ESS Topic 2.5 - Zonation and Succession
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Zonation
Changes in community composition along an environmental gradient (like altitude and distance from water)
Examples of Zonation
Mountains: vegetation shifts from forests to alpine meadows ro bare rocks
Seashores: Tidal zones with distinct species like barnacles and mussels
Intertidal Zonation
Wave action, salinity, temperature, and submersion (time of exposure to open air) are abiotic factors that organisms have to adapt to to live in the environment. (watch the video on slide 7 maybe)
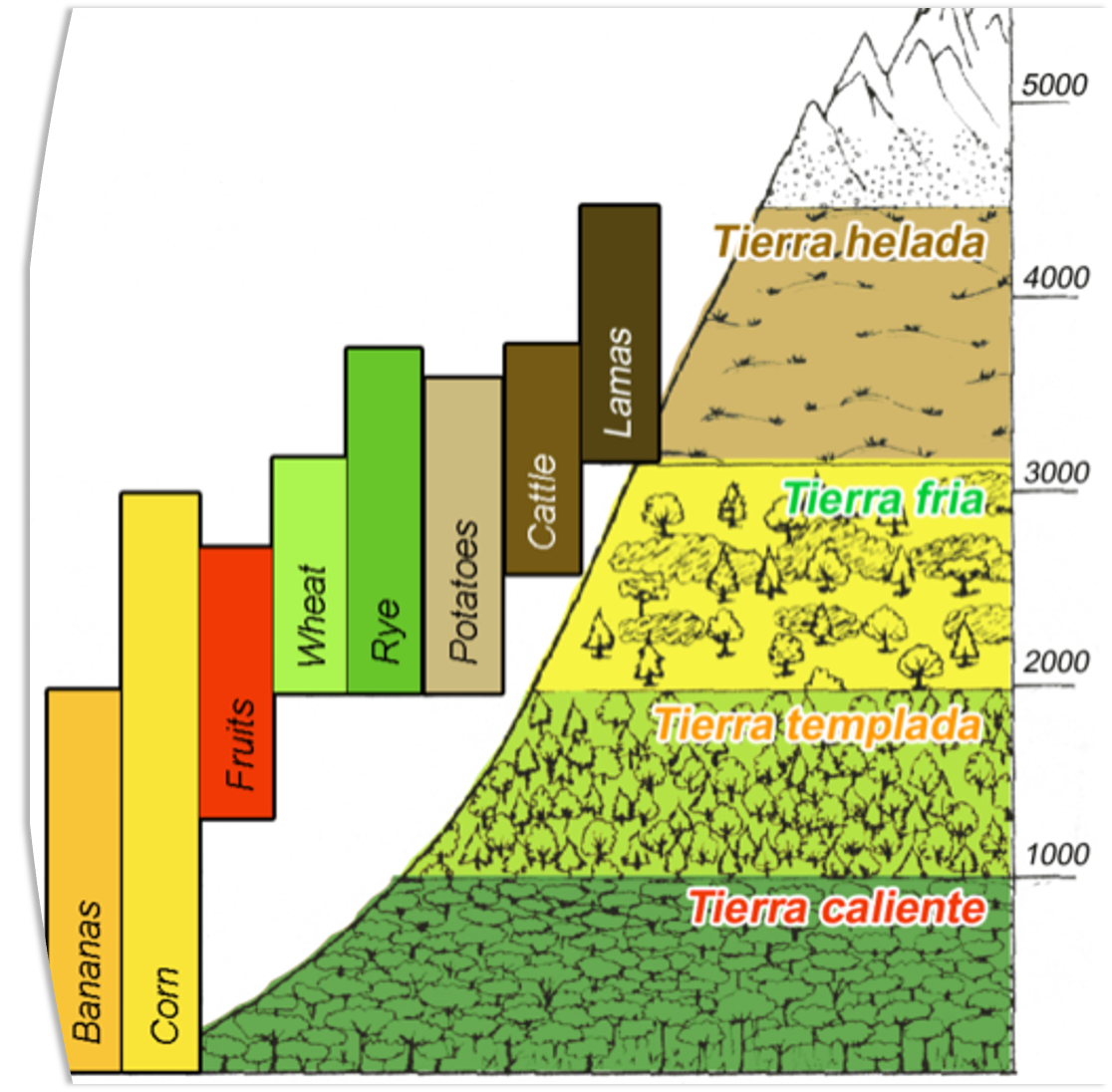
Montane Zonation
Different altitudes goin down a mountain call for different communities of agriculture and livestock in the different altitudinal zones. Temperature and oxygen availability are the major abiotic factors determining the zones. Ultraviolet radiation could also be a factor
Ocean Zonation
Going down into the ocean from the sand, will find different zones. Major abiotic factors seen are light availability, pressure, temperature, and salinity
Littoral Zonation
Going down into a lack from the ground there will be changes is soil humidity, oxygen availability (for the roots), and as one enters the lake, light availability and temperature will change
Tidal Deltas
Rivers near the sea will be different around the world, like mangroves are found in tropical and sub-tropical areas. Some abiotic factors to note in deltas are the degree of submersion, salinity, variability of salinity, temperature, oxygen availability during submersion, and wave/water velocity
How to measure zonation
use transects to study biotic and abiotic factors along the gradient , uses a kite diagram to visualize species distribution
Application of data
fieldwork, place quadrats along the transect to record species and conditions
Succession
the natural, gradual changes in communities in an area over time
Primary Succession
Has an environment start from zero, meaning there is no soil or organisms that exist
Example of Primary Succession
Islands made from underwater volcanoes will only have rock on them, lichen will grow on the rocks and break down the rocks, the lichen will die adding nutrients to the newly developed soil which will allow plants to start growing
Pioneer Species
The first species to populate this newly developed area, travel y wind or water, break down rocks to soil, die, and allow plants to grow
Example of a Pioneer Species
Lichen, breaks up rocks
Step 1 to Primary Succession
Start with bare rock
Step 2 to Primary Succession
Pioneer species such as lichen start to grow
Step 3 to Primary Succession
As pioneer species die soil creation occurs. Plants can grow in this new soil
Step 4 to Primary Succession
As more plants die, they decompose creating fertile soil. Maturing plants thrive and new plant communities grow
Secondary Succession
more common and includes the series of changes that occur in an area where the soil had been disturbed (usually by a natural disaster), by where an ecosystem still exists
Step 1 to Secondary Succession
An event occurs to disturb the soil (like fire, farming, logging)
Step 2 to Secondary Succession
In a short period of time, grasses and tree seedling repopulate the soil
Step 3 to Secondary Succession
As trees begin to grow they crowd out many low-growing plants
Step 4 to Secondary Succession
