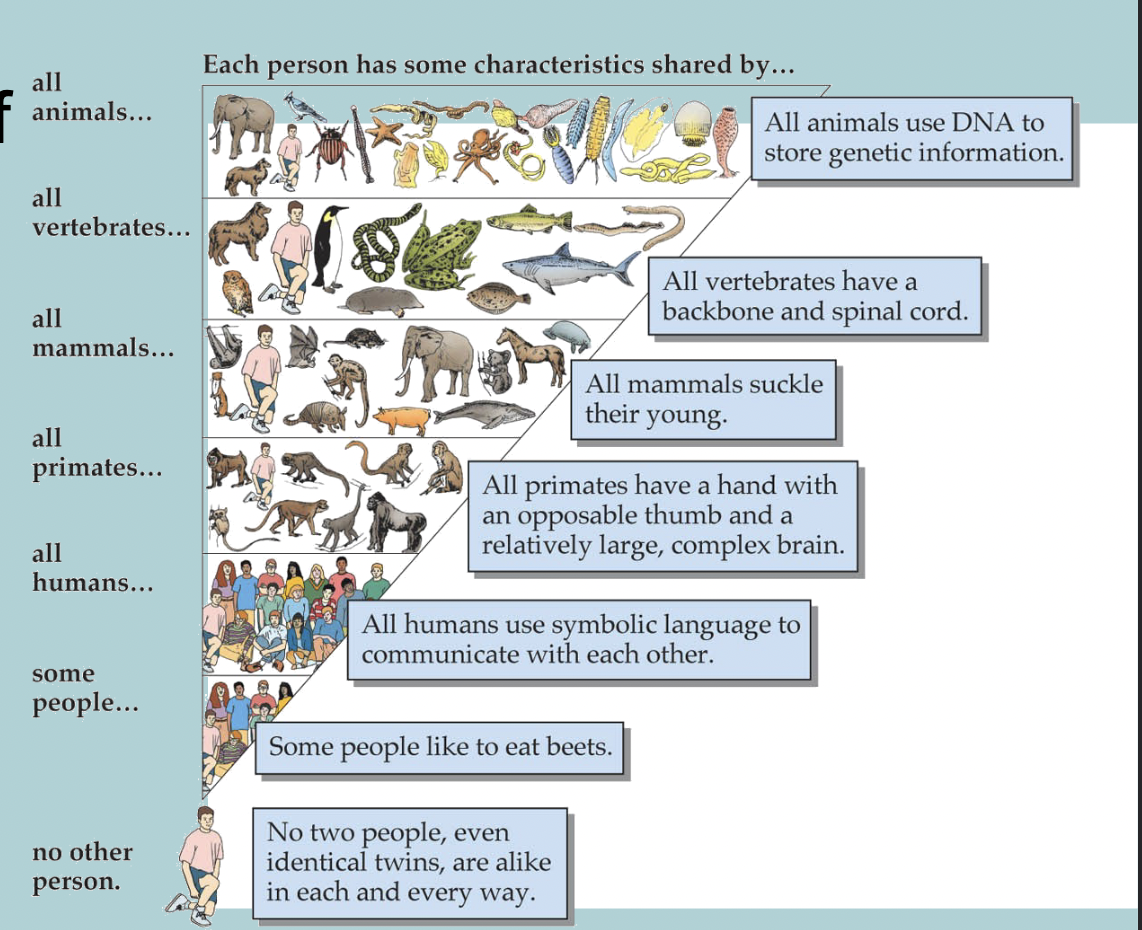
Traits are passed from WHAT to WHAT
Traits are passed from GENERATION to GENERATION
Traits can WHAT over time to adapt to WHAT (that also changes)
Traits can CHANGE over time to adapt to PARTICULAR ENVIRONMENTS (that also changes)
Evolution and natural selection changes WHAT, but retains the same WHAT
Evolution and natural selection changes TRAITS, but retains the same BASIC PLAN
Neurons are found in all WHAT, and work in the same WHAT
Neurons are found in all ANIMALS, and work in the same BASIC WAY
Neurons are very old WHAT
Adaptations
Darwin and Natural selection:
Based on 3 facts:
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
and 1 inference:
WHAT
Darwin and Natural selection:
Based on 3 facts:
Individuals of a given species are NOT IDENTICAL
some of this variation can be INHERITED
NOT all offspring SURVIVE
and 1 inference:
VARIATIONS among individuals affects the probability taht they will SURVIVE, REPRODUCE, and PASS along their CHARACTERISTICS
What did Mendel do ?
