PHR 937 - RA Pharmacology kaitlyn
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
non-pharm treatments
- patient and family education
- exercise (PT/OT)
- weight loss (decreases pressure on joints)
- ambulatory devices
- surgery
pharm treatments (overview)
- NSAIDs, COX-2 inhibitors
- salicylates
- corticosteroids
- DMARDs
> synthetic (conventional)
> biologics
> target specific
non-selective NSAIDs
ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac
use: reduce joint pain & swelling, improve joint function
- does NOT slow progression - sx relief only!!
MOA: inhibit COX-1 and COX-2
caution: renal dysfunction, CHF
ADE: GI toxicity, edema, HTN, renal impairment
monitoring: SCr, BP, GI symptoms, edema

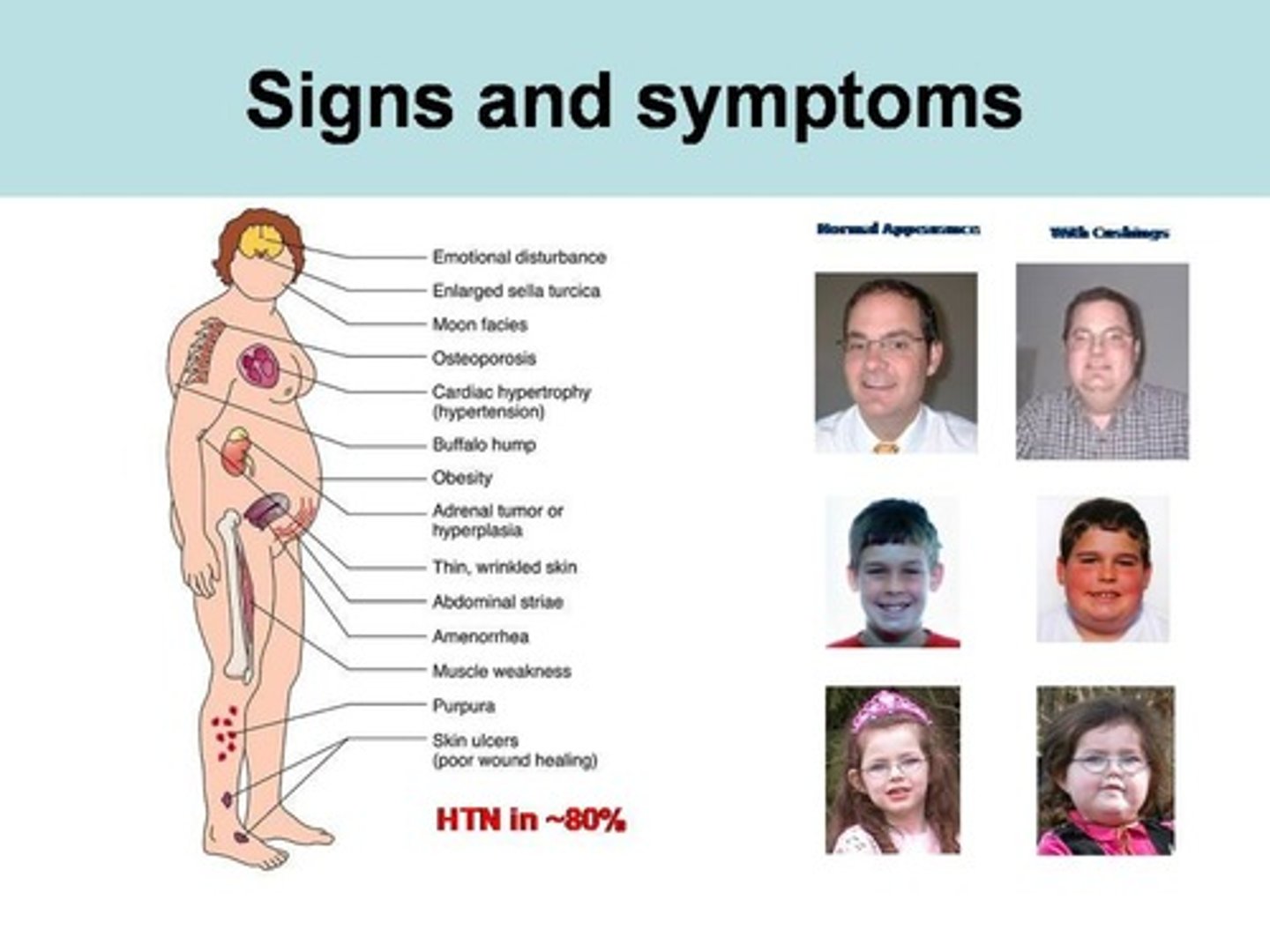
corticosteroids
prednisone, methylprednisolone
use: reduce joint pain and swelling
- bridge therapy ONLY, not for long term!!
