Module 12.2: The Hippocampus & the Striatum
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Describe patient HM
was suffering about 10 minor epileptic seizures per day and a major seizure about once a week, despite trying every available antiepileptic drug
Scoville (surgeon that performed lobotomies) removed the hippocampus and nearby structures of the medial temporal cortex from both of H. M.’s hemispheres. Researchers knew almost nothing about the hippocampus at the time, and no one knew what to expect after the surgery
Although the operation reduced H. M.’s epilepsy to no more than two major seizures per year, he suffered severe memory impairment
How was HM affected by the surgery?
Although the operation reduced H. M.’s epilepsy to no more than two major seizures per year, he suffered severe memory impairment
He suffered massive anterograde amnesia, as well as retrograde amnesia
was able to form a few weak semantic memories
severe impairment of episodic memories
anterograde amnesia
inability to form memories for events that happened after brain damage
retrograde amnesia
loss of memory for events that occurred before brain damage
H. M. is representative of other people who have suffered amnesia after damage to the hippocampus and surrounding structures of the medial temporal lobe …
All show both anterograde and retrograde amnesia, with the retrograde amnesia being most severe for the time leading up to the damage.
How was HM’s (and most other patients with severe amnesia) working memory?
They showed normal working memory, as long as they avoided distraction
semantic knowledge
memories of factual information
episodic memories
memories of single personal events
Describe patient KC
suffered widespread brain damage after a motorcycle accident, with scattered damage in the hippocampus and other locations, leading to an apparently complete loss of episodic memories
He cannot describe a single event from any time of his life, although he remembers many facts.
How would memory loss affect someone’s ability to imagine the future?
Studies using fMRI show that describing past events and imagining future events activate mostly the same areas, including the hippocampus
People with amnesia are just as impaired at imagining the future as they are at describing the past, although they have no trouble describing the present
Nearly all patients with amnesia show better ___ than ___ memory
implicit; explicit
explicit memory (declarative memory)
deliberate recall of information that one recognizes as a memory
implicit memory
an influence of experience on behavior, even if the influence is not recognized; ex. procedural memory
procedural memory
the development of motor skills and habits; a special kind of implicit memory
Which types of memory were most impaired in H. M. and people with similar amnesia?
H. M. had severe anterograde amnesia (difficulty forming new long-term memories) and a severe loss of episodic memories.
Which types of memory were least impaired in H. M. and people with similar amnesia?
H. M. had nearly intact working memory, implicit memory, and procedural memory.
Exactly how does the hippocampus contribute to memory?
Larry Squire (1992) proposed that the hippocampus is critical for declarative memory, especially episodic memory.
delayed matching-to-sample task
task in which an animal sees a sample object and then after a delay must choose an object that matches the sample
delayed nonmatching-to-sample task
task in which an animal sees an object and then after a delay must choose an object that does not match the sample
Another hypothesis relates the hippocampus to memory for ___
context
Describe how the hippocampus might relate to context for memory
Clearly, that memory could not be stored in a single location in the brain; it has to be spread over many locations. Perhaps the hippocampus is a coordinator, a director that brings together representations from various locations, in the correct order. In short, it reconstructs the context.
According to the context hypothesis, why does hippocampal damage impair recent memories more than distant memories?
Recent memories include details of context, and the hippocampus is essential for memory of context. Most old memories include only the gist of the event, and the hippocampus is less important for memories of that type.
Several types of evidence demonstrate the importance of the hippocampus and nearby areas for ___
spatial memory
radial maze
an apparatus used to test spatial memory in nonhumans
A rat’s best strategy in a radial maze is to explore each arm once and only once, remembering where it has already gone. In a variation of the task, a rat might learn that the arms with a rough floor never have food or that the arms pointing toward the window never have food. Thus, a rat can make a mistake either by entering a never-correct arm or by entering any arm twice.
