Lecture 24 Reptiles
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
reptiles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Raptiles evolved from _______-like ancestors
amphibian
Amniotic eggs did what for reproduction
Allowed reproduction without needing water, enabling reptiles to colonize diverse environments
Skin for reptiles
Waterproof, scaly skin to reduce water loss and protect from harsh environments
Lungs in reptiles
Are more efficient for air breathing
What is the Amniotic egg
-Protective membranes & porous shell around embryo
-Shell may be hard or leathery & waterproof
-Egg is fertilized internally, before shell is formed
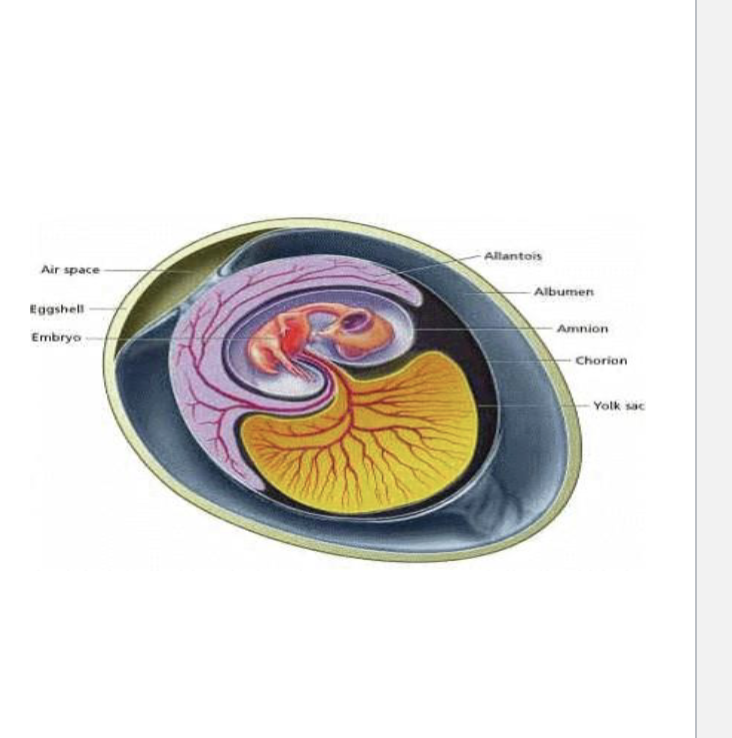
Ectothermic
Body temperature controlled by the environment
Skin characteristics
Dry, watertight skin covered by scales to prevent desiccation (water loss)
Integumentary system
Is heavily keratinized with little subcutaneous space and has many ______ and some have bony plates called _______
chromatophores, osteoderms
What are scales?
-Keratinized skin that provides protection and prevents water loss
-many different types of scales
-can be used for identification
Ribs
typically short in the neck and long in the trunk
turtles-
snakes-
crocodiles-
Turtles – fused to carapace
Snakes – long and curved
Crocodiles – Gastralia are NOT ribs

what do some boids like pythons and boa contrictors have?
pelvic remnants with bony components of their skeletal system
Muscle systems:
tetrapod reptiles are similar to_____
mammals
Muscle systems:
Snakes, how is the muscle system different than other animals
Much longer and more numerous than in many other animals
epaxial/ hypaxial muscles are more important
Nervous system
Most _____ and legless ____ are missing CN ___
snakes, legless lizards, XI
What is Jacobson’s organ:
critical for detecting scents, odors, and chemical information from the reptile’s environment.