MOA: potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects
caution: DM, HTN, CHF
ADE: (Cushings) osteoporosis, HTN, weight gain, edema, hyperglycemia, skin thinning
monitoring: CBC, BP, DEXA scans (bone density)
DMARDs
use: reduces / prevents joint damage
- should be started within 3 months of diagnosis!!
3 types:
> synthetic (conventional)
> biologics
> target specific
concerns: takes weeks to months for benefit; women can NOT get pregnant on most
synthetic DMARDs
hydroxychloroquine
sulfasalazine
methotrexate
leflunomide
(there are a few more, but these are most used)
hydroxychlorquine
Plaquenil
synthetic DMARD
use: mild-moderate RA without poor prognostic features
MOA: unclear - thought to affect antigen presentation
time to benefit: 2-4 months
ADE: macular damage, retinopathy
monitoring: annual eye exam
dose: 200-400 mg PO daily
notes: safe in pregnancy; may be used in triple DMARD with sulfasalazine + MTX/LEF
sulfasalazine
synthetic DMARD
use: mild-moderate RA without poor prognostic features
MOA: unknown - has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects
time to benefit: 1-3 months
CI: sulfa allergy or G6PD deficiency, liver disease
toxicities: dose dependent; myelosuppression, GI effects
monitoring: CBC, AST/ALT Q2-4 weeks, then Q3 months after stable dose for 3 months
dose: 1000 - 1500 mg PO BID
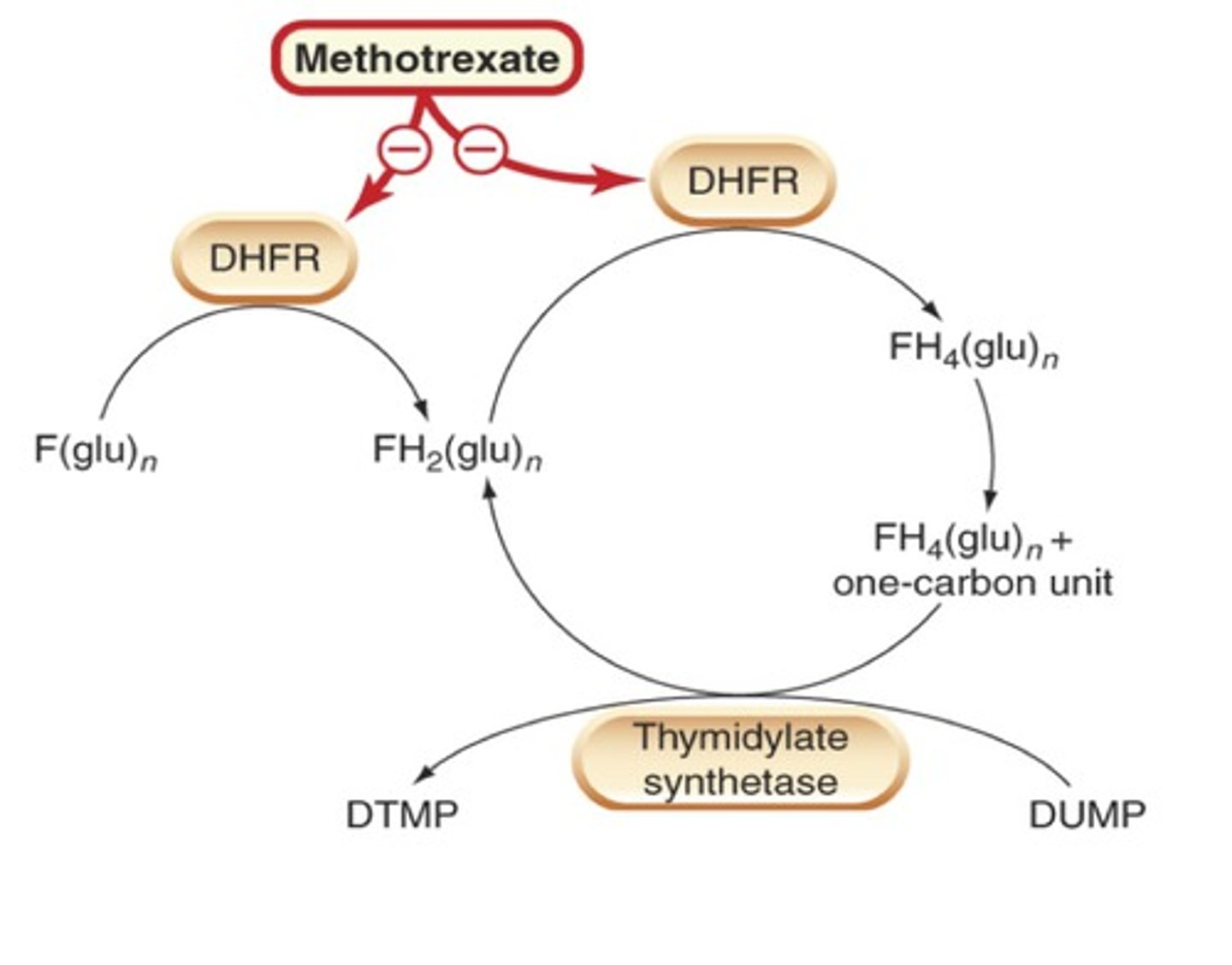
methotrexate
synthetic DMARD
use: ALL levels of disease
MOA: anti-inflammatory and immunosuppresive DHF reductase inhibitor
- inhibits purine biosynthesis and proliferation of inflammatory cytokines
time to benefit: 1-3 months
CI: pregnancy, chronic liver disease, CrCl <30
toxicities: stomatitis, GI, myelosuppression, pulmonary fibrosis, hepatic fibrosis
