Geography - Earthquakes and Volcanoes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
constructive/ divergent plate boundary
when 2 plates move apart, allowing magma to rise and create new land/ crust (mid oceanic ridge), often resulting in volcanic activity and earthquakes.
destructive/ convergent plate boundary
when oceanic and continental plates collide. oceanic heavier/ denser so it is forced beneath continental, forming subduction zone.
friction and pressure built up can cause earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountain ranges.
oceanic plate melts, leading to magma formation that can result in volcanic eruptions.
collision/ convergent plate boundary
when two continental plates collide, since neitehr can be destroyed, they are forced up against eachother forming mountain ranges.
conservative/ transform
when 2 plates slide past eachotherhorizontally, causing friction that can lead to earthquakes. This boundary type does not create or destroy crust.
why do people live near earthquake prone areas?
poverty and overpopulation - forced to live on marginal land
tourism
cheaper land - housing
economic opportunities - jobs in industries such as agriculture (coastal areas offer easy access to the sea) and tourism
infrequent timings of earthquakes - presume that wont occur in their lifetime
generational residence and cultural ties
hypocentre/ focus
exact location of where earthquake occurs beneath the surface
epicentre
location on the surface that is directly above the focus
secondary hazards caused by earthquakes
tsunamis
dam failure
natural disasters
landslides
fire/ wildfires
disease outbreak
liquefaction of land
factors that affect earthquake
duration
depth of hypocentre
location
magnitude
readiness of people
time
geology
population density of surrounding area
building conditions - whether they are built strong enough to withstand quake
magma
melted rock in mantle/ under crust
lava
molten rock ejected onto earths surface
vent
long tube/ pipe/ channel inside volcano that transports magma
active volcano
a volcano that has recently erupted
dormat volcano
a volcano that has not recently erupted by is expected to in the near future
extinct volcano
a volcano that is not expected to erupt again
volcanic hazards
lava flow
pyrocrastic flow
lava bombs
ash clouds
acid rain
lahar/ mudflow
why do people live near volcanoes?
geothermal energy
rich in minerals - mining jobs
fertile land - agriculture jobs
unlikely that volcano will erupt during lifetime
tourism
what are some ways to minimize the impact of volcanic eruptions?
lava diversion channels
mudflow barriers
stronger infastructure/ buildings to prevent collapse from ash volume
education
monitor rise in ground temperatures using heat seeking cameras
install warning systems
satellite global positioning systems
tiltmeters
train emergency services
observe volcanic activty such as an increase in gas and steam emissons
evacuation route - plan
hazard mapping
lava cooling - dump water
what are some ways to minimize the impact of earthquakes?
train emergency services
epicentre and focus mapping - observe for any patterns in location or time
install seismometers/ devices that can measure an increase in earth tremors, pressure and release of radon gas
earthquake drills
warning and information systems on tv and radio
educate public
construct buildings strong enough to withstand
ritcher scale
measures magnitude via seismometer and uses a logarithmic scale
mercalli scale
measures intensity via observation of effects and impacts
hotspots
small areas inwhich magma rises through a plate that glides above
characteristics of a shield volcano
wide base
gentler slope
low height to width ratio
less violent eruptions
frequent eruptions
runny and thin lava
characteristics of a cone/ stratovolcano
steeper slope
more violent eruptions
formed out of layers of lava and ash
sticky lava consistency - builds up around vent, hence steeper sides
hazardous - Due to their explosive nature, stratovolcanoes can produce pyroclastic flows, ash clouds, lahars (mudflows), and
causes of japan 2011 earthquake
eurasian (continental) and pacific (oceanic) plate
destructive plate boundary
pacific pushed under eurasian, forming subduction zone
pressure and friction builds - causing megathrust earthquake
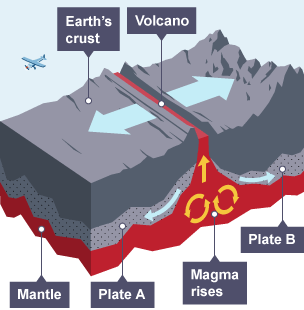
why are volcanoes formed at destructive boundaries?
At a destructive (convergent) boundary, the tectonic plates are moving towards each other:
The heavier, denser oceanic plate subducts under the lighter continental plate
In the subduction zone, the two plates come together, causing friction
Friction causes heat and the plate material melts, forming magma
The magma rises to the surface through cracks in the crust
The cooling lava and ash build up, forming a volcano
impacts/ effect of 2011 jp earthquake
26,000 injured
16,000 dead
23,000 displaced
largescale blackout - 4.4 million households lost electricity
large amounts of infrastructure destoryed/ damaged
tsunami
us $235 billion lost
nuclear reactor power station meltdown
responses to 2011 jp earthquake
rescue teams
financial support from global organsations
The U.S. provided a significant amount of aid, including search and rescue teams, military assets, humanitarian supplies, and financial assistance.
medical assitance
Many countries offered humanitarian aid in the form of medical supplies, food, water, and other essential supplies to support those affected by the disaster.
causes of the 2010 e15 eruption
constructive plate boundary
north alantic and eurasian plate
several magma chambers combined to make a heavy amount of magma below surface
impacts of the e15 eruption
substanial ash cloud
infastructure damaged
airline suspended services due to ash cloud
crops destoryed
billions lost in revenue due to flight delays
cancelled sporting events
floods
water supply contaminate
airline shares plummeted in price
food imports pauses which impacted industries
responses to e15 eruption
rescue teams sent
food provision
mass evacuation
physcological support
explain why it is necessary to provide clean water and sanitation after an earthquake
People need clean water supply/water to drink/to live/survive/prevent dehydration [1]
Water/sewage pipes/water treatment stations will be cut off/damaged/broken [1]
No running water [1]
People cannot wash/bath/shower [1]
No flush toilets [1] sewage will spill out/contaminate (water supplies/area) [1]
Disease/germs from dirty/polluted water or people sick from dirty [1] water/waterborne
diseases/examples of such as cholera [1]