Reptiles flick tongue to capture chemical signals within the environment
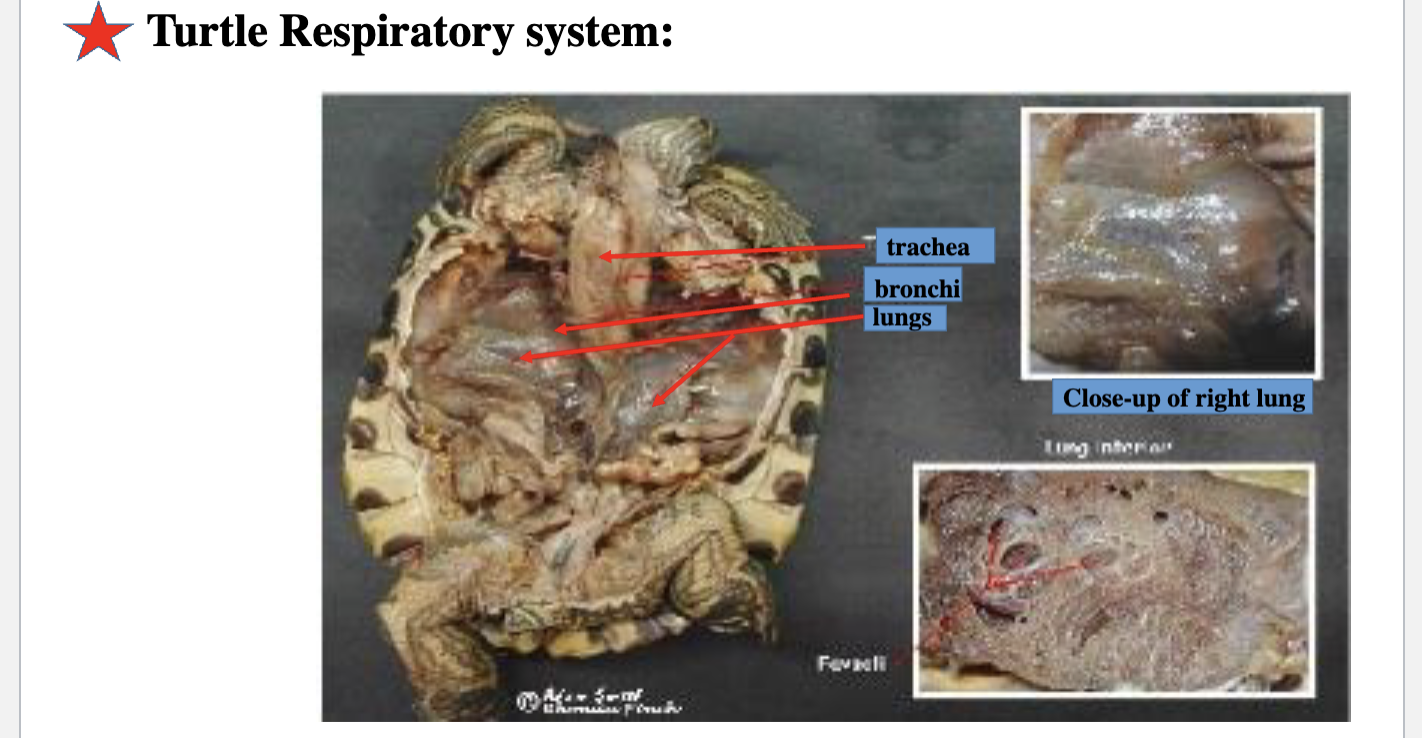
Respiration:
What do reptiles breath with since they lack a diaphragm
Breathing happens completely by the intercostal muscles
Lack a true partition between the pleural and peritoneal cavities,
Turtles cant move intercostal muscles due to their shell so how do they breath
Use flank muscles to breath
label turtle respiratory system
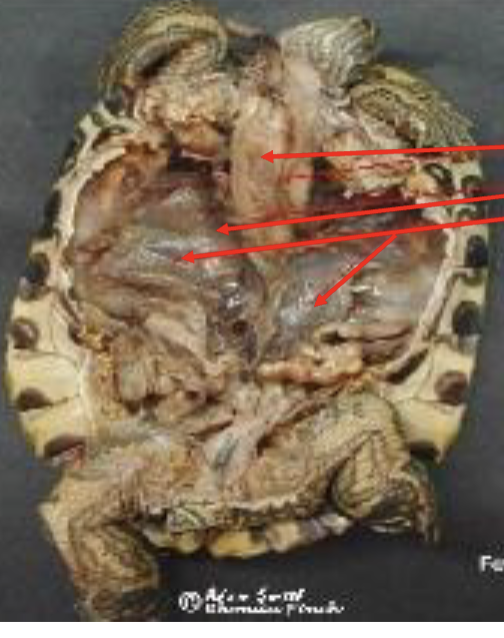
Turtles: Enternal respiratory system
Cloaca tissue allows for what?
