Mechanisms of Edema
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
***NEED TO ADD PICTURES WITH INFORMATION
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
how much body weight is water
60%
what portion of water is intracellular
2/3
what portion of water is extacellular
1/3
how does water shift in and out of cells
concentration gradients
the difference between hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries and interstitum combined with
oncotic pressure determines the direction water moves
what is the starlings force equation
K[(Pcap-Pint)- reflection coefficent(picap-piint)]
how much of the plasma osmolarity is electrolytes
84%
what is the most important protein responsible for the oncotic pressure gradient
albumin
albumin concentration is greater in which oncotic pressure
plasma
what does albumin do in the plasma
pulls fluid from the interstitum into the intravascular compartment
alterations in any of the starlings forces results in
edema
what are the mechanisms of edema
increased microvascular permeability
increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure
decreased oncotic pressure
decreased lymphatic drainage
increased microvascular permeability occurs from
inflammation that results in release of mediators causing vasodilation
water moves from intravascular space into interstitium
increased microvascular permeability will result in
tissue swelling (inflammation)
what causes increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure
increased blood flow (hyperemia)
passive accumulation of blood
increased blood volume
increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure can be
localized or generalized
what causes decreased oncotic pressure
decreased plasma proteins!! (hypoalbuminemia)
what mechanisms of hypoalbuminemia that result in edema
severe blood loss
protein losing enteropathy and nephropathy
sever burns
loss of hepatic functional mass
profound malnutrition
what causes decreased lymphatic drainage
lymphatic vessel compression
lymphatic vessel constriction
lymphatic vessel blockage
what is decreased lymphatic drainage
reduced ability of the lymphatic system to remove excess fluid
when fluid accumulates in a body cavity that means
effusion
what are the types of effusion
abdominal
thoracic
pericardial
pure transudate has
low fibrinogen
translucent, clear to straw colored fluid
modified transudate has
low protein or low cellularity (or combination)
exudate has
high fibrinogen (bc inflammatory)
cloudy or opaque
transudative effusions are generally a result of
increased intravascular hydrostatic pressure
decreased oncotic pressure
thoraicc transudative effusion is
hydrothorax
pericardial tranudative effusion is
hydropericerdium
abdominal transudative effusion is
hydroperitoneum or ascites
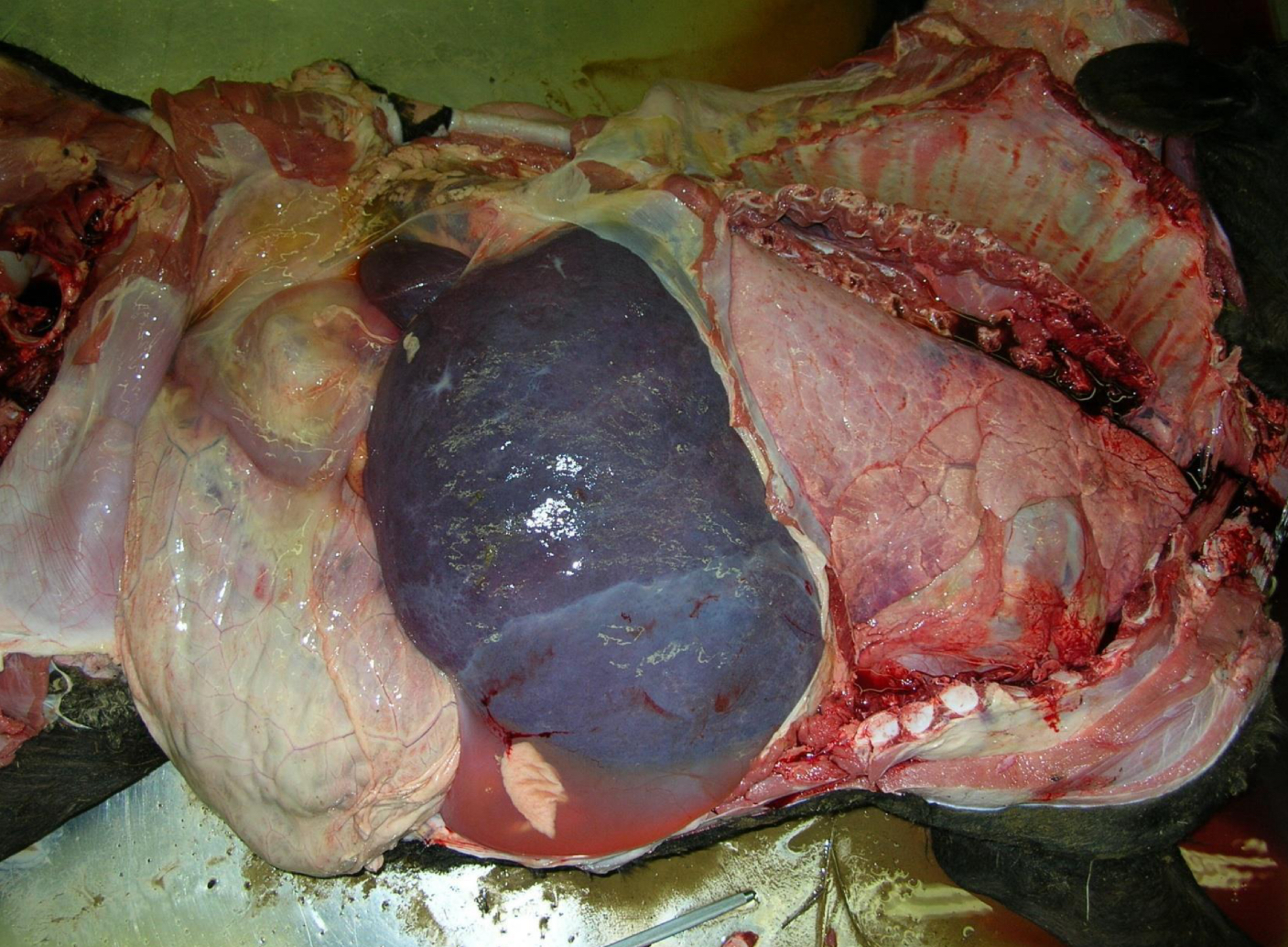
what is being shown **
ascites
exudative effusion is a result of
increased vascular permeability due to INFLAMMATION
what is chylous effusion
effusion due to obstruction of thoracic duct
chylous effusions have
opaque white to pink tinged fluid