Defined the laws of inheritance
Law of inheritance:
Genes come on PAIRS of TWO and are inherited as DISTINCT UNITS, one from each PARENT
What did Hugo de Vries do ?
Described the mechanism of MUTATION that leads to novel traits
What are novel traits ?
NEW or INTRODUCED CHARACTERISTICS in a plant species that are NOT PREVIOUSLY found in its cultivated populations
Traits are passed on through WHAT
DNA
We receive a WHAT of these genes from each WHAT
We receive a COPY of these genes from each PARENT
We have HOW MANY copies of almost every WHAT, except for WHAT
We have 2 copies of almost every GENE, except for GAMETES (eg, sperm and egg cells)
Modern taxonomy:
Compare WHAT
Based on WHAT, predict how long ago two species WHAT
Modern taxonomy:
Compare DNA
Based on SPONTANEOUS MUTATION RATES, predict how long ago two species DIVERGED (finding the common ancestor)
Nervous system provides means to WHAT, WHAT, WHAT and WHAT external environments
Nervous system provides means to SENSE, REACT, INTERACT and INTERPRET external environments
Darwin’s legacy:
If all animals are related, then so must be their WHAT
If all animals are related, then so must be their WHAT
The nervous system and associated behaviours have been built bit by bit over time from WHAT to WHAT (called WHAT)
If we can study the animal nervous system and behaviour then we can study WHAT
Darwin’s legacy:
If all animals are related, then so must be their NERVOUS SYSTEM
If all animals are related, then so must be their BEHAVIOURS
The nervous system and associated behaviours have been built bit by bit over time from SIMPLE SYSTEMS to COMPLEX ORGANISMS (called EVOLUTION)
If we can study the animal nervous system and behaviour then we can study OUR OWN
The brain’s functional units are WHAT
Neurons
The “Neuron Doctrine”
Nervous systems are made up of discrete WHAT, WHAT cells: called WHAT
Neurons contact each other at WHAT: called WHAT
Together they form the WHAT, WHAT, WHAT and WHAT units of nervous systems
The “Neuron Doctrine”
Nervous systems are made up of discrete INDIVIDUAL, POLARIZED (nerve) cells: called NEURONS
Neurons contact each other at SPECIALIZED JUNCTION: called SYNAPSES
Together they form the DEVELOPMENTAL, FUNCTIONAL, STRUCTURAL and TROPHIC units of nervous systems
What did Anthony van Leeuwenhoek do
Anthony van Leeuwenhoek:
Postulated that nerves are TUBES containing FLUIDS (spirits) carrying SENSATONS from and to the brain
What did Jan E. Purkinje do
Jan E. Purkinje:
Identified existence of CELLS in the nervous system
What did Theodor Schwann do
Created the CELL THEORY
What did Augustus Waller do?
Discovered the concept of ANTROGRADE NERVE DEGENERATION
What did B.A. Gudden do
Discovered concept of TROPHIC support. Traced CONNECTIONS between the MAIN CENTERS of the brain
What did Albrecht von Kolliker do
Supplied proof that NERVE FIBRES are CONTINUOUS with NERVE CELLS
What are the two innovations leading to the Neuron Doctrine
Microscopy
Golgi stain
What was imperfect about the Golgi stain
it showed neurons but NOT ALL neurons
The neuron is a fundamental WHAT, WHAT, WHAT and WHAT unit for the nervous system
The neuron is a fundamental STRUCTURAL, DEVELOPMENTAL, FUNCTIONAL and METABOLIC unit for the nervous system
Neurons are WHAT cell which are NOT WHAT with other cells
Neurons are DISCRETE cell which are NOT CONTINUOUS with other cells
The neuron is composed of 3 parts:
The dendrites (receive info), a single axon and a cell body
Information flows along the neuron in WHAT direction (from WHAT to the WHAT via the WHAT)
Information flows along the neuron in ONE direction (from DENDRITES to the AXON via the CELL BODY)
What is a SYNAPSE
A barrier to TRANSMISSION exists at the site of CONTACT between two neurons that may permit a TRANSMISSION
What is a unity of transmission
Synaptic contacts between two cels can be either INHIBITORY or EXCITATORY, but will always be the same type
What does an inhibitory do
Decreases the likelihood of a receiving neuron firing an action potential
What does an excitatory do
Increase the probability of a neuron firing an action potential
What is Dale’s law
Each nerve terminal releases a SINGLE type of TRANSMITTER (ex: dopamine, serotonin, but that transmitter will only release that specific one)