gas exchange
Digestive track of turtle:
similar to mammals until the end (cloaca)
Some reptiles have converted salivary glands into ______ glands
poison
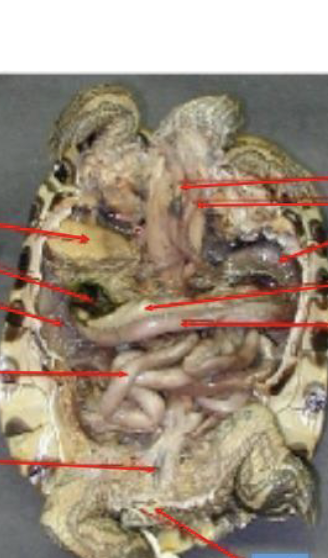
label turlte
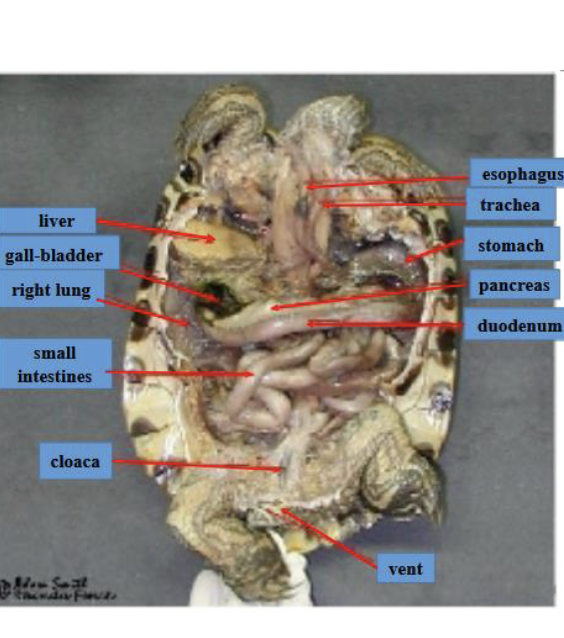
Reptile repro
most are asexual, but most are?
sexual
egglayers
cloacal transfer
Copulatory organ
Hemipenes in snakes and lizards