monitoring: CBC, SCr, liver enzymes monthly; then CBC monthly + SCr/ liver panel Q2-3 months once dose is stable for 1 year
dose: 7.5-10 mg PO/ SQ QW -> 25 mg max
notes: often 1st line, superior efficacy; must co-admin with folic acid 1 mg QD
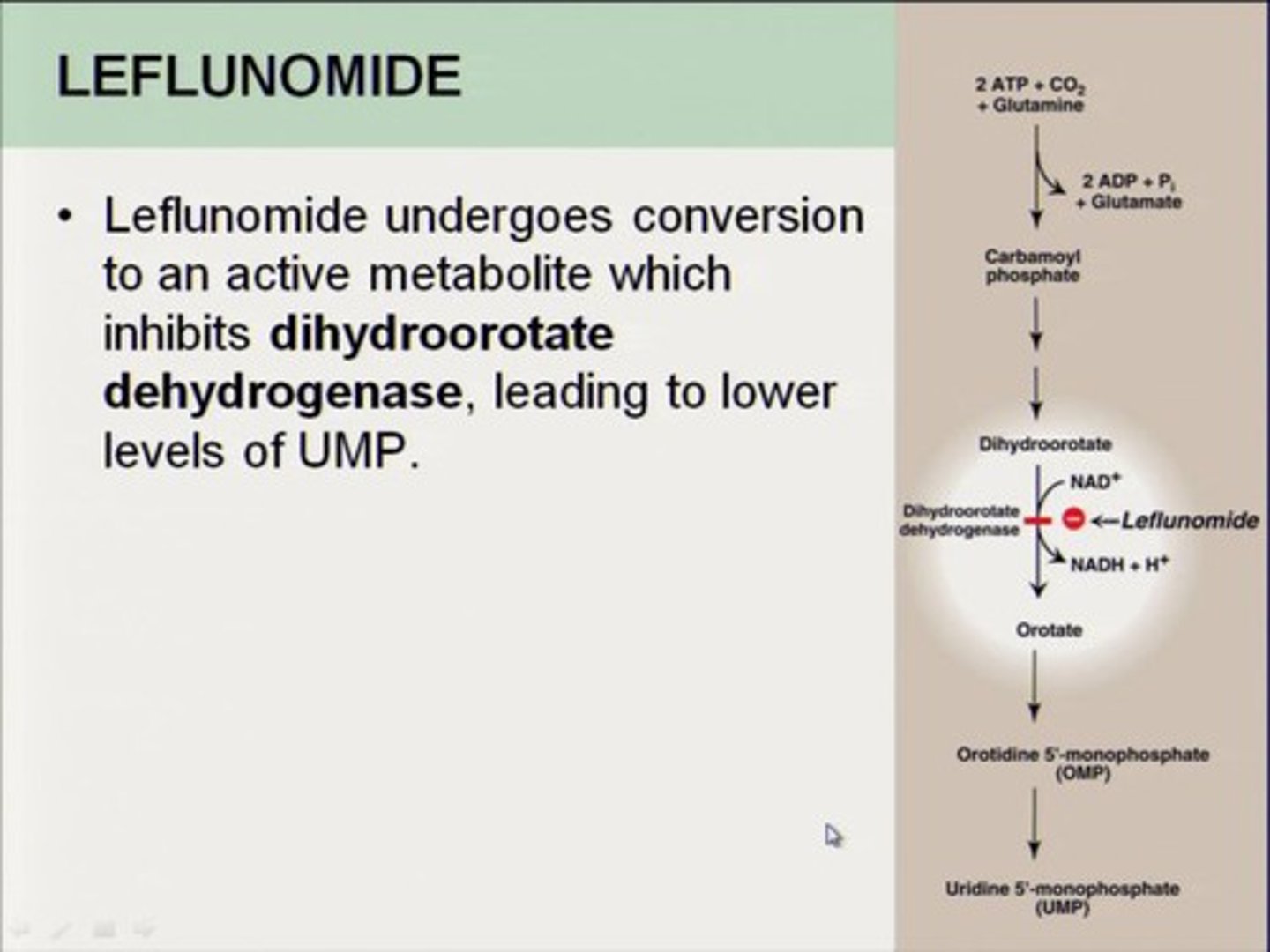
leflunomide
synthetic DMARD
use: ALL levels of disease
MOA: inhibits pyrimidine biosynthesis
- disrupts DNA synthesis + impacts proliferation/ activation of lymphocytes
- selectively target autoimmune lymphocytes (reduces ADEs)
time to benefit: 1-2 months
CI: liver disease, pregnancy
toxicities: GI, hepatotoxicity
monitoring: CBC, liver enzymes monthly; then every 3 months once dose is stable for 3 months
dose: 10-20 mg PO QD
biologic DMARDs
TNF-a inhibitors
JAK inhibitors
B-cell depletion
T-cell inhibitor
IL-6 receptor antagonist
IL-1 antagonist
- screen for TB/ hepatitis for all
TNF-a inhibitors
use: an alternative to methotrexate in DMARD-naive patients with moderate to high disease activity OR as an adjunctive therapy in pts not at treatment goals with methotrexate
MOA: binds soluble and membrane bound TNF-a
ADE: injection site rxn, increased risk of infection, headache, N/V
[box warning]: increased risk of infection, malignancy
CI: heart failure, lupus
- not recommended in MS
adalimumab
Humira
TNF-a inhibitor
40 mg Q 2 weeks
- alt: 40 mg Q weekly if not on MTX
etanercept
Enbrel
TNF-a inhibitor
- "safer" for the liver
certolizumab
Cimzia
TNF-a inhibitor
- only pregnancy safe biologic!!!!!
golimumab
Simponi
TNF-a inhibitor
infliximab
Remicade
TNF-a inhibitor
IL-6 receptor antagonists
tocilizumab (Actemra)
sarilumab (Kevzara)
- both self injectable
