Biology C4.1
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
define population
a group of organisms of the same species living in an area at the same time
define community
A community comprises several populations of organisms living and interacting with each other.
how is quadrat sampling calculated
average # x total area = estimated population size
what organisms are quadrat sampling used for
sessile organisms
define climax species
species that has been sustained for a long period of time in a specific ecosystem
describe to me high vs low standard deviation
high= uneven population distribution
low= even population distribution
how to calculate capture-mark- release-recapture
M = number of individuals marked
N = total # caught in the 2nd sample
R = # of marked individuals captured
M*N/R
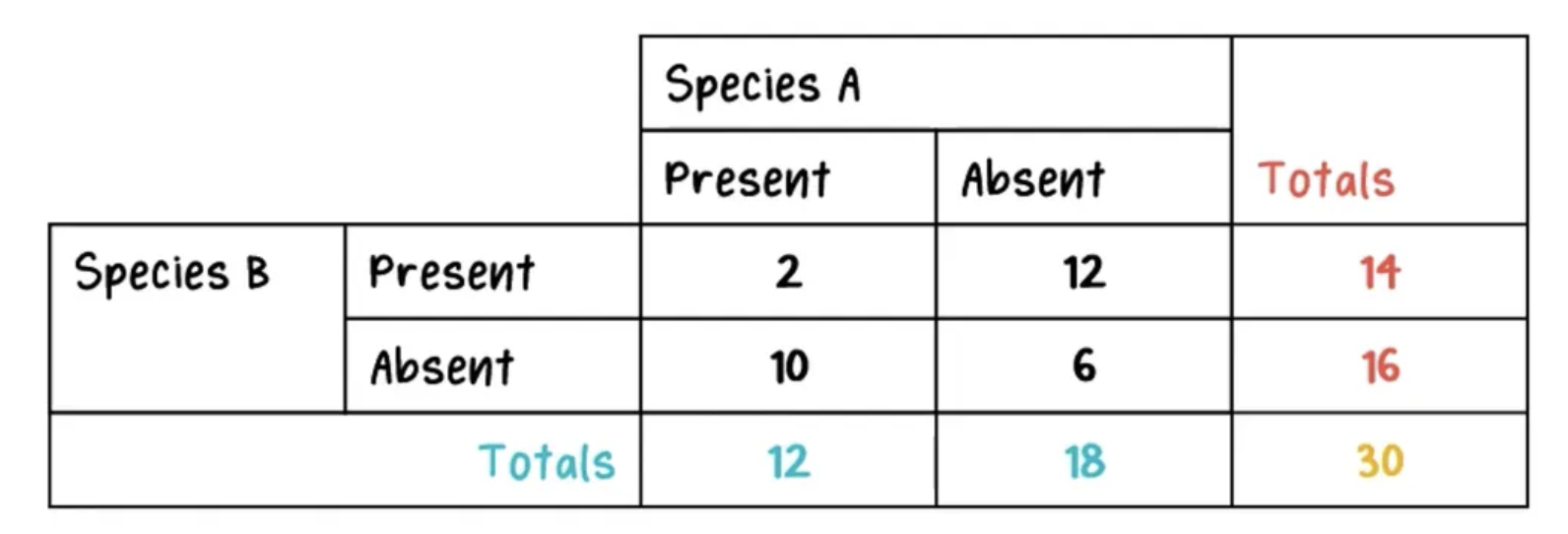
this is the observed table can you calculate and determine if species r independent (randomly distributed) or associated, define what test this is
chi-squared test
what is the carrying capacity
the maximum population size that a given environment can sustain over a certain period of time

what is a density dependent factor and what makes it so important
density dependent factors
have different effect at different population densities
eg. predation, disease
density-dependent factors tend to act to keep a population at or below its carrying capacity; this is a negative feedback effect
what do you call an interspecific reaction between HIV and humans
Pathogenicity involves the organism/virus living and reproducing in the host organism and causing negative impacts on the likelihood of survival.
what do you call the types of symbiosis relationship between 1. Barnacle and whales 2. bees and flowers and 3. tapeworm and humans
Commensalism - good for one, no impact on the other. (+/0) Barnacle and whales, desmodex mites
Mutualism - both species benefit (+/+) eg. Crocodile and tooth cleaning bird, Clown fishes/anemone, fungus and trees
Parasitism - good for parasite, bad for the other (host) (+/-) eg: tapeworm, tick, leeches, mosquitoes
define intraspecific
interactions that take place between members of the same species
define top-down control and bottom up control
Top-down control: something from higher in the food chain affects a lower level (predation)
Bottom-up control: something from a lower level affects a higher one
what are the difference of antibiotics and Allopathic agents
Antibiotics are secreted by microorganisms to kill other microorganisms
Allopathic Agents secreted by plants into the soil to kill other plants
what does a gas need to contribute to be a greenhouse gas
For a gas to contribute to the greenhouse effect it has to have the following property: it has to absorb longer wavelength radiation. Two other gases, methane and nitrous oxides (NO2 and NO) have that property and contribute.