Unit 1 Biological Basis of Behavior
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Nature
Refers to genetic or predisposed characteristics that influence physical, behavioral, and mental traits and processes.
Nurture
Environmental factors, refers to the external factors that one experiences such as family interactions or education
Evolutionary perspective
Explores how natural selection affects the expression of behavior and mental processes to increase survival and reproductive success
Eugenics
Principles of the evolutionary perspective in ways that discriminate against others
Central nervous system (CNS)
The brain and the spinal cord; interacts with all processes of the body
Peripheral Nervous system (PNS)
Relays messages from the central nervous system to the rest of the body and includes the autonomic and somatic nervous systems
Autonomic nervous system
Governs processes that are involuntary and includes the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Governs processes that are voluntary
Parasympathetic nervous system
Responsible for the body’s rest and digest response, promoting relaxation and recovery
Sympathetic Nervous System
Body’s fight or flight response system, preparing the body for physical activity
Neurons
Neural cells that transmit information, form the basis of the nervous system and are the building blocks of all behavior and mental processes
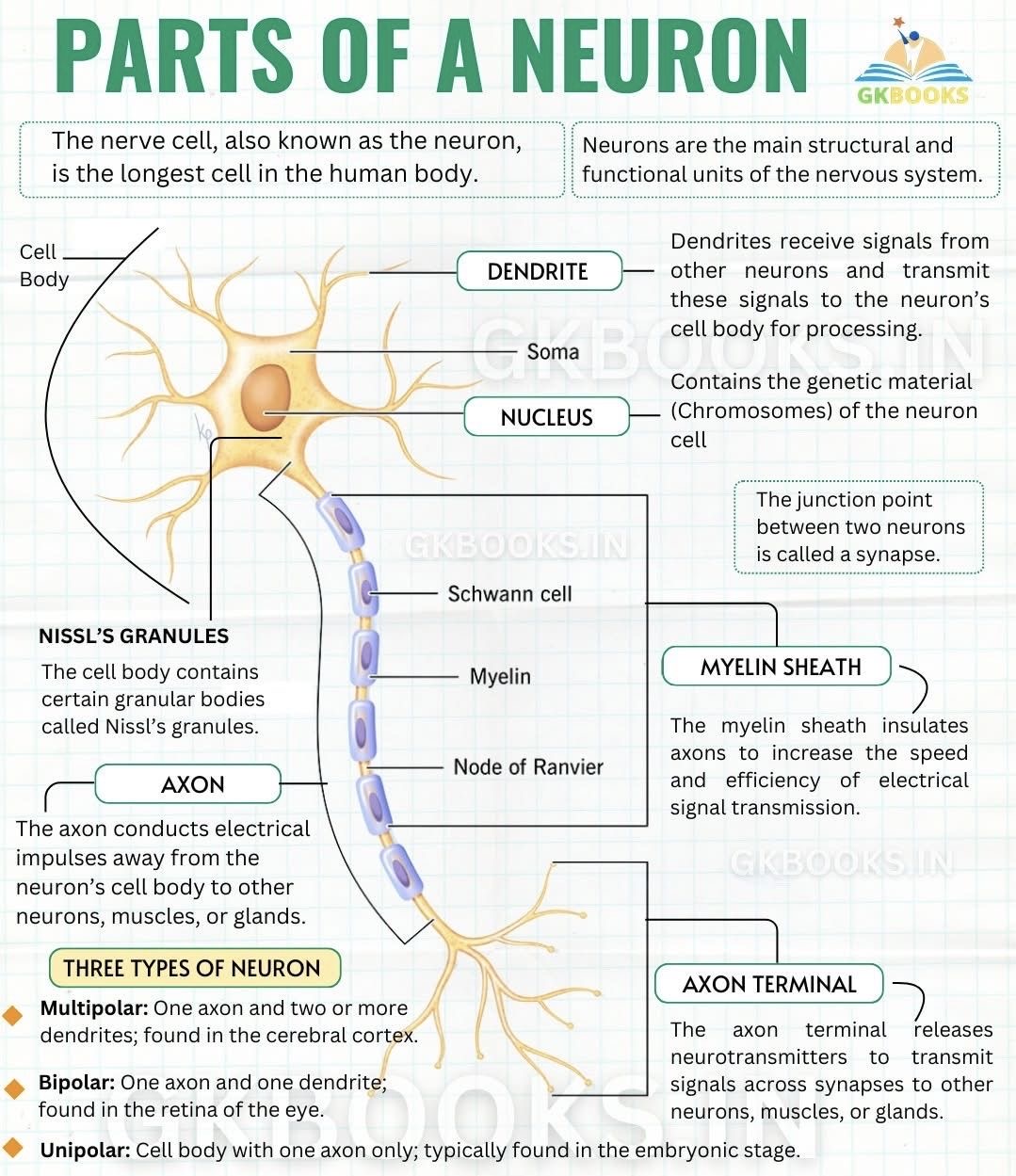
Glial cells
Cells that provide structure, insulation, communication, and waste transport.