-can protrude
Turtles and crocs have a penis as a thickening on floor of cloaca.
In male snakes, hemipenes become engorged with lymph fluid rather than whole blood as in mammals

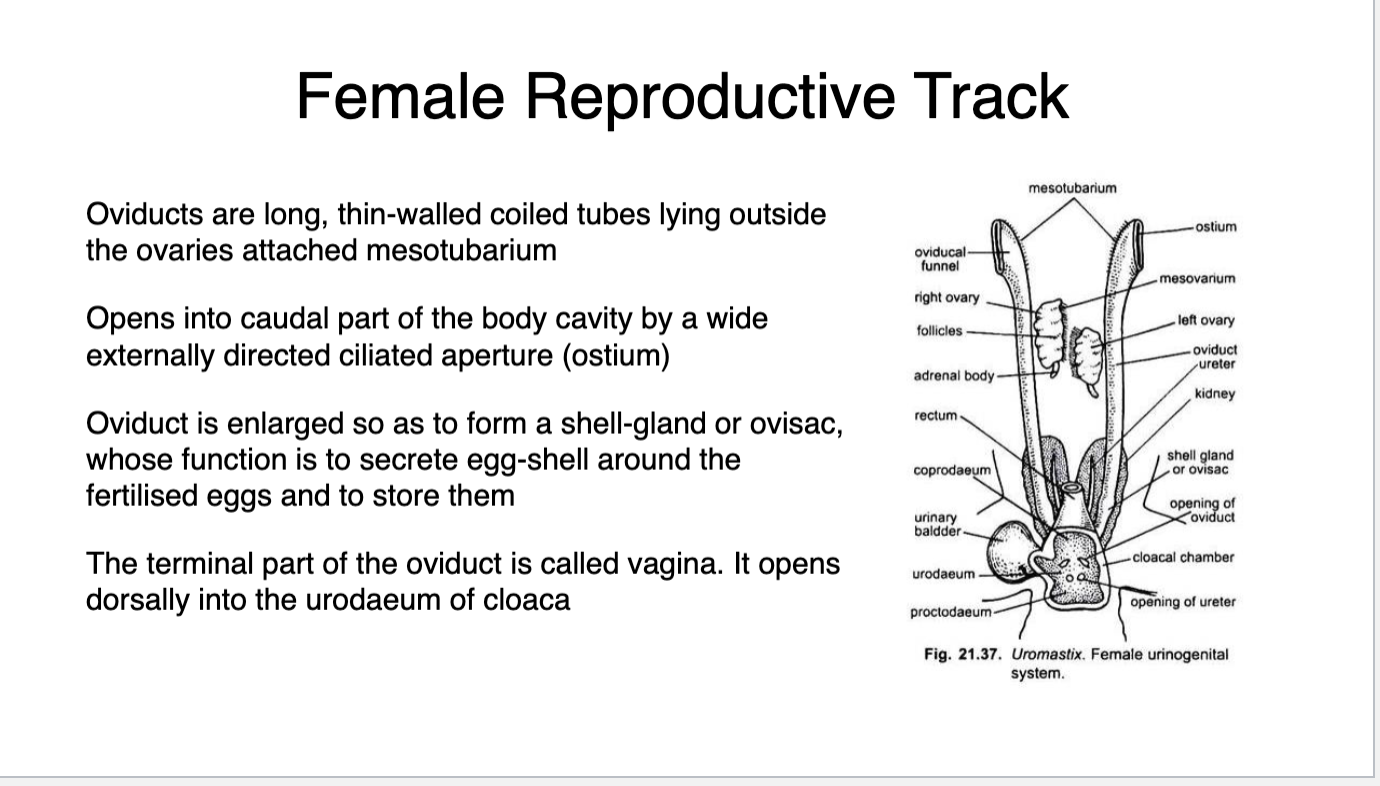
female repro
Hearing
specialized in subterranean life
Lack of many _______ error components
Highly sensitice to ______ frequency
