lec 13: identifying stem cells
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
surface protein expression
stem cells express specifc surface proteins (markers)
can be.used to isolate, identifty and characterize stem cells
change during different stages of differentiation and migration
allow cells to interact and respond to info from their environment
several surface markers have been identified as cluster of differentiation (CD) and are used to characterize stem cells
flow cytometry
analyzes single cells as they flow past single or multiple lasers while suspended in a buffered salt-based solution
determining cell volume, size, and purity of subpopulations which are isolated
uses lasers to produce both scattered and fluorescent light signals that are read by detectors
cell populations are analyzed based on their fluorescent or light scattering characteristics
typical experiment begins with flourescently labeled cells in a single cell suspension
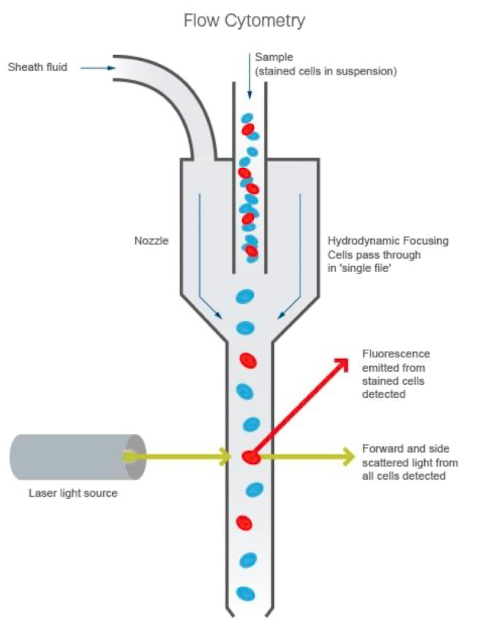
components of flow cytometer
fluidics system: transporting the sample from the sample tube to the flow cell. once through the flow cell, the sample is either sorted or transported to waste
optical system: excitation light sources, lenses, and filters to collect and move light around the instrument and the detection system that generates photocurrent
electronics: the brains → photocurrent from the detector is digitized and processed to be saved for subsequent analysis
foward scatter light signals
light refracted in the forward direction
used to determine the relative size of the cell
bigger particles produce more than smaller ones, and stronger forward scatter signal
side scatter light signals
light refracted in a different direction than its original path
provides information on granularity and complexity of the cells
low granularity and complexity → less side scattered light
more sensitve to membranes, cytoplasm
florescent light emission signals
detecting the flourescense signal from the conjugated flourophore
must be careful for autoflourescence → occur from naturally flouroscing substances in the cell
western blot
detecting certain markers of interest
separate macomolecules in sample using gel electrophoresis
transfered or blotted onto a second matrix, generally a nitrocellulose mebrane → membrane is blocked to prevent any nonspecifc binding of antibodies to the surface of the membrane
transferred protein is then probed with a combination of antibodies:
one specific to the protein of interest (primary antibody)
one specific to the host species of the primary antibody (secondary antibody)
complexed with an enzyme, which when combined with an appropriate substrate, will produce a detectable signal
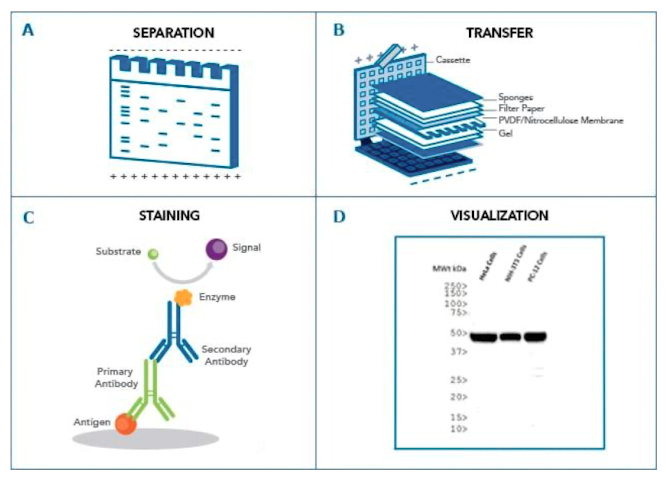
mechanism of detection chemistries
a detectable signal is generated following binding of an antibody speciic for the protein of interest
colorimetric → signal is a coloured precipitate
chemiluminescence: reaction emits light
flourescence: antibody is labeled with florophore
polymerase chain reaction
selectively amplify and detect DNA sequences → molecular photocopier
temp of the sample is repeatedly raised and lowered to help DNA replication enzyme copy the target DNA sequence
can produce billion copies of target sequence
3 main steps
denaturation of the template DNA into a single strand
annealing of primers to each original strand for new stand synthesis
extension of the new DNA strand form the primers
verifies genetic stability
pluripotency marker expression
detecting contamination