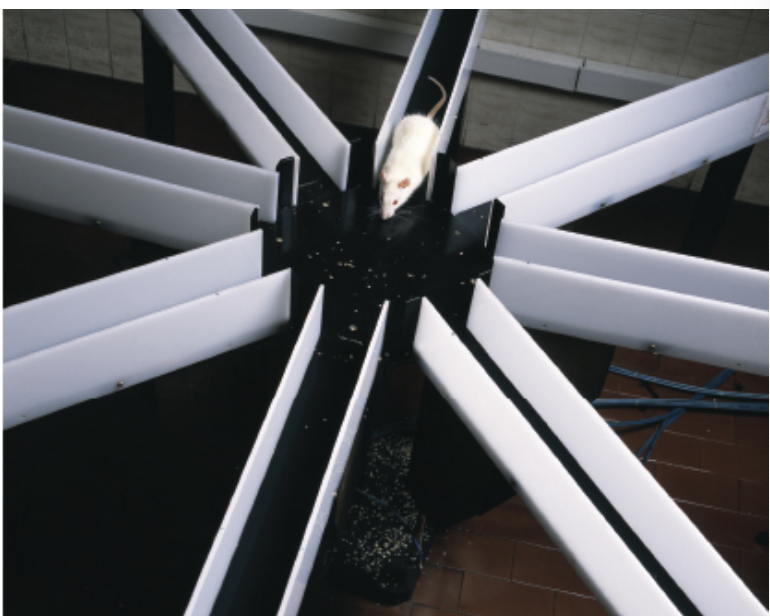

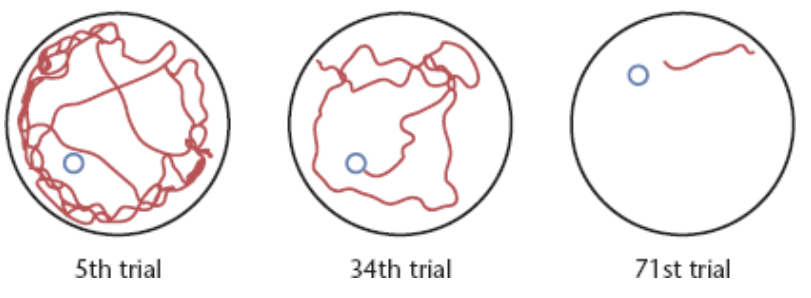
Morris water maze
a procedure used to test for spatial memory in nonhumans
a rat swims through murky water to find a rest platform that is just under the surface
A rat with hippocampal damage slowly learns to find the platform if it always starts from the same place and can always turn the same direction to find the rest platform. However, if it has to start from a different location or if the rest platform occasionally moves from one location to another, the rat is disoriented
Evidently the hippocampus is essential for remembering locations.
Describe what MRI scans found when looking at taxi drivers’ brains and what that means
MRI scans also revealed that the taxi drivers have a larger than average posterior hippocampus and that the longer they had been taxi drivers, the larger their posterior hippocampus
This result suggests actual growth of the adult human hippocampus in response to spatial learning experiences
place cells
hippocampal neurons that respond most strongly when an animal is in a particular place and headed in a particular direction
time cells
hippocampal neurons that respond most strongly at a particular point within a sequence of times
grid cells
entorhinal cortex cells that respond when an animal is in any of a number of places arranged in a hexagonal grid pattern
In addition to an animal’s location, what else do many place cells monitor?
Some also respond to time or the direction the animal is heading.
What is the evidence that rats can imagine the future?
When a rat pauses at a choice point in a maze, place cells respond in sequence as if the animal were traveling down one arm or another of the maze.
How do grid cells at ventral levels of the entorhinal cortex differ from those at dorsal levels?
Moving dorsal to ventral, the grid cells respond to larger areas.
striatum
combined of the caudate nucleus and the putamen (parts of the basal ganglia)
important for gradually learning habits, or learning what probably will or will not happen under certain circumstances
People with amnesia after hippocampal damage perform randomly on the weather task for many trials, because they form no declarative memories and they do not remember that mostly blue or mostly purple symbols would mean anything. However, if they continue for a very long time, they …
show gradual improvement, based on habits supported by the striatum
What are the different effects the hippocampus and striatum have on memory?
…
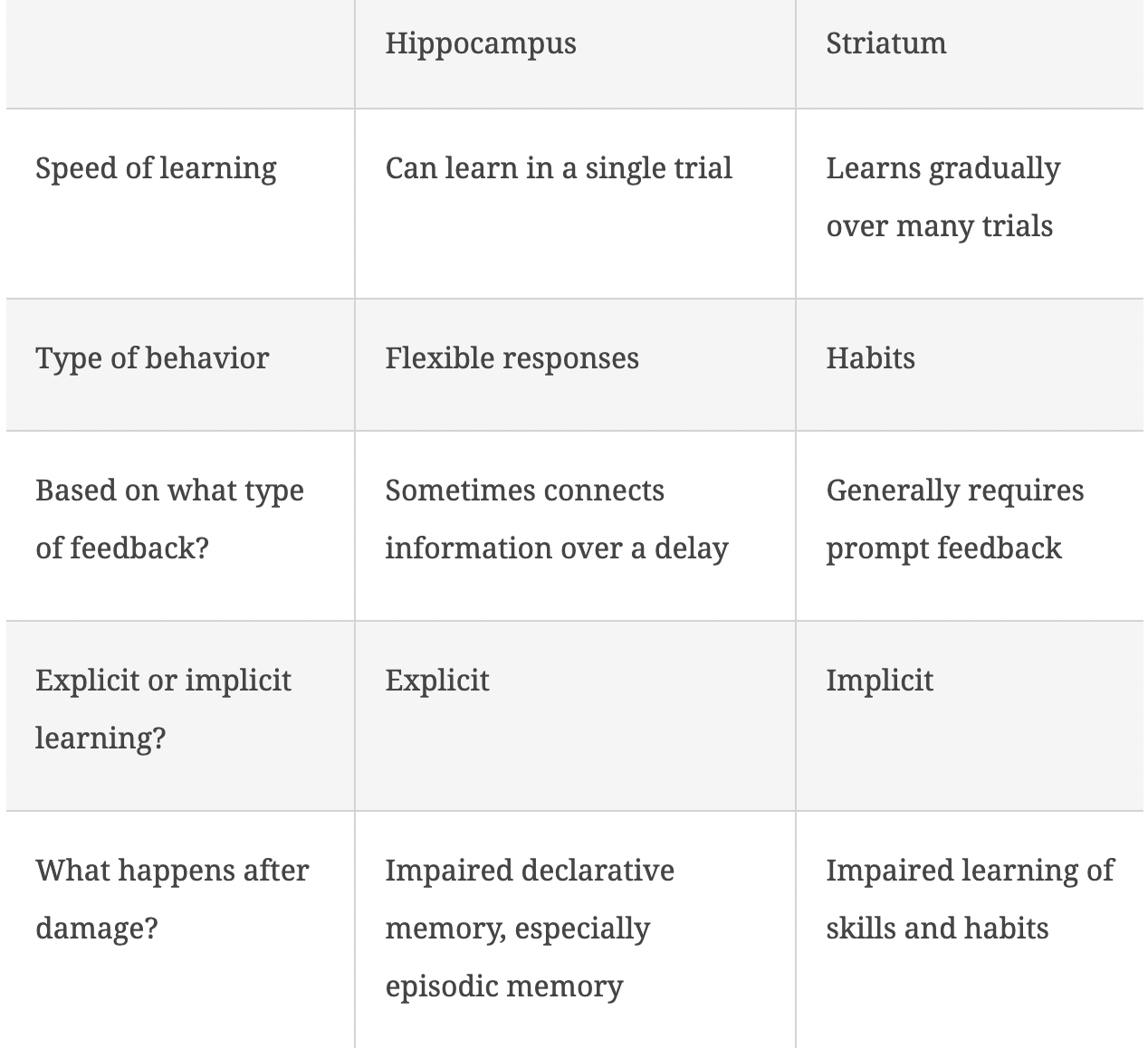
Which type of memory would be easier to describe in words, memory based on the hippocampus or the striatum?