Snakes and turtles are more sensitive to ____ based sound waves than ______ based
external
lower
earth, aerial
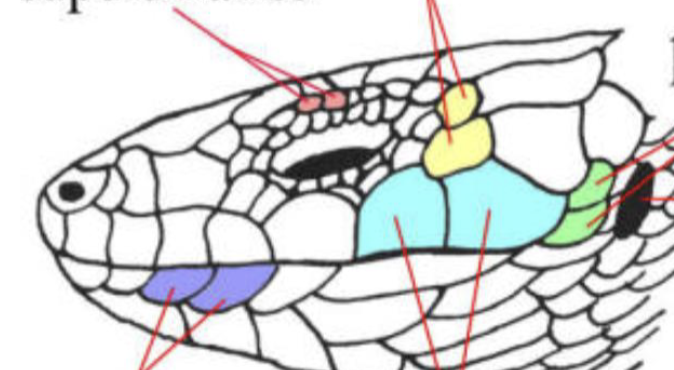
label color regions
Supercilaries
Temporals
Post labials
ear opening
supralabials
infralabials

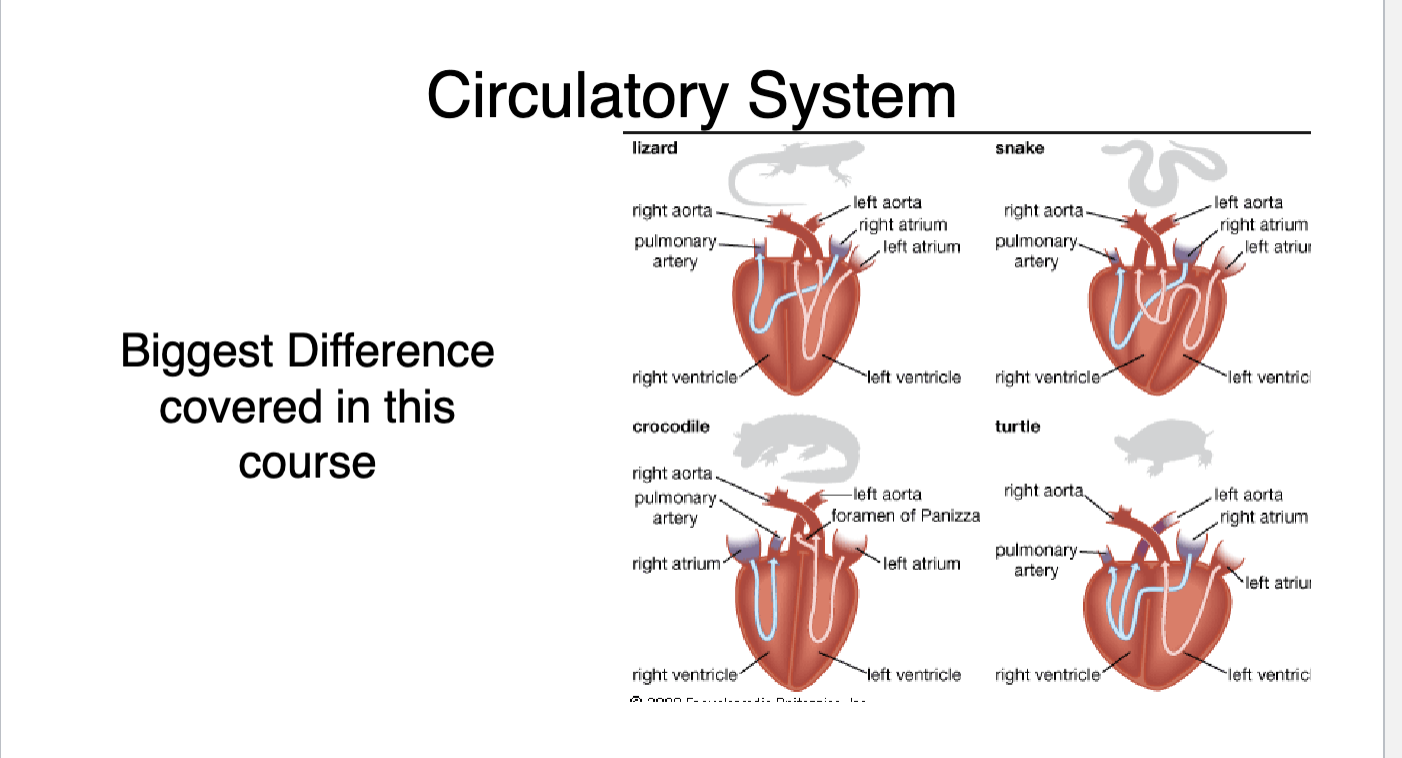
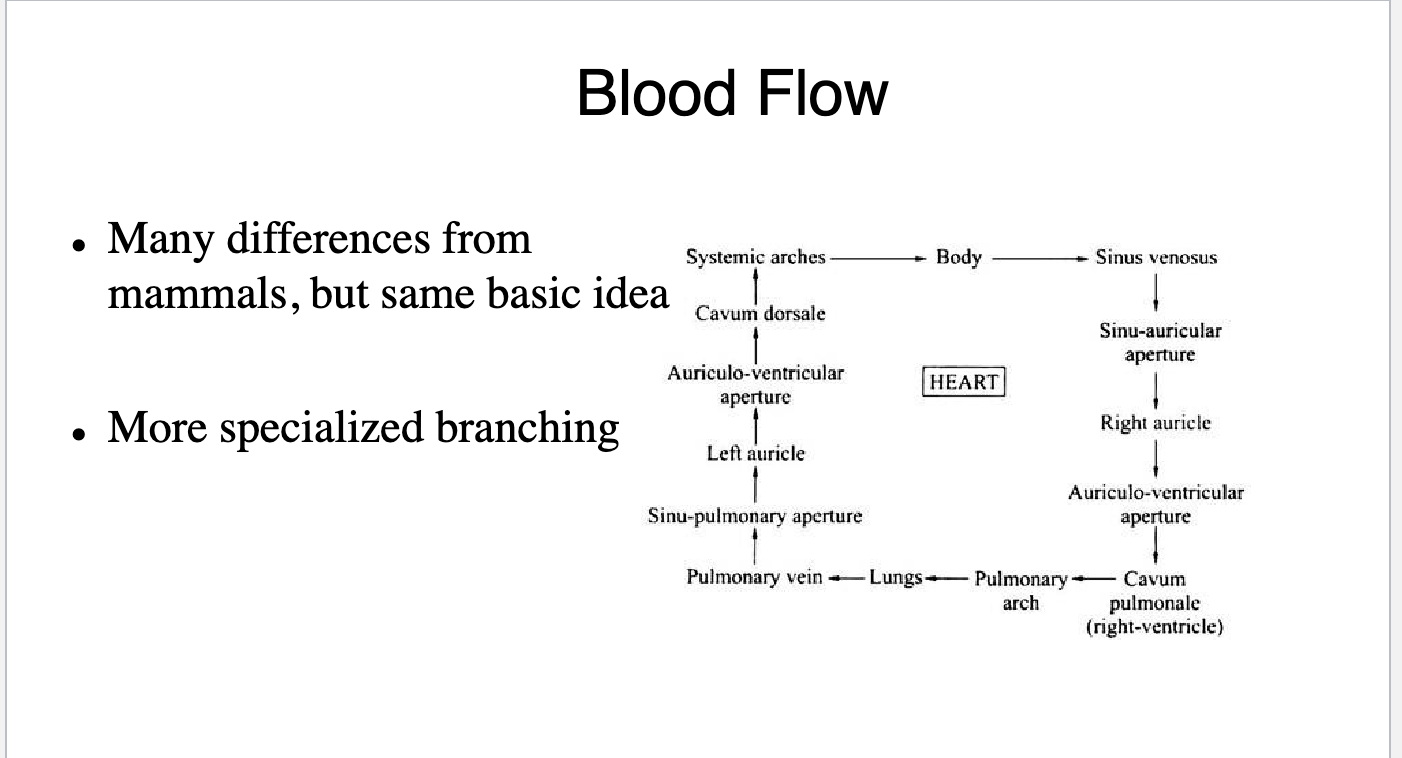
What chambers are present in a three chambered heart