use: moderate to severe active RA in pts who have had an inadequate response OR contraindication to 1+ TNF-a therapies
MOA: binds soluble and membrane bound IL-6 receptors
ADE: increased liver enzymes, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, lipid effects
caution with GI perforation
monitoring: CBC, AST, ALT, lipid panel
JAK inhibitors
use: moderate to severe active RA who have had an inadequate response OR intolerance to methotrexate
MOA: prevents activation of cytokine signaling pathways
ADE: increased ALTs, elevated lipids, UTIs, headache, diarrhea, nasopharyngitis
[black box]: thrombosis, serious infections, GI perforations, lymphomas
monitoring: CBC, LFT, FLP
- oral!
tofacitinib
Xeljanz
JAK inhibitors
- non selective JAK
upadacitinib
Rinvoq
JAK inhibitors
- higher selectivity for JAK 1
baracitinib
Olumiant
JAK inhibitors
- higher selectivity for JAK 1 and 2
T cell costimulation inhibitor
abatacept (Orencia)
- self injectable or IV infusion
MOA: inhibits T cell activation by binding CD80 and CD86 on the APC, blocking the required interaction with CD28
ADE: URIs
CI: precaution in COPD pts
B cell depletion
rituximab (Rituxan)
- IV
use: patients with moderate to severe RA with inadequate response to 1+ TNF-a inhibitors
MOA: chimeric monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody that selectively depletes B cells
ADE: infusion site reactions (premedication REQUIRED)
caution with GI perforation and history of arrythmia
monitoring: CBC and platelets
IL-1 receptor antagonist
anakinra (Kineret)
- subq daily
- LAST RESORT
MOA: competitively inhibits binding of IL-1 to the IL-1 type receptor
- mono or in combo with MTX
ADE: injection site reactionsm increased infection risk
CI: hypersensitivity to E coli derived proteins
monitoring: CBC