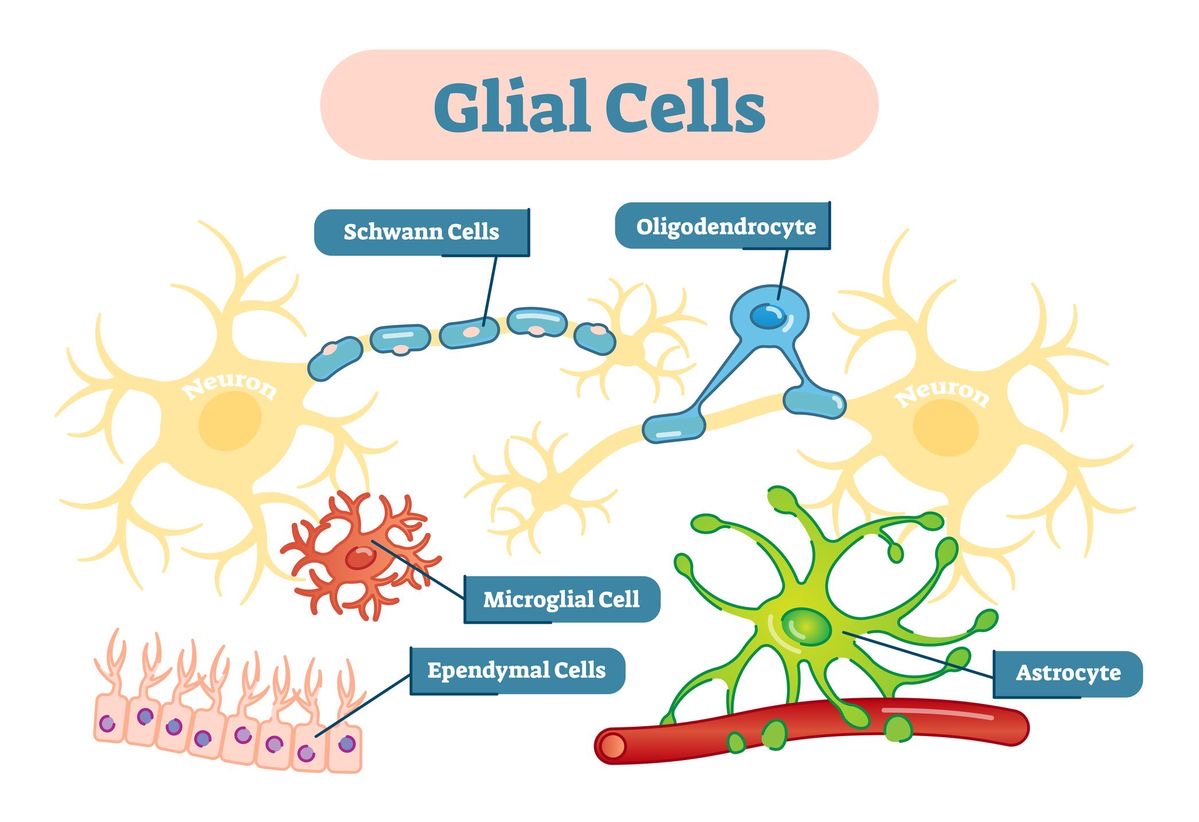
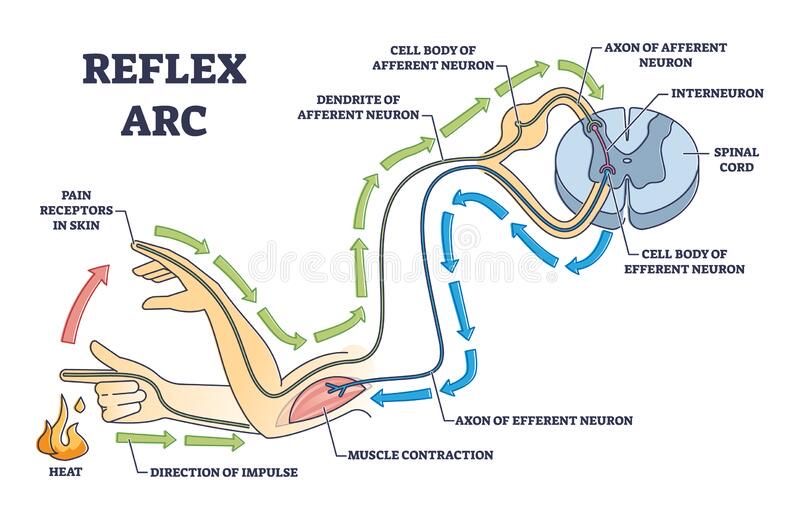
Reflex arc
Demonstrates how neurons within the central nervous system work together to respond to stimuli. Three types of neurons work together in the spinal cord to create it: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons.
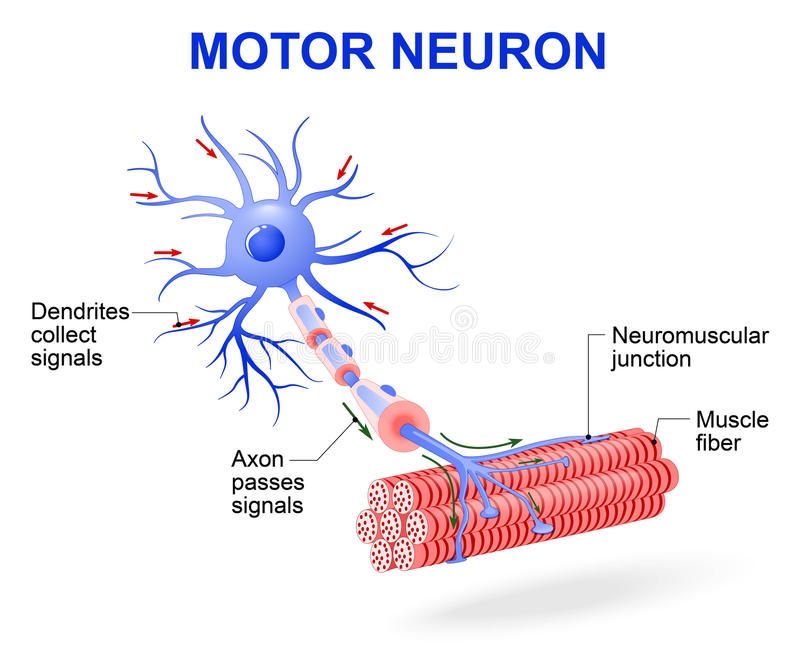
Sensory neurons
Nerve cell forming part of a pathway along which impulses pass from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands
Interneurons
a neuron which transmits impulses between other neurons especially as part of a reflex arc
Neural transmission
Most commonly occurs in an orderly systematic way and involves the all or nothing principle, depolarization, refractory, period, resting potential, reuptake, and threshold. Disruptions to this process could lead to disorders such as multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis
All or nothing principle
A cognitive bias where situations are seen in black and white like good or bad, success or failur3
Depolarization
Reduction in the difference of electrical charge across a cell’s membrane making the inside of a cell less negative and positive on the outside
Refractory period
Neuron cannot fire another action potential due to a previous stimulus
Resting potential
The stable electrical charge difference scores a neurons membrane