two atriums
one ventricle
alligators have pseudo 4 chambered heart
valve that can be closed and split the ventricle
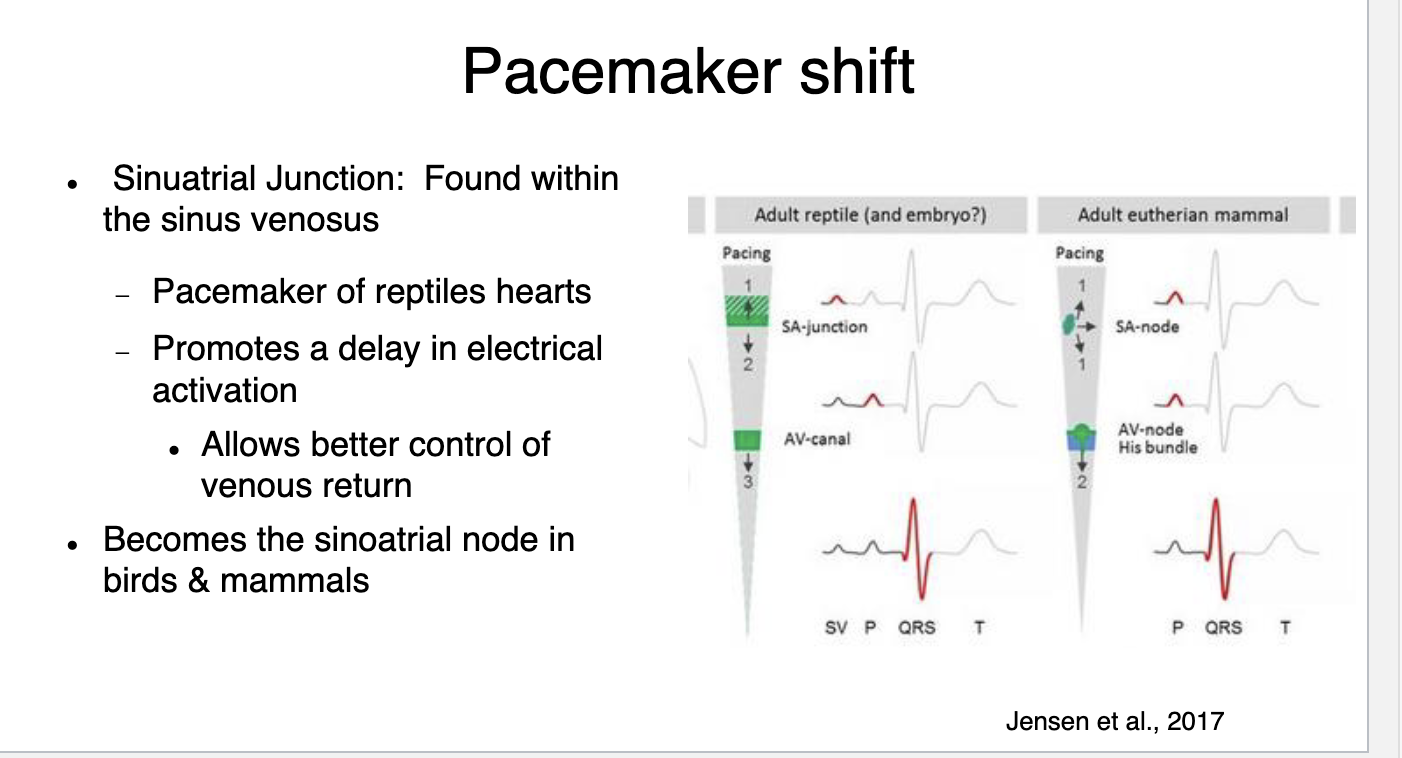
sinus venosus
Large thin-walled and bilobed chamber on the dorsal side of the heart covering both the auricles
found in the fetus of mammals, but gets absorbed into the right atrium.
