CONCEPTUAL ISSUES IN EVOLUTIONARY PSYCHOLOGY
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Describe the origins of modern humans.
Homo-sapiens migrated out of Africa → Asia and outlived the Neanderthals
Why did Homo-sapiens out-survive the stronger Neanderthals?
Baron-Cohen’s Empathising-Systemising theory suggests that homo-sapiens were better organised for networking so our social groups allowed us to share knowledge and survive best.
What evidence informed Baron-Cohen’s Empathising-Systemising theory?
Ancient people’s footprint fossils at Formby Point Merseyside, UK.
For evolutionary psychologists what has a major influence on behaviour?
Genes and inherited information developed through evolution have a major influence on behaviour.
What are 3 theories on the origins of life on earth?
1) Creationism - god created earth
2) Seeding theory - aliens put life on earth
3) Evolution - life on earth comes from evolution by natural selection
What was the evolutionary view before Darwin?
Evolution was described as change over time in organic structures. Characteristics seemed to have a purpose but little attempt was made to understand how they appeared - what was the advantage of giraffes having long necks?
Describe Darwin’s evolutionary theory.
Differences in inherited physical attributes that, if they enhanced opportunities to survive, would become the dominant characteristics of a species and could lead to the development of new species.
Describe how lactose tolerance is an example of evolution.
It used to be that humans were only able to have milk for the first few years in life and then would become lactose intolerant in later life. When humans stopped being nomadic and started herding cows, some inherited the mutant gene of being able to digest lactose and this meant they would digest the cow’s milk so this was advantageous and was therefore passed on.
What is a fit gene?
A genetic mutation that enhances the opportunity to survive - evolutionary psychologists believe this has a major influence on behaviour.
What are 2 examples of when fit genes can change?
1) Kettlewell (1955) found that pepper grey moths went from being mainly white to mainly black as this was advantageous as the industrial revolution released soot that made tree bark black. This genetic mutation became a ‘fit gene’
2) Darwin found 16 species of finches across UK and Europe - each with their own variations to help them best survive e.g. beak size and diet.
What are 3 examples of behaviours that are present in humans because they are evolutionarily adaptive?
1) Stress - fight or flight
2) Attachment behaviour - biological preparedness
3) Empathy
How are biological preparedness and adaptive responses affected by evolution?
Genotype (genetic potential) and phenotype (extent of physical expression of genetic potential) are both seen through traits such as separation anxiety THIS IS EVOLUTIONARILY ADAPTIVE.
Which part of the brain did Lockwood (2016) find was activated when people are being generous and empathetic?
Subgenual anterior cingulate cortex.
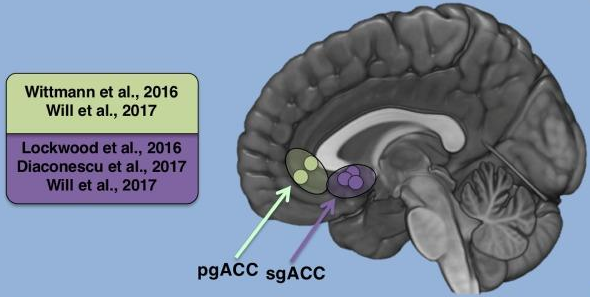
Could empathy have a biological background or is it learnt?
Empathy could have a background in both but evidence for the biological side (Lockwood, 2016) shows participants with higher empathy scores for certain tasks have higher activation of the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex.
What 2 parts of the brain are involved in creating emotional long-term memories?
1) Amygdala
2) Hippocampus
What 3 processes does the amygdala deal with?
1) Aggression
2) Fear
3) Threat

What is Long-term Potentiation?
This refers to the amygdala’s ability to change the strength of connections between neurons by hardwiring emotional events to avoid future threat.
How does evolution explain obesity?
We are stuck in bodies that no longer match our environment - we used to be in roaming mosaic tribes with uncertain meal times and so our bodies wanted to take in as much sugar and fat as possible when available. The modern world is abundant in sugar and fat and this is no longer the need.
What is inclusive fitness (Trivers, 1972)?
The level of altruism or aggression depends on the extent to which we share genes with the other party e.g. mother-child