Eventually a mature tree community becomes established
Climax Community
the stable balance of all organisms within a community, will remain stable unless a disaster occurs and the cycle of succession has to start all over again
Sere
The sequence of vegetation types which occur in primary succession
Xerosere
Ecological succession that occurs in dry environments. Like deserts and rocky areas
Hyrdosere
Ecological succession that occurs in wet environments. Like lakes, ponds, and wetlands
Lithosere
Ecological succession that occurs on barren rock surfaces. Like lava flows, glaciated areas, and landslides
Biotic Factors Influencing Succession
Birds contribute to soil enrichment via pooping (guano), aiding nutrient cycling
Abiotic Factors Influencing Succession
Proximity to the ocean brings seeds and organic debris
Succession is Temporal
Zonation is Spacial
Changes Over Time in Succession
Productivity increases, species richness grows (biodiversity), and depth and nutrient cycling in soil improves
Importance of Ecosystem Resilience and Stability
Enhances ecosystem resilience to disturbances and promotes long-term stability
Human Impacts on Ecosystem Resilience and Stability
Activities like deforestation reduce resilience by decreasing biodiversity
Pioneer Stage
Energy flow is simple and low efficiency, gross productivity is low, net productivity is relatively high, species diversity is low, soil depth is shallow
Early Successional Stage
Energy flow has an increased efficiency, gross productivity is high, net productivity is high, species diversity is low to moderate, soil depth has increased
Mid Successional Stage
energy flow is more complex, gross productivity is high, net productivity is high, species diversity is moderate, soil depth has increased depth with organic matter accumulation
Late Successional Stage (Climax)
energy flow most complex and efficient, gross productivity us high, net productivity is low, species diversity is high, soil depth is deepest with rich organic layer
Climatic and Geological Factors Shaping Succession
Steep slopes limit soil formation
Biotic Influences Shaping Succession
Wolves in Yellowstone reshaping trophic cascades
Early Productivity Patterns during Succession
Low GP (harsh conditions) High NP (biomass builds)
Late Productivity Patterns during Succession
High GP and Larger consumers; NP ≈ 0 in climax communities.
r-strategists and K-strategists in Succession
these species have reproductive strategies that are better adapted to pioneer and climax communities
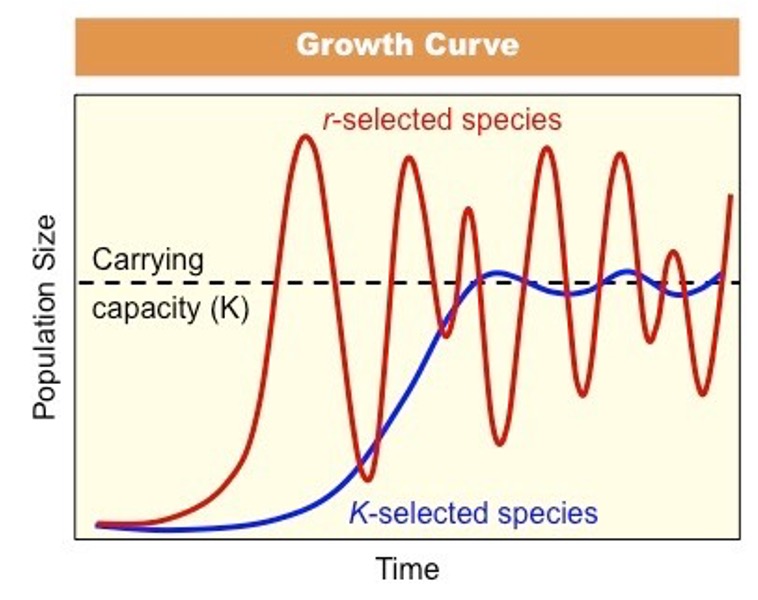
r-strategists
many offspring and shorter lifespan
K-strategists
fewer offspring and longer lifespan
Plagioclimax
human activities halt of redirect succession (like grazing and forest management)
Diverted seres
Sometimes the natural sequence of succession is halted or diverted by some external factor which influences the vegetation structure or community composition
Fire
environmental constraints are applied by grazing animals and by fire, resulting in stable grassland communities maintained by heavy grazing pressure or regular fires
Grass vs. Shrubs and Trees
Grasses are fire-resistant and can recover faster than shrubs or trees, regulate fires help maintain grasslands by preventing shrub and tree encroachment
Impact of Herbivores
close cropping by herbivores removes fire-prone long grass, this absence allows unpalatable shrubs to dominate in some areas