formed by fusion of several veins
gather venous blood from different parts of the body
Pacemaker shift
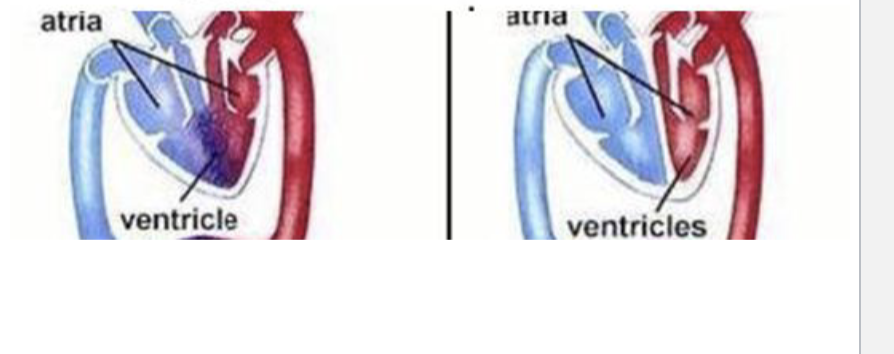
mixed oxygenated blood
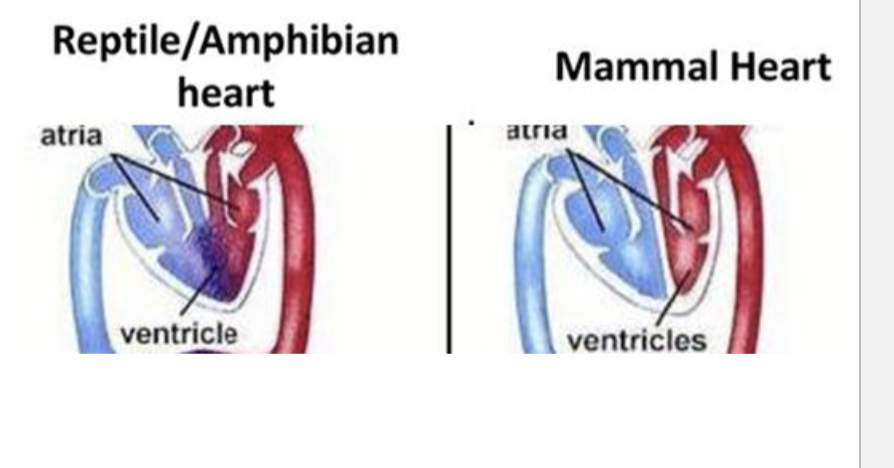
Combined ventricle allows for mixing of oxygenated blood from lung and less oxygenated blood from the body
Which is reptile/ amphibian heart and which is mammal heart