Hippocampal-based memory, being explicit, is generally easier to describe in words. The habits based on the striatum are sometimes harder to describe.
In people with parietal lobe damage…
the process of associating one piece with another is impaired
semantic dementia
a loss of semantic memory
caused by damage in the anterior temporal cortex
What is anterograde amnesia?
a. Loss of factual memory
b. Loss of memory for personal experiences
c. Loss of memory for space and time
d. Inability to form new memories
d. Inability to form new memories
What was the status of working memory in patient H. M.?
a. He had a complete loss of working memory.
b. His working memory seemed normal unless he was distracted.
c. He had reasonable working memory only for facts that he found highly interesting.
d. Shortly after his damage, his working memory was poor, but it later recovered.
b. His working memory seemed normal unless he was distracted.
Which of the following was most severely impaired in patient H. M.?
a. Episodic memory
b. Procedural memory
c. Implicit memory
d. Short-term memory
a. Episodic memory
Why is it unsurprising that H. M. had intact procedural memory?
a. Procedural memory can develop in a single trial.
b. Procedural memory depends on high-frequency gamma oscillations.
c. Procedural memory does not require synaptic modifications in the brain.
d. Procedural memory depends on the striatum, not the hippocampus.
d. Procedural memory depends on the striatum, not the hippocampus.
What type of memory do the radial maze and Morris water maze test?
a. Episodic memory
b. Verbal memory
c. Social memory
d. Spatial memory
d. Spatial memory
Evidence that rats can imagine the future came from recordings from what type of cell?
a. Glia cells
b. Place cells
c. Face-recognition cells
d. Visual cortex cells
b. Place cells
Why are certain cells in the entorhinal cortex called grid cells?
a. They respond to locations distributed in a hexagonal grid.
b. They have axons that spread out in the shape of a grid.
c. They have dendrites that spread out in the shape of a grid.
d. They respond when an animal sees something shaped like a grid.
a. They respond to locations distributed in a hexagonal grid.
The striatum is primarily responsible for which type of learning?
a. Gradually learning habits
b. Acquiring and storing episodic memories
c. Memories that people can easily describe in words
d. Quickly adapting learned behaviors to new circumstances
a. Gradually learning habits
Someone with semantic dementia has lost which of the following?
a. Ability to understand speech
b. Factual knowledge
c. Ability to find the way to something
d. Face recognition
b. Factual knowledge