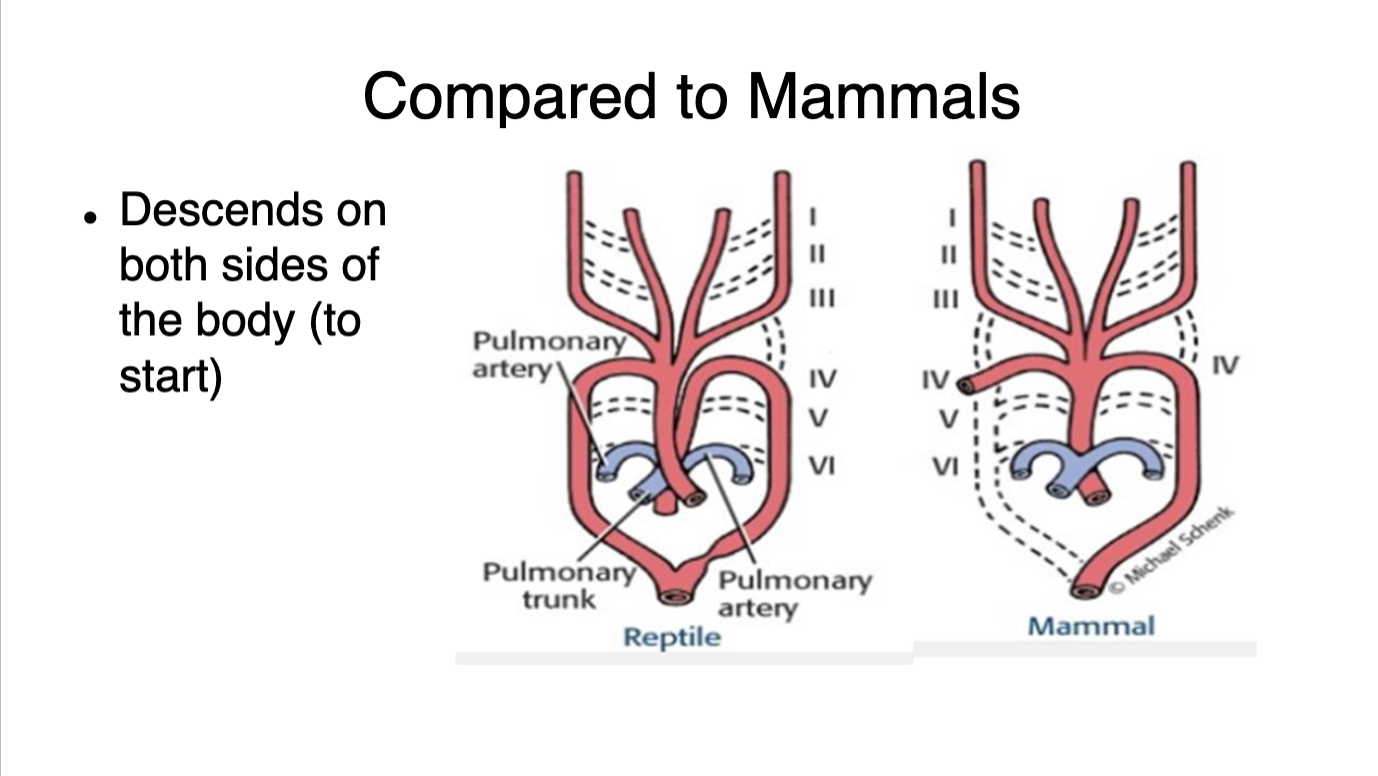
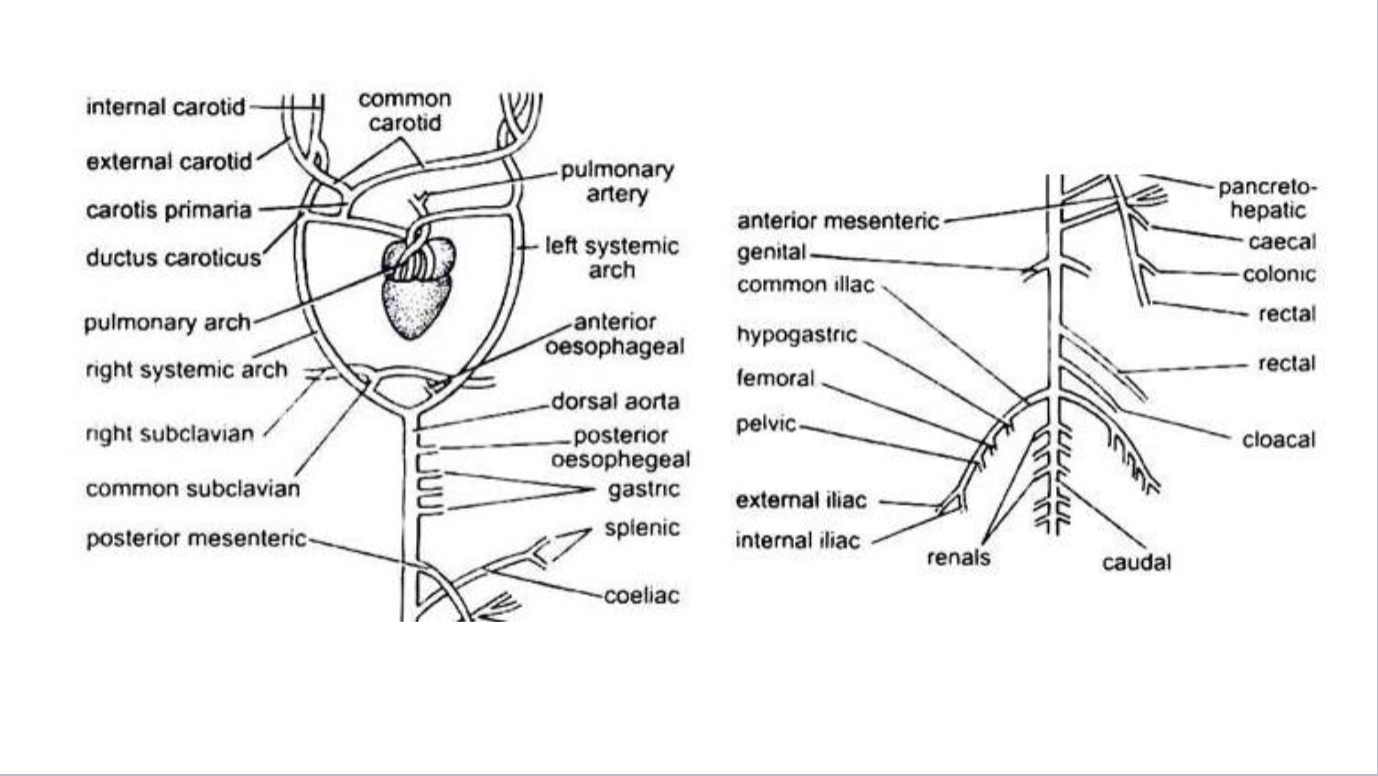
Thermoregulation
lack the ability to control their own temperature
hypothalmus processes thermal information
controlled by behavioral changes
blood shunting
controlling temp
can alter blood flow to increase or decrease